Allomyrina Dichotoma Larvae Regulate Food Intake and Body Weight in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Through mTOR and Mapk Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Cells
2.2. Preparation of Allomyrina Dichotoma Larvae Extract (ADE)
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Mice
2.5. Intracerebro-Ventricular Cannulation and ADE Administration
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Reverse Transcription-PCR
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Induces Hypothalamic Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
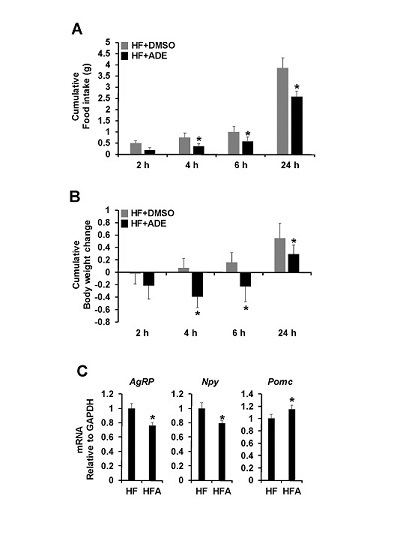
3.2. Central Administration of ADE Reduces Food Intake and Body Weight through Regulation of Appetite-Related Neuropeptides in High Fat Diet-Induced Mice
3.3. Central Administration of ADE Reduces Hypothalamic Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
3.4. Central Administration of ADE Regulates Appetite through MAPK and mTOR Signaling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzman, A.K.; Ding, M.; Xie, Y.; Martin, K.A. Pharmacogenetics of obesity drug therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2014, 14, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, R.J.; Tschop, M.H.; Wilding, J.P. Anti-obesity drugs: Past, present and future. Dis. Models Mech. 2012, 5, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Graubard, B.I.; Williamson, D.F.; Gail, M.H. Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. Jama 2007, 298, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagisaka, A.; Miyanoshita, A.; Ishibashi, J.; Yamakawa, M. Purification, characterization and gene expression of a glycine and proline-rich antibacterial protein family from larvae of a beetle, Allomyrina dichotoma. Insect Mol. Biol. 2001, 10, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanoshita, A.; Hara, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Asaoka, A.; Taniai, K.; Yukuhiro, F.; Yamakawa, M. Isolation and characterization of a new member of the insect defensin family from a beetle, Allomyrina dichotoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 220, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, H.J.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, K.S.; Park, S.; Kang, S.C. Antioxidant activity of various solvent extracts from Allomyrina dichotoma (Arthropoda: Insecta) larvae. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2010, 99, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.I.; Chung, M.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, M.S.; Goo, T.W.; Yun, E.Y. Allomyrina dichotoma (Arthropoda: Insecta) larvae confer resistance to obesity in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1978–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Umetsu, K.; Shinzawa, H.; Yuasa, I.; Maruyama, K.; Ohkura, T.; Yamashita, K.; Suzuki, T. Determination of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin separated by lectin affinity chromatography for detecting chronic alcohol abuse. FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.Y.; Yoon, Y.I.; Hwang, J.S.; Goo, T.W.; Yun, E.Y. Anti-obesity effect of Allomyrina dichotoma (Arthropoda: Insecta) larvae ethanol extract on 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. Entomol. Res. 2014, 44, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, G.J.; Cummings, D.E.; Baskin, D.G.; Barsh, G.S.; Schwartz, M.W. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 2006, 443, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmquist, J.K.; Coppari, R.; Balthasar, N.; Ichinose, M.; Lowell, B.B. Identifying hypothalamic pathways controlling food intake, body weight, and glucose homeostasis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 493, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupachyk, S.; Watcho, P.; Obrosov, A.A.; Stavniichuk, R.; Obrosova, I.G. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to prediabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 247, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnop, M.; Foufelle, F.; Velloso, L.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, R.G.; Arruda, A.P.; Romanatto, T.; Milanski, M.; Coope, A.; Solon, C.; Razolli, D.S.; Velloso, L.A. TNF-α transiently induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and an incomplete unfolded protein response in the hypothalamus. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.C.; Jang, P.G.; Namkoong, C.; Koh, E.H.; Kim, S.K.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Kim, M.S. Central administration of an endoplasmic reticulum stress inducer inhibits the anorexigenic effects of leptin and insulin. Obesity 2009, 17, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.H.; Yun, E.Y.; Park, H.; Jung, K.