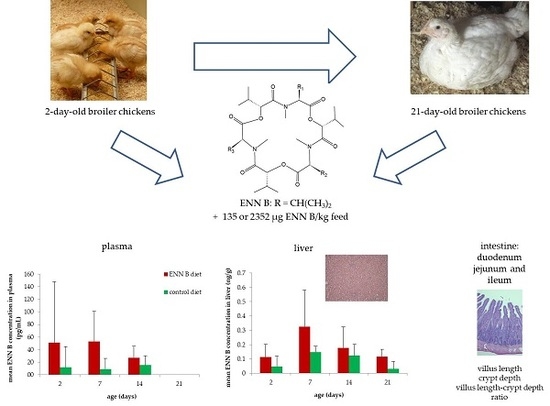
Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation for Liver Tissue Analysis
2.2. Feeding Trial
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Products and Reagents
4.2. Stock and Working Solutions
4.3. Experimental Diets
4.4. Feeding Trial
4.5. Quantification of ENN B in Plasma and Liver
4.6. Method Validation for Liver Tissue
4.6.1. Calibration Curves
4.6.2. Accuracy and Precision
4.6.3. Limit of Quantitation and Limit of Detection
4.6.4. Carry-Over
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraeyman, S.; Croubels, S.; Devreese, M.; Antonissen, G. Emerging Fusarium and Alternaria mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicity and toxicokinetics. Toxins 2017, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svingen, T.; Lund Hansen, N.; Taxvig, C.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Jensen, U.; Have Rasmussen, P. Enniatin B and beauvericin are common in Danish cereals and show high hepatotoxicity on a high-content imaging platform. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panel, E.C. Scientific opinion on the risks to human and animal health related to the presence of beauvericin and enniatins in food and feed. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3802. [Google Scholar]
- Ficheux, A.S.; Sibiril, Y.; Parent-Massin, D. Effects of beauvericin, enniatin B and moniliformin on human dendritic cells and macrophages: An in vitro study. Toxicon 2013, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayou, S.; Ndossi, D.; Frizzell, C.; Groseth, P.K.; Connolly, L.; Sørlie, M.; Verhaegen, S.; Ropstad, E. An investigation of the endocrine disrupting potential of enniatin B using in vitro bioassays. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meca, G.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Comparative cytotoxicity study of enniatins A, A(1), A(2), B, B(1), B(4) and J(3) on Caco-2 cells, Hep-g(2) and HT-29. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2464–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosperini, A.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Reactive oxygen species involvement in apoptosis and mitochondrial damage in Caco-2 cells induced by enniatins A, A(1), B and B(1). Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 222, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jestoi, M. Emerging Fusarium-mycotoxins fusaproliferin, beauvericin, enniatins, and moniliformin-a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2008, 48, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callebaut, F.; Tangni, E.K.; Debongnie, P.; Stals, E.; Huybrechts, B.; Waegeneers, N.; Delezie, E.; Van Pamel, E.; Daeseleire, E. Carry-over of mycotoxins to animal products: Case study poultry. In Scientific Report 211/212 CODA-CERVA (Centrum Voor Onderzoek in Diergeneeskunde en Agrochemie-Centre d’Étude et de Recherches Vétérinaires et Agrochemiques); Kerkhofs: Brussels, Belgium, 2011–2012; pp. 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fraeyman, S.; Devreese, M.; Antonissen, G.; De Baere, S.; Rychlik, M.; Croubels, S. Comparative oral bioavailability, toxicokinetics, and biotransformation of enniatin B1 and enniatin B in broiler chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7259–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonissen, G.; Van Immerseel, F.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Janssens, G.P.; De Baere, S.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Su, S.; Wong, E.A.; De Meulenaer, B.; et al. Mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and fumonisins alter the extrinsic component of intestinal barrier in broiler chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10846–10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springler, A.; Vrubel, G.J.; Mayer, E.; Schatzmayr, G.; Novak, B. Effect of Fusarium-derived metabolites on the barrier integrity of differentiated intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC-J2). Toxins 2016, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviagen (Ed.) Ross 308 Broiler Performance Objectives; Aviagen: Scotland, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Devreese, M.; Broekaert, N.; De Mil, T.; Fraeyman, S.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Pilot toxicokinetic study and absolute oral bioavailability of the Fusarium mycotoxin enniatin B1 in pigs. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 63, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jestoi, M.; Rokka, M.; Peltonen, K. An integrated sample preparation to determine coccidiostats and emerging Fusarium-mycotoxins in various poultry tissues with LC-MS/MS. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jestoi, M.; Rokka, M.; Järvenpää, E.; Peltonen, K. Determination of Fusarium mycotoxins beauvericin and enniatins (A, A1, B, B1) in eggs of laying hens using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Rychlik, M. Biosynthesis of 15N3-labeled enniatins and beauvericin and their application to stable isotope dilution assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7129–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monbaliu, S.; Van Poucke, C.; Detavernier, C.; Dumoulin, F.; Van De Velde, M.; Schoeters, E.; Van Dyck, S.; Averkieva, O.; Van Peteghem, C.; De Saeger, S. Occurrence of mycotoxins in feed as analyzed by a multi-mycotoxin LC-MS/MS method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Recommendation of 17 August 2006 on the presence of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, ochratoxin a, T-2 and HT-2 and fumonisins in products intended for animal feeding (2006/576/EC). Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L 229/7.
