Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multi-GNSS ZTD Estimation in Real-Time
3. Multi-GNSS Data and Products
3.1. Multi-GNSS Orbit and Clock Products from IGS RTS
3.2. Multi-GNSS Data
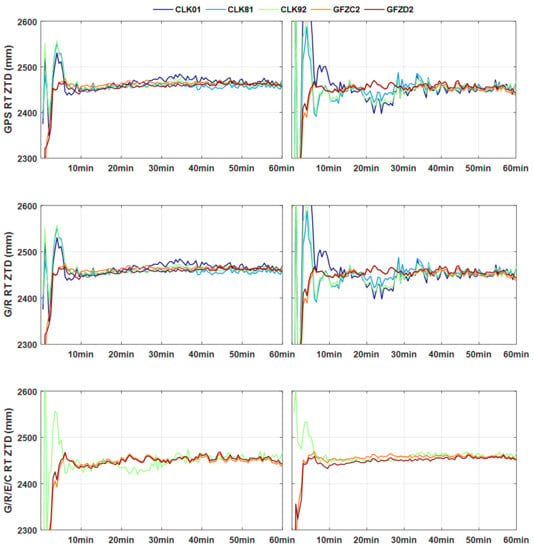
4. Results and Validations
4.1. Assessment of IGS-RT Orbit and Clock Products
4.2. ZTD Validation with the Final Tropospheric Products
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niell, A.E.; Coster, A.J.; Solheim, F.S.; Mendes, V.B.; Toor, P.C.; Langley, R.B.; Upham, C.A. Comparison of measurements of atmospheric wet delay by radiosonde, water vapor radiometer, GPS, and VLBI. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 830–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teke, K.; Böhm, J.; Nilsson, T.; Schuh, H.; Steigenberger, P.; Dach, R.; Heinkelmann, R.; Willis, P.; Haas, R.; Espada, S.G.; et al. Multi-technique comparison of troposphere zenith delays and gradients during CONT08. J. Geodesy 2011, 85, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using GPS. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocken, C.; Van Hove, T.; Ware, R.H. Near real-time GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 3221–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Bevis, M.; Bock, Y.; Gutman, S.; Wolfe, D. GPS meteorology: Reducing systematic errors in geodetic estimates for zenith delay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3583–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendt, G.; Dick, G.; Reigber, C.; Tomassini, M.; Liu, Y.; Ramatschi, M. Near real time GPS water vapor monitoring for numerical weather prediction in Germany. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 82, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J.; Bender, M. Real-time GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor: Precise point positioning with orbit, clock and phase delay corrections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Nilsson, T.; Ning, T.; Heinkelmann, R.; Ge, M.; Glaser, S.; Schuh, H. Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS and BeiDou observations. J. Geodesy 2015, 89, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Wickert, J. A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time precise point positioning. J. Geodesy 2013, 87, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousa, J.; Vaclavovic, P. Real-time zenith tropospheric delays in support of numerical weather prediction applications. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Rohm, W.; Choy, S.; Norman, R.; Wang, C.S. Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from GPS Precise Point Positioning. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 10044–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real-Time PPP Demonstration Campaign. Available online: http://www.pecny.cz/COST/RT-TROPO/about.php (accessed on 1 April 2015).
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Khachikyan, R.; Weber, G.; Langley, R.B.; Mervart, L.; Hugentobler, U. IGS-MGEX: Preparing the ground for multi-constellation GNSS science. Inside GNSS 2014, 9, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Dick, G.; Lu, C.; Ge, M.; Nilsson, T.; Ning, T.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Multi-GNSS meteorology: Real-time retrieving of atmospheric water vapor from BeiDou, Galileo, GLONASS, and GPS observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Teferle, F.N.; Kazmierski, K.; Laurichesse, D.; Yuan, Y. An evaluation of real-time troposphere estimation based on GNSS Precise Point Positioning. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurichesse, D. The CNES real-time PPP with un-differenced integer ambiguity resolution demonstrator. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2011, Portland, OR, USA, 19–23 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. 2009. Available online: http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2009).
