Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Protocol 1: Comparison of Different Protein Sources
2.3. Experimental Protocol 2: Dose-Dependent Effects of MP
2.4. Administration of Metabolic Tracer
2.5. Plasma Measurements
2.6. Intramuscular Free Amino Acid Concentrations
2.7. Measurement of Protein Synthesis
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fractional Rates of Protein Synthesis (FSR)
3.2. Plasma Insulin Levels
3.3. Plasma Amino Acids Levels
3.4. Intramuscular Amino Acids Levels
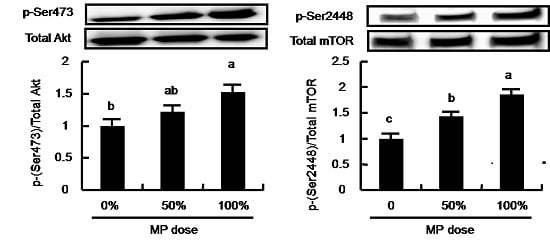
3.5. Dose-Dependent Effect of MP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCAA | branched-chain amino acids |
| CA | caseinate |
| MP | milk protein |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| WP | whey protein |
References
- Welle, S.; Thornton, C.; Statt, M.; McHenry, B. Postprandial myofibrillar and whole body protein synthesis in young and old human subjects. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, E599–E604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Karl, I.E. Response of muscle protein turnover to insulin after acute exercise and training. Biochem. J. 1986, 240, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohm, G.L.; Kasperek, G.J.; Tapscott, E.B.; Beecher, G.R. Effect of exercise on synthesis and degradation of muscle protein. Biochem. J. 1980, 188, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautsch, T.A.; Anthony, J.C.; Kimball, S.R.; Paul, G.L.; Layman, D.K.; Jefferson, L.S. Availability of eIF4E regulates skeletal muscle protein synthesis during recovery from exercise. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, C406–C414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williamson, D.L.; Kubica, N.; Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. Exercise-induced alterations in extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling to regulatory mechanisms of mrna translation in mouse muscle. J. Physiol. 2006, 573, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, J.M.; Fry, C.S.; Drummond, M.J.; Gundermann, D.M.; Walker, D.K.; Glynn, E.L.; Timmerman, K.L.; Dhanani, S.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activation is required for the stimulation of human skeletal muscle protein synthesis by essential amino acids. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S.; Nguyen, H.V.; Suryawan, A.; Bush, J.A.; Davis, T.A. Feeding stimulates protein synthesis in muscle and liver of neonatal pigs through an mtor-dependent process. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279, E1080–E1087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anthony, J.C.; Yoshizawa, F.; Anthony, T.G.; Vary, T.C.; Jefferson, L.S.; Kimball, S.R. Leucine stimulates translation initiation in skeletal muscle of postabsorptive rats via a rapamycin-sensitive pathway. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norton, L.E.; Layman, D.K.; Bunpo, P.; Anthony, T.G.; Brana, D.V.; Garlick, P.J. The leucine content of a complete meal directs peak activation but not duration of skeletal muscle protein synthesis and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in rats. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, M.J.; Glynn, E.L.; Fry, C.S.; Timmerman, K.L.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. An increase in essential amino acid availability upregulates amino acid transporter expression in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E1011–E1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boirie, Y.; Dangin, M.; Gachon, P.; Vasson, M.P.; Maubois, J.L.; Beaufrere, B. Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997, 94, 14930–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.E.; Phillips, S.M. Maximizing muscle protein anabolism: The role of protein quality. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2009, 12, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangin, M.; Boirie, Y.; Garcia-Rodenas, C.; Gachon, P.; Fauquant, J.; Callier, P.; Ballevre, O.; Beaufrere, B. The digestion rate of protein is an independent regulating factor of postprandial protein retention. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E340–E348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tipton, K.D.; Elliott, T.A.; Cree, M.G.; Wolf, S.E.; Sanford, A.P.; Wolfe, R.R. Ingestion of casein and whey proteins result in muscle anabolism after resistance exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, D.W.; Burd, N.A.; Coffey, V.G.; Baker, S.K.; Burke, L.M.; Hawley, J.A.; Moore, D.R.; Stellingwerff, T.; Phillips, S.M. Rapid aminoacidemia enhances myofibrillar protein synthesis and anabolic intramuscular signaling responses after resistance exercise. