Selenium in Cancer Rehabilitation—A Retrospective Study from a Specialized Clinic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Measurement of Whole Blood Selenium and Zinc
2.3. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life Questionnaire Core-30 (EORTC QLQ-C30)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
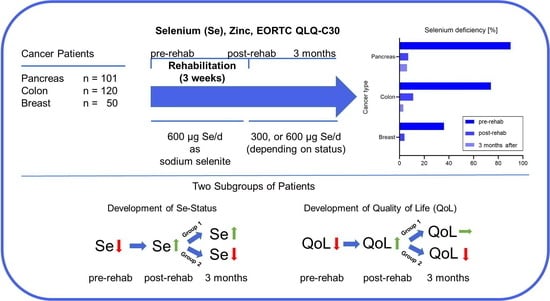
3.2. High Prevalence of Selenium Deficiency Depending on Tumor Localization
3.3. Selenium Supplementation during Rehabilitation Corrects Selenium Deficiency
3.4. Different Development of Whole Blood Selenium Concentration
3.5. Differences in EORTC QLQ-C30 Results Depending on Tumor Localization
3.6. Differences in EORTC QLQ-C30 Results Depending on Selenium Status
4. Discussion
4.1. Selenium Deficiency in Cancer Patients in Rehabilitation
4.2. Selenium Supplementation Corrects Selenium Deficiency
4.3. Effect of Rehabilitation and Selenium Supplementation on Quality of Life
4.4. Effect of Rehabilitation and Selenium Supplementation on Key Domains
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, R.S.; Engle, J. Rehabilitation of Individuals with Cancer. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 46, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, A.; Gerber, L.H.; Marshall, T.F.; Livinski, A.; Alfano, C.M.; Harrington, S.; Flores, A.M.; Virani, A.; Hu, X.; Mitchell, S.A.; et al. Systematic Review of Functional Outcomes in Cancer Rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 1807–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Süß, P.; Schulte, D.M.; Letsch, A.; Jensen, W. Supportive Care in Oncology-From Physical Activity to Nutrition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jia, T.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, E. Underlying Causes and Co-Existence of Malnutrition and Infections: An Exceedingly Common Death Risk in Cancer. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 814095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langius, J.A.E.; Bakker, S.; Rietveld, D.H.F.; Kruizenga, H.M.; Langendijk, J.A.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Leemans, C.R. Critical Weight Loss Is a Major Prognostic Indicator for Disease-Specific Survival in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Receiving Radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressoir, M.; Desné, S.; Berchery, D.; Rossignol, G.; Poiree, B.; Meslier, M.; Traversier, S.; Vittot, M.; Simon, M.; Gekiere, J.P.; et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Clinical Implications of Malnutrition in French Comprehensive Cancer Centres. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, N.M. The Global Challenge of Hidden Hunger: Perspectives from the Field. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrauzer, G.N.; White, D.A.; Schneider, C.J. Cancer Mortality Correlation Studies—III: Statistical Associations with Dietary Selenium Intakes. Bioinorg. Chem. 1977, 7, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Fan, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Selenium Exposure and Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.D.; Droz, B.; Greve, P.; Gottschalk, P.; Poffet, D.; McGrath, S.P.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Smith, P.; Winkel, L.H.E. Selenium Deficiency Risk Predicted to Increase under Future Climate Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2848–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Rayman, M.P.; Lv, H.; Schomburg, L.; Cui, B.; Gao, C.; Chen, P.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, X.; et al. Low Population Selenium Status Is Associated with Increased Prevalence of Thyroid Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 4037–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wei, J.; Lv, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Peng, X.; Rijntjes, E.; et al. Increased Incidence of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis in Selenium Deficiency: A Prospective Six-Year Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3603–e3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benstoem, C.; Goetzenich, A.; Kraemer, S.; Borosch, S.; Manzanares, W.; Hardy, G.; Stoppe, C. Selenium and Its Supplementation in Cardiovascular Disease—What Do We Know? Nutrients 2015, 7, 3094–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alehagen, U.; Johansson, P.; Björnstedt, M.; Rosén, A.; Post, C.; Aaseth, J. Relatively High Mortality Risk in Elderly Swedish Subjects with Low Selenium Status. