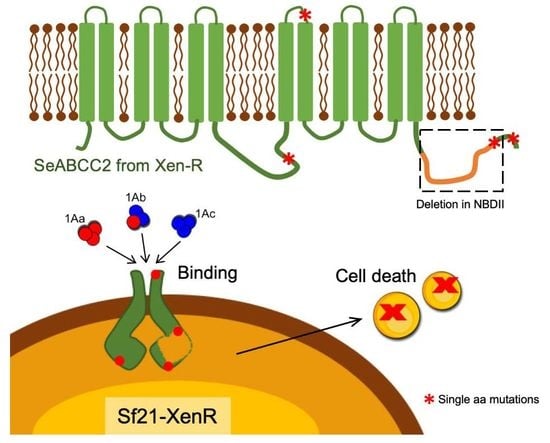
The Spodoptera exigua ABCC2 Acts as a Cry1A Receptor Independently of its Nucleotide Binding Domain II
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization and 3D Prediction of the Structure of the Truncated SeABCC2 Gene
2.2. The Truncated SeABCC2-XenR is Located in the Membrane of the Sf21 Cells
2.3. The Truncated SeABCC2 Still Acts as a Functional Receptor for Cry1A Toxins
2.4. The Truncated SeABCC2 Still Mediates Binding to Cry1A Toxins
2.5. The Irreversible Cry1Ac Binding Component is not Altered in the Truncated SeABCC2
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture Maintenance
4.2. SeABCC2-XenR Structural Characterization
4.3. Generation of Sf21 Clones Expressing SeABCC2-XenR
4.4. RT-qPCR
4.5. Detection of the SeABCC-XenR Protein
4.6. Cry Proteins Preparation
4.7. Viability Assays
4.8. Binding of 125I-Cry1Ac to Sf21 Cells
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crickmore, N. Beyond the spore—past and future developments of Bacillus thuringiensis as a biopesticide. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Li, M.S.; Jin, B.R.; Je, Y.H. Bacillus thuringiensis as a specific, safe, and effective tool for insect pest control. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 547–559. [Google Scholar]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.C.; Yu, Z.; Sung, M. Structural insights into Bacillus thuringiensis Cry, Cyt and Parasporin Toxins. Toxins 2014, 6, 2732–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adang, M.J.; Crickmore, N.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxins and mechanism of action. Adv. in Insect Phys. 2014, 47, 39–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, V.; Laprade, R.; Schwartz, J.L. Current models of the mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins: A critical review. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, J.; Van Rie, J. Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 501–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamudi, R.K.; Weber, E.; Ji, I.; Ji, T.H.; Bulla, L.A.J. Cloning and expression of a receptor for an insecticidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5490–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, P.J.K.; Crickmore, N.; Ellar, D.J. The receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis CrylA(c) delta-endotoxin in the brush border membrane of the lepidopteran Manduca sexta is aminopeptidase N. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 11, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Adang, M.J. Characterization of a Cry1Ac-receptor alkaline phosphatase in susceptible and resistant Heliothis virescens larvae. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahan, L.J.; Pauchet, Y.; Vogel, H.; Heckel, D.G. An ABC transporter mutation is correlated with insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, S.; Gechev, T.; Bakker, P.L.; Moar, W.J.; de Maagd, R.A. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ca-resistant Spodoptera exigua lacks expression of one of four Aminopeptidase N genes. BMC Genomics 2005, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiewsiri, K.; Wang, P. Differential alteration of two aminopeptidases N associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac in cabbage looper. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14037–14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Karumbaiah, L.; Jakka, S.R.; Ning, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, K.; Jackson, J.; Gould, F.; Blanco, C.; Portilla, M.; et al. Reduced levels of membrane- bound alkaline phosphatase are common to lepidopteran strains resistant to Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Chang, X.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Wang, Z.; Edwards, M.G.; He, K. Downregulation and Mutation of a Cadherin Gene Associated with Cry1Ac Resistance in the Asian Corn Borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). Toxins 2014, 6, 2676–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Kang, S.; Chen, D.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xie, W.; Zhu, W.; Baxter, S.W.; Zhou, X.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Zhang, Y. MAPK Signaling Pathway Alters Expression of Midgut ALP and ABCC Genes and Causes Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac Toxin in Diamondback Moth. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, S.W.; Zhao, J.Z.; Gahan, L.J.; Shelton, A.M.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Heckel, D.G. Novel genetic basis of field-evolved resistance to Bt toxins in Plutella xylostella. Ins. Molec. Biol. 2005, 14, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martínez, P.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C.S.; Krishnan, V.; Crickmore, N.