A Review of the Health Benefits of Food Enriched with Kynurenic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Targets of Kynurenic Acid
3. Absorption of Kynurenic Acid from the Digestive Tract
3.1. Human Studies
3.2. Animal Studies
4. Distribution of Kynurenic Acid
4.1. Human Studies
4.1.1. Serum
4.1.2. Saliva
4.1.3. Gastric Juice
4.1.4. Bile
4.1.5. Intestinal Fluid
4.1.6. Synovial Fluid
4.1.7. Sweat
4.1.8. Cerebrospinal Fluid
4.1.9. Brain
4.1.10. Other Organs
4.1.11. Breast Milk
4.1.12. Urine
4.2. Animal Studies
4.2.1. Distribution of Kynurenic Acid Administered via the Alimentary Route
4.2.2. Blood–Brain Barrier
4.2.3. Blood–Placental Barrier
5. Metabolism of Kynurenic Acid
5.1. Human Studies
5.2. Animal Studies
6. Excretion of Kynurenic Acid
6.1. Human Studies
6.1.1. Urine
6.1.2. Feces
6.1.3. Sweat
6.1.4. Total Daily Excretion of Kynurenic Acid
7. Kynurenic Acid in Food
7.1. Human Food
7.1.1. Meat
7.1.2. Vegetables
7.1.3. Fruit
7.1.4. Spices and Herbs for Cooking
7.1.5. Honey
7.1.6. Dairy
7.1.7. Fermented Food and Beverages
7.1.8. Medicinal Herbs and Supplements
7.1.9. Baby Food
7.2. Animal Food
8. Kynurenic Acid Supplementation
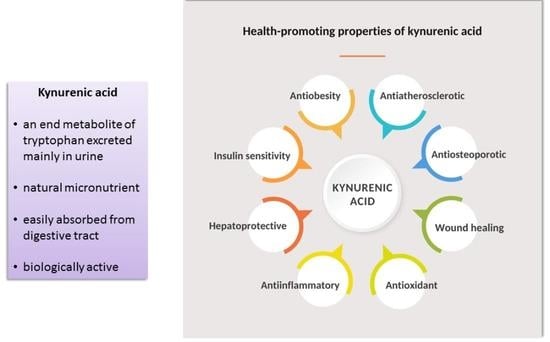
8.1. Health Effects of Kynurenic Acid Supplementation
8.2. Clinical Trials
8.3. Patents
9. Perspectives
9.1. Food as a Dietary Source of Kynurenic Acid
9.2. Chestnut Honey as a Dietary Source of Kynurenic Acid
9.3. Other Sources of Kynurenic Acid
10. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turski, M.P.; Turska, M.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Parada-Turska, J.; Oxenkrug, G.F. Kynurenic Acid in the Digestive System-New Facts, New Challenges. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2013, 6, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapolka, N.J.; Taghon, G.J.; Rowe, J.B.; Morgan, W.M.; Enten, J.F.; Lambert, N.A.; Isom, D.G. DCyFIR: A High-Throughput CRISPR Platform for Multiplexed G Protein-Coupled Receptor Profiling and Ligand Discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13117–13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Abraham, W.C. Glutamate Receptors and Synaptic Plasticity: The Impact of Evans and Watkins. Neuropharmacology 2022, 206, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Does Kynurenic Acid Act on Nicotinic Receptors? An Assessment of the Evidence. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shore, D.M.; Reggio, P.H. The Therapeutic Potential of Orphan GPCRs, GPR35 and GPR55. Front. Pharm. 2015, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic Acid as a Ligand for Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Dowd, B.F.; Nguyen, T.; Marchese, A.; Cheng, R.; Lynch, K.R.; Heng, H.H.Q.; Kolakowski, L.F.; George, S.R. Discovery of Three Novel G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Genes. Genomics 1998, 47, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, S.; Baba, H.; Kumada, T.; Nanmoku, K.; Nakajima, H.; Nakane, Y.; Hioki, K.; Ikenaka, K. Cloning of a G-Protein-Coupled Receptor That Shows an Activity to Transform NIH3T3 Cells and Is Expressed in Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaya, B.; Melhem, H.; Niess, J.H. GPR35 in Intestinal Diseases: From Risk Gene to Function. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quon, T.; Lin, L.-C.; Ganguly, A.; Tobin, A.B.; Milligan, G. Therapeutic Opportunities and Challenges in Targeting the Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR35. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turska, M.; Rutyna, R.; Paluszkiewicz, M.; Terlecka, P.; Dobrowolski, A.; Pelak, J.; Turski, M.P.; Muszyńska, B.; Dabrowski, W.; Kocki, T.; et al. Presence of Kynurenic Acid in Alcoholic Beverages—Is This Good News, or Bad News? Med Hypotheses 2019, 122, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihara, M.; Price, J.M.; Takahashi, H. The Conversion of Kynurenic Acid to Quinaldic Acid by Humans and Rats. J Biol Chem 1956, 223, 705–708. [Google Scholar]
- Turski, M.P.; Chwil, S.; Turska, M.; Chwil, M.; Kocki, T.; Rajtar, G.; Parada-Turska, J. An Exceptionally High Content of Kynurenic Acid in Chestnut Honey and Flowers of Chestnut Tree. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 48, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska, M.; Pelak, J.; Turski, M.P.; Kocki, T.; Dukowski, P.; Plech, T.; Turski, W. Fate and Distribution of Kynurenic Acid Administered as Beverage. Pharm. Rep. 2018, 70, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zheng, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Kynurenine Pathway in Patients with Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iłzecka, J.; Kocki, T.; Stelmasiak, Z.; Turski, W.A. Endogenous Protectant Kynurenic Acid in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003, 107, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Tong, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Tan, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Kochunov, P.; Chiappelli, J.; et al. Effects of Neuroactive Metabolites of the Tryptophan Pathway on Working Memory and Cortical Thickness in Schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartai, Z.; Klivenyi, P.; Janaky, T.; Penke, B.; Dux, L.; Vecsei, L. Kynurenine Metabolism in Plasma and in Red Blood Cells in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 239, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Y.; Ni, X.; Lu, H.; Wen, Y.; Fan, N. Preliminary Comparative Analysis of Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in Chronic Ketamine Users, Schizophrenic Patients, and Healthy Controls. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 35, e2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tömösi, F.; Kecskeméti, G.; Cseh, E.K.; Szabó, E.; Rajda, C.; Kormány, R.; Szabó, Z.; Vécsei, L.; Janáky, T. A Validated UHPLC-MS Method for Tryptophan Metabolites: Application in the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepplinger, B.; Baran, H.; Kainz, A.; Ferraz-Leite, H.; Newcombe, J.; Kalina, P. Age-Related Increase of Kynurenic Acid in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid—IgG and Beta2-Microglobulin Changes. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirkhani, A.; Heldin, E.; Markides, K.E.; Bergquist, J. Quantitation of Tryptophan, Kynurenine and Kynurenic Acid in Human Plasma by Capillary Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2002, 780, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milart, P.; Urbańska, E.M.; Turski, W.A.; Paszkowski, T.; Sikorski, R. Intrapartum Levels of Endogenous Glutamate Antagonist-Kynurenic Acid in Amniotic Fluid, Umbilical and Maternal Blood. Neurosci. Res. Comm. 1999, 24, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milart, P.; Sikorski, R. Kynurenic acid concentration in blood and urine during normal pregnancy. Ginekol. Pol. 1998, 69, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shestopalov, A.V.; Shatova, O.P.; Gaponov, A.M.; Moskaleva, N.E.; Appolonova, S.A.; Tutelyan, A.V.; Makarov, V.V.; Yudin, S.M.; Rumyantsev, S.A. The study of tryptophan metabolite concentrations in blood serum and fecal extracts from obese children. Biomed. Khim. 2020, 66, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuc, D.; Rahnama, M.; Tomaszewski, T.; Rzeski, W.; Wejksza, K.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T.; Parada-Turska, J.; Wielosz, M.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic Acid in Human Saliva--Does It Influence Oral Microflora? Pharm. Rep. 2006, 58, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Paluszkiewicz, P.; Zgrajka, W.; Saran, T.; Schabowski, J.; Piedra, J.L.V.; Fedkiv, O.; Rengman, S.; Pierzynowski, S.G.; Turski, W.A. High Concentration of Kynurenic Acid in Bile and Pancreatic Juice. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, K.; Dąbrowski, W.; Langner, E.; Zgrajka, W.; Piłat, J.; Kocki, T.; Rzeski, W.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic Acid Synthesis and Kynurenine Aminotransferases Expression in Colon Derived Normal and Cancer Cells. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada-Turska, J.; Zgrajka, W.; Majdan, M. Kynurenic Acid in Synovial Fluid and Serum of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Spondyloarthropathy, and Osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, T.; Turska, M.; Kocki, T.; Zawadka, M.; Zieliński, G.; Turski, W.A.; Gawda, P. Effect of 4-Week Physical Exercises on Tryptophan, Kynurenine and Kynurenic Acid Content in Human Sweat. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcan, H.; Chaumond, R.; Emond, P.; Benz-De Bretagne, I.; Lefèvre, A.; Bakkouche, S.-E.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Vourc’h, P.; Andres, C.; Corcia, P.; et al. Some CSF Kynurenine Pathway Intermediates Associated with Disease Evolution in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.B.; Byrne, L.M.; Lowe, A.J.; Tortelli, R.; Heins, M.; Flik, G.; Johnson, E.B.; De Vita, E.; Scahill, R.I.; Giorgini, F.; et al. Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood as Potential Biomarkers in Huntington’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepplinger, B.; Baran, H.; Kronsteiner, C.; Reuss, J. Increased Levels of Kynurenic Acid in the Cerebrospinal Fluid in Patients with Hydrocephalus. Neurosignals 2019, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, L.K.; Linderholm, K.R.; Engberg, G.; Paulson, L.; Blennow, K.; Lindström, L.H.; Nordin, C.; Karanti, A.; Persson, P.; Erhardt, S. Elevated Levels of Kynurenic Acid in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Male Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erhardt, S.; Schwieler, L.; Engberg, G. Kynurenic Acid and Schizophrenia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003, 527, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejdak, K.; Bartosik-Psujek, H.; Dobosz, B.; Kocki, T.; Grieb, P.; Giovannoni, G.; Turski, W.A.; Stelmasiak, Z. Decreased Level of Kynurenic Acid in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Relapsing-Onset Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 331, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, K.J.; Matson, W.R.; MacGarvey, U.; Ryan, E.A.; Beal, M.F. Measurement of Kynurenic Acid in Mammalian Brain Extracts and Cerebrospinal Fluid by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorometric and Coulometric Electrode Array Detection. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 185, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Murakami, H.; Horiguchi, K.; Egawa, B. Studies on Cerebrospinal Fluid Kynurenic Acid Concentrations in Epileptic Children. Brain Dev. 1995, 17, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Nakamura, M.; Todd, W.P.; Carpenter, B.K.; Whetsell, W.O.; Schwarcz, R. Identification and Quantification of Kynurenic Acid in Human Brain Tissue. Brain Res. 1988, 454, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connick, J.H.; Carlà, V.; Moroni, F.; Stone, T.W. Increase in Kynurenic Acid in Huntington’s Disease Motor Cortex. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Russi, P.; Lombardi, G.; Beni, M.; Carlà, V. Presence of Kynurenic Acid in the Mammalian Brain. J. Neurochem. 1988, 51, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, H.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Kepplinger, B.; Mazal, P.R.; Schmid, H.; Budka, H. Kynurenic Acid Metabolism in the Brain of HIV-1 Infected Patients. J. Neural. Transm. 2000, 107, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, H.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Kepplinger, B. Kynurenic Acid Metabolism in Various Types of Brain Pathology in HIV-1 Infected Patients. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2012, 5, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarcz, R.; Rassoulpour, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Medoff, D.; Tamminga, C.A.; Roberts, R.C. Increased Cortical Kynurenate Content in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, L.; Clarke, G.; Nolan, A.; Watkins, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A. Tryptophan Metabolic Profile in Term and Preterm Breast Milk: Implications for Health. J. Nutr. Sci. 2018, 7, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milart, P.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Dobrowolski, P.; Tomaszewska, E.; Smolinska, K.; Debinska, I.; Gawel, K.; Walczak, K.; Bednarski, J.; Turska, M.; et al. Kynurenic Acid as the Neglected Ingredient of Commercial Baby Formulas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oluwagbemigun, K.; Anesi, A.; Clarke, G.; Schmid, M.; Mattivi, F.; Nöthlings, U. An Investigation into the Temporal Reproducibility of Tryptophan Metabolite Networks Among Healthy Adolescents. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2021, 14, 11786469211041376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gomez, A.; Marcos, J.; Aguilera, P.; To-Figueras, J.; Pozo, O.J. Comprehensive Analysis of the Tryptophan Metabolome in Urine of Patients with Acute Intermittent Porphyria. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1060, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlanetto, S.; Tognini, C.; Carpenedo, R.; La Porta, E.; Pinzauti, S. Set-up and Validation of an Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetric Method for Kynurenic Acid Determination in Human Urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 18, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, B.; Bishop, M.; Paliakov, E.; Norton, D.; George, J.; Bralley, J.A. Analysis of Urinary Aromatic Acids by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawatari, K.; Iinuma, F.; Watanabe, M. Fluorometric Determination of Urinary Kynurenic Acid by Flow Injection Analysis Equipped with a “Bypass Line” . Anal. Biochem. 1990, 190, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kuzhiumparambil, U.; Bandodkar, S.; Solowij, N.; Fu, S. Development and Validation of a Simple, Rapid and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for the Measurement of Urinary Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 7191–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Ni, P.; Xu, B.; Luo, X.; Zhan, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhu, D. Simultaneous Determination of Urinary Tryptophan, Tryptophan-Related Metabolites and Creatinine by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet and Fluorimetric Detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 2720–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leklem, J.E. Quantitative Aspects of Tryptophan Metabolism in Humans and Other Species: A Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1971, 24, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Hirose, J.; Fukuwatari, T. Method for Evaluation of the Requirements of B-Group Vitamins Using Tryptophan Metabolites in Human Urine. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2015, 8, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiratsuka, C.; Fukuwatari, T.; Shibata, K. Fate of Dietary Tryptophan in Young Japanese Women. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2012, 5, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, C.; Fukuwatari, T.; Sano, M.; Saito, K.; Sasaki, S.; Shibata, K. Supplementing Healthy Women with up to 5.0 g/d of L-Tryptophan Has No Adverse Effects. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadour, Z.; Simian, C.; Laprévote, O.; Loriot, M.