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomer, N.; Grote Beverborg, N.; Hoes, M.F.; Streng, K.W.; Vermeer, M.; Dokter, M.M.; IJmker, J.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Hillege, H.L.; et al. Selenium and Outcome in Heart Failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 22, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiero, H.; Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. The Antioxidant Role of Selenium and Seleno-Compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinggi, U. Selenium: Its Role as Antioxidant in Human Health. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2008, 13, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Rose, A.H.; Hoffmann, P.R. The Role of Selenium in Inflammation and Immunity: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 705–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Discovery of Human Zinc Deficiency: Its Impact on Human Health and Disease. Adv. Nutr. An. Int. Rev. J. 2013, 4, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrajnowska, D.; Bobrowska-Korczak, B. Role of Zinc in Immune System and Anti-Cancer Defense Mechanisms. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, Y.; Demircan, K.; Rosendahl, A.H.; Borgquist, S.; Sandsveden, M.; Manjer, J. Zinc and Breast Cancer Survival: A Prospective Cohort Study of Dietary Intake and Serum Levels. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, K.; Bengtsson, Y.; Sun, Q.; Brange, A.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Rijntjes, E.; Malmberg, M.; Saal, L.H.; Rydén, L.; Borg, Å.; et al. Serum Selenium, Selenoprotein P and Glutathione Peroxidase 3 as Predictors of Mortality and Recurrence Following Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Multicentre Cohort Study. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikawa, T.; Utsunomiya, M.; Yokota, K.; Munekage, M.; Uemura, S.; Maeda, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanazaki, K. Association between Serum Zinc Levels and Clinicopathological Characteristics in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Gastrointest. Tumors 2023, 10, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Sempos, C.T.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Muti, P.; Smit, E. Serum Iron, Copper and Zinc Concentrations and Risk of Cancer Mortality in US Adults. Ann. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Chu, A.; Zhen, S.; Taylor, A.W.; Dai, Y.; Riley, M.; Samman, S. Association between Dietary Zinc Intake and Mortality among Chinese Adults: Findings from 10-Year Follow-up in the Jiangsu Nutrition Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandsveden, M.; Nilsssson, E.; Borgquist, S.; Rosendahl, A.H.; Manjer, J. Pre-Diagnostic Serum Selenium Levels in Relation to Breast Cancer Survival and Tumor Characteristics. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubinski, J.; Marciniak, W.; Muszynska, M.; Huzarski, T.; Gronwald, J.; Cybulski, C.; Jakubowska, A.; Debniak, T.; Falco, M.; Kladny, J.; et al. Serum Selenium Levels Predict Survival after Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 167, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, C.A.S.; Nogueira, C.R.; Ramalho, A.; Carvalho, A.C.P.; Vieira, S.L.; Penna, A.B.R.C. Serum Levels of Selenium in Patients with Breast Cancer before and after Treatment of External Beam Radiotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.C.; Xue, M.; Chi, F.; Xu, Z.G.; Fan, G.L.; Fan, Y.C.; Zheng, M.H.; Zhong, W.Z.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Serum Levels of Selenium in Patients with Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer before and after Radiotherapy. Cancer/Radiothérapie 2012, 16, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalabopoulos, K.; Kotsalos, A.