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Guo, F. Satellite clock estimation at 1 Hz for realtime kinematic PPP applications. GPS Solut. 2012, 15, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Hugentobler, U. Combined multi-system GNSS analysis for time and frequency transfer. In Proceedings of the European Frequency Time Forum, Braunschweig, Germany, 27–30 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- David, A. Maximum likelihood approaches to variance component estimation and to related problems. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1997, 72, 320–338. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global mapping function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction—Part II. Refraction corrections in satellite geodesy. Bull. Géodésique 1973, 47, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zus, F.; Lu, C.; Ning, T.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Retrieving high-resolution tropospheric gradients from multiconstellation GNSS observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagler, K.; Schindelegger, M.; Böhm, J.; Krásná, H.; Nilsson, T. GPT2: Empirical slant delay model for radio space geodetic techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GNSS Data Center. Available online: http://igs.bkg.bund.de/ntrip/download (accessed on 15 March 2008).
- Elsobeiey, M.; Al-Harbi, S. Performance of real-time precise point positioning using IGS real-time service. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IGS MGEX. Available online: http://igs.org/mgex (accessed on 25 October 2012).
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Qu, L.; Hu, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system. J. Geodesy 2013, 5, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Loyer, S. Galileo orbit and clock quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Teunissen, P.; Nakamura, S. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2012, 17, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Hugentobler, U.; Fridez, P.; Meindl, M. Bernese GPS Software Version 5.0; Astronomical Institute, University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Offiler, D. Product Requirements Document Version 1.0—21 December 2010; EIG EUMETNET GNSS Water Vapour Programme (EGVAP-II); Met Office: Exeter, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]













| Item | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Estimator | All multi-GNSS observations are processed together in one sequential least square estimator. |
| Sources of satellite orbits & clocks | As shown in Table 2 |
| Observations | Carrier phase and pseudorange observations; GPS + GLONASS + Galileo + BDS, about 80 navigation satellites |
| Signal selection | GPS: L1/L2; GLONASS: L1/L2; Galileo: E1/E5a; BDS: B1/B2 |
| Sampling rate | 5 s |
| Elevation cutoff | 7° |
| Weight for observations | The variance component estimation weighting method |
| Satellite orbit | Fixed |
| Satellite clock | Fixed |
| Zenith Tropospheric delay | Initial model (ZHD estimated using Saastamoinen model based on GPT2) + random-walk process (process noise: 5 mm/h1/2) |
| Tropospheric gradients | No |
| Mapping function | Global Mapping Function (GMF) |
| Phase-windup effect | Corrected |
| Receiver clock | Estimated, white noise |
| ISB and IFB | Estimated as constant, GPS as reference |
| Station displacement | Solid Earth tide, pole tide, ocean tide loading, IERS Convention 2010 |
