Exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to Dietary Nε-Carboxymethyllysine Emphasizes Endocytosis as a New Route for Intestinal Absorption of Advanced Glycation End Products
Abstract
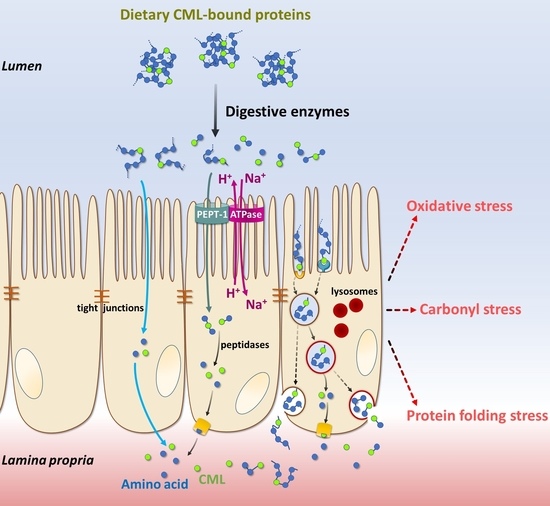
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematode and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Culture of OP50 Strain and Maintenance of C. elegans
2.3. Preparation of CML-Bound BSA and CML-Bound Bacteria
2.4. Immunofluorescence of Control and CML-Bound Bacteria
2.5. Pepsin Digestion of Control and CML-Bound Bacteria and BSA
2.6. Exposure of Worms to dCML
2.7. Whole Protein Extraction and Western and Dot Blotting
2.8. Isolation of Total RNAs and Gene Expression Analysis
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Glycation of Bacteria and Detection of CML Epitopes
3.2. Analysis of the Integrity of CML-Bound Bacteria
3.3. Glycated Bacterial Proteins Were Ingested by the Worms and Impaired Their Reproduction
3.4. dCML Induced Different Stresses
3.5. Glycated Bacterial Proteins Are Digested by the Worms
3.6. CML-Bound Proteins Are Endocytosed by the Worms’ Enterocytes
3.7. Endocytosis of CML-Bound Bacterial Proteins Is Specific of CML
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, C.; Kaur, A.; Thind, S.S.; Singh, B.; Raina, S. Advanced glycation End-products (AGEs): An emerging concern for processed food industries. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7561–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowotny, K.; Schröter, D.; Schreiner, M.; Grune, T. Dietary advanced glycation end products and their relevance for human health. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 47, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Dietary advanced glycation end-products: Perspectives linking food processing with health implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2559–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pino, A.; Currenti, W.; Urbano, F.; Mantegna, C.; Purrazzo, G.; Piro, S.; Purrello, F.; Rabuazzo, A.M. Low advanced glycation end product diet improves the lipid and inflammatory profiles of prediabetic subjects. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Moreno, J.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Camargo, A.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Tinahones, F.J.; Striker, G.E.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Supplemented With Coenzyme Q10Modulates the Postprandial Metabolism of Advanced Glycation End Products in Elderly Men and Women. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 73, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macías-Cervantes, M.H.; Rodríguez-Soto, J.M.D.; Uribarri, J.; Díaz-Cisneros, F.J.; Cai, W.; Garay-Sevilla, M.E. Effect of an advanced glycation end product-restricted diet and exercise on metabolic parameters in adult overweight men. Nutrition 2015, 31, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tantalaki, E.; Piperi, C.; Livadas, S.; Kollias, A.; Adamopoulos, C.; Koulouri, A.; Christakou, C.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Impact of dietary modification of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on the hormonal and metabolic profile of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hormones 2014, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribarri, J.; Cai, W.; Ramdas, M.; Goodman, S.; Pyzik, R.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H. Restriction of Advanced Glycation End Products Improves Insulin Resistance in Human Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harcourt, B.E.; Sourris, K.C.; Coughlan, M.T.; Walker, K.Z.; Dougherty, S.L.; Andrikopoulos, S.; Morley, A.L.; Thallas-Bonke, V.; Chand, V.; Penfold, S.A.; et al. Targeted reduction of advanced glycation improves renal function in obesity. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luévano-Contreras, C.; Garay-Sevilla, M.E.; Wrobel, K.; Malacara, J.M.; Wrobel, K. Dietary advanced glycation end products restriction diminishes inflammation markers and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2013, 52, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yacoub, R.; Nugent, M.; Cai, W.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Chaves, L.D.; Abyad, S.; Honan, A.M.; Thomas, S.A.; Zheng, W.; Valiyaparambil, S.A.; et al. Advanced glycation end products dietary restriction effects on bacterial gut microbiota in peritoneal dialysis patients; a randomized open label controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulsen, M.W.; Hedegaard, R.V.; Andersen, J.M.; de Courten, B.; Bügel, S.; Nielsen, J.; Skibsted, L.H.; Dragsted, L.O. Advanced glycation endproducts in food and their effects on health. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlouez-Aragon, I.; Saavedra, G.; Tessier, F.; Galinier, A.; Ait-Ameur, L.; Lacoste, F.; Niamba, C.-N.; Alt, N.; Somoza, V.; Lecerf, J.