Estimation of SOS and EOS for Midwestern US Corn and Soybean Crops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Data Preprocessing
2.2. Estimate Crop Phenology Using Time-Series MODIS Data
2.3. Comparison of MODIS-Derived Crop Phenology Parameters with CPRs
2.4. Analysis of Phenological Spatial Pattern
3. Results
3.1. MODIS-Derived SOS and EOS Metrics Using a Default Threshold Value
3.2. MODIS-Derived SOS Metrics with Various Threshold Values
3.3. MODIS-Derived EOS Metrics with Various Threshold Values
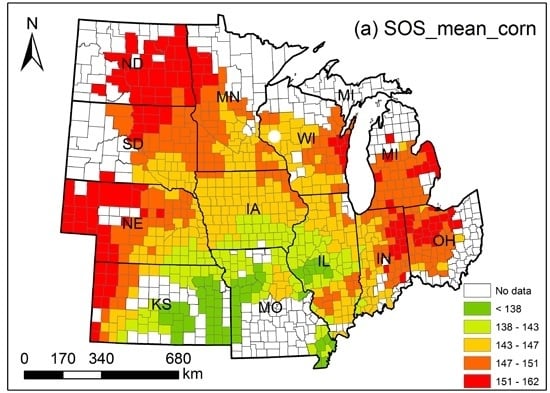
3.4 Spatial Patterns of SOS and EOS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boschetti, M.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.; Bocchi, S. Multi-Year Monitoring of Rice Crop Phenology through Time Series Analysis of MODIS Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4643–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M.; Toritani, H.; Shibayama, M.; Ishitsuka, N.; Ohno, H. A Crop Phenology Detection Method Using Time-Series MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Yu, Z.; van Leeuwen, L.; Driessen, P.M. Mapping Crop Key Phenological Stages in the North China Plain Using Noaa Time Series Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2002, 4, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Yokozawa, M.; Xu, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Zhang, Z. Climate Changes and Trends in Phenology and Yields of Field Crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 138, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D.K.; Friedl, M.A. Forecasting Crop Yield Using Remotely Sensed Vegetation Indices and Crop Phenology Metrics. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 173, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Zhu, X.; Sulla-Menashe, D. Winter Wheat Area Estimation from MODIS-Evi Time Series Data Using the Crop Proportion Phenology Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping Paddy Rice Agriculture in South and Southeast Asia Using Multi-Temporal MODIS Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doraiswamy, P.; Hatfield, J.; Jackson, T.; Akhmedov, B.; Prueger, J.; Stern, A. Crop Condition and Yield Simulations Using Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liang, S.; Hoogenboom, G. Integration of MODIS Lai and Vegetation Index Products with the Csm–Ceres–Maize Model for Corn Yield Estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 1039–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A.; Thornton, P.E.; Running, S.W. A Continental Phenology Model for Monitoring Vegetation Responses to Interannual Climatic Variability. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvick, D.N. Possible genetic causes of increased variability in U.S. maize yields. In Variability in Grain Yields: Implications for Agricultural Research and Policy in Developing Countries; Anderson, J.R., Hazel, P.B.R., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Kucharik, C.J. A Multidecadal Trend of Earlier Corn Planting in the Central USA. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, X. Phenological Changes of Corn and Soybeans over Us by Bayesian Change-Point Model. Sustainability 2015, 7, 6781–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.; Atzberger, C.; Høgda, K.A.; Johansen, B.; Skidmore, A.K. Improved Monitoring of Vegetation Dynamics at Very High Latitudes: A New Method Using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklundh, L.; Olsson, L. Vegetation Index Trends for the African Sahel 1982–1999. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heumann, B.W.; Seaquist, J.; Eklundh, L.; Jönsson, P. Avhrr Derived Phenological Change in the Sahel and Soudan, Africa, 1982–2005. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, A.; Johnson, D.M. Land-Surface Phenologies from Avhrr Using the Discrete Fourier Transform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, S.; Kergoat, L.; Viovy, N.; Dedieu, G. Global-Scale Assessment of Vegetation Phenology Using Noaa/Avhrr Satellite Measurements. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1154–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Hodges, J.C.; Gao, F.; Reed, B.C.; Huete, A. Monitoring Vegetation Phenology Using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Morisette, J.T.; Wolfe, R.E.; Gao, F.; Ederer, G.A.; Nightingale, J.; Pedelty, J.A. An Enhanced Timesat Algorithm for Estimating Vegetation Phenology Metrics from MODIS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Kastens, J.H.; Egbert, S.L. Using Usda Crop Progress Data for the Evaluation of Greenup Onset Date Calculated from MODIS 250-Meter Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Wardlow, B.D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.E.; Arkebauer, T.J. A Two-Step Filtering Approach for Detecting Maize and Soybean Phenology with Time-Series MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S.; Wheeler, B.; Iiames, J.S.; Campbell, J.B. An Evaluation of Time-Series Smoothing Algorithms for Land-Cover Classifications Using MODIS-NDVI Multi-Temporal Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beurs, K.M.; Henebry, G.M. Spatio-Temporal Statistical Methods for Modelling Land Surface Phenology. In Phenological Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 177–208. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Morisette, J.T.; Wolfe, R.E.; Ederer, G.; Pedelty, J.; Masuoka, E.; Myneni, R.; Tan, B.; Nightingale, J. An Algorithm to Produce Temporally and Spatially Continuous MODIS-Lai Time Series. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality Extraction by Function Fitting to Time-Series of Satellite Sensor Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Timesat—A Program for Analyzing Time-Series of Satellite Sensor Data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Friedl, M.A.; Tan, B.; Zhang, X.; Verma, M. Land Surface Phenology from MODIS: Characterization of the Collection 5 Global Land Cover Dynamics Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the Radiometric and Biophysical Performance of the MODIS Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, P.R.; Robertson, G.P.; Millar, N.; Colunga-Garcia, M.; Basso, B.; Gage, S.H.; Hoben, J. The Contribution of Maize Cropping in the Midwest USA to Global Warming: A Regional Estimate. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boryan, C.; Yang, Z.; Mueller, R.; Craig, M. Monitoring Us Agriculture: The US Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Statistics Service, Cropland Data Layer Program. Geocarto Int. 2011, 26, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Kastens, J.H.; Coutinho, A.C.; de Castro Victoria, D.; Bishop, C.R. Classifying multiyear agricultural land use data from Mato Grosso using time-series MODIS vegetation index data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Corn | Soybean | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |
| Illinois | 6.70 | 0.60 | 5.88 | 0.57 |
| Indiana | 5.28 | 0.96 | 3.94 | 0.98 |
| Iowa | 3.56 | 0.89 | 5.51 | 0.83 |
| Kansas | 4.49 | 0.44 | 3.11 | 0.79 |
| Michigan | 3.95 | 0.45 | 4.23 | 0.34 |
| Minnesota | 6.83 | 0.79 | 7.12 | 0.57 |
| Missouri | 4.24 | 0.75 | 5.53 | 0.74 |
| Nebraska | 5.17 | 0.62 | 5.74 | 0.32 |
| North Dakota | 4.94 | 0.66 | 5.90 | 0.54 |
| Ohio | 2.84 | 0.97 | 5.54 | 0.73 |
| South Dakota | 4.02 | 0.44 | 5.23 | 0.21 |
| Wisconsin | 4.11 | 0.61 | 4.60 | 0.46 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Campbell, J.B.; Shao, Y. Estimation of SOS and EOS for Midwestern US Corn and Soybean Crops. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070722
Ren J, Campbell JB, Shao Y. Estimation of SOS and EOS for Midwestern US Corn and Soybean Crops. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070722
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jie, James B. Campbell, and Yang Shao. 2017. "Estimation of SOS and EOS for Midwestern US Corn and Soybean Crops" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070722
APA StyleRen, J., Campbell, J. B., & Shao, Y. (2017). Estimation of SOS and EOS for Midwestern US Corn and Soybean Crops. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070722