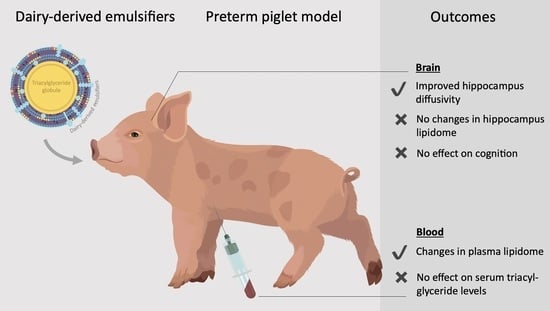
Dairy-Derived Emulsifiers in Infant Formula Show Marginal Effects on the Plasma Lipid Profile and Brain Structure in Preterm Piglets Relative to Soy Lecithin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Nutrition
2.3. Animal Housing and Treatment
2.4. In Vitro Lipolysis and Serum Triacyl-Glyceride Measurements
2.5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.6. Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics
2.7. Acquisition of Basic Motor Skills, Home Cage Activity and Short-Term Memory
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcomes, Growth and Organ Weights
3.2. In Vitro Lipolysis and Serum Triacyl-Glyceride Measurements
3.3. Brain Weights, Water Content and MRI Analysis
3.4. In-Depth Lipidomics
3.5. Acquisition of Basic Motor Skills, Home Cage Activity and Short-Term Memory
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Twilhaar, E.S.; Wade, R.M.; De Kieviet, J.F.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Van Elburg, R.M.; Oosterlaan, J. Cognitive outcomes of children born extremely or very preterm since the 1990s and associated risk factors: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. JAMA Pediatrics 2018, 172, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnoudse-Moens, C.S.H.; Weisglas-Kuperus, N.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Oosterlaan, J. Meta-analysis of neurobehavioral outcomes in very preterm and/or very low birth weight children. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kieviet, J.F.; Piek, J.P.; Aarnoudse-Moens, C.S.; Oosterlaan, J. Motor development in very preterm and very low-birth-weight children from birth to adolescence: A meta-analysis. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 302, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieff, M.K. Nutrition and the developing brain: Nutrient priorities and measurement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 614S–620S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Johnstone, B.M.; Remley, D.T. Breast-feeding and cognitive development: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta, B.L.; Loret De Mola, C.; Victora, C.G. Breastfeeding and intelligence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2015, 104, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, C.; Nadjar, A.; Lebbadi, M.; Calon, F.; Laye, S. N-3 LCPUFA improves cognition: The young, the old and the sick. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2014, 91, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, E.L.; Richard, C.; Hoffman, D.R. DHA and ARA addition to infant formula: Current status and future research directions. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 128, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, E.C.; Farquharson, J.; Logan, R.W.; Howatson, A.G.; Patrick, W.J.; Weaver, L.T.; Cockburn, F. Infant cerebellar gray and white matter fatty acids in relation to age and diet. Lipids 1999, 34, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquharson, J.; Jamieson, E.C.; Abbasi, K.A.; Patrick, W.J.A.; Logan, R.W.; Cockbum, F. Effect of diet on the fatty acid composition of the major phospholipids of infant cerebral cortex. Arch. Dis. Child. 1995, 72, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verfuerden, M.L.; Dib, S.; Jerrim, J.; Fewtrell, M.; Gilbert, R.E. Effect of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in infant formula on long-term cognitive function in childhood: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.; Rao, S.C.; Schulzke, S.M.; Patole, S.K.; Simmer, K. Longchain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 12, CD000375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, M.; Hamosh, M.; Mehta, N.R.; Angelus, P.A.; Philpott, J.R.; Henderson, T.R.; Dwyer, N.K.; Lairon, D.; Hamosh, P. Effect of human milk or formula on gastric function and fat digestion in the premature infant. Pediatrics Res. 1996, 40, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindquist, S.; Hernell, O. Lipid digestion and absorption in early life: An update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.; Ménard, O. Human milk fat globules: Polar lipid composition and in situ structural investigations revealing the heterogeneous distribution of proteins and the lateral segregation of sphingomyelin in the biological membrane. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwlani, R.; Fonseka, P.; Chitti, S.V.; Mathivanan, S. Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Inter-Organism, Cross-Species Communication and Drug Delivery. Proteomes 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skotland, T.; Hessvik, N.P.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Exosomal lipid composition and the role of ether lipids and phosphoinositides in exosome biology. