Toxin Profiles of Okadaic Acid Analogues and Other Lipophilic Toxins in Dinophysis from Japanese Coastal Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dinophysis acuminata
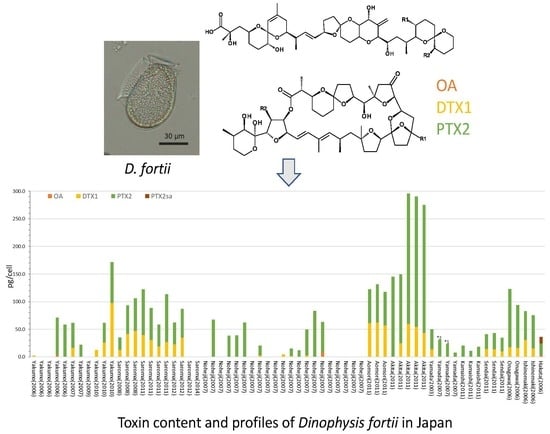
2.2. Dinophysis fortii
2.3. Other Dinophysis Species
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Sampling Locations and Dinophysis Sample Preparation
4.3. Extraction
4.4. LC/MS/MS and LC/MS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M. Marine Toxins. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Sugawara, W.; Fukuyo, Y.; Oguri, H.; Igarashi, T.; Fujita, N. Identification of Dinophysis fortii as the causative organism of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. 1980, 46, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO and WHO. Standard for Live and Raw Bivalve Molluscs. Codex Stan 292-2008. 2008, pp. 1–9. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/codex-texts/list-standards/en/ (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins. EFSA J. 2009, 1306, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Draisci, R.; Lucentini, L.; Giannetti, L.; Boria, P.; Poletti, R. First report of pectenotoxin-2 (PTX-2) in algae (Dinophysis fortii) related to seafood poisoning in Europe. Toxicon 1996, 34, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Mitsuya, T.; Imai, M.; Yamasaki, M. DSP toxin contents in Dinophysis fortii and scallops collected at Mutsu Bay, Japan. J. Appl. Phycol. 1997, 8, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.J.; Bishop, A.G.; Healy, B.M.; Roden, C.; Sherlock, I.R.; Twohig, M.; Draisci, R.; Giannetti, L.; Lucentini, L. Efficient isolation of the rare diarrhoeic shellfish toxin, dinophysistoxin-2, from marine phytoplankton. Toxicon 1999, 37, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Walter, J.A.; LeBlanc, P.; MacKinnon, S.; Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Beuzenberg, V.; MacKenzie, A.L.; Jensen, D.J.; et al. Identification of pectenotoxin-11 as 34 S-hydroxypectenotoxin-2, a new pectenotoxin analogue in the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta from New Zealand. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Suzuki, T.; Reguera, B. First detection of Pectenotoxin-11 and confirmation of OA-D8 diol-ester in Dinophysis acuta from European waters by LC–MS/MS. Toxicon 2008, 52, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiyama, T.; Suzuki, T. Production of dinophysistoxin-1 and pectenotoxin-2 by a culture of Dinophysis acuminata (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.L.; Vershinin, A.; Smith, L.L.; Leighfield, T.A.; Pankov, S.; Quilliam, M.A. Seasonality of Dinophysis spp. and Prorocentrum lima in Black Sea phytoplankton and associated shellfish toxicity. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Guzman, L.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin profiles of five geographical isolates of Dinophysis spp. from North and South America. Toxicon 2011, 57, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Kamiyama, T. Differences in the production and excretion kinetics of okadaicacid, dinophysistoxin-1, and pectenotoxin-2 between cultures of Dinophysis acuminata and Dinophysis fortii isolated from western japan. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, S.; Suzuki, T.; Kamiyama, T. Successful cultivation of the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis tripos (Dinophyceae). Plankton Benthos Res. 2013, 8, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.P.; Karlsson, C.; Pallon, J.; Yasumoto, T.; Granéli, E. Cellular nutrient content measured with the nuclear microprobe and toxins produced by Dinophysis norvegica (Dinophyceae) from the Trondheim fjord (Norway). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L.L., Jr.; Lopes, D.; Bonilauri, V.C.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T. Persistent contamination of octopuses and mussels with lipophilic shellfish toxins during spring Dinophysis blooms in a subtropical estuary. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3920–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basti, L.; Uchida, H.; Matsushima, R.; Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, T.; Yamatogi, T.; Nagai, S. Influence of Temperature on Growth and Production of Pectenotoxin-2 by a Monoclonal Culture of Dinophysis caudata. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7124–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Hansen, P.J.; Krock, B.; Vismann, B. Accumulation, transformation and breakdown of DSP toxins from the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta in blue mussels, Mytilus edulis. Toxicon 2016, 117, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Igarashi, T.; Santiago, F.; Einal, D.; Peter, H.