Experimental Evaluation of Several Key Factors Affecting Root Biomass Estimation by 1500 MHz Ground-Penetrating Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Transect Configuration
1.2. Detection of Dead Roots
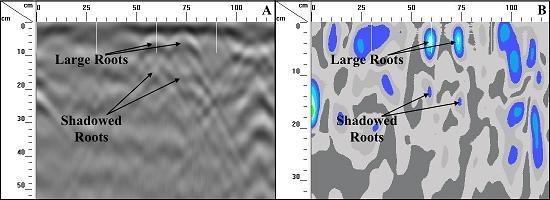
1.3. Root Shadowing
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Dielectric Constant Determination
2.3. Root Biomass Estimation
2.4. GPR Potential for Discrimination between Live and Dead Roots
2.5. Possible Impacts of Root Shadowing on GPR Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Biomass Estimation
3.2. GPR Potential for Discrimination between Live and Dead Roots
3.3. Impacts of Root Shadowing on GPR Measurements
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Scan Directions on Biomass Estimation
4.2. GPR Potential for Discrimination between Live and Dead Roots
4.3. Impacts of Root Shadowing on GPR Measurements
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deans, J.D. Dynamics of coarse root production in a young plantation of Piceasitchensis. Forestry 1981, 54, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveria, M.R.G.; van Noordwijk, M.; Gazeand, S.R.; Brouwer, G. Auger sampling, ingrowth cores and pinboard methods. In Root Methods: A Handbook; Smit, A.L., Bengough, A.G., van Noordwijk, M., Pellerin, S., van de Geijn, S.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 175–210. [Google Scholar]
- Polomski, J.; Kuhn, N. Root research methods. In Plant Roots: The Hidden Half, 3rd ed.; Weisel, Y., Eshel, A., Kafkafi, U., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 447–488. [Google Scholar]
- Reubens, B.; Poesen, J.; Danjon, F.; Geudens, G.; Muys, B. The role of fine and coarse roots in shallow slope stability and soil erosion control with a focus on root system architecture: A review. Trees 2007, 21, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitter, A.H.; Stickland, T.R. Architectural analysis of plant root systems III: Studies on plants under field conditions. New Phytol. 1992, 121, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.J.; Lynch, J.P.; Weiss, H.N. Fractal geometry of bean root systems: Correlations between spatial and fractal dimension. Am. J. Bot. 1997, 84, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butnor, J.R.; Doolittle, J.A.; Johnsen, K.H.; Samuelson, L.; Stokes, T.; Kress, L. Utility of ground-penetrating radar as a root biomass survey tool in forest systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; Hays, D.B.; Bruton, R.K.; Ceballos, H.; Novo, A.; Boi, E.; Selvaraj, M.G. Ground penetrating radar: A case study for estimating root bulking rate in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Plant Methods 2017, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bledsoe, C.S.; Fahey, T.J.; Ruess, R.; Day, F.P. Measurement of static root parameters—Biomass, length, distribution. In Standard Soil Methods for Long-Term Ecological Research; Robertson, G.P., Bledsoe, C.S., Coleman, D.C., Sollins, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 413–436. [Google Scholar]
- Fahey, T.J.; Bledsoe, C.S.; Day, F.P.; Ruess, R.; Smucker, A. Root production and demography. In Standard Soil Methods for Long-Term Ecological Research; Robertson, G.P., Bledsoe, C.S., Coleman, D.C., Sollins, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Norby, R.J.; Jackson, R.B. Root dynamics and global change: Seeking an ecosystem perspective. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntson, G.M.; Farnsworth, E.J.; Bazzaz, F.A. Allocation, within and between organs, and the dynamics of root length changes in two birch species. Oecologia 1995, 101, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruska, J.; Cermak, J.; Sustek, S. Mapping tree root systems with ground-penetrating radar. Tree Physiol. 1999, 19, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cermak, J.; Nadezhdina, N.; Meiresonne, L.; Ceulemans, R. Scots pine root distribution derived from radial sap flow patterns in stems of large leaning trees. Plant Soil 2008, 305, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenone, T.; Morelli, G.; Teobaldelli, M.; Fischanger, F.; Matteucci, M.; Sordini, M.; Armani, A.; Ferre, C.; Chiti, T.; Seufert, G. Preliminary use of ground-penetrating radar and electrical resistivity tomography to study tree roots in pine forests and poplar plantations. Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucci, G. The use of three geophysical methods for 3D images of total root volume of soil in urban environments. Explor. Geophys. 2010, 41, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Fan, B.; Lin, H. Application of ground penetrating radar for coarse root detection and quantification: A review. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielopolski, L.; Hendey, G.; McGuigan, M. Imaging tree root systems in situ. Proc. SPIE 2000, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnor, J.R.; Doolittle, J.A.; Kress, L.; Cohen, S.; Johnsen, K.H. Use of ground-penetrating radar to study tree roots in the southeastern United States. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, D.B.; Day, F.P.; Butnor, J.R.; Drake, B.G. Application of ground penetrating radar to quantify the effects of long-term CO2 enrichment on coarse root biomass in a scrub-oak ecosystem at Kennedy Space Center. Ecology 2007, 88, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butnor, J.R.; Stover, D.B.; Roth, B.; Johnsen, K.H.; Day, F.P.; McInnis, D. Using ground penetrating radar to estimate tree root mass: Comparing results from two Florida surveys. In Handbook of Agricultural Geophysics; Allred, B., Daniels, J.J., Ehsani, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, P.M.; Ferrara, C.; Salvati, L. Tree root system imaging using Ground Penetrating Radar. Ann. Silvic. Res. 2017, 41, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, C.; Barone, P.M.; Pettinelli, E.; Salvati, L. Ground penetrating radar as a remote-sensing approach to investigate the root system architecture. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2014, 12, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, J.E.; McKay, S.K.; McComas, R.W.; Fischenich, J.C. In situ root volume estimation using ground penetrating radar. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2017, 22, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnor, J.R.; Roth, B.; Johnsen, K. Feasibility of Using Ground-Penetrating Radar to Quantify Root Mass in Florida’s Intensively Managed Pine Plantation; Technical Report #38, Forest Biology Research Cooperative; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dannoura, M.; Hirano, Y.; Igarashi, T.; Ishii, M.; Aono, K.; Yamase, K.; Kanazawa, Y. Detection of Cryptomeria japonica roots with ground penetrating radar. Plant Biosyst. 2008, 142, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, L.J.; Butnor, J.R.; Maier, C.; Stokes, T.A.; Johnsen, K.; Kane, M. Growth and physiology of loblolly pine in response to long-term resource management: Defining growth potential in the southern United States. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, K.A.; Isaac, M.E.; Thevathasan, N.V.; Gordon, A.M.; Thomas, S.C. Estimating coarse root biomass with ground penetrating radar in a tree-based intercropping system. Agrofor. Syst. 2014, 88, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, C.M.; Montagu, K.D. Detection of tree roots and determination of root diameters by ground penetrating radar under optimal conditions. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, Y.; Dannoura, M.; Aono, K.; Igarashi, T.; Ishii, M.; Yamase, K.; Makita, N.; Kanazawa, Y. Limiting factors in the detection of tree roots using ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.J. Ground Penetrating Radar, 2nd ed.; Institution of Electrical Engineers: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Al Hagrey, S.A. Geophysical imaging of root-zone, trunk, and moisture heterogeneity. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jol, H.M. Ground Penetrating Radar Theory and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Annan, A.P.; Cosway, S.W. GPR frequency selection. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar, Waterloo Center for Groundwater Research, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 12–16 June 1994; pp. 747–760. [Google Scholar]
- Conyers, L.B. Ground-Penetrating Radar for Archaeology, 2nd ed.; Altamira Press: Walnut Creek, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, C.; Barone, P.M.; Steelman, C.; Pettinelli, E.; Endres, A.L. Monitoring shallow soil water content under natural field conditions using the early-time GPR signal technique. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nuaimy, W.; Huang, Y.; Nakhkash, M.; Fang, M.; Nguyen, V.; Eriksen, A. Automatic detection of buried utilities and solid objects with GPR using neural networks and pattern recognition. J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 43, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigui, H.; Gader, P. Detection and discrimination of land mines in ground-penetrating radar based on edge histogram descriptors and a possibilistic-nearest neighbor classifier. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2009, 17, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.; Carin, L.; Gader, P.D.; Wilson, J.N. An investigation of using the spectral characteristics from ground penetrating radar for landmine/clutter discrimination. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrione, P.; Collins, L.M. Texture features for antitank landmine detection using ground penetrating radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Scherm, H.; Serman, N. Ground-penetrating radar to detect and quantify residual root fragments following peach orchard clearing. HortTechnology 2005, 15, 600–607. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.H.; Chen, J.; Shen, J.S.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.H.; Zhu, X.L. Modeling tree root diameter and biomass by ground-penetrating radar. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F.P.; Schroeder, R.E.; Stover, D.B.; Brown, A.L.; Butnor, J.R.; Dilustro, J.; Hungate, B.A.; Dijkstra, P.; Duval, B.D.; Seller, T.J.; et al. The effects of 11 yr of CO2 enrichment on roots in a Florida scrub-oakecosystem. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, L.J.; Stokes, T.A.; Butnor, J.R.; Johnsen, K.H.; Gonzalez-Benecke, C.A.; Anderson, P.; Jackson, J.; Ferrari, L.; Martin, T.A.; Cropper, W.P. Ecosystem carbon stocks in Pinus palustris forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2014, 44, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, L.J.; Stokes, T.A.; Butnor, J.R.; Johnsen, K.H.; Gonzalez-Benecke, C.A.; Martin, T.A.; Cropper, W.P.; Anderson, P.H.; Ramirez, M.R.; Lewis, J.C. Ecosystem carbon density and allocation across a chronosequence of longleaf pine forests. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanikawa, T.; Hirano, Y.; Dannoura, M.; Yamase, K.; Aono, K.; Ishii, M.; Igarashi, T.; Ikeno, H.; Kanazawa, K. Root orientation can affect detection accuracy of ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, W.; Cui, X.H.; Chen, J. Comment on: Root orientation can affect detection accuracy of ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 2014, 380, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hirano, Y.; Tanikawa, T.; Li, W.; Cui, X.H. Calibrating the impact of root orientation on root quantification using ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 2015, 395, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A.; Fourcaud, T.; Hruska, J.; Cermak, J.; Nadyezdhina, N.; Nadyezhdin, V.; Praus, L. An evaluation of different methods to investigate root system architecture of urban trees in situ: 1. Ground-penetrating radar. J. Arboric. 2002, 28, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tanikawa, T.; Ikeno, H.; Dannoura, M.; Yamase, K.; Aono, K.; Hirano, Y. Leaf litter thickness, but not plant species, can affect root detection by ground penetrating radar. Plant Soil 2016, 408, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Protection of urban trees from trenching damage in compact city environments. Cities 2003, 20, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, C.C.; Musselman, L.J. History and vegetation of the Blackwater Ecologic Preserve. Castanea 1987, 52, 15–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, L.; Cui, X.H.; Chen, J.; Cao, X.; Lin, H. Ground-penetrating radar-based automatic reconstruction of three-dimensional coarse root system architecture. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.H.; Guo, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.H.; Zhu, X.L. Estimating tree-root biomass in different depths using ground-penetrating radar: Evidence from a controlled experiment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3410–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Application | Soil Water Cont. (%) | Soil Dielectric (Unitless) | Scan/m | Range (ns) | Collection Filters | Post-Collection Filters | Image Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos. | Back. | Mig. | Hilbert | Amplitude | ||||||
| Corr. | Rem. | Trans. | Threshold | |||||||
| Cores | 8 | 2.42 | 400 | 10 | FIR (boxcar), gain −15, 15, 20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 70–240 |
| Biomass Plots | 7 | 2.02 | 400 | 10 | FIR (boxcar), gain −15, 15, 20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 70–215 |
| Live vs. Dead Exp. | 6 | 4.25 | 400 | 10 | FIR (boxcar), gain −15, 15, 20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 70–205 |
| Root Shadow. Exp. | 7 | 3.39 | 400 | 10 | FIR (boxcar), gain −15, 15, 20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 70–205 |
| Scan Dir. | Regression | R2 | Biomass Est. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Used | Equation | (g/m2) | ||
| 1 | y = 0.0179x + 30.209 | 0.62419 | 2821 | 0.21 |
| 2 | y = 0.0221x + 35.812 | 0.42631 | 3399 | 0.35 |
| 3 | y = 0.0188x + 47.427 | 0.2789 | 3851 | 0.08 |
| 4 | y = 0.0206x + 29.858 | 0.41167 | 2969 | 0.44 |
| 1 & 2 | y = 0.025x + 21.532 | 0.67607 | 2771 | 0.52 |
| 1 & 3 | y = 0.0314x + 12.092 | 0.78542 | 2637 | 0.69 |
| 1 & 4 | y = 0.0205x + 29.963 | 0.41099 | 2967 | 0.44 |
| 2 & 3 | y = 0.0264x + 32.071 | 0.45089 | 3454 | 0.18 |
| 2 & 4 | y = 0.0311x + 13.18 | 0.6107 | 2677 | 0.96 |
| 3 & 4 | y = 0.0282x + 23.23 | 0.49127 | 3066 | 0.73 |
| 1, 2, & 3 | y = 0.032x + 13.519 | 0.73571 | 2752 | 0.79 |
| 1, 2, & 4 | y = 0.029x + 12.286 | 0.71708 | 2496 | 0.36 |
| 1, 3, & 4 | y = 0.032x + 8.8377 | 0.74547 | 2487 | 0.49 |
| 2, 3, & 4 | y = 0.0328x + 15.297 | 0.59245 | 2902 | 0.66 |
| 1, 2, 3, & 4 | y = 0.0338x + 7.5286 | 0.75361 | 2525 | 0.94 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bain, J.C.; Day, F.P.; Butnor, J.R. Experimental Evaluation of Several Key Factors Affecting Root Biomass Estimation by 1500 MHz Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121337
Bain JC, Day FP, Butnor JR. Experimental Evaluation of Several Key Factors Affecting Root Biomass Estimation by 1500 MHz Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121337
Chicago/Turabian StyleBain, John C., Frank P. Day, and John R. Butnor. 2017. "Experimental Evaluation of Several Key Factors Affecting Root Biomass Estimation by 1500 MHz Ground-Penetrating Radar" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121337
APA StyleBain, J. C., Day, F. P., & Butnor, J. R. (2017). Experimental Evaluation of Several Key Factors Affecting Root Biomass Estimation by 1500 MHz Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121337