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breakefield, X.O.; Abels, E.R. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, T.A.; Lippolis, J.D.; Nonnecke, B.J.; Sacco, R.E. Bovine milk exosome proteome. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiassen, J.H.; Nejrup, R.G.; Frøkiær, H.; Nilsson, Å.; Ohlsson, L.; Hellgren, L.I. Emulsifying triglycerides with dairy phospholipids instead of soy lecithin modulates gut lipase activity. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1522–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.K.; Hindmarsh, J.P.; Haisman, D.; Rades, T.; Singh, H. Comparison of the structure and properties of liposomes prepared from milk fat globule membrane and soy phospholipids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurnida, D.A.; Rowan, A.M.; Idjradinata, P.; Muchtadi, D.; Sekarwana, N. Association of complex lipids containing gangliosides with cognitive development of 6-month-old infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Hosozawa, M.; Kudo, N.; Yoshikawa, N.; Hisata, K.; Shoji, H.; Shinohara, K.; Shimizu, T. The pilot study: Sphingomyelin-fortified milk has a positive association with the neurobehavioural development of very low birth weight infants during infancy, randomized control trial. Brain Dev. 2013, 35, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, E.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Domellöf, M. Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-proteinformula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Wu, S.S.; Berseth, C.L.; Harris, C.L.; Richards, J.D.; Wampler, J.L.; Zhuang, W.; Cleghorn, G.; Rudolph, C.D.; Liu, B.; et al. Improved Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Associated with Bovine Milk Fat Globule Membrane and Lactoferrin in Infant Formula: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Pediatrics 2019, 215, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Radlowski, E.C.; Conrad, M.S.; Li, Y.; Dilger, R.N.; Johnson, R.W. Early supplementation of phospholipids and gangliosides affects brain and cognitive development in neonatal piglets. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshida, K.; Shimizu, T.; Takase, M.; Tamura, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Yamashiro, Y. Effects of dietary sphingomyelin on central nervous system myelination in developing rats. Pediatrics Res. 2003, 53, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mudd, A.T.; Alexander, L.S.; Berding, K.; Waworuntu, R.V.; Berg, B.M.; Donovan, S.M.; Dilger, R.N. Dietary prebiotics, milk fat globule membrane, and lactoferrin affects structural neurodevelopment in the young piglet. Front. Pediatrics 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fil, J.E.; Fleming, S.A.; Chichlowski, M.; Gross, G.; Berg, B.M.; Dilger, R.N. Evaluation of Dietary Bovine Milk Fat Globule Membrane Supplementation on Growth, Serum Cholesterol and Lipoproteins, and Neurodevelopment in the Young Pig. Front. Pediatrics 2019, 7, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrad, M.S.; Dilger, R.N.; Johnson, R.W. Brain growth of the domestic pig (Sus scrofa) from 2 to 24 weeks of age: A longitudinal MRI study. Dev. Neurosci. 2012, 34, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobbing, J.; Sands, J. Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum. Dev. 1979, 311, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odle, J.; Lin, X.; Jacobi, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Stahl, C.H. The suckling piglet as an agrimedical model for the study of pediatric nutrition and metabolism. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 419–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, A.D.; Sangild, P.T.; Munch, S.L.; van der Beek, E.M.; Renes, I.B.; van Ginneken, C.; Greisen, G.O.; Thymann, T. Delayed growth, motor function and learning in preterm pigs during early postnatal life. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R481–R492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obelitz-Ryom, K.; Bering, S.B.; Overgaard, S.H.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Ringgaard, S.; Olesen, J.L.; Skovgaard, K.; Pankratova, S.; Wang, B.; Brunse, A.; et al. Bovine milk oligosaccharides with sialyllactose improves cognition in preterm pigs. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangild, P.T.; Thymann, T.; Schmidt, M.; Stoll, B.; Burrin, D.G.; Buddington, R.K. Invited review: The preterm pig as a model in pediatric gastroenterology. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4713–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, K.B.K.; Heerup, C.; Jensen, T.R.S.; Geng, X.; Drachmann, N.; Nordby, P.