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, N.; Graneli, E.; Yasumoto, T.; Carlsson, P.; Legrand, C. Toxin production by Dinophysis acuminata and D. acuta cells grown under nutrient sufficient and deficient conditions. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Bloom; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Comission of UNESCO: Sendai, Japan, 1996; pp. 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.L.; Reguera, B.; Ramilo, I.; Martínez, A. Toxin content of Dinophysis acuminata, D. acuta, D. caudata from the Galician Rias Bajas. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Bloom; Hallegraeff, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J., Lewis, R.J., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Comission of UNESCO: Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 2001; pp. 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, J.; Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E. Identification of pectenotoxins in plankton, filter feeders, and isolated cells of a Dinophysis acuminata with an atypical toxin profile, from Chile. Toxicon 2007, 49, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyazono, A.; Baba, K.; Sugawara, R.; Kamiyama, T. LC–MS/MS analysis of okadaic acid analogues and other lipophilic toxins in single-cell isolates of several Dinophysis species collected in Hokkaido, Japan. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Samdal, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Petersen, D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Naustvoll, L.J.; Rundberget, T.; Torgersen, T.; Hovgaard, P.; et al. A novel pectenotoxin, PTX-12, in Dinophysis spp. and shellfish from Norway. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, G.; Moroño, A.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Pazos, Y.; Reguera, B. Evaluation of Passive Samplers as a Monitoring Tool for Early Warning of Dinophysis Toxins in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3823–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Koike, K.; Kodama, M. Seasonal variation of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-1 in Dinophysis spp. in association with the toxicity of scallop. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Bloom; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Comission of UNESCO: Sendai, Japan, 1996; pp. 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- James, K.J.; Bishop, A.G.; Gillman, M.; Kelly, S.S.; Roden, C.; Draisci, R.; Lucentini, L.; Giannetti, L. The Diarrhoeic Shellfish Poisoning toxins of Dinophysis acuta: Identification and isolation of dinophysistoxin-2 (DTX-2). In Harmful and Toxic Algal Bloom; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, L.M., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Comission of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Puente, P.F.; Sáez, M.J.F.; Hamilton, B.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Studies of polyether toxins in the marine phytoplankton, Dinophysis acuta, in Ireland using multiple tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2004, 44, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, L.M.; Reguera, B.; González, G.S.; Mguez, A. Pectenotoxin-2 in single-cell isolates of Dinophysis caudata and Dinophysis acuta from the Galician Rías (NW Spain). Toxicon 2006, 48, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; González, G.S.; Franco, J.M.; Reguera, B. Seasonal variability of lipophilic toxins during a Dinophysis acuta bloom in Western Iberia: Differences between picked cells and plankton concentrates. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasigan, A.N.; Sato, S.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Accumulation of a high level of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in the green mussel Perna viridis during a bloom of Dinophysis caudata and Dinophysis miles in Sapian Bay, Panay Island, the Philippines. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Z.; Wu, H.; Jiang, T.; Lu, S. Occurrence of marine algal toxins in oyster and phytoplankton samples in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raho, N.; Pizarro, G.; Escalera, L.; Reguera, B.; Marin, I. Morphology, toxin composition and molecular analysis of Dinophysis ovum Schütt, a dinoflagellate of the “Dinophysis acuminata complex”. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, G.S.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Velo-Suarez, L.; Reguera, B. Considerations on thetoxigenic nature and prey sources of Phalacroma rotundatum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 64, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselin, P.; Lassus, P.; Bardouil, M. High performance liquid chromatography analysis of diarrhetic toxins in Dinophysis spp. from French coast. J. Appl. Phycol. 