A Robust Algorithm for Estimating Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover from Landsat Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
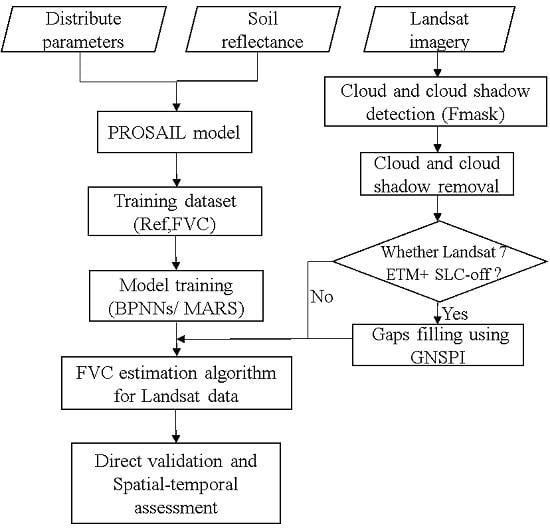
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data and Pre-Processing
2.1.1. Cloud and cloud shadow detection
2.1.2. Cloud and cloud shadow removal
2.1.3. Gap filling for Landsat 7 ETM+ data
2.2. Training Dataset Generated from PROSAIL Radiative Transfer Model
2.3. Machine Learning Methods
2.3.1. The BPNNs Model
2.3.2. The MARS Model
2.4. Direct Validation and Spatial-Temporal Assessment
2.4.1. Accuracy Assessment in Heihe Region
2.4.2. Accuracy Assessment in Chengde Region
2.4.3. Spatial-Temporal Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment Over the Simulated Dataset
3.2. Accuracy Assessment Using Field Survey FVC
3.2.1. Accuracy Assessment in Heihe Region
3.2.2. Accuracy Assessment in Chengde Region
3.3. Spatial-Temporal Analysis
3.3.1. Spatial Analysis
3.3.2. Time Series Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholcyzk, P.; Smets, B. GEOV1: LAI and FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, C.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Fractional vegetation cover estimation in arid and semi-arid environments using HJ-1 satellite hyperspectral data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Ignatov, A. The derivation of the green vegetation fraction from NOAA/AVHRR data for use in numerical weather prediction models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Lakshmi, V.; Small, E.E. The Effects of satellite-derived vegetation cover variability on simulated land–atmosphere interactions in the NAMS. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Ling, F.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, N.; Yuan, C. Identification of priority areas for controlling soil erosion. Catena 2010, 83, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitch, S.; Smith, B.; Prentice, I.C.; Arneth, A.; Bondeau, A.; Cramer, W.; Kaplan, J.O.; Levis, S.; Lucht, W.; Sykes, M.T.; et al. Evaluation of ecosystem dynamics, plant geography and terrestrial carbon cycling in the LPJ dynamic global vegetation model. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Moody, A. A comparison of methods for estimating fractional green vegetation cover within a desert-to-upland transition zone in central New Mexico, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Hill, M.J.; Renzullo, L.J.; Barrett, D.J.; Marks, A.S.; Botha, E.J. Estimating fractional cover of photosynthetic vegetation, non-photosynthetic vegetation and bare soil in the Australian tropical savanna region upscaling the EO-1 Hyperion and MODIS sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiapaer, G.; Chen, X.; Bao, A. A comparison of methods for estimating fractional vegetation cover in arid regions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R.; Rundquist, D. Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetz, R.D.; Pech, R.P.; Davis, A.W. The assessment and monitoring of sparsely vegetated rangelands using calibrated Landsat data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Plaza, A.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J.; Martinez, P. Comparison between fractional vegetation cover retrievals from vegetation indices and spectral mixture analysis: Case study of PROBA/CHRIS data over an agricultural area. Sensors 2009, 9, 768–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.; Tateishi, R.; Kobayashi, T. Remote sensing of fractional green vegetation cover using spatially-interpolated endmembers. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2619–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, M.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Yan, C. Developing method of vegetation fraction estimation by remote sensing for soil loss equation: A case in the upper basin of miyun reservoir. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 6, pp. 4352–4355. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.J.; Chen, J.M.; Gong, P.; Liang, S.; Zhan, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Li, D. Fractional vegetation cover estimation over large regions using GF-1 satellite data. In Proceedings of the Land Surface Remote Sensing II, Beijing, China, 13 October 2014; Volume 9260, p. 92604B. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Marsett, R.C.; Moran, M.S.; Goodrich, D.C.; Heilman, P.; Kerr, Y.H.; Dedieu, G.; Chehbouni, A.; Zhang, X.X. Spatial and temporal dynamics of vegetation in the San Pedro River basin area. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 105, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, D.S.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Abuelgasim, A.A.; Gao, F. Inversion methods for physically-based models. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 381–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.-L. Global mapping of vegetation parameters from POLDER multiangular measurements for studies of surface-atmosphere interactions: A pragmatic method and its validation. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Kalra, A.; Stephen, H. Estimating soil moisture using remote sensing data: A machine learning approach. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, A.; Baret, F.; Camacho, F. Optimal modalities for radiative transfer-neural network estimation of canopy biophysical characteristics: Evaluation over an agricultural area with CHRIS/PROBA observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Gu, X.; Baret, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Fractional vegetation cover estimation algorithm for Chinese GF-1 wide field view data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Tang, H.; et al. A long-term Global LAnd Surface Satellite (GLASS) data-set for environmental studies. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Hagolle, O.; Geiger, B.; Bicheron, P.; Miras, B.; Huc, M.; Berthelot, B.; Niño, F.; Weiss, M.; Samain, O.; et al. LAI, fAPAR and fCover CYCLOPES global products derived from VEGETATION. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Global land surface fractional vegetation cover estimation using general regression neural networks from MODIS surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Comparison of four machine learning methods for generating the GLASS fractional vegetation cover product from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Haro, F.J.; Camacho-de Coca, F.; Miralles, J.M. Inter-comparison of SEVIRI/MSG and MERIS/ENVISAT biophysical products over Europe and Africa. In Proceedings of the 2nd MERIS/(A)ATSR User Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 22–26 September 2008; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Weiss, M.; Waldner, F.; Defourny, P.; Demarez, V.; Morin, D.; Hagolle, O.; Baret, F. A Generic algorithm to estimate LAI, FAPAR and FCOVER variables from SPOT4_HRVIR and Landsat sensors: Evaluation of the consistency and comparison with ground measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15494–15516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.L.; Goward, S.; Arvidson, T. Landsat. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidson, T.; Goward, S.; Gasch, J.; Williams, D. Landsat-7 long-term acquisition plan. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Roy, D.P. The availability of cloud-free Landsat ETM+ data over the conterminous United States and globally. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1196–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontgis, C.; Schneider, A.; Ozdogan, M. Mapping rice paddy extent and intensification in the Vietnamese Mekong River Delta with dense time stacks of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrence, M.; Nong, D.; Tran, C.; Young, L.; Fox, J. Mapping urban transitions using multi-temporal Landsat and DMSP-OLS night-time lights imagery of the Red River Delta in Vietnam. Land 2014, 3, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Seitz, N.; White, J.C.; Gao, F.; Masek, J.G.; Stenhouse, G. Generation of dense time series synthetic Landsat data through data blending with MODIS using a spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Goward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.; Vogelmann, J.E. An automated approach for reconstructing recent forest disturbance history using dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A. Monitoring land cover change in urban and peri-urban areas using dense time stacks of Landsat satellite data and a data mining approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.G.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.K. A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for north America, 1990–2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiersperger, T.K.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Leigh, L.; Shrestha, S.; Gallo, K.P.; Jenkerson, C.B.; Dwyer, J.L. Characterizing LEDAPS surface reflectance products by comparisons with AERONET, field spectrometer, and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J. A Modified neighborhood similar pixel interpolator approach for removing thick clouds in Landsat images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Gao, F.; Jin, S. A simple and effective method for filling gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; Garcia-Haro, F.J.; Moreno, A.; Gilabert, M.A.; Martinez, B.; Sanchez-Ruiz, S.; Camps-Valls, G. Development of an earth observation processing chain for crop bio-physical parameters at local scale. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT+SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, W. Light scattering by leaf layers with application to canopy reflectance modeling: The SAIL model. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 16, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F. PROSPECT: A model of leaf optical properties spectra. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 34, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S. Comparison of Four Radiative Transfer models to simulate plant canopies reflectance direct and inverse mode. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.A.; Gausman, H.W.; Richardson, A.J.; Thomas, J.R. Interaction of isotropic light with a compact plant leaf. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilson, T. A theoretical analysis of the frequency of gaps in plant stands. Agric. Meteorol. 1971, 8, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Palm, C.A.; Gachengo, C.N.; Vanlauwe, B. Rapid Characterization of organic resource quality for soil and livestock management in tropical agroecosystems using near-infrared spectroscopy. Agron. J. 2003, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, P.E.; Halligan, K.Q.; Roberts, D.A. A comparison of error metrics and constraints for multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis and spectral angle mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Wei, X.; Li, Q.; Du, X.; Jiang, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Fractional forest cover changes in northeast China from 1982 to 2011 and its relationship with climatic variations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, A.R.; Xiao, X. Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann. Stat. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Multivariate adaptive regression splines (with discussion). Ann. Stat. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Huang, S.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Song, W.; Ruan, G. Validating GEOV1 fractional vegetation cover derived from coarse-resolution remote sensing images over croplands. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xie, D.; Mu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, G. Accuracy evaluation of the ground-based fractional vegetation cover measurement by using simulated images. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 3347–3350. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Mu, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, G.; Henebry, G. A novel method for extracting green fractional vegetation cover from digital images. J. Veg. Sci. 2012, 23, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Yao, Y.; Xie, X. Forest cover classification using Landsat ETM+ data and time series MODIS NDVI data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montavon, G.; Braun, M.L.; Krueger, T.; Muller, K.-R. Analyzing local structure in kernel-based learning: Explanation, complexity, and reliability assessment. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Grau-Muedra, G.; Nutini, F.; Crema, A.; Boschetti, M. Multitemporal and multiresolution leaf area index retrieval for operational local rice crop monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parameters | Units | Range (or Value) | Step | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROSPECT | Cab | μg/cm2 | 30−60 | 10 |
| Cm | g/cm2 | 0.005−0.015 | 0.005 | |
| Car | g/cm2 | 0 | - | |
| Cw | cm | 0.005−0.015 | 0.005 | |
| Cbrown | - | 0−0.5 | 0.5 | |
| SAIL | N | - | 1−1.5 | 0.5 |
| FVC | - | 0−0.95 | 0.05 | |
| ALA | ° | 30−70 | 10 | |
| Hot | - | 0.1 | - | |
| SZA | ° | 25−55 | 10 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Wei, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X. A Robust Algorithm for Estimating Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover from Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080857
Yang L, Jia K, Liang S, Wei X, Yao Y, Zhang X. A Robust Algorithm for Estimating Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover from Landsat Data. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080857
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Linqing, Kun Jia, Shunlin Liang, Xiangqin Wei, Yunjun Yao, and Xiaotong Zhang. 2017. "A Robust Algorithm for Estimating Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover from Landsat Data" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080857
APA StyleYang, L., Jia, K., Liang, S., Wei, X., Yao, Y., & Zhang, X. (2017). A Robust Algorithm for Estimating Surface Fractional Vegetation Cover from Landsat Data. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080857