- Commission Directive 2002/32/EC of the European parliament and the council of 7 May 2002 on undesirable substances in animal feed. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, L 140.
- De Baere, S.G.J.; Osselaere, A.; Devreese, M.; Vandenbroucke, V.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Quantitative determination of T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, deoxynivalenol and deepoxy-deoxynivalenol in animal body fluids using LC-MS/MS detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing council directive 96/23/EC concerning the performances of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, 8–36.
- VICH GL 49. Guidance for industry. In Studies to Evaluate the Metabolism and Residue Kinetics of Veterinary Drugs in Food Producing Animals: Validation of Analytical Methods Used in Residue Depletion Studies; VICH: Brussel, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, H.M.; Causey, A.G.; Lessard, D.; Selinger, K.; Herman, J. Choice and optimization of calibration functions. Meth. Surv. A 1992, 22, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Knecht, J.; Stork, G. Percentage and logarithmic procedures for calculation of calibration curves. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1974, 270, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Duodenum | ||||||
| Age (Days) | Villus Length (µm) | Crypt Depth (µm) 3 | Villus Length/Crypt Depth | |||
| ENN B | Control | ENN B | Control | ENN B | Control | |
| 2 | 761 ± 207.9 | 976 ± 169.5 | 83 ± 15.0 | 109 ± 34.7 | 9 ± 2.3 | 12 ± 0.9 |
| 7 | 1283 ± 169.6 | 1303 ± 87.6 | 105 ± 32.6 | 137 ± 21.8 | 13 ± 4.6 | 10 ± 0.8 |
| 14 | - 1 | 1526 ± 193.4 | - 1 | 158 ± 6.7 | - 1 | 10 ± 1.6 |
| 21 | 2109 ± 491.8 | 1780 2 | 133 ± 7.5 | 158 2 | 14 ± 1.2 | 11 2 |
| Jejunum | ||||||
| Age (Days) | Villus Length (µm) | Crypt Depth (µm) | Villus Length/Crypt Depth | |||
| ENN B | Control | ENN B | Control | ENN B | Control | |
| 2 | 376 ± 34.6 | 389 ± 65.2 | 83 ± 11.2 | 87 ± 10.7 | 5 ± 0.6 | 5 ± 0.6 |
| 7 | 518 ± 225.8 | 561 ± 114.7 | 92 ± 13.3 | 122 ± 21.7 | 6 ± 0.6 | 4 ± 1.9 |
| 14 | 951 2 | 932 ± 217.0 | 132 2 | 142 ± 62.6 | 7 2 | 7 ± 0.8 |
| 21 | 868 ± 232.6 | 887 ± 171.8 | 128 ± 17.6 | 134 ± 32.7 | 7 ± 2.4 | 7 ± 1.6 |
| Ileum | ||||||
| Age (Days) | Villus Length (µm) | Crypt Depth (µm) | Villus Length/Crypt Depth | |||
| ENN B | Control | ENN B | Control | ENN B | Control | |
| 2 | 322 ± 40.2 | 301 ± 56.9 | 80 ± 7.5 | 71 ± 15.6 | 4 ± 0.4 | 4 ± 0.8 |
| 7 | 509 ± 177.2 | 488 ± 81.1 | 105 ± 35.8 | 116 ± 15.2 | 5 ± 2.5 | 4 ± 0.3 |
| 14 | 613 ± 213.9 | 466 ± 123.2 | 123 ± 28.4 | 116 ± 43.6 | 4 ± 0.6 | 4 ± 0.9 |
| 21 | 598 ± 180.9 | 685 ± 133.1 | 165 ± 24.3 | 150 ± 32.2 | 4 ± 1.1 | 5 ± 1.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fraeyman, S.; Croubels, S.; Devreese, M.; Ducatelle, R.; Rychlik, M.; Antonissen, G. Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue. Toxins 2018, 10, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010045
Fraeyman S, Croubels S, Devreese M, Ducatelle R, Rychlik M, Antonissen G. Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue. Toxins. 2018; 10(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraeyman, Sophie, Siska Croubels, Mathias Devreese, Richard Ducatelle, Michael Rychlik, and Gunther Antonissen. 2018. "Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue" Toxins 10, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010045
APA StyleFraeyman, S., Croubels, S., Devreese, M., Ducatelle, R., Rychlik, M., & Antonissen, G. (2018). Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue. Toxins, 10(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010045