1992, 4, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis Toxins: Causative Organisms, Distribution and Fate in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reguera, B.; Pizarro, G. Planktonic Dinoflagellates That Contain Polyether Toxins of the Old “DSP Complex”. In Seefood and Freshwater Toxins, Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection, 2nd ed.; Luis, M.B., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 258–276. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Quilliam, M.A. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) Toxins, Okadaic Acid and Dinophysistoxin Analogues, and Other Lipophilic Toxins. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, A.L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Suzuki, T.; Selwood, A. Pectenotoxin and okadaic acid-based toxin profiles in Dinophysis acuta and Dinophysis acuminata from New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, A.L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Selwood, A. Solid phase adsorption toxin tracking (SPATT): A new monitoring tool that simulates the biotoxin contamination of filter feeding bivalves. Toxicon 2004, 44, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. Guidelines for Risk Management of Shellfish Toxins in Bivalves. 2015. Available online: http://www.maff.go.jp/j/syouan/tikusui/gyokai/g_kenko/busitu/pdf/150306_kaidoku_guide.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a New Type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Ishige, M.; Kawase, S.; Tazawa, T.; Nakagawa, T. First cases of Paralytic and Diarrhoetic shellfish poisoning in Hokkaido. Rep. Hokkaido Inst. Public Health 1983, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, M.; Uneyama, C.; Toyofuku, H.; Morikawa, K. Trends of Food Poisonings Caused by Natural Toxins in Japan, 1989–2011. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 53, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Jin, T.; Shirota, Y.; Mitsuya, T.; Okumura, Y.; Kamiyama, T. Quantification of lipophilic toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in Japanese bivalves by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and comparison with mouse bioassay. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kamiyama, T.; Okumura, Y.; Ishihara, K.; Matsushima, R.; Kaneniwa, M. Liquid-chromatographic hybrid triple–quadrupole linear-ion-trap MS/MS analysis of fatty-acid esters of dinophysistoxin-1 in bivalves and toxic dinoflagellates in Japan. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare. Food Sanitation Research; Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare: Toyko, Japan, 1981; Volume 7, p. 60.
- Suzuki, T.; Mitsuya, T.; Matsubara, H.; Yamasaki, M. Determination of pectenotoxin-2 after solid-phase extraction from seawater and from the dinoflagellate Dinophysis fortii by liquid chromatography with electrospray mass spectrometry and ultraviolet detection Evidence of oxidation of pectenotoxin-2 to pectenotoxin-6 in scallops. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 815, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Igarashi, T.; Sekiguchi, R.; Tanno, K.; Satake, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. A Japanese project for production and distribution of shellfish toxins as calibrants for HPLC analysis. In Proc. VIII International Conference on Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Vigo, Spain, 1998; pp. 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Hess, P.; Dell’Aversano, C. Recent developments in the analysis of phycotoxins by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. In Perspective at the Turn of the Millenium, Proceedings of the 10th International IUPAC Symposium on Mycotoxins and Phycotoxins, Guaruja, Brazil, 21–25 May 2000; De Koe, W.J., Samson, R.A., van Egmond, H.P., Gilbert, J., Sabino, M., Eds.; IRIS: Guaruja, Brazil, 2001; pp. 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam, M.A. The role of chromatography in the hunt for red tide toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Species | pg/cell | Location | Analysis Method | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | DTX1 | DTX2 | PTX2 | ||||
| Dinophysis acuminata | 1.6 | - | - | - | Le Havre, France | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| Trace | - | - | - | Tokyo Bay, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [19] | |
| 9.1 | - | - | - | Gullmar, Sweden | HPLC-FLD | [20] | |
| 9.9–21.7 | - | - | - | Galicia, Spain | HPLC-FLD | [21] | |
| - | - | - | 180.0 | Bahia Inglesa, Chile | LC/MS/MS | [22] | |
| - | 0.3–0.7 | - | 10.7–22.4 | Abashiri, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