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Vezyraki, P.; Peschos, D.; Kalfakakou, V.; Evangelou, A. Selenium in Serum and Neoplastic Tissue in Breast Cancer: Correlation with CEA. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lener, M.R.; Scott, R.J.; Wiechowska-Kozłowska, A.; Serrano-Fernández, P.; Baszuk, P.; Jaworska-Bieniek, K.; Sukiennicki, G.; Marciniak, W.; Muszyńska, M.; Kładny, J.; et al. Serum Concentrations of Selenium and Copper in Patients Diagnosed with Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 48, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikac-Dević, M.; Vukelić, N.; Kljaić, K. Serum Selenium Level in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1992, 33, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psathakis, D.; Wedemeyer, N.; Oevermann, E.; Krug, F.; Siegers, C.P.; Bruch, H.P. Blood Selenium and Glutathione Peroxidase Status in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Colon. Rectum 1998, 41, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnefeld, K.; Dawczynski, H.; Schirrmeister, W.; Adam, G.; Friedrich, U.; Hein, S. Selenium in Serum and Whole Blood in Patients with Surgical Interventions. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1995, 50, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, P.D. The Essential Guide to Effect Sizes: Statistical Power, Meta-Analysis, and the Interpretation of Research Results, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-521-19423-5. [Google Scholar]
- Giesinger, J.M.; Kuijpers, W.; Young, T.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Friend, E.; Zabernigg, A.; Holzner, B.; Aaronson, N.K. Thresholds for Clinical Importance for Four Key Domains of the EORTC QLQ-C30: Physical Functioning, Emotional Functioning, Fatigue and Pain. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, A.; Schubert, D.; Katalinic, A. Normative Data of the EORTC QLQ-C30 For the German Population: A Population-Based Survey. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalabopoulos, K.; Kotsalos, A.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Peschos, D.; Vezyraki, P.; Kalfakakou, V.; Metsios, A.; Charalampopoulos, A.; Macheras, A.; et al. Serum and Tissue Selenium Levels in Gastric Cancer Patients and Correlation with CEA. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3465–3467. [Google Scholar]
- Muecke, R.; Klotz, T.; Giedl, J.; Buentzel, J.; Kundt, G.; Kisters, K.; Prott, F.-J.; Micke, O. Whole Blood Selenium Levels (WBSL) in Patients with Prostate Cancer (PC), Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Healthy Male Inhabitants (HMI) and Prostatic Tissue Selenium Levels (PTSL) in Patients with PC and BPH. Acta Oncol. 2009, 48, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, K.; Gupta, S.; Durda, K.; Muszyńska, M.; Sukiennicki, G.; Jaworowska, E.; Grodzki, T.; Sulikowski, M.; Waloszczyk, P.; Woloszczyk, P.; et al. A Low Selenium Level Is Associated with Lung and Laryngeal Cancers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, J.; Muenstedt, K.; Prott, F.J.; Stoll, C.; Micke, O.; Buentzel, J.; Muecke, R.; Senf, B. Online Survey of Patients with Breast Cancer on Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Breast Care 2014, 9, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretta, M.; Della Pepa, C.; Tralongo, P.; Fulvi, A.; Martellotta, F.; Lleshi, A.; Nasti, G.; Fisichella, R.; Romano, C.; De Divitiis, C.; et al. Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) in Cancer Patients: An Italian Multicenter Survey. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 24401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.; Waters, R.; Sieniawska, C.; Kassam, S.; Montoto, S.; Fitzgibbon, J.; Rohatiner, A.; Lister, A.; Joel, S. Serum Selenium Concentration at Diagnosis and Outcome in Patients with Haematological Malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.F.; Blackford, A.L.; Sussman, J.; Bainbridge, D.; Howell, D.; Seow, H.Y.; Carducci, M.A.; Wu, A.W. Identifying Changes in Scores on the EORTC-QLQ-C30 Representing a Change in Patients’ Supportive Care Needs. Qual. Life Res. 2015, 24, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, J.; Thyrolf, A.; Mau, W. Health-Related Quality of Life in Rehabilitants with Different Cancer Entities. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2017, 26, e12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Joo, S.; Nolte, S.; Yoo, H.K.; Patel, N.; Byrnes, H.F.; Costa-Cabral, S.; Johnson, C.D. Health-Related Quality of Life Scores of Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients Responsive to First Line Chemotherapy Compared to Newly Derived EORTC QLQ-C30 Reference Values. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.; Schulte, T. Quality of life in elderly cancer patients--need for and benefit of inpatient rehabilitation. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2009, 134, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.; Thompson, A.; Warren-Perry, M.; Galassini, R.; Catterick, J.; Hall, E.; Lawrence, D.; Bliss, J. Impact of Selenium on Mood and Quality of Life: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, S.; Jansen, L.; Boakye, D.; Hoffmeister, M.; Brenner, H. Changes in Health-Related Outcomes among Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Inpatient Rehabilitation Therapy: A Systematic Review of Observational and Interventional Studies. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.L.D.S.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Costa, L.G.; Beltrame, R.L.; de Chaves, C.M.S.; Cartum, J.; do Alves, S.I.P.M.N.; Azzalis, L.A.; Junqueira, V.B.C.; Pereria, E.C.; et al. Supplementation with Selenium Can Influence Nausea, Fatigue, Physical, Renal, and Liver Function of Children and Adolescents with Cancer. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Oltra, E.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Chillon, T.S.; Seemann, P.; Asaad, S.; Demircan, K.; Espejo-Oltra, J.A.; Sánchez-Fito, T.; Martín-Martínez, E.; et al. Autoantibodies to Selenoprotein P in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Suggest Selenium Transport Impairment and Acquired Resistance to Thyroid Hormone. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, V.; Merx, H.; Stegmaier, C.; Ziegler, H.; Brenner, H. Quality of Life in Patients with Colorectal Cancer 1 Year after Diagnosis Compared with the General Population: A Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4829–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, M.S.Y.; Koch-Gallenkamp, L.; Jansen, L.; Bertram, H.; Eberle, A.; Holleczek, B.; Waldeyer-Sauerland, M.; Waldmann, A.; Zeissig, S.R.; Brenner, H.; et al. Age-Specific Health-Related Quality of Life in Long-Term and Very Long-Term Colorectal Cancer Survivors versus Population Controls—A Population-Based Study. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | Breast Cancer | Pancreatic Cancer | Colon Cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample, n | 50 | 101 | 120 |
| Sex (f/m) | 98%/2% | 64%/36% | 53%/47% |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 62 ± 10 | 71 ± 11 | 69 ± 11 |
| Operation | 100% | 87% | 97% |
| Chemotherapy | |||
| planned | 26% | 40% | 7% |
| ongoing | 0% | 20% | 6% |
| after | 34% | 28% | 41% |
| none | 40% | 11% | 47% |
| Radiotherapy | 76% | 4% | 21% |
| Hormone therapy | 78% | - | - |
| Selenium status †, µg/L, mean± SD | 107.2 ± 18.4 | 80.5 ± 15.5 | 90.0 ± 17.6 |
| Prior selenium supplementation | 28% | 1% | 8% |
| Zinc status §, mg/L, mean ± SD | 5.9 ± 0.8 | 6.0 ± 0.8 | 6.0 ± 0.9 |
| Prior zinc supplementation | 0% | 0% | 2% |
| Characteristic | Breast Cancer | Pancreatic Cancer | Colon Cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample, n | 50 | 101 | 120 |
| Selenium deficiency † | |||
| beginning of rehabilitation | 36% | 90% | 74% |
| end of rehabilitation | 4% | 7% | 11% |
| 3 months after rehabilitation | 0% | 6% | 3% |
| Zinc deficiency § | |||
| beginning of rehabilitation | 0% | 0% | 1% |
| end of rehabilitation | 0% | 0% | 1% |
| 3 months after rehabilitation | 0% | 0% | 1% |
| Pre-Rehab | Post-Rehab | 3 Months after Rehabilitation | p-Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functional scales and global QoL | ||||
| Physical functioning | 73.6 (16.5) | 80.0 (16.7) | 83.1 (14.6) | 0.0012 |
| Role functioning | 56.1 (26.5) | 68.7 (26.1) | 62.8 (26.5) | 0.0253 |
| Emotional functioning | 57.6 (27.3) | 75.4 (20.3) | 58.3 (21.0) | <0.0001 |