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Jeong, E.J.; Moon, K.S. Subchronic oral dose toxicity of freeze-dried powder of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, I.; Cyr, N.E.; Perello, M.; Litvinov, B.P.; Romero, A.; Stuart, R.C.; Nillni, E.A. Obesity induces hypothalamic endoplasmic reticulum stress and impairs proopiomelanocortin (POMC) post-translational processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17675–17688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.P.; Wang, F.; Xiang, X.S.; Cao, R.; Zhang, W.B.; Gao, S.B. Intracerebroventricular administration of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) inhibits food intake by decreasing gene expression of NPY and AgRP. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 418, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.P.; Dube, M.G.; Pu, S.; Xu, B.; Horvath, T.L.; Kalra, P.S. Interacting appetite-regulating pathways in the hypothalamic regulation of body weight. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 68–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullschleger, S.; Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006, 124, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, R. Electron-microscopic studies on the pathogenesis of exencephaly and cranioschisis induced in the rat after neural tube closure: Role of the neuroepithelium and choroid plexus. Acta Anat. 1990, 137, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A Review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A. Minireview: A hypothalamic role in energy balance with special emphasis on leptin. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A. Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus: Emphasis on energy homeostasis and leptin resistance. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2003, 24, 225–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W. Brain pathways controlling food intake and body weight. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001, 226, 978–981. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanovic, D.; Trajkovic, V.; Muller-Luhlhoff, S.; Brandt, E.; Abplanalp, W.; Bumke-Vogt, C.; Liehl, B.; Wiedmer, P.; Janjetovic, K.; Starcevic, V.; et al. Ghrelin-induced food intake and adiposity depend on central mtorc1/s6k1 signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 381, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.; Fernandez-Mallo, D.; Novelle, M.G.; Vazquez, M.J.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Nogueiras, R.; Lopez, M.; Dieguez, C. Hypothalamic mtor signaling mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanovic, D.; Starcevic, V.; Vilimanovich, U.; Nesic, D.; Vucicevic, L.; Misirkic, M.; Janjetovic, K.; Savic, E.; Popadic, D.; Sudar, E.; et al. Immunomodulatory actions of central ghrelin in diet-induced energy imbalance. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Oh, T.H.; Yune, T.Y. Ghrelin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptotic cell death of oligodendrocytes via erk and p38MAPK signaling. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.Z.; Cao, Y.L.; Huo, H.Y.; Zhao, W.H.; Hu, J. Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on nicotine-induced VCAM-1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Youn, B.S.; Shin, M.S.; Namkoong, C.; Park, K.H.; Baik, J.H.; Kim, J.B.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Kim, Y.B.; et al. Hypothalamic angptl4/fiaf is a novel regulator of food intake and body weight. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Liu, T. Hypothalamic inflammation: A double-edged sword to nutritional diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1243, E1–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Ahmed, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, D. Neural dysregulation of peripheral insulin action and blood pressure by brain endoplasmic reticulum stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrin, P.; Canfield, T. Cuffed endotracheal tubes: Mucosal pressures and tracheal wall blood flow. Am. J. Surg. 1977, 133, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Yeo, H.; Yun, E.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Jun, M. Fatty acid and volatile oil compositions of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, 17, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Goo, T.W.; Yun, E.Y. Analysis of general composition and harmful material of Protaetia breviatarsis. J. Life Sci. 2013, 23, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Hwang, J.S.; Goo, T.W.; Yun, E.Y. Comparative analysis of nutritional and harmful components in Korean and Chinese meal worms (Tenebrio molitor). J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 42, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.Y.; Kown, E.