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Ifaoui, I.; Müllertz, A.; Sangild, P.T.; et al. Milk-derived emulsifiers increase triglyceride absorption in newborn formula-fed pigs. Nutrients 2021, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerup, C.; Ebbesen, M.F.; Geng, X.; Madsen, S.F.; Berthelsen, R.; Müllertz, A. Effects of recombinant human gastric lipase and pancreatin during in vitro pediatric gastro-intestinal digestion. Food Funct. 2021. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, H.D.; Sassene, P.; Kleberg, K.; Bakala-N’Goma, J.C.; Calderone, M.; Jannin, V.; Igonin, A.; Partheil, A.; Marchaud, D.; Jule, E.; et al. Toward the establishment of standardized in vitro tests for lipid-based formulations, Part 1: Method parameterization and comparison of in vitro digestion profiles across a range of representative formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3360–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharova, K.; Pierzynowski, S.G.; Grujic, D.; Kirko, S.; Szwiec, K.; Wang, J.; Kovalenko, T.; Osadchenko, I.; Ushakova, G.; Shmigel, H.; et al. A piglet with surgically induced exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as an animal model of newborns to study fat digestion. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veraart, J.; Novikov, D.S.; Christiaens, D.; Ades-aron, B.; Sijbers, J.; Fieremans, E. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. Neuroimage 2016, 142, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellner, E.; Dhital, B.; Kiselev, V.G.; Reisert, M. Gibbs-ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel-shifts. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veraart, J.; Sijbers, J.; Sunaert, S.; Leemans, A.; Jeurissen, B. Weighted linear least squares estimation of diffusion MRI parameters: Strengths, limitations, and pitfalls. Neuroimage 2013, 81, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avants, B.B.; Tustison, N.J. The ITK Image Registration Framework. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida, R.; Pauling, J.K.; Sokol, E.; Hannibal-Bach, H.K.; Ejsing, C.S. Comprehensive lipidome analysis by shotgun lipidomics on a hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap-linear ion trap mass spectrometer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, S.F.; Højlund, K.; Ejsing, C.S. Easy, Fast, and Reproducible Quantification of Cholesterol and Other Lipids in Human Plasma by Combined High Resolution MSX and FTMS Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 29, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.R.; Paine, M.R.L.; Eijkel, G.B.; Pauling, J.K.; Husen, P.; Jervelund, M.W.; Hermansson, M.; Ejsing, C.S.; Heeren, R.M.A. Automated, parallel mass spectrometry imaging and structural identification of lipids. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejsing, C.S.; Duchoslav, E.; Sampaio, J.; Simons, K.; Bonner, R.; Thiele, C.; Ekroos, K.; Shevchenko, A. Automated identification and quantification of glycerophospholipid molecular species by multiple precursor ion scanning. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6202–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2012, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmore, M.R.P.; Dilger, R.N.; Johnson, R.W. Place and direction learning in a spatial T-maze task by neonatal piglets. Anim. Cogn. 2012, 15, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallier, S.; Vocking, K.; Post, J.A.; Van De Heijning, B.; Acton, D.; Van Der Beek, E.M.; Van Baalen, T. A novel infant milk formula concept: Mimicking the human milk fat globule structure. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schipper, L.; van Dijk, G.; Broersen, L.M.; Loos, M.; Bartke, N.; Scheurink, A.J.W.; van der Beek, E.M. A postnatal diet containing phospholipids, processed to yield large, phospholipid-coated lipid droplets, affects specific cognitive behaviors in healthy male mice1-3. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhinder, G.; Allaire, J.M.; Garcia, C.; Lau, J.T.; Chan, J.M.; Ryz, N.R.; Bosman, E.S.; Graef, F.A.; Crowley, S.M.; Celiberto, L.S.; et al. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Supplementation in Formula Modulates the Neonatal Gut Microbiome and Normalizes Intestinal Development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Huërou-Luron, I.; Bouzerzour, K.; Ferret-Bernard, S.; Ménard, O.; Le Normand, L.; Perrier, C.; Le Bourgot, C.; Jardin, J.; Bourlieu, C.; Carton, T.; et al. A mixture of milk and vegetable lipids in infant formula changes gut digestion, mucosal immunity and microbiota composition in neonatal piglets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M. Tissue levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids during early human development. J. Pediatr. 