-A.; Larabi, I.A.; Pallet, N. Validation of a Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Tryptophan and 10 Key Metabolites of the Kynurenine Pathway in Plasma and Urine: Application to a Cohort of Acute Kidney Injury Patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 534, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberos, J.; Romero, J.; Molina-Carballo, A.; Muñoz-Hoyos, A. Melatonin and Elimination of Kynurenines in Children with Down’s Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 23, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Carballo, A.; Cubero-Millán, I.; Fernández-López, L.; Checa-Ros, A.; Machado-Casas, I.; Jerez-Calero, A.; Blanca-Jover, E.; Cantarero-Malagón, A.-M.; Uberos, J.; Muñoz-Hoyos, A. Methylphenidate Ameliorates the Homeostatic Balance between Levels of Kynurenines in ADHD Children. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 303, 114060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Hoyos, A.; Molina-Carballo, A.; Macías, M.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, T.; Martín-Medina, E.; Narbona-López, E.; Valenzuela-Ruiz, A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Comparison between Tryptophan Methoxyindole and Kynurenine Metabolic Pathways in Normal and Preterm Neonates and in Neonates with Acute Fetal Distress. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 139, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñóz-Hoyos, A.; Molina-Carballo, A.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, T.; Uberos-Fernández, J.; Ruiz-Cosano, C.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Relationships between Methoxyindole and Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in Plasma and Urine in Children Suffering from Febrile and Epileptic Seizures. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 47, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, S.; Schwarcz, R.; Rapoport, S.I.; Takada, Y.; Smith, Q.R. Blood-Brain Barrier Transport of Kynurenines: Implications for Brain Synthesis and Metabolism. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füvesi, J.; Somlai, C.; Németh, H.; Varga, H.; Kis, Z.; Farkas, T.; Károly, N.; Dobszay, M.; Penke, Z.; Penke, B.; et al. Comparative Study on the Effects of Kynurenic Acid and Glucosamine-Kynurenic Acid. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, N.; Csapó, E.; Majláth, Z.; Ilisz, I.; Krizbai, I.A.; Wilhelm, I.; Knapp, L.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L.; Dékány, I. Targeting of the Kynurenic Acid across the Blood-Brain Barrier by Core-Shell Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 86, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goeden, N.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Pocivavsek, A.; Beggiato, S.; Bonnin, A.; Schwarcz, R. Prenatal Dynamics of Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism in Mice: Focus on Kynurenic Acid. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 39, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.R.; Price, J.M. Quantitative Studies on Metabolites of Tryptophan in the Urine of the Dog, Cat, Rat, and Man. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 219, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Schwarcz, R. On the Disposition of Intrahippocampally Injected Kynurenic Acid in the Rat. Exp. Brain Res. 1988, 71, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Hao, F.; Murray, I.A.; Smith, P.B.; Koo, I.; Tindall, A.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Gowda, K.; Amin, S.G.; Patterson, A.D.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites Are Predictive of Ah Receptor Activity. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Feces. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_feces (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Uttekar, P. How Much Does an Average Person Sweat in a Day? 2021. Available online: https://www.medicinenet.com/how_much_does_an_average_person_sweat_in_a_day/article.htm (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Perspiration. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perspiration (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Turski, M.P.; Turska, M.; Zgrajka, W.; Kuc, D.; Turski, W.A. Presence of Kynurenic Acid in Food and Honeybee Products. Amino Acids 2009, 36, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, G.; Artali, R.; Caneva, E.; Orlandini, S.; Centini, M.; Facino, R.M. Quinoline Alkaloids in Honey: Further Analytical (HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS, Multidimensional Diffusion-Ordered NMR Spectroscopy), Theoretical and Chemometric Studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszynska, B.; Sutkowska-Ziaja, K.; Ekiert, H. Indole Compounds in Some Culinary-Medicinal Higher Basidiomycetes from Poland. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2011, 13, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, M.P.; Kamiński, P.; Zgrajka, W.; Turska, M.; Turski, W.A. Potato- an Important Source of Nutritional Kynurenic Acid. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2012, 67, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turski, M.P.; Turska, M.; Kocki, T.; Turski, W.A.; Paluszkiewicz, P. Kynurenic Acid Content in Selected Culinary Herbs and Spices. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yılmaz, C.; Gökmen, V. Determination of Tryptophan Derivatives in Kynurenine Pathway in Fermented Foods Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, C.; Gökmen, V. Formation of Amino Acid Derivatives in White and Red Wines during Fermentation: Effects of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts and Oenococcus Oeni. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Quantitative Analysis of Kynurenic Acid in Chestnut Honey from Different Regions and Method Validation. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 2022, 53, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, A.; Kołodziejczyk, M.; Michalska-Ciechanowska, A.; Brzezowska, J.; Wicha-Komsta, K.; Turski, W. The Effect of Thermal Treatment on Selected Properties and Content of Biologically Active Compounds in Potato Crisps. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, M.P.; Turska, M.; Zgrajka, W.; Bartnik, M.; Kocki, T.; Turski, W.A. Distribution, Synthesis, and Absorption of Kynurenic Acid in Plants. Planta Med 2011, 77, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgrajka, W.; Turska, M.; Rajtar, G.; Majdan, M.; Parada-Turska, J. Kynurenic Acid Content in Anti-Rheumatic Herbs. Ann Agric Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 800–802. [Google Scholar]
- Turski, M.P.; Zgrajka, W.; Siwicki, A.K.; Paluszkiewicz, P. Presence and Content of Kynurenic Acid in Animal Feed. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Kelly, D.L.; Rowland, L.M.; Hare, S.M.; Chen, S.; Mo, C.; Buchanan, R.W.; Schwarcz, R. Tryptophan Challenge in Healthy Controls and People with Schizophrenia: Acute Effects on Plasma Levels of Kynurenine, Kynurenic Acid and 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Małaczewska, J.; Marciniak, S.; Bednarski, J.; Turski, M.P.; Jabłoński, M.; Siwicki, A.K. On the Toxicity of Kynurenic Acid in Vivo and in Vitro. Pharm. Rep. 2014, 66, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małaczewska, J.; Siwicki, A.K.; Wójcik, R.M.; Kaczorek, E.; Turski, W.A. Effect of Oral Administration of Kynurenic Acid on the Activity of the Peripheral Blood Leukocytes in Mice. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 39, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Małaczewska, J.; Siwicki, A.K.; Wójcik, R.M.; Turski, W.A.; Kaczorek, E. The Effect of Kynurenic Acid on the Synthesis of Selected Cytokines by Murine Splenocytes—In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 41, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bądzyńska, B.; Zakrocka, I.; Turski, W.A.; Olszyński, K.H.; Sadowski, J.; Kompanowska-Jezierska, E. Kynurenic Acid Selectively Reduces Heart Rate in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2020, 393, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, S.; Wu, D.-R.; Liu, J.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.-M.D.; et al. The Beneficial Effects of Edible Kynurenic Acid from Marine Horseshoe Crab (Tachypleus Tridentatus) on Obesity, Hyperlipidemia, and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8874503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Muszyński, S.; Kuc, D.; Dobrowolski, P.; Lamorski, K.; Smolińska, K.; Donaldson, J.; Świetlicka, I.; Mielnik-Błaszczak, M.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; et al. Chronic Dietary Supplementation with Kynurenic Acid, a Neuroactive Metabolite of Tryptophan, Decreased Body Weight without Negative Influence on Densitometry and Mandibular Bone Biomechanical Endurance in Young Rats. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozlowska, M. Biochemical, Genetic and Behavioural Aspects of Dietary Supplementation with Kynurenic Acid in Rats. Doctoral Dissertation. Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo, L.Z.; Ferreira, D.M.S.; Cervenka, I.; Bryzgalova, G.; Dadvar, S.; Jannig, P.R.; Pettersson-Klein, A.T.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Sustarsic, E.G.; Porsmyr-Palmertz, M.; et al. Kynurenic Acid and Gpr35 Regulate Adipose Tissue Energy Homeostasis and Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 378–392.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Tang, J. Intestinal Flora-Derived Kynurenic Acid Protects Against Intestinal Damage Caused by Candida Albicans Infection via Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 934786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavin, G.B.; Pinsky, C. Kynurenic Acid Attenuates Experimental Ulcer Formation and Basal Gastric Acid Secretion in Rats. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharm. 1989, 64, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolski, P.; Prejbisz, A.; Kuryłowicz, A.; Baska, A.; Burchard, P.; Chlebus, K.; Dzida, G.; Jankowski, P.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Jaworski, P.; et al. Zespół metaboliczny—Nowa definicja i postępowanie w praktyce. Lek. POZ 2022, 8, 147–170. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Shi, Y.; Gao, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shen, S.; Shao, X.; Gong, W.; Chen, X.; Qin, J.; et al. Exercised Accelerated the Production of Muscle-Derived Kynurenic Acid in Skeletal Muscle and Alleviated the Postmenopausal Osteoporosis through the Gpr35/NFκB P65 Pathway. J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, F.; Cozzi, A.; Sili, M.; Mannaioni, G. Kynurenic Acid: A Metabolite with Multiple Actions and Multiple Targets in Brain and Periphery. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, L.; Rutai, A.; Fejes, R.; Tallósy, S.P.; Poles, M.Z.; Szabó, A.; Szatmári, I.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; Boros, M.; et al. Divergent Effects of the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist Kynurenic Acid and the Synthetic Analog SZR-72 on Microcirculatory and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Experimental Sepsis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 566582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poles, M.Z.; Nászai, A.; Gulácsi, L.; Czakó, B.L.; Gál, K.G.; Glenz, R.J.; Dookhun, D.; Rutai, A.; Tallósy, S.P.; Szabó, A.; et al. Kynurenic Acid and Its Synthetic Derivatives Protect Against Sepsis-Associated Neutrophil Activation and Brain Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Rats. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.; Chen, R.; Yeh, Y.; Lin, M.; Hsieh, J.; Chen, S. Kynurenic Acid Attenuates Multiorgan Dysfunction in Rats after Heatstroke. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2011, 32, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszaki, J.; Palásthy, Z.; Erczes, D.; Rácz, A.; Torday, C.; Varga, G.; Vécsei, L.; Boros, M. Kynurenic Acid Inhibits Intestinal Hypermotility and Xanthine Oxidase Activity during Experimental Colon Obstruction in Dogs. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marciniak, A. Rola Kwasu Kynureninowego w Utrzymaniu Integralności Układu Zewnątrzwydzielniczego Trzustki w Doświadczalnym Ceruleinowym Ostrym Zapaleniu Trzustki. Habilitation Dissertation. Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Poormasjedi-Meibod, M.-S.; Hartwell, R.; Kilani, R.T.; Ghahary, A. Anti-Scarring Properties of Different Tryptophan Derivatives. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysik-Woźniak, A.; Turski, W.A.; Turska, M.; Paduch, R.; Łańcut, M.; Piwowarczyk, P.; Czuczwar, M.; Rejdak, R. Kynurenic Acid Accelerates Healing of Corneal Epithelium In Vitro and In Vivo. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, M.S.; Berman, B.; Fischer, D.L.; Han, H.; Gade, A.; Arnold, D.; Lawson, A. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Active- and Placebo-Controlled Trial Evaluating a Novel Topical Treatment for Keloid Scars. J. Drugs Derm. 2021, 20, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabai, L.; Ghahary, A.; Jackson, J. Localized Controlled Release of Kynurenic Acid Encapsulated in Synthetic Polymer Reduces Implant—Induced Dermal Fibrosis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wejksza, K.; Rzeski, W.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic Acid Protects against the Homocysteine-Induced Impairment of Endothelial Cells. Pharm. Rep. 2009, 61, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, K.; Bao, L.; Chen, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X. Kynurenic Acid Protects against Mastitis in Mice by Ameliorating Inflammatory Responses and Enhancing Blood-Milk Barrier Integrity. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 137, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csáti, A.; Edvinsson, L.; Vécsei, L.; Toldi, J.; Fülöp, F.; Tajti, J.; Warfvinge, K. Kynurenic Acid Modulates Experimentally Induced Inflammation in the Trigeminal Ganglion. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, G.; Erces, D.; Fazekas, B.; Fülöp, M.; Kovács, T.; Kaszaki, J.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; Boros, M. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonism Decreases Motility and Inflammatory Activation in the Early Phase of Acute Experimental Colitis in the Rat. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 217–225.e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbow, T.; Teja, F.; Sheikhi, A.; Exposto, F.G.; Svensson, P.; Cairns, B.E. Peripheral N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Activation Contributes to Monosodium Glutamate-Induced Headache but Not Nausea Behaviours in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körtési, T.; Tuka, B.; Tajti, J.; Bagoly, T.; Fülöp, F.; Helyes, Z.; Vécsei, L. Kynurenic Acid Inhibits the Electrical Stimulation Induced Elevated Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide Expression in the TNC. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oláh, G.; Herédi, J.; Menyhárt, A.; Czinege, Z.; Nagy, D.; Fuzik, J.; Kocsis, K.; Knapp, L.; Krucsó, E.; Gellért, L.; et al. Unexpected Effects of Peripherally Administered Kynurenic Acid on Cortical Spreading Depression and Related Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. Drug Des. Dev. 2013, 7, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knyihar-Csillik, E.; Mihaly, A.; Krisztin-Peva, B.; Robotka, H.; Szatmari, I.; Fulop, F.; Toldi, J.; Csillik, B.; Vecsei, L. The Kynurenate Analog SZR-72 Prevents the Nitroglycerol-Induced Increase of c-Fos Immunoreactivity in the Rat Caudal Trigeminal Nucleus: Comparative Studies of the Effects of SZR-72 and Kynurenic Acid. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 61, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez Ortega, D.; Ugalde Muñiz, P.E.; Blanco Ayala, T.; Vázquez Cervantes, G.I.; Lugo Huitrón, R.; Pineda, B.; González Esquivel, D.F.; Pérez de la Cruz, G.; Pedraza Chaverrí, J.; Sánchez Chapul, L.; et al. On the Antioxidant Properties of L-Kynurenine: An Efficient ROS Scavenger and Enhancer of Rat Brain Antioxidant Defense. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavin, G.B.; Bose, R.; Pinsky, C. Kynurenic Acid Protects against Gastroduodenal Ulceration in Mice Injected with Extracts from Poisonous Atlantic Shellfish. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 13, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Yu, B. Active Components in Ephedra Sinica Stapf Disrupt the Interaction between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD: Potent COVID-19 Therapeutic Agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, V.S.S.; Mariano, D.O.C.; Vigerelli, H.; Janussi, S.C.; Baptista, T.V.L.; Claudino, M.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Sciani, J.M. Effects of Kynurenic Acid on the Rat Aorta Ischemia-Reperfusion Model: Pharmacological Characterization and Proteomic Profiling. Molecules 2021, 26, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyant, G.A.; Yu, W.; Doulamis, I.P.; Nomoto, R.S.; Saeed, M.Y.; Duignan, T.; McCully, J.D.; Kaelin, W.G. Mitochondrial Remodeling and Ischemic Protection by G Protein-Coupled Receptor 35 Agonists. Science 2022, 377, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, S.; Wnorowski, A.; Smolińska, K.; Walczyna, B.; Turski, W.; Kocki, T.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Parada-Turska, J. Kynurenic Acid Protects against Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Injury in Rats. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2018, 2018, 1270483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pyun, D.H.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, S.A.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Jung, T.W. Endogenous Metabolite, Kynurenic Acid, Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via AMPK/Autophagy- and AMPK/ORP150-Mediated Signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 4902–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolecka, J.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T.; Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Parada-Turska, J. Effect of Kynurenic Acid on the Viability of Probiotics in Vitro. Pharm. Rep. 2011, 63, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensley, L.; Van Eenwyk, J.; Bruemmer, B.A. Measuring Fruit and Vegetable Consumption: Providing Serving Size Information Doubles Estimated Percent Eating Five per Day. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellano, M.G.; Beccaro, G.L.; Donno, D.; Marinoni, D.T.; Boccacci, P.; Canterino, S.; Cerutti, A.K.; Bounous, G. Castanea Spp. Biodiversity Conservation: Collection and Characterization of the Genetic Diversity of an Endangered Species. Genet Resour Crop. Evol. 2012, 59, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honey. Available online: https://www.rxlist.com/honey/supplements.htm (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Terzo, S.; Calvi, P.; Nuzzo, D.; Picone, P.; Galizzi, G.; Caruana, L.; Di Carlo, M.; Lentini, L.; Puleio, R.; Mulè, F.; et al. Preventive Impact of Long-Term Ingestion of Chestnut Honey on Glucose Disorders and Neurodegeneration in Obese Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, H.; Kaltalioglu, K.; Erisgin, Z.; Coskun-Cevher, S.; Kolayli, S. Protective Effects of Aqueous Extracts of Some Honeys against HCl/Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulceration in Rats. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saral, Ö.; Yildiz, O.; Aliyazicioğlu, R.; Yuluğ, E.; Canpolat, S.; Öztürk, F.; Kolayli, S. Apitherapy Products Enhance the Recovery of CCL4-Induced Hepatic Damages in Rats. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nisbet, H.O.; Nisbet, C.; Yarim, M.; Guler, A.; Ozak, A. Effects of Three Types of Honey on Cutaneous Wound Healing. Wounds 2010, 22, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atalay, K.; Cabuk, K.S.; Kirgiz, A.; Caglar, A.K. Treatment of Corneal Alkali Burn with Chestnut Honey, Royal Jelly, and Chestnut Honey-Royal Jelly Mixture. Beyoglu. Eye J. 2019, 4, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, M.F.; Yılmaz, E.; Timirci-Kahraman, Ö.; Saygılı, N.; Kısakesen, H.İ.; Eronat, A.P.; Ceviz, A.B.; Bilgiç Gazioğlu, S.; Yılmaz-Aydoğan, H.; Öztürk, O. Anatolian Honey Is Not Only Sweet but Can Also Protect from Breast Cancer: Elixir for Women from Artemis to Present. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, O.; Karahalil, F.; Can, Z.; Sahin, H.; Kolayli, S. Total Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibition by Chestnut Honey, Pollen and Propolis. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem 2014, 29, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, H. Honey as an Apitherapic Product: Its Inhibitory Effect on Urease and Xanthine Oxidase. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Combarros-Fuertes, P.; M Estevinho, L.