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, T.G.; McDaniel, B.J.; Knoll, P.; Bunpo, P.; Paul, G.L.; McNurlan, M.A. Feeding meals containing soy or whey protein after exercise stimulates protein synthesis and translation initiation in the skeletal muscle of male rats. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.E.; Moore, D.R.; Kujbida, G.W.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Hector, A.J.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Josse, A.R.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance exercise enhances myofibrillar protein synthesis with graded intakes of whey protein in older men. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Burd, N.A.; Breen, L.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Myofibrillar protein synthesis following ingestion of soy protein isolate at rest and after resistance exercise in elderly men. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitelseder, S.; Agergaard, J.; Doessing, S.; Helmark, I.C.; Lund, P.; Kristensen, N.B.; Frystyk, J.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Schjerling, P.; van Hall, G.; et al. Whey and casein labeled with l-[1-13c]leucine and muscle protein synthesis: Effect of resistance exercise and protein ingestion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E231–E242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.B.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Macdonald, M.J.; Macdonald, J.R.; Armstrong, D.; Phillips, S.M. Consumption of fluid skim milk promotes greater muscle protein accretion after resistance exercise than does consumption of an isonitrogenous and isoenergetic soy-protein beverage. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartman, J.W.; Tang, J.E.; Wilkinson, S.B.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Lawrence, R.L.; Fullerton, A.V.; Phillips, S.M. Consumption of fat-free fluid milk after resistance exercise promotes greater lean mass accretion than does consumption of soy or carbohydrate in young, novice, male weightlifters. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soop, M.; Nehra, V.; Henderson, G.C.; Boirie, Y.; Ford, G.C.; Nair, K.S. Coingestion of whey protein and casein in a mixed meal: Demonstration of a more sustained anabolic effect of casein. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E152–E162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butteiger, D.N.; Cope, M.; Liu, P.; Mukherjea, R.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Krul, E.S. A soy, whey and caseinate blend extends postprandial skeletal muscle protein synthesis in rats. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidy, P.T.; Walker, D.K.; Dickinson, J.M.; Gundermann, D.M.; Drummond, M.J.; Timmerman, K.L.; Fry, C.S.; Borack, M.S.; Cope, M.B.; Mukherjea, R.; et al. Protein blend ingestion following resistance exercise promotes human muscle protein synthesis. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, A.; Nakayama, K.; Fukasawa, T.; Koga, J.; Kanegae, M.; Kawanaka, K.; Higuchi, M. Post-exercise whey protein hydrolysate supplementation induces a greater increase in muscle protein synthesis than its constituent amino acid content. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradstreet, R.B. Kjeldahl method for organic nitrogen. Anal. Chem. 1954, 26, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morifuji, M.; Ishizaka, M.; Baba, S.; Fukuda, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Koga, J.; Kanegae, M.; Higuchi, M. Comparison of different sources and degrees of hydrolysis of dietary protein: Effect on plasma amino acids, dipeptides, and insulin responses in human subjects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8788–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bark, T.H.; McNurlan, M.A.; Lang, C.H.; Garlick, P.J. Increased protein synthesis after acute igf-i or insulin infusion is localized to muscle in mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, E118–E123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morifuji, M.; Kanda, A.; Koga, J.; Kawanaka, K.; Higuchi, M. Preexercise ingestion of carbohydrate plus whey protein hydrolysates attenuates skeletal muscle glycogen depletion during exercise in rats. Nutrition 2011, 27, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, S.R.; Farrell, P.A.; Jefferson, L.S. Invited review: Role of insulin in translational control of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle by amino acids or exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Stenberg, M.; Frid, A.H.; Holst, J.J.; Bjorck, I.M. Glycemia and insulinemia in healthy subjects after lactose-equivalent meals of milk and other food proteins: The role of plasma amino acids and incretins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Holst, J.J.; Bjorck, I.M. Metabolic effects of amino acid mixtures and whey protein in healthy subjects: Studies using glucose-equivalent drinks. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Escobar, J.; Frank, J.W.; Suryawan, A.; Nguyen, H.V.; Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S.; Davis, T.A. Physiological rise in plasma leucine stimulates muscle protein synthesis in neonatal pigs by enhancing translation initiation factor activation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E914–E921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomstrand, E.; Eliasson, J.; Karlsson, H.K.; Kohnke, R. Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 269S–273S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koopman, R.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Manders, R.J.; Zorenc, A.H.; Senden, J.M.; Gorselink, M.; Keizer, H.A.; van Loon, L.J. Combined ingestion of protein and free leucine with carbohydrate increases postexercise muscle protein synthesis in vivo in male subjects. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E645–E653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, J.C.; Anthony, T.G.; Layman, D.K. Leucine supplementation enhances skeletal muscle recovery in rats following exercise. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glynn, E.L.; Fry, C.S.; Drummond, M.J.; Timmerman, K.L.; Dhanani, S.; Volpi, E.; Rasmussen, B.B. Excess leucine intake enhances muscle anabolic signaling but not net protein anabolism in young men and women. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debras, E.; Prod'homme, M.; Rieu, I.; Balage, M.; Dardevet, D.; Grizard, J. Postprandial leucine deficiency failed to alter muscle protein synthesis in growing and adult rats. Nutrition 2007, 23, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.W.; Escobar, J.; Suryawan, A.; Nguyen, H.V.; Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S.; Davis, T.A. Dietary protein and lactose increase translation initiation factor activation and tissue protein synthesis in neonatal pigs. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E225–E233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, M.T.; Poppi, D.P.; Cant, J.P. Protein elongation rates in tissues of growing and adult sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, M.J.; Dreyer, H.C.; Fry, C.S.; Glynn, E.L.; Rasmussen, B.B. Nutritional and contractile regulation of human skeletal muscle protein synthesis and mtorc1 signaling. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| MP | CA | WP | SP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/100 g | ||||
| Ala | 3.14 | 2.81 | 4.69 | 4.15 |
| Arg | 3.30 | 3.50 | 2.73 | 7.58 |
| Asx | 7.33 | 6.71 | 11.22 | 11.66 |
| Cys | 0.70 | 0.32 | 2.99 | 1.25 |
| Glx | 20.62 | 21.25 | 16.27 | 19.50 |
| Gly | 1.77 | 1.71 | 1.97 | 4.12 |
| His | 2.81 | 2.89 | 2.31 | 2.63 |
| Ile | 4.92 | 4.86 | 5.31 | 4.55 |
| Leu | 9.34 | 8.81 | 11.89 | 7.84 |
| Lys | 7.75 | 7.57 | 9.39 | 6.20 |
| Met | 2.58 | 2.72 | 2.15 | 1.27 |
| Phe | 4.66 | 4.82 | 3.61 | 5.23 |
| Pro | 9.48 | 10.13 | 4.60 | 5.27 |
| Ser | 5.19 | 5.26 | 4.52 | 5.09 |
| Thr | 4.20 | 4.09 | 5.19 | 3.84 |
| Trp | 1.29 | 1.14 | 2.27 | 1.36 |
| Tyr | 4.84 | 5.22 | 3.61 | 3.74 |
| Val | 6.08 | 6.19 | 5.27 | 4.72 |
| Carbohydrate | Protein | Fat | Energy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/100 g) | (kcal/100 g) | |||
| MP | 9.2 | 76.7 | 1.4 | 356.2 |
| CA | 0.1 | 91.4 | 0.7 | 372.3 |
| WP | 6.6 | 79.3 | 5.9 | 396.7 |
| SP | 4.0 | 85.8 | 0.2 | 361.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanda, A.; Nakayama, K.; Sanbongi, C.; Nagata, M.; Ikegami, S.; Itoh, H. Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise. Nutrients 2016, 8, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8060339
Kanda A, Nakayama K, Sanbongi C, Nagata M, Ikegami S, Itoh H. Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise. Nutrients. 2016; 8(6):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8060339
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanda, Atsushi, Kyosuke Nakayama, Chiaki Sanbongi, Masashi Nagata, Shuji Ikegami, and Hiroyuki Itoh. 2016. "Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise" Nutrients 8, no. 6: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8060339
APA StyleKanda, A., Nakayama, K., Sanbongi, C., Nagata, M., Ikegami, S., & Itoh, H. (2016). Effects of Whey, Caseinate, or Milk Protein Ingestion on Muscle Protein Synthesis after Exercise. Nutrients, 8(6), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8060339