-M. A diet based on high-heat-treated foods promotes risk factors for diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semba, R.D.; Gebauer, S.K.; Baer, D.J.; Sun, K.; Turner, R.; Silber, H.A.; Talegawkar, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Novotny, J.A. Dietary Intake of Advanced Glycation End Products Did Not Affect Endothelial Function and Inflammation in Healthy Adults in a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semba, R.D.; Ang, A.; Talegawkar, S.; Crasto, C.; Dalal, M.; Jardack, P.; Traber, M.; Ferrucci, L.; Arab, L. Dietary intake associated with serum versus urinary carboxymethyl-lysine, a major advanced glycation end product, in adults: The Energetics Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 66, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poulsen, M.W.; Bak, M.J.; Andersen, J.M.; Monošík, R.; Giraudi-Futin, A.C.; Holst, J.J.; Nielsen, J.; Lauritzen, L.; Larsen, L.H.; Bügel, S.; et al. Effect of dietary advanced glycation end products on postprandial appetite, inflammation, and endothelial activation in healthy overweight individuals. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.B.; Love, M. The Impact of Food Processing on the Nutritional Quality of Vitamins and Minerals. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 459, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, F.J.; Birlouez-Aragon, I. Health effects of dietary Maillard reaction products: The results of ICARE and other studies. Amino Acids 2010, 42, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheijen, J.L.; Clevers, E.; Engelen, L.; Dagnelie, P.C.; Brouns, F.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Schalkwijk, C.G. Analysis of advanced glycation endproducts in selected food items by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: Presentation of a dietary AGE database. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Hou, F.; Liang, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Xie, D.; Tian, J.; Liu, Z. Restricted intake of dietary advanced glycation end products retards renal progression in the remnant kidney model. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, S.M.; Dong, H.-J.; Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Altomonte, J.; Thung, S.N.; Zeng, F.; Fisher, E.A.; Vlassara, H. Improved Insulin Sensitivity Is Associated With Restricted Intake of Dietary Glycoxidation Products in the db/db Mouse. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, S.-S.; Sheu, M.-L.; Yang, R.-S.; Chan, D.-C.; Wu, C.-T.; Yang, T.-H.; Chiang, C.-K.; Liu, S.-H. The pathological role of advanced glycation end products-downregulated heat shock protein 60 in islet β-cell hypertrophy and dysfunction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 23072–23087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, M.T.N.S.; Howsam, M.; Anton, P.M.; Delayre-Orthez, C.; Tessier, F.J. Effect of Advanced Glycation End-Products and Excessive Calorie Intake on Diet-Induced Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation Biomarkers in Murine Models. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Baker, S.S.; Liu, W.; Desai, S.; Alkhouri, R.; Kozielski, R.; Mastrandrea, L.; Sarfraz, A.; Cai, W.; Vlassara, H.; et al. Effect of Dietary Advanced Glycation End Products on Mouse Liver. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, I.; Ricny, J.; Atrakchi-Baranes, D.; Shemesh, C.; Kravitz, E.; Liraz-Zaltsman, S.; Maksin-Matveev, A.; Cooper, I.; Leibowitz, A.; Uribarri, J.; et al. High dietary advanced glycation end products are associated with poorer spatial learning and accelerated Aβ deposition in an Alzheimer mouse model. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Uribarri, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Swamy, S.; Zhao, Z.; Grosjean, F.; Simonaro, C.; Kuchel, G.; Schnaider-Beeri, M.; et al. Oral glycotoxins are a modifiable cause of dementia and the metabolic syndrome in mice and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4940–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lund, M.N.; Ray, C. Control of Maillard Reactions in Foods: Strategies and Chemical Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4537–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, N.S.; Joung, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, J.G.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.H. Glycated milk protein fermented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus ameliorates the cognitive health of mice under mild-stress condition. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1643–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossin, N.; Auger, F.; Niquet-Leridon, C.; Durieux, N.; Montaigne, D.; Schmidt, A.M.; Susen, S.; Jacolot, P.; Beuscart, J.-B.; Tessier, F.; et al. Dietary CML-enriched protein induces functional arterial aging in a RAGE-dependent manner in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupa, P.; Mine, Y. Comparison of Glycated Ovalbumin–Monosaccharides in the Attenuation of Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Response in a BALB/C Mouse Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8138–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuyen, N.; Arai, H.; Nakanishi, T.; Utsunomiya, N. Are Food Advanced Glycation End Products Toxic in Biological Systems? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; Jedrzejczak, W.W. Albumin-biological functions and clinical significance. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2001, 55, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, M. Food-derived peptides and intestinal functions. BioFactors 2004, 21, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiga, A.; Fiorio, F.; Di Marco, F.; Trevisani, F.; Romani, A.; Porrini, E.; Salonia, A.; Montorsi, F.; Vago, R. The Modern Western Diet Rich in Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs): An Overview of Its Impact on Obesity and Early Progression of Renal Pathology. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellwig, M.; Matthes, R.; Peto, A.; Löbner, J.; Henle, T. N-ε-fructosyllysine and N-ε-carboxymethyllysine, but not lysinoalanine, are available for absorption after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Rai, V.; Singer, D.; Chabierski, S.; Xie, J.; Reverdatto, S.; Burz, D.S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Hoffmann, R.; Shekhtman, A. Advanced Glycation End Product Recognition by the Receptor for AGEs. Structure 2011, 19, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuma, P.L.; Hubbard, A.L. Transcytosis: Crossing Cellular Barriers. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 871–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Yuan, J.; Nazertehrani, S.; Ni, Z.; Liu, S. Chronic Kidney Disease Causes Disruption of Gastric and Small Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellwig, M.; Geissler, S.; Matthes, R.; Peto, A.; Silow, C.; Brandsch, M.; Henle, T. Transport of Free and Peptide-Bound Glycated Amino Acids: Synthesis, Transepithelial Flux at Caco-2 Cell Monolayers, and Interaction with Apical Membrane Transport Proteins. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, S.; Krause, R.; Bruch, M.; Henle, T.; Brandsch, M. Transepithelial flux of early and advanced glycation compounds across Caco-2 cell monolayers and their interaction with intestinal amino acid and peptide transport systems. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Yang, Z. The fate of dietary advanced glycation end products in the body: From oral intake to excretion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3475–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Masilamani, M.; Li, X.-M.; Sampson, H.A. The false alarm hypothesis: Food allergy is associated with high dietary advanced glycation end-products and proglycating dietary sugars that mimic alarmins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.K.; Gupta, K.; Sharma, A.; Das, M.; Ansari, I.A.; Dwivedi, P.D. Maillard reaction in food allergy: Pros and cons. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Loh, Z.; Gan, W.J.; Zhang, V.; Yang, H.; Li, J.H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Schmidt, A.M.; Armour, C.L.; Hughes, J.M.; et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products and its ligand high-mobility group box-1 mediate allergic airway sensitization and airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 440–450.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Li, L.; Zhengyang, B.; Ye, F.; Shao, C.; Sun, Z.; Bao, Z.; Dai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Jing, L.; et al. CML/CD36 accelerates atherosclerotic progression via inhibiting foam cell migration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, A.; Yap, F.Y.; Bruce, C.; Leung, C.; Plan, M.R.; Sullivan, M.; Herath, C.; McCarthy, D.; Sourris, K.C.; Kantharidis, P.; et al. Increased liver AGEs induce hepatic injury mediated through an OST48 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelson, M.; Tan, S.M.; Thallas-Bonke, V.; Sourris, K.; Ziemann, M.; El-Osta, A.; Cooper, M.; Forbes, J.; Coughlan, M. Thermally Processed Diet-Induced Albuminuria, Complement Activation and Intestinal Permeability Are Attenuated by Resistant Starch in Experimental Diabetes. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2021, 5, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamad, F.; Brunel, B.; Vuiblet, V.; Gillery, P.; Jaisson, S.; Piot, O. In depth investigation of collagen non-enzymatic glycation by Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 251, 119382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courjol, F.; Jouault, T.; Mille, C.; Hall, R.; Maes, E.; Sendid, B.; Mallet, J.M.; Guerardel, Y.; Gow, N.A.R.; Poulain, D.; et al. β-1,2-Mannosyltransferases 1 and 3 Participate in Yeast and Hyphae O- and N-Linked Mannosylation and Alter Candida al-bicans Fitness During Infection. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretton, C.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Dubois, C.; Tessier, F.J.; Fradin, C.; Prost-Camus, E.; Prost, M.; Haumont, M.; Nigay, H. Investigation of the antioxidant capacity of caramels: Combination of laboratory assays and C. elegans model. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 78, 104308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerr, J.S. Immunohistochemistry. WormBook. 2006. Available online: http://www.wormbook.org/chapters/www_immunohistochemistry/immunohistochemistry.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Estey, T.; Kang, J.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Carpenter, J.F. BSA Degradation Under Acidic Conditions: A Model For Protein Instability During Release From PLGA Delivery Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fierro-González, J.C.; González-Barrios, M.; Miranda-Vizuete, A.; Swoboda, P. The thioredoxin TRX-1 regulates adult lifespan extension induced by dietary restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thornalley, P.J. Endogenous α-Oxoaldehydes and Formation of Protein and Nucleotide Advanced Glycation Endproducts in Tissue Damage. In Acetaldehyde-Related Pathology: Bridging the Trans-Disciplinary Divide; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 285, pp. 229–246. ISBN 978-0-470-51184-8. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhou, C.; Huang, M.; Tang, C.; Liu, X.; Yue, Y.; Diao, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, D. Glyoxalase system: A systematic review of its biological activity, related-diseases, screening methods and small molecule regulators. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanier, B. Transcriptional and functional regulation of the intestinal peptide transporter PEPT. J. Physiol. 2013, 592, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S. Ubiquitin: Same Molecule, Different Degradation Pathways. Cell 2010, 143, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ott, C.; Jacobs, K.; Haucke, E.; Santos, A.N.; Grune, T.; Simm, A. Role of advanced glycation end products in cellular signaling. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmer, K.-P.; De Laffolie, J.; Barone, M.V.; Naim, H.Y.; Zimmer, U.-P.D.K.-P. Endocytosis in enterocytes. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2016, 166, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Pangilinan, K.; Sanjabi, K.; Savic, D. Starvation of Adult Caenorhabditis Elegans and Its Effect on Health and Reproduc-tion. Available online: File:///C:/Users/MDPI/Downloads/184795-Article%20Text-191480-1-10-20140604.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Kang, C.; You, Y.-J.; Avery, L. Dual roles of autophagy in the survival of Caenorhabditis elegans during starvation. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, C.; Pophillat, M.; Audebert, S.; Fourquet, P.; Lecomte, C.; Dubourg, N.; Galas, S.; Camoin, L.; Frelon, S. Differential modification of the C. elegans proteome in response to acute and chronic gamma radiation: Link with reproduction decline. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Lugt, T.; Opperhuizen, A.; Bast, A.; Vrolijk, M.F. Dietary Advanced Glycation Endproducts and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundquist, P.; Artursson, P. Oral absorption of peptides and nanoparticles across the human intestine: Opportunities, limitations and studies in human tissues. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Hernández, T.; Haucke, V.; Maritzen, T. Endocytosis in the adaptation to cellular stress. Cell Stress 2020, 4, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhausen, T. Bending membranes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubois, C.; Litke, R.; Rianha, S.; Paul-Constant, C.; Lo Guidice, J.-M.; Taront, S.; Tessier, F.J.; Boulanger, E.; Fradin, C. Exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to Dietary Nε-Carboxymethyllysine Emphasizes Endocytosis as a New Route for Intestinal Absorption of Advanced Glycation End Products. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124398
Dubois C, Litke R, Rianha S, Paul-Constant C, Lo Guidice J-M, Taront S, Tessier FJ, Boulanger E, Fradin C. Exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to Dietary Nε-Carboxymethyllysine Emphasizes Endocytosis as a New Route for Intestinal Absorption of Advanced Glycation End Products. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124398
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubois, Constance, Rachel Litke, Stéphane Rianha, Charles Paul-Constant, Jean-Marc Lo Guidice, Solenne Taront, Frédéric J. Tessier, Eric Boulanger, and Chantal Fradin. 2021. "Exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to Dietary Nε-Carboxymethyllysine Emphasizes Endocytosis as a New Route for Intestinal Absorption of Advanced Glycation End Products" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124398
APA StyleDubois, C., Litke, R., Rianha, S., Paul-Constant, C., Lo Guidice, J. -M., Taront, S., Tessier, F. J., Boulanger, E., & Fradin, C. (2021). Exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to Dietary Nε-Carboxymethyllysine Emphasizes Endocytosis as a New Route for Intestinal Absorption of Advanced Glycation End Products. Nutrients, 13(12), 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124398