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Goo, T.W.; Yun, E.Y. Establishment of food processing methods for larvae of Allomyrina dichotoma, Korean horn beetle. J. Life Sci. 2013, 23, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moesgaard, S.G.; Ahren, B.; Carr, R.D.; Gram, D.X.; Brand, C.L.; Sundler, F. Effects of high-fat feeding and fasting on ghrelin expression in the mouse stomach. Regul. Pept. 2004, 120, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyasu, H.; Takaya, K.; Hosoda, H.; Iwakura, H.; Ebihara, K.; Mori, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Akamizu, T.; Kojima, M.; et al. Delayed short-term secretory regulation of ghrelin in obese animals: Evidenced by a specific ria for the active form of ghrelin. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3341–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshinai, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Nakazato, M.; Date, Y.; Murakami, N.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. Upregulation of ghrelin expression in the stomach upon fasting, insulin-induced hypoglycemia, and leptin administration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, T.; Doi, A.; Nosaka, T.; Furuta, H.; Akamizu, T.; Kitamura, T.; Senba, E.; Morikawa, Y. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling by AFF4 protein, member of AF4 (ALL1-fused gene from chromosome 4) family of transcription factors, in hypothalamic neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19985–19996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousseaux, D.; Le Gallic, L.; Ryan, J.; Oiry, C.; Gagne, D.; Fehrentz, J.A.; Galleyrand, J.C.; Martinez, J. Regulation of ERK1/2 activity by ghrelin-activated growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a involves a PLC/PKCε pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, L.; Tabas, I. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disease and other disorders. Ann. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H. ER stress and diseases. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 630–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Mouse cDNAs | Primer Sequences | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| For Real-time PCR | ||
| Xbp-1s | Forward, 5′-AGGCTTGGTGTATACATGG-3′ Reverse, 5′-GGTCTGCTGAGTCCGCAGCAGG-3′ | NM_013842 |
| Atf4 | Forward, 5′-GCAAGGAGGATGCCTTTTC-3′ Reverse, 5′-GTTTCCAGGTCATCCATTCG-3′ | NM_009716 |
| Chop | Forward, 5′-CCACCACACCTGAAAGCAGAA-3′ Reverse, 5′-AGGTGAAAGGCAGGGACTCA-3′ | NM_007837 |
| Grp78 | Forward, 5′-GGCCTGCTCCGAGTCTGCTTC-3′ Reverse, 5′-CCGTGCCCACATCCTCCTTCT-3′ | NM_022310 |
| Erdj4 | Forward, 5′-CCCCAGTGTCAAACTGTACCAG-3′ Reverse, 5′-AGCGTTTCCAATTTTCCATAAATT-3′ | NM_013760 |
| Agrp | Forward, 5′-TAGATCCACAGAACCGCGAGT-3′ Reverse, 5′-GAAGCGGCAGTAGCACGTA-3′ | NM_007427 |
| Npy | Forward, 5′-CTCCGCTCTGCGACACTAC-3′ Reverse, 5′-AGGGTCTTCAAGCCTTGTTCT-3′ | NM_023456 |
| Pomc | Forward, 5′-CTGGAGACGCCCGTGTTTC-3′ Reverse, 5′-TGGACTCGGCTCTGGACTG-3′ | NM_001278584 |
| Socs3 | Forward, 5′-GAGTACCCCCAAGAGAGCTTACTA-3′ Reverse, 5′-CTCCTTAAAGTGGAGCATCATACTG-3′ | NM_007707 |
| Gapdh | Forward, 5′-CTTCAACAGCAACTCCCACTCTTCC-3′ Reverse, 5′-TGGGTGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCCTT-3′ | NM_001289726 |
| For Traditional PCR | ||
| Xbp-1 | Forward, 5′-CAACCAGGAGTTAAGAACACG-3′ Reverse, 5′-AGGCAACAGTGTCAGAGTCC-3′ | NM_013842 |
| Atf4 | Forward, 5′-GACCTGGAAACCATGCCAGA-3′ Reverse, 5′-TGGCTGCTGTCTTGTTTTGC-3′ | NM_009716 |
| Chop | Forward, 5′-TCCCCAGGAAACGAAGAGGA-3′ Reverse, 5′-TTGAGCCGCTCGTTCTCTTC-3′ | NM_007837 |
| Gapdh | Forward, 5′-GACCACAGTCCATGCCATCA-3′ Reverse, 5′-CATTGAGAGCAATGCCAGCC-3′ | NM_001289726 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Yun, E.-Y.; Park, S.-W.; Goo, T.-W.; Seo, M. Allomyrina Dichotoma Larvae Regulate Food Intake and Body Weight in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Through mTOR and Mapk Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2016, 8, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8020100
Kim J, Yun E-Y, Park S-W, Goo T-W, Seo M. Allomyrina Dichotoma Larvae Regulate Food Intake and Body Weight in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Through mTOR and Mapk Signaling Pathways. Nutrients. 2016; 8(2):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8020100
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jongwan, Eun-Young Yun, Seong-Won Park, Tae-Won Goo, and Minchul Seo. 2016. "Allomyrina Dichotoma Larvae Regulate Food Intake and Body Weight in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Through mTOR and Mapk Signaling Pathways" Nutrients 8, no. 2: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8020100
APA StyleKim, J., Yun, E. -Y., Park, S. -W., Goo, T. -W., & Seo, M. (2016). Allomyrina Dichotoma Larvae Regulate Food Intake and Body Weight in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Through mTOR and Mapk Signaling Pathways. Nutrients, 8(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8020100