1992, 120, S129–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, C.; Martinez, M.; Ballabriga, A. Some chemical aspects of human brain development. I. neutral glycosphingolipids, sulfatides, and sphingomyelin. Pediatr. Res. 1974, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, D.; Barone, S. Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: Evidence from humans and animal models. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.L.; Chen, J.J.; Su, H.M. Fish oil supplementation of control and (n-3) fatty acid-deficient male rats enhances reference and working memory performance and increases brain regional docosahexaenoic acid levels. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, T.; Greiner, R.S.; Salem, N. Behavioral deficits associated with dietary induction of decreased brain docosahexaenoic acid concentration. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 2563–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on in vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Maekawa, K.; Saito, K.; Senoo, Y.; Urata, M.; Murayama, M.; Tajima, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Saito, Y. Plasma and serum lipidomics of healthy white adults shows characteristic profiles by subjects’ gender and age. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grip, T.; Dyrlund, T.S.; Ahonen, L.; Domellöf, M.; Hernell, O.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Knip, M.; Lönnerdal, B.; Orešič, M.; Timby, N. Serum, plasma and erythrocyte membrane lipidomes in infants fed formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes. Pediatrics Res. 2018, 84, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moukarzel, S.; Dyer, R.A.; Garcia, C.; Wiedeman, A.M.; Boyce, G.; Weinberg, J.; Keller, B.O.; Elango, R.; Innis, S.M. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Supplementation in Formula-fed Rat Pups Improves Reflex Development and May Alter Brain Lipid Composition. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vickers, M.H.; Guan, J.; Gustavsson, M.; Krägeloh, C.U.; Breier, B.H.; Davison, M.; Fong, B.; Norris, C.; McJarrow, P.; Hodgkinson, S.C. Supplementation with a mixture of complex lipids derived from milk to growing rats results in improvements in parameters related to growth and cognition. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzner, D.; Bader, J.M.; Penkert, H.; Bergner, C.G.; Su, M.; Weil, M.T.; Surma, M.A.; Mann, M.; Klose, C.; Simons, M. Cell-Type- and Brain-Region-Resolved Mouse Brain Lipidome. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bartke, N.; Van Daele, H.; Lawrence, P.; Qin, X.; Park, H.G.; Kothapalli, K.; Windust, A.; Bindels, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Higher efficacy of dietary DHA provided as a phospholipid than as a triglyceride for brain DHA accretion in neonatal piglets. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijendran, V.; Huang, M.C.; Diau, G.Y.; Boehm, G.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Brenna, J.T. Efficacy of dietary arachidonic acid provided as triglyceride or phospholipid as substrates for brain arachidonic acid accretion in baboon neonates. Pediatrics Res. 2002, 51, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manca, S.; Upadhyaya, B.; Mutai, E.; Desaulniers, A.T.; Cederberg, R.A.; White, B.R.; Zempleni, J. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, M.; Dubois, J.; Yu, Q.; Mukherjee, P.; Huang, H. Delineation of early brain development from fetuses to infants with diffusion MRI and beyond. Neuroimage 2019, 185, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapponi, C.; Piras, F.; Piras, F.; Fagioli, S.; Caltagirone, C.; Spalletta, G. Cortical Grey Matter and Subcortical White Matter Brain Microstructural Changes in Schizophrenia Are Localised and Age Independent: A Case-Control Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Callow, D.D.; Canada, K.L.; Riggins, T. Microstructural Integrity of the Hippocampus During Childhood: Relations with Age and Source Memory. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 568953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, R.; Cristiano, C.; Avagliano, C.; De Caro, C.; La Rana, G.; Raso, G.M.; Canani, R.B.; Meli, R.; Calignano, A. Gut-brain Axis: Role of Lipids in the Regulation of Inflammation, Pain and CNS Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, L.C.; Sun, Y.; Carter, C.S.; Buford, T.W. Crosstalk Between the Gut Microbiome and Bioactive Lipids: Therapeutic Targets in Cognitive Frailty. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Lu, L.; Yu, Y.; Cluette-Brown, J.; Martin, C.R.; Claud, E.C. Effects of Intestinal Microbiota on Brain Development in Humanized Gnotobiotic Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walfisch, A.; Sermer, C.; Cressman, A.; Koren, G. Breast milk and cognitive development-the role of confounders: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, S.A.; Dilger, R.N. Young pigs exhibit differential exploratory behavior during novelty preference tasks in response to age, sex, and delay. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 321, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme Nielsen, C.; Bladt Brandt, A.; Thymann, T.; Obelitz-Ryom, K.; Jiang, P.; Vanden Hole, C.; Van Ginneken, C.; Pankratova, S.; Sangild, P.T. Rapid Postnatal Adaptation of Neurodevelopment in Pigs Born Late Preterm. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 40, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomgaard, A.M.; Andersen, A.D.; Petersen, T.H.; van de Looij, Y.; Thymann, T.; Sangild, P.T.; Thomsen, C.; Sizonenko, S.V.; Greisen, G. Structural brain maturation differs between preterm and term piglets, whereas brain activity does not. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2019, 108, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Constituents 1 | WPC-A-EV Diet | WPC-PL Diet | SL Diet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | kJ/L | 3462 | 3460 | 3382 |
| Protein | g/L | 50 | 49 | 46 |
| Carbohydrate | g/L | 43 | 43 | 43 |
| Fat | g/L | 51 | 51 | 51 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | g/L | 0.1150 | 0.1150 | 0.1150 |
| Arachidonic acid | g/L | 0.0580 | 0.0580 | 0.0580 |
| Constituents (% of Sample) | WPC-A-EV | WPC-PL | SL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter | 96.7 | 95.7 | N/A |
| Ash | 4.9 | 1.9 | N/A |
| Lactose | 0.23 | 0.5 | N/A |
| Fat | 24.1 | 18.0 | N/A |
| Phospholipids | 11.04 | 6.87 | 43.29 |
| Phosphatidyl-choline | 2.99 | 1.88 | 13.49 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylcholine | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.63 |
| Phosphatidylinositol | 0.60 | 0.45 | 11.34 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylinositol | N/A | N/A | ND |
| Phosphatidylserine | 1.06 | 0.73 | 0.26 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylserine | N/A | N/A | ND |
| Sphingomyelin | 2.94 | 1.69 | ND |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine | 3.28 | 2.06 | 7.20 |
| Lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.25 |
| N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine | N/A | N/A | 3.73 |
| Phosphatidylglycerol | N/A | N/A | 0.42 |
| Di-phosphatidylglycerol | N/A | N/A | 0.44 |
| Phosphatidic acid | 0 | 0.01 | 4.34 |
| Lysophosphatidic acid | N/A | N/A | 0.16 |
| Other phospholipids | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.96 |
| Ganglioside D3 (mg/kg) | 2942 | 1702 | N/A |
| Cholesterol | 1.43 | 0.68 | N/A |
| Protein | 65.7 | 73.0 | N/A |
| Native α-lactalbumin | 4.68 | 0.88 | N/A |
| Native β-lactoglobulin | 22.4 | 19.1 | N/A |
| Native cGMP | 0 | 2.87 | N/A |
| Total α-lactalbumin | 5.41 | 3.49 | N/A |
| Total β-lactoglobulin | 25.8 | 28.1 | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henriksen, N.L.; Aasmul-Olsen, K.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Nygaard, M.K.E.; Sprenger, R.R.; Heckmann, A.B.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Ejsing, C.S.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Müllertz, A.; et al. Dairy-Derived Emulsifiers in Infant Formula Show Marginal Effects on the Plasma Lipid Profile and Brain Structure in Preterm Piglets Relative to Soy Lecithin. Nutrients 2021, 13, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030718
Henriksen NL, Aasmul-Olsen K, Venkatasubramanian R, Nygaard MKE, Sprenger RR, Heckmann AB, Ostenfeld MS, Ejsing CS, Eskildsen SF, Müllertz A, et al. Dairy-Derived Emulsifiers in Infant Formula Show Marginal Effects on the Plasma Lipid Profile and Brain Structure in Preterm Piglets Relative to Soy Lecithin. Nutrients. 2021; 13(3):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030718
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenriksen, Nicole L., Karoline Aasmul-Olsen, Ramakrishnan Venkatasubramanian, Mikkel K. E. Nygaard, Richard R. Sprenger, Anne B. Heckmann, Marie S. Ostenfeld, Christer S. Ejsing, Simon F. Eskildsen, Anette Müllertz, and et al. 2021. "Dairy-Derived Emulsifiers in Infant Formula Show Marginal Effects on the Plasma Lipid Profile and Brain Structure in Preterm Piglets Relative to Soy Lecithin" Nutrients 13, no. 3: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030718
APA StyleHenriksen, N. L., Aasmul-Olsen, K., Venkatasubramanian, R., Nygaard, M. K. E., Sprenger, R. R., Heckmann, A. B., Ostenfeld, M. S., Ejsing, C. S., Eskildsen, S. F., Müllertz, A., Sangild, P. T., Bering, S. B., & Thymann, T. (2021). Dairy-Derived Emulsifiers in Infant Formula Show Marginal Effects on the Plasma Lipid Profile and Brain Structure in Preterm Piglets Relative to Soy Lecithin. Nutrients, 13(3), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030718