| Satellite antenna phase center | Corrected using MGEX and IGS values |
| Receiver antenna phase center | Corrected |
| Station coordinate | Fixed to coordinates of weekly solution/kinematic estimated |
| Phase ambiguities | Constant for each continuous arc, without ambiguity resolution |
| IGS RTS | Reference Point | GNSS | Analysis Center |
|---|---|---|---|
| IGS01 | APC | GPS | SE Combination |
| IGS02 | APC | GPS | KF Combination |
| IGS03 | APC | GPS/GLO | KF Combination |
| CLK70 | APC | GPS | GFZ |
| CLK01 | APC | GPS/GLO | BKG |
| CLK21 | APC | GPS/GLO | DLR/GSOC |
| CLK16 | APC | GPS | WUHAN |
| CLK81 | APC | GPS/GLO | GMV |
| CLK92 | CM | GPS/GLO/GAL/BDS | CNES |
| GFZC2 | APC | GPS/GLO/GAL/BDS | GFZ |
| GFZD2 | APC | GPS/GLO/GAL/BDS | GFZ |
| IGS-RT Service | TYPE | Along (cm) | Cross (cm) | Radial (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLK01 | GPS | 4.00 | 2.12 | 1.34 |
| GLONASS | 9.15 | 4.30 | 2.99 | |
| CLK81 | GPS | 6.46 | 3.65 | 1.83 |
| GLONASS | 8.70 | 6.06 | 2.83 | |
| CLK92 | GPS | 6.54 | 6.34 | 3.00 |
| GLONASS | 9.69 | 7.81 | 2.99 | |
| Galileo | 8.31 | 4.66 | 2.68 | |
| BDS GEO | 59.79 | 43.33 | 28.97 | |
| BDS IGSO | 50.22 | 24.74 | 16.58 | |
| BDS MEO | 17.13 | 9.68 | 4.48 | |
| GFZC2 | GPS | 15.13 | 12.92 | 5.61 |
| GLONASS | 19.50 | 13.67 | 5.85 | |
| Galileo | 29.56 | 13.67 | 9.44 | |
| BDS GEO | 65.83 | 12.90 | 14.63 | |
| BDS IGSO | 22.02 | 40.96 | 25.28 | |
| BDS MEO | 34.05 | 17.23 | 7.23 | |
| GFZD2 | GPS | 10.56 | 9.77 | 3.89 |
| GLONASS | 13.68 | 9.57 | 4.04 | |
| Galileo | 14.31 | 13.60 | 8.56 | |
| BDS GEO | 60.37 | 15.70 | 14.47 | |
| BDS IGSO | 24.98 | 27.54 | 10.48 | |
| BDS MEO | 16.00 | 10.95 | 4.40 |
| Solution | CLK01 (s) | CLK81 (s) | CLK92 (s) | GFZC2 (s) | GFZD2 (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | 588 | 600 | 570 | 522 | 540 |
| GPS/GLONASS | 540 | 552 | 522 | 492 | 510 |
| GPS/GLONASS/Galileo/BDS | - | - | 510 | 480 | 498 |
| IGS Service | Solution | Fix Coordinate Mode | Kinematic Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS | STD | RMS | STD | ||
| CLK01 | G | 9.80 | 5.78 | 18.21 | 18.00 |
| G/R | 8.92 | 4.83 | 14.31 | 13.66 | |
| CLK81 | G | 13.61 | 12.73 | 33.50 | 32.97 |
| G/R | 11.39 | 10.44 | 25.57 | 25.21 | |
| CLK92 | G | 7.70 | 4.85 | 17.94 | 17.13 |
| G/R | 6.18 | 3.46 | 14.64 | 13.01 | |
| G/R/E/C | 6.16 | 3.45 | 14.39 | 12.70 | |
| GFZC2 | G | 6.50 | 5.32 | 14.73 | 14.11 |
| G/R | 5.04 | 3.94 | 13.57 | 13.45 | |
| G/R/E/C | 5.06 | 3.97 | 13.74 | 12.60 | |
| GFZD2 | G | 10.81 | 10.84 | 23.40 | 23.41 |
| G/R | 9.67 | 9.69 | 20.40 | 21.42 | |
| G/R/E/C | 9.46 | 9.48 | 20.32 | 21.32 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Dick, G.; Wickert, J.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, K.; Schuh, H. Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121317
Lu C, Chen X, Liu G, Dick G, Wickert J, Jiang X, Zheng K, Schuh H. Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121317
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Cuixian, Xinghan Chen, Gen Liu, Galina Dick, Jens Wickert, Xinyuan Jiang, Kai Zheng, and Harald Schuh. 2017. "Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121317
APA StyleLu, C., Chen, X., Liu, G., Dick, G., Wickert, J., Jiang, X., Zheng, K., & Schuh, H. (2017). Real-Time Tropospheric Delays Retrieved from Multi-GNSS Observations and IGS Real-Time Product Streams. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121317