| - | ND–0.7 | - | 25.9–50.2 | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
| ND–0.8 | - | - | 0.9–8.7 | Flødevigen Bay, Noway | LC/MS/MS | [24] | |
| 3.7 | - | - | - | Bueu, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [25] | |
| Dinophysis fortii | - | 13.0–191.5 | - | 42.5 | Mutsu Bay, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| 23.0 | - | - | - | Inland Sea, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [19] | |
| ND–57.7 | ND–16.0 | - | - | Ofunato, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [26] | |
| - | 8.4–10.9 | - | 51.4–63.8 | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
| Dinophysis acuta | 9.4 | - | - | - | Vigo, Spain | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| 4.0 | 4.2 | - | - | Sogndal, Norway | HPLC-FLD | [19] | |
| - | 6.6 | - | - | Gullmar, Sweden | HPLC-FLD | [20] | |
| 58.0 | - | 78.0 | - | Ireland | HPLC-FLD | [27] | |
| 6.3–33.1 | - | 1.0–22.0 | - | Galicia, Spain | HPLC-FLD | [21] | |
| 85.0 | - | 77.0 | 14.0 | Glandore, Ireland | LC/MS/MS | [28] | |
| - | - | - | 29.1–32.3 | Galicia, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [29] | |
| 0.7–9.4 | - | 0.9–6.6 | 0.3–3.3 | Pontevedra, Spain | LC/MS | [30] | |
| 1.0–8.5 | - | - | 0.2–3.3 | Flødevigen Bay, Noway | LC/MS/MS | [24] | |
| 2.9 | - | 1.9 | 1.5 | Bueu, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [25] | |
| Dinophysis caudata | 0.7 | - | - | - | Galicia, Spain | HPLC-FLD | [21] |
| 7.9–56.5 | ND–53.9 | - | - | Sapian, Phillipines | HPLC-FLD | [31] | |
| - | - | - | 100.0–127.4 | Galicia, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [29] | |
| 0.6 | - | 2.8 | 5.0 | Moana, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [25] | |
| - | - | - | 2.0–14.5 | Day Bay, China | LC/MS/MS | [32] | |
| Dinophysis infundibulus | - | - | - | 14.8 | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] |
| Dinophysis miles | 5.7–20.9 | ND–10.7 | - | - | Sapian, Phillipines | HPLC-FLD | [31] |
| Dinophysis mitra | - | 10.0 | - | - | Mutsu Bay, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| - | - | - | - | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
| Dinophysis norvegica | - | 14.0 | - | - | Sogndal, Norway | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| - | - | - | 50.8–67.4 | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
| ND–0.2 | - | - | 0.3–1.7 | Flødevigen Bay, Noway | LC/MS/MS | [24] | |
| Dinophysis ovum | 7.1 | - | - | - | Vigo, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [33] |
| Dinophysis rotundata | ND–0.4 | - | ND–0.5 | ND–0.3 | Bueu, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [34] |
| - | 101.0 | - | - | Mutsu Bay, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [19] | |
| - | - | - | - | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
| - | - | - | 0.8 | Flødevigen Bay, Noway | LC/MS/MS | [24] | |
| Dinophysis sacculus | 16.5 | - | - | - | Le Croisic, France | HPLC-FLD | [35] |
| 14.0 | - | - | - | Morgat, France | HPLC-FLD | [35] | |
| 29.6 | - | - | - | Kervel, France | HPLC-FLD | [35] | |
| 12.9 | - | - | - | Pont-Aven, France | HPLC-FLD | [35] | |
| Dinophysis skagii | - | - | - | - | Bueu, Spain | LC/MS/MS | [25] |
| Dinophysis tripos | - | 36.0 | - | - | Kesennuma, Japan | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| - | - | - | - | Yakumo, Japan | LC/MS/MS | [23] | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchida, H.; Watanabe, R.; Matsushima, R.; Oikawa, H.; Nagai, S.; Kamiyama, T.; Baba, K.; Miyazono, A.; Kosaka, Y.; Kaga, S.; et al. Toxin Profiles of Okadaic Acid Analogues and Other Lipophilic Toxins in Dinophysis from Japanese Coastal Waters. Toxins 2018, 10, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110457
Uchida H, Watanabe R, Matsushima R, Oikawa H, Nagai S, Kamiyama T, Baba K, Miyazono A, Kosaka Y, Kaga S, et al. Toxin Profiles of Okadaic Acid Analogues and Other Lipophilic Toxins in Dinophysis from Japanese Coastal Waters. Toxins. 2018; 10(11):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110457
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchida, Hajime, Ryuichi Watanabe, Ryoji Matsushima, Hiroshi Oikawa, Satoshi Nagai, Takashi Kamiyama, Katsuhisa Baba, Akira Miyazono, Yuki Kosaka, Shinnosuke Kaga, and et al. 2018. "Toxin Profiles of Okadaic Acid Analogues and Other Lipophilic Toxins in Dinophysis from Japanese Coastal Waters" Toxins 10, no. 11: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110457
APA StyleUchida, H., Watanabe, R., Matsushima, R., Oikawa, H., Nagai, S., Kamiyama, T., Baba, K., Miyazono, A., Kosaka, Y., Kaga, S., Matsuyama, Y., & Suzuki, T. (2018). Toxin Profiles of Okadaic Acid Analogues and Other Lipophilic Toxins in Dinophysis from Japanese Coastal Waters. Toxins, 10(11), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110457