Mapping of Aedes albopictus Abundance at a Local Scale in Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Mosquito Data
2.2. Environmental Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
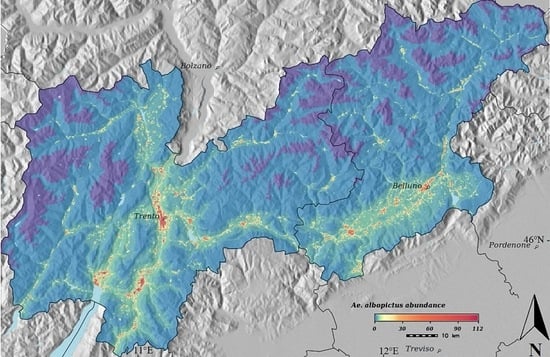
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lessler, J.; Chaisson, L.H.; Kucirka, L.M.; Bi, Q.F.; Grantz, K.; Salje, H.; Carcelen, A.C.; Ott, C.T.; Sheffield, J.S.; Ferguson, N.M. Assessing the global threat from Zika virus. Science 2016, 353, aaf8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffner, F.; Mathis, A. Dengue and dengue vectors in the WHO European region: Past, present, and scenarios for the future. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.P.; Luther, C.; Moo-Llanes, D.; Ramsey, J.M.; Danis-Lozano, R.; Peterson, A.T. Climate change influences on global distributions of dengue and chikungunya virus vectors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Sinka, M.E.; Duda, K.A.; Mylne, A.Q.N.; Shearer, F.M.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Carvalho, R.G.; Coelho, G.E.; Van Bortel, W.; et al. The global distribution of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. Elife 2015, 4, e08347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffner, F.; Medlock, J.M.; Van Bortel, W. Public health significance of invasive mosquitoes in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R. Species distribution models: Ecological explanation and prediction across space and time. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purse, B.V.; Golding, N. Tracking the distribution and impacts of diseases with biological records and distribution modelling. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 115, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleckner, H.L.; Allen, T.R.; Bellows, A.S. Remote sensing and modeling of mosquito abundance and habitats in coastal Virginia, USA. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2663–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, K.; Gunay, F.; Tuzer, E.; Linton, Y.M.; Bellini, R.; Alten, B. First record of Stegomyia albopicta in Turkey determined by active ovitrap surveillance and DNA Barcoding. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochlin, I.; Ninivaggi, D.V.; Hutchinson, M.L.; Farajollahi, A. Climate change and range expansion of the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) in Northeastern USA: Implications for public health practitioners. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetta, G.; Montarsi, F.; Baldacchino, F.A.; Metz, M.; Capelli, G.; Rizzoli, A.; Pugliese, A.; Rosà, R.; Poletti, P.; Merler, S. Potential risk of dengue and chikungunya outbreaks in Northern Italy based on a population model of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Thomas, S.M.; Neteler, M.; Tjaden, N.B.; Beierkuhnlein, C. Climatic suitability of Aedes albopictus in Europe referring to climate change projections: Comparison of mechanistic and correlative niche modelling approaches. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatchikian, C.; Sangermano, F.; Kendell, D.; Livdahl, T. Evaluation of species distribution model algorithms for fine-scale container-breeding mosquito risk prediction. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unlu, I.; Klingler, K.; Indelicato, N.; Faraji, A.; Strickman, D. Suppression of Aedes albopictus, the Asian tiger mosquito, using a ‘hot spot’ approach. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 72, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunze, S.; Kochmann, J.; Koch, L.K.; Klimpel, S. Aedes albopictus and its environmental limits in Europe. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, E.A.; Blackmore, M.S.; Golladay, S.W.; Covich, A.P. Weather and landscape factors associated with adult mosquito abundance in southwestern Georgia, USA. J. Vector Ecol. 2011, 36, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, B.G.; Morris, J.A.; Caamano, E.X.; Griffith, D.A.; Novak, R.J. Geomapping generalized eigenvalue frequency distributions for predicting prolific Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus habitats based on spatiotemporal field-sampled count data. Acta Trop. 2011, 117, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwambeke, S.O.; Bennett, S.N.; Kapan, D.D. Spatially disaggregated disease transmission risk: Land cover, land use and risk of dengue transmission on the island of Oahu. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2011, 16, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagny Beilhe, L.; Arnoux, S.; Delatte, H.; Lajoie, G.; Fontenille, D. Spread of invasive Aedes albopictus and decline of resident Aedes aegypti in urban areas of Mayotte 2007–2010. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett-Healy, K.; Unlu, I.; Obenauer, P.; Hughes, T.; Healy, S.; Crepeau, T.; Farajollahi, A.; Kesavaraju, B.; Fonseca, D.; Schoeler, G.; et al. Larval mosquito habitat utilization and community dynamics of Aedes albopictus and Aedes japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; Ippoliti, C.; Balenghien, T.; Conte, A.; Gely, M.; Calistri, P.; Goffredo, M.; Baldet, T.; Chevalier, V. A Geographical information system-based multicriteria evaluation to map areas at risk for Rift valley fever vector-borne transmission in Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, B.; Leger, L.; L’Ambert, G.; Lacour, G.; Foussadier, R.; Besnard, G.; Barre-Cardi, H.; Simard, F.; Fontenille, D. The spread of Aedes albopictus in metropolitan France: Contribution of environmental drivers and human activities and predictions for a near future. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, D.M.; Archer, R.S.; Alimi, T.O.; Arheart, K.L.; Impoinvil, D.E.; Oscar, R.; Fuller, D.O.; Qualls, W.A. New baseline environmental assessment of mosquito ecology in northern Haiti during increased urbanization. J. Vector Ecol. 2015, 40, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcantonio, M.; Metz, M.; Baldacchino, F.; Arnoldi, D.; Montarsi, F.; Capelli, G.; Carlin, S.; Neteler, M.; Rizzoli, A. First assessment of potential distribution and dispersal capacity of the emerging invasive mosquito Aedes koreicus in Northeast Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrarese, U. Monitoring of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera, Culicidae) around a focus in Rovereto (northern Italy). Ann. Mus. Civ. Rovereto 2004, 19, 281–295. [Google Scholar]
- Montarsi, F.; Martini, S.; Dal Pont, M.; Delai, N.; Milone, N.F.; Mazzucato, M.; Soppelsa, F.; Cazzola, L.; Cazzin, S.; Ravagnan, S.; et al. Distribution and habitat characterization of the recently introduced invasive mosquito Aedes koreicus (Hulecoeteomyia koreica), a new potential vector and pest in north-eastern Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. Guidelines for the Surveillance of Invasive Mosquito Species in Europe; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Petrić, D.; Bellini, R.; Scholte, E.-J.; Rakotoarivony, L.M.; Schaffner, F. Monitoring population and environmental parameters of invasive mosquito species in Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajollahi, A.; Kesavaraju, B.; Price, D.C.; Williams, G.M.; Healy, S.P.; Gaugler, R.; Nelder, M.P. Field efficacy of BG-sentinel and industry-standard Traps for Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and West Nile virus surveillance. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhken, R.; Pfitzner, W.P.; Borstler, J.; Garms, R.; Huber, K.; Schork, N.; Steinke, S.; Kiel, E.; Becker, N.; Tannich, E.; et al. Field evaluation of four widely used mosquito traps in Central Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldacchino, F.; Montarsi, F.; Arnoldi, D.; Barategui, C.; Ferro Milone, N.; Da Rold, G.; Capelli, G.; Rizzoli, A. A 2-yr mosquito survey focusing on Aedes koreicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Northern Italy and implications for adult trapping. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obenauer, P.J.; Kaufman, P.E.; Kline, D.L.; Allan, S.A. Detection of and monitoring for Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in suburban and sylvatic Habitats in North Central Florida using four sampling techniques. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffner, E.; Angel, G.; Geoffroy, B.; Hervy, J.-P. Les Moustiques d’Europe/The Mosquitoes of Europe; CD-ROM; Institut de Recherche pour le développement/EID Méditerranée: Montpellier, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetta, G.; Poletti, P.; Montarsi, F.; Baldacchino, F.; Capelli, G.; Rizzoli, A.; Rosà, R.; Merler, S. Assessing the potential risk of Zika virus epidemics in temperate areas with established Aedes albopictus populations. Euro Surveill. 2016, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminade, C.; Medlock, J.M.; Ducheyne, E.; McIntyre, K.M.; Leach, S.; Baylis, M.; Morse, A.P. Suitability of European climate for the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus: Recent trends and future scenarios. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, M.; Rocchini, D.; Neteler, M. Surface temperatures at the continental scale: Tracking changes with remote sensing at unprecedented detail. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3822–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldock, J.; Chandra, N.L.; Lelieveld, J.; Proestos, Y.; Michael, E.; Christophides, G.; Parham, P.E. The role of environmental variables on Aedes albopictus biology and chikungunya epidemiology. Pathog. Glob. Health 2013, 107, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. Available online: http://qgis.osgeo.org (accessed on 15 June 2016).