| Cognitive functioning | 67.7 (29.5) | 76.9 (24.5) | 61.6 (26.7) | 0.0752 |
| Social functioning | 64.2 (27.5) | 74.8 (24.1) | 74.4 (26.0) | 0.0191 |
| Global QoL | 55.6 (15.9) | 68.4 (15.3) | 64.1 (15.7) | <0.0001 |
| Symptom Scales | ||||
| Fatigue | 48.6 (27.6) | 38.2 (22.7) | 45.3 (20.0) | 0.0030 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 5.5 (11.5) | 2.7 (9.2) | 2.6 (6.3) | 0.0324 |
| Pain | 39.8 (32.2) | 28.9 (27.4) | 32.1 (26.8) | 0.0329 |
| Dyspnea | 29.9 (33.9) | 26.5 (28.9) | 25.6 (20.0) | 0.3564 |
| Sleep disturbance | 54.4 (31.7) | 44.2 (36.3) | 51.3 (37.6) | 0.0395 |
| Appetite loss | 10.4 (24.0) | 7.5 (20.7) | 10.3 (16.0) | 0.3470 |
| Constipation | 14.6 (25.6) | 10.4 (21.9) | 10.3 (28.5) | 0.2214 |
| Diarrhea | 6.1 (16.2) | 8.2 (21.0) | 7.7 (14.6) | 0.4660 |
| Financial problems | 19.1 (28.4) | 15.0 (27.3) | 7.7 (14.6) | 0.1754 |
| Pre-Rehab | Post-Rehab | 3 Months after Rehabilitation | p-Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functional scales and global QoL | ||||
| Physical functioning | 54.5 (24.6) | 63.4 (22.6) | 63.2 (19.6) | <0.0001 |
| Role functioning | 41.5 (33.4) | 54.5 (30.4) | 52.9 (29.6) | 0.0004 |
| Emotional functioning | 58.3 (28.5) | 67.6 (25.6) | 60.6 (28.1) | 0.0041 |
| Cognitive functioning | 70.3 (27.4) | 76.8 (23.6) | 72.7 (26.2) | 0.0653 |
| Social functioning | 51.7 (33.6) | 62.0 (33.1) | 57.9 (34.8) | 0.0136 |
| Global QoL | 42.9 (23.1) | 54.1 (20.8) | 51.7 (21.3) | <0.0001 |
| Symptom Scales | ||||
| Fatigue | 60.9 (29.6) | 49.1 (25.7) | 49.4 (23.1) | <0.0001 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 17.0 (26.2) | 11.0 (20.4) | 9.7 (13.4) | 0.2027 |
| Pain | 41.1 (34.1) | 32.3 (28.3) | 31.0 (27.1) | 0.0162 |
| Dyspnea | 31.6 (32.4) | 31.9 (29.5) | 27.8 (28.2) | 0.4334 |
| Sleep disturbance | 44.6 (34.8) | 36.9 (33.0) | 38.9 (31.4) | 0.0782 |
| Appetite loss | 47.3 (40.3) | 37.6 (36.5) | 26.9 (29.6) | 0.0016 |
| Constipation | 17.7 (30.2) | 37.6 (36.5) | 9.3 (2.5) | <0.0001 |
| Diarrhea | 33.7 (35.8) | 17.8 (30.2) | 30.6 (33.2) | 0.0007 |
| Financial problems | 18.9 (27.2) | 16.9 (24.0) | 24.1 (31.5) | 0.3145 |
| Pre-Rehab | Post-Rehab | 3 Months after Rehabilitation | p-Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functional scales and global QoL | ||||
| Physical functioning | 66.1 (21.5) | 73.1 (20.4) | 76.0 (19.3) | <0.0001 |
| Role functioning | 51.8 (33.4) | 65.8 (28.2) | 64.0 (27.8) | <0.0001 |
| Emotional functioning | 65.7 (24.5) | 77.2 (22.6) | 69.3 (27.7) | <0.0001 |
| Cognitive functioning | 81.7 (27.3) | 82.7 (23.1) | 72.0 (28.3) | 0.0244 |
| Social functioning | 65.7 (31.8) | 76.0 (27.4) | 74.2 (28.0) | 0.0257 |
| Global QoL | 51.9 (22.2) | 64.4 (16.8) | 62.9 (18.7) | <0.0001 |
| Symptom Scales | ||||
| Fatigue | 48.6 (27.6) | 35.7 (26.1) | 37.0 (27.1) | <0.0001 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 6.4 (14.8) | 5.4 (15.0) | 4.2 (16.1) | 0.2520 |
| Pain | 36.3 (32.9) | 25.3 (27.5) | 20.1 (26.1) | <0.0001 |
| Dyspnea | 23.8 (30.7) | 26.8 (29.6) | 16.7 (26.4) | 0.0871 |
| Sleep disturbance | 43.5 (35.0) | 38.0 (32.4) | 34.9 (28.7) | 0.0868 |
| Appetite loss | 18.3 (28.9) | 12.3 (20.9) | 11.4 (22.7) | 0.2797 |
| Constipation | 17.1 (28.9) | 11.1 (22.9) | 12.4 (20.6) | 0.3007 |
| Diarrhea | 27.7 (32.7) | 16.4 (25.2) | 22.7 (25.7) | 0.0004 |
| Financial problems | 19.1 (29.3) | 18.8 (30.3) | 13.6 (28.1) | 0.3350 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfister, C.; Schoenemann, J. Selenium in Cancer Rehabilitation—A Retrospective Study from a Specialized Clinic. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173827
Pfister C, Schoenemann J. Selenium in Cancer Rehabilitation—A Retrospective Study from a Specialized Clinic. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173827
Chicago/Turabian StylePfister, Christina, and Joerg Schoenemann. 2023. "Selenium in Cancer Rehabilitation—A Retrospective Study from a Specialized Clinic" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173827
APA StylePfister, C., & Schoenemann, J. (2023). Selenium in Cancer Rehabilitation—A Retrospective Study from a Specialized Clinic. Nutrients, 15(17), 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173827