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; G Rodrigues, A.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Fresno, J.M.; Tornadijo, M.E. Antibacterial Action Mechanisms of Honey: Physiological Effects of Avocado, Chestnut, and Polyfloral Honey upon Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli. Molecules 2020, 25, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronsisvalle, S.; Lissandrello, E.; Fuochi, V.; Petronio Petronio, G.; Straquadanio, C.; Crascì, L.; Panico, A.; Milito, M.; Cova, A.M.; Tempera, G.; et al. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Casteanea Sativa Miller Chestnut Honey Produced on Mount Etna (Sicily). Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Lopes, M.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Is Honey Able to Potentiate the Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Properties of Medicinal Plants Consumed as Infusions for Hepatoprotective Effects? Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolayli, S.; Can, Z.; Yildiz, O.; Sahin, H.; Karaoglu, S.A. A Comparative Study of the Antihyaluronidase, Antiurease, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Physicochemical Properties of Different Unifloral Degrees of Chestnut (Castanea Sativa Mill.) Honeys. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Can, Z.; Yildiz, O.; Sahin, H.; Akyuz Turumtay, E.; Silici, S.; Kolayli, S. An Investigation of Turkish Honeys: Their Physico-Chemical Properties, Antioxidant Capacities and Phenolic Profiles. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, C.; Illuminati, S.; Annibaldia, A.; Finale, C.; Rossetti, M.; Scarponi, G. Physicochemical Properties of Honey from Marche, Central Italy: Classification of Unifloral and Multifloral Honeys by Multivariate Analysis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escuredo, O.; Míguez, M.; Fernández-González, M.; Carmen Seijo, M. Nutritional Value and Antioxidant Activity of Honeys Produced in a European Atlantic Area. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atayoğlu, A.T.; Soylu, M.; Silici, S.; İnanç, N. Glycemic Index Values of Monofloral Turkish Honeys and the Effect Oftheir Consumption on Glucose Metabolism. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdomichali, T.; Papakonstantinou, E. Short-Term Effects of Six Greek Honey Varieties on Glycemic Response: A Randomized Clinical Trial in Healthy Subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deibert, P.; König, D.; Kloock, B.; Groenefeld, M.; Berg, A. Glycaemic and Insulinaemic Properties of Some German Honey Varieties. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wróbel-Kwiatkowska, M.; Turski, W.; Kocki, T.; Rakicka-Pustułka, M.; Rymowicz, W. An Efficient Method for Production of Kynurenic Acid by Yarrowia Lipolytica. Yeast 2020, 37, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakicka-Pustułka, M.; Ziuzia, P.; Pierwoła, J.; Szymański, K.; Wróbel-Kwiatkowska, M.; Lazar, Z. The Microbial Production of Kynurenic Acid Using Yarrowia Lipolytica Yeast Growing on Crude Glycerol and Soybean Molasses. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 936137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| KYNA Excretion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Minimal Level (mg/day) | Maximal Level (mg/day) | |
| Urine | 1.14 | 6.29 |
| Feces | 0.010 | 0.707 |
| Sweat | 0.00069 | 0.00503 |
| Total | 1.15 | 7.00 |
| Species | KYNA Treatment (Dose, Schedule) | Effect/Properties | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult animals | |||
| Rats, mice | 25 or 250 mg/L in drinking water for 3–21 days |
| [86] |
| Mice | 2.5, 25, or 250 mg/L in drinking water for 3, 7, 14, 28 days |
| [87] |
| Mice | 2.5, 25, or 250 mg/L in drinking water for 7–14 days |
| [88] |
| Spontaneously hypertensive rats | 25 mg/kg/day in drinking water for 3 weeks |
| [89] |
| Mice | 5 mg/kg/day, intragastric; once a day for 8 weeks | High-fat diet induced:
| [90] |
| Young animals | |||
| Rats | 25 or 250 mg/L in drinking water; from PND 1 to PND 60 |
| [91] |
| Rats | 250 mg/L in drinking water; from PND 1 to PND 21 |
| [46] |
| Rats | 25 mg/L in drinking water; from PND 21 until 9th week of life |
| [92] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turska, M.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Turski, W.A.; Parada-Turska, J. A Review of the Health Benefits of Food Enriched with Kynurenic Acid. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194182
Turska M, Paluszkiewicz P, Turski WA, Parada-Turska J. A Review of the Health Benefits of Food Enriched with Kynurenic Acid. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194182
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurska, Monika, Piotr Paluszkiewicz, Waldemar A. Turski, and Jolanta Parada-Turska. 2022. "A Review of the Health Benefits of Food Enriched with Kynurenic Acid" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194182
APA StyleTurska, M., Paluszkiewicz, P., Turski, W. A., & Parada-Turska, J. (2022). A Review of the Health Benefits of Food Enriched with Kynurenic Acid. Nutrients, 14(19), 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194182