- Marini, F.; Caputo, B.; Pombi, M.; Tarsitani, G.; Della Torre, A. Study of Aedes albopictus dispersal in Rome, Italy, using sticky traps in mark-release-recapture experiments. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, M.C.; Boothe, E.C.; Roark, E.B.; Hamer, G.L. Dispersal of male and female Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes using stable isotope enrichment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcantonio, M. Environmental Modelling and Spatial Ecology with Focus on Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes and Emergent Mosquito-Borne Pathogens; Technische Universität Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 22 April 2016).
- Fournier, D.; Skaug, H.; Ancheta, J.; Ianelli, J.; Magnusson, A.; Maunder, M.; Nielsen, A.; Sibert, J. AD Model Builder: Using automatic differenciation for statistical inference of highly parameterized complex nonlinear models. Optim. Methods Softw. 2012, 27, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawley, M.J. The R Book; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. R Package Version 1.15.6. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 4 May 2016).
- Rosà, R.; Marini, G.; Bolzoni, L.; Neteler, M.; Metz, M.; Delucchi, L.; Chadwick, E.A.; Balbo, L.; Mosca, A.; Giacobini, M.; et al. Early warning of West Nile virus mosquito vector: Climate and land use models successfully explain phenology and abundance of Culex pipiens mosquitoes in north-western Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N. A protocol for conducting and presenting results of regression-type analyses. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M.; Bowman, M.H.; Landa, M.; Metz, M. GRASS GIS: A multi-purpose open source GIS. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2012, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M.; Roiz, D.; Rocchini, D.; Castellani, C.; Rizzoli, A. Terra and Aqua satellites track tiger mosquito invasion: Modelling the potential distribution of Aedes albopictus in north-eastern Italy. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roiz, D.; Neteler, M.; Castellani, C.; Arnoldi, D.; Rizzoli, A. Climatic factors driving invasion of the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) into new areas of Trentino, Northern Italy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrieri, M.; Angelini, P.; Venturelli, C.; Maccagnani, B.; Bellini, R. Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) population size survey in the 2007 chikungunya outbreak Area in Italy. I. characterization of breeding sites and evaluation of sampling methodologies. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Kamara, F.; Zhou, G.F.; Puthiyakunnon, S.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yao, L.J.; Yan, G.Y.; Chen, X.G. Urbanization increases Aedes albopictus larval habitats and accelerates mosquito development and survivorship. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manica, M.; Filipponi, F.; D’Alessandro, A.; Screti, A.; Neteler, M.; Rosà, R.; Solimini, A.; della Torre, A.; Caputo, B. Spatial and temporal hot spots of Aedes albopictus abundance inside and outside a South European metropolitan area. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; L’Ambert, G.; Lacour, G.; Benoit, R.; Demarchi, M.; Cros, M.; Cailly, P.; Aubry-Kientz, M.; Balenghien, T.; Ezanno, P. A rainfall- and temperature-driven abundance model for Aedes albopictus populations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1698–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ECDC. Development of Aedes Albopictus Risk Maps; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alto, B.W.; Juliano, S.A. Temperature effects on the dynamics of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) populations in the laboratory. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delatte, H.; Gimonneau, G.; Triboire, A.; Fontenille, D. Influence of temperature on immature development, survival, longevity, fecundity, and gonotrophic cycles of Aedes albopictus, vector of chikungunya and dengue in the Indian ocean. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunze, S.; Koch, L.K.; Kochmann, J.; Klimpel, S. Aedes albopictus and Aedes japonicus—Two invasive mosquito species with different temperature niches in Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.M.; Obermayr, U.; Fischer, D.; Kreyling, J.; Beierkuhnlein, C. Low-temperature threshold for egg survival of a post-diapause and non-diapause European aedine strain, Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrieri, M.; Angelini, P.; Venturelli, C.; Maccagnani, B.; Bellini, R. Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) population size survey in the 2007 chikungunya outbreak area in Italy. II: Estimating epidemic thresholds. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manica, M.; Rosà, R.; della Torre, A.; Caputo, B. From eggs to bites: Do ovitrap data provide reliable estimates of Aedes albopictus biting females? Peerj 2017, 5, e2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrieri, M.; Albieri, A.; Urbanelli, S.; Angelini, P.; Venturelli, C.; Matrangolo, C.; Bellini, R. Quality control and data validation procedure in large-scale quantitative monitoring of mosquito density: The case of Aedes albopictus in Emilia-Romagna region, Italy. Pathog. Glob. Health 2017, 111, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2013: The Phyical Science Basis Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, B.; Zullo, F. Half a century of urbanization in southern European lowlands: A study on the Po Valley (Northern Italy). Urban Res. Practice 2016, 9, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Explanatory Variables | Mean (Standard Deviation) | Range | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean temperature of the coldest month (°C) | 2.15 (1.01) | 0.66–4.46 | Land surface temperature (LST) data from the MODIS version 5 |
| Mean temperature of the warmest quarter (°C) | 20.80 (1.98) | 17.54–24.86 | Land surface temperature (LST) data from the MODIS version 5 |
| Total annual precipitation (mm) | 1483.6 (646.8) | 683.4–2624.0 | http://www.arpa.veneto.it/; http://www.meteotrentino.it/ |
| Total precipitation of the second quarter (mm) | 275.7 (72.4) | 174.6–414.8 | http://www.arpa.veneto.it/; http://www.meteotrentino.it/ |
| Total precipitation of the third quarter (mm) | 394.1 (130.5) | 211.8–645.4 | http://www.arpa.veneto.it/; http://www.meteotrentino.it/ |
| Artificial areas (%) | 51.4 (27.9) | 4.5–99.7 | http://dati.trentino.it/; http://dati.veneto.it/ |
| Agricultural areas (%) | 29.9 (24.1) | 0–83.7 | http://dati.trentino.it/; http://dati.veneto.it/ |
| Forests and semi-natural areas (%) | 17.4 (17.2) | 0–61.6 | http://dati.trentino.it/; http://dati.veneto.it/ |
| Fixed Explanatory Variables | Estimate | Standard Error | z-Value | Pr (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 2.675 | 0.246 | 10.86 | <0.001 |
| Mean temperature warmest quarter | 0.501 | 0.059 | 8.48 | <0.001 |
| Percentage of artificial areas | 0.793 | 0.242 | 3.27 | 0.0011 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldacchino, F.; Marcantonio, M.; Manica, M.; Marini, G.; Zorer, R.; Delucchi, L.; Arnoldi, D.; Montarsi, F.; Capelli, G.; Rizzoli, A.; et al. Mapping of Aedes albopictus Abundance at a Local Scale in Italy. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070749
Baldacchino F, Marcantonio M, Manica M, Marini G, Zorer R, Delucchi L, Arnoldi D, Montarsi F, Capelli G, Rizzoli A, et al. Mapping of Aedes albopictus Abundance at a Local Scale in Italy. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070749
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldacchino, Frédéric, Matteo Marcantonio, Mattia Manica, Giovanni Marini, Roberto Zorer, Luca Delucchi, Daniele Arnoldi, Fabrizio Montarsi, Gioia Capelli, Annapaola Rizzoli, and et al. 2017. "Mapping of Aedes albopictus Abundance at a Local Scale in Italy" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070749
APA StyleBaldacchino, F., Marcantonio, M., Manica, M., Marini, G., Zorer, R., Delucchi, L., Arnoldi, D., Montarsi, F., Capelli, G., Rizzoli, A., & Rosà, R. (2017). Mapping of Aedes albopictus Abundance at a Local Scale in Italy. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070749