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Lack of Cry1Fa binding to the midgut brush border membrane in a resistant colony of Plutella xylostella moths with a mutation in the ABCC2 locus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6759–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Has, J.; Meagher, R.; Nagoshi, R.; Hietala, L.; Huang, F.; Narva, K.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Mechanism and DNA-based detection of field-evolved resistance to transgenic Bt corn in fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermauw, W.; Van Leeuwen, T. The ABC gene family in arthropods: Comparative genomics and role in insecticide transport and resistance. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 45, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; He, F.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Ai, H.; Peng, J.; Hong, H.; Liu, K. Endogenous expression of a Bt toxin receptor in the Cry1Ac-susceptible insect cell line and its synergistic effect with cadherin on cytotoxicity of activated Cry1Ac. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 59, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; González-Martínez, R.M.; Navarro-Cerrillo, G.; Chakroun, M.; Kim, Y.; Ziarsolo, P.; Blanca, J.; Cañizares, J.; Ferré, J.; Herrero, S. ABCC transporters mediate insect resistance to multiple Bt toxins revealed by bulk segregant analysis. BMC Biol. 2004, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Tanaka, S.; Imamura, K.; Adegawa, S.; Kikuta, S.; Sato, R. Cry toxin specificities of insect ABCC transporters closely related to lepidopteran ABCC2 transporters. Peptides 2017, 98, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Adegawa, S.; Li, X.; Tanaka, S.; Endo, H. Function and role of ATP-binding cassette transporters as receptors for 3D-Cry toxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Mahon, R.J.; Heckel, D.G.; Walsh, T.K.; Downes, S.; James, W.J.; Lee, S.; Reineke, A.; Williams, A.K.; Gordon, K.H.J. Insect Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Cry2Ab Is Conferred by Mutations in an ABC Transporter Subfamily A Protein. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauchet, Y.; Bretschneider, A.; Augustin, S.; Heckel, D.G. A P-Glycoprotein Is Linked to Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Aa Toxin in a Leaf Beetle. Toxins 2016, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, L.G.; Ponnuraj, J.; Mallappa, B.; Chowdary, L.R.; Zhang, J.; Tay, W.T.; Walsh, T.K.; Gordon, K.H.J.; Heckel, D.G.; Downes, S.; et al. ABC transporter mis-splicing associated with resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, S.W.; Badenes-pérez, F.R.; Morrison, A.; Vogel, H.; Crickmore, N.; Kain, W.; Wang, P.; Heckel, D.G.; Jiggins, C.D. Parallel Evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Resistance in Lepidoptera. Genetics 2011, 189, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Narukawa, J.; Kawai, S.; Sezutsu, H.; Kobayashi, I.; Uchiho, K.; Tamura, T.; Mita, K.; et al. Single amino acid mutation in an ATP-binding cassette transporter gene causes resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ab in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1591–E1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretschneider, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Pauchet, Y. Three toxins, two receptors, one mechanism: Mode of action of Cry1A toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis in Heliothis virescens. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 76, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Noda, H.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Endo, H.; Sato, R. The ATP-binding cassette transporter subfamily C member 2 in Bombyx mori larvae is a functional receptor for Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Endo, H.; Adegawa, S.; Kikuta, S.; Sato, R. Functional characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxin receptors explains resistance in insects. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 4474–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.; Song, S.; Bruning, J.B.; Choo, A.; Baxter, S.W. Expressing a moth abcc2 gene in transgenic Drosophila causes susceptibility to Bt Cry1Ac without requiring a cadherin-like protein receptor. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 80, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegawa, S.; Nakama, Y.; Endo, H.; Shinkawa, N.; Kikuta, S.; Sato, R. The domain II loops of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Aa form an overlapping interaction site for two Bombyx mori larvae functional receptors, ABC transporter C2 and cadherin-like receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1865, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Solís, M.; Pinos, D.; Endo, H.; Sato, R.; Ferré, J.; Herrero, S.; Hernández-martínez, P. Role of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxins domains in the binding to the ABCC2 receptor from Spodoptera exigua. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 101, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelotl, J.; Sánchez, J.; Gómez, I.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. ABCC2 is associated with Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin oligomerization and membrane insertion in diamondback moth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, D.G. Learning the ABCs of Bt: ABC transporters and insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis provide clues to a crucial step in toxin mode of action. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 104, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Endo, H.; Adegawa, S.; Iizuka, A.; Imamura, K.; Kikuta, S.; Sato, R. Bombyx mori ABC transporter C2 structures responsible for the receptor function of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Aa toxin. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 91, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martínez, P.; Navarro-Cerrillo, G.; Caccia, S.; de Maagd, R.A.; Moar, W.J.; Ferré, J.; Escriche, B.; Herrero, S. Constitutive activation of the midgut response to Bacillus thuringiensis in Bt-resistant Spodoptera exigua. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Heckel, D.G.; Li, X.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Wu, K. Mis-splicing of the ABCC2 gene linked with Bt toxin resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K. A single amino acid polymorphism in ABCC2 loop 1 is responsible for differential toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin in different Spodoptera (Noctuidae) species. Ins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 100, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Banks, D.; Adang, M.J. Toxicity, binding, and permeability analyses of four Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 δ-endotoxins using brush border membrane vesicles of Spodoptera exigua and Spodoptera frugiperda. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Escriche, B.; Ferré, J.; Silva, F.J. Occurrence of a common binding site in Mamestra brassicae, Phthorimaea operculella, and Spodoptera exigua for the insecticidal crystal proteins CryIA from Bacillus thuringiensis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 27, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Crickmore, N. Specificity determinants for Cry insecticidal proteins: insights from their mode of action. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 142, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Patel, S.S.; Dean, D.H. Irreversible binding kinetics of Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA delta-endotoxins to gypsy moth brush border membrane vesicles is directly correlated to toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 24719–24724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, S.; Bel, Y.; Hernández-Martínez, P.; Ferré, J. Susceptibility, mechanisms of response and resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in Spodoptera spp. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 15, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wetering, K.; Burkon, A.; Feddema, W.; Bot, A.; de Jonge, H.; Somoza, V.; Borst, P. Intestinal breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)/Bcrp1 and multidrug resistance protein 3 (MRP3)/Mrp3 are involved in the pharmacokinetics of resveratrol. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estela, A.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins with larval midgut binding sites of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: noctuidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, J.R.; Jansens, S.; Höfte, H.; Degheele, D.; Van, H.M. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Importance of specific receptors on the brush border membrane of the mid-gut of target insects. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 186, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Munson, P.J.; Rodbard, D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 107, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinos, D.; Martínez-Solís, M.; Herrero, S.; Ferré, J.; Hernández-Martínez, P. The Spodoptera exigua ABCC2 Acts as a Cry1A Receptor Independently of its Nucleotide Binding Domain II. Toxins 2019, 11, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030172
Pinos D, Martínez-Solís M, Herrero S, Ferré J, Hernández-Martínez P. The Spodoptera exigua ABCC2 Acts as a Cry1A Receptor Independently of its Nucleotide Binding Domain II. Toxins. 2019; 11(3):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030172
Chicago/Turabian StylePinos, Daniel, María Martínez-Solís, Salvador Herrero, Juan Ferré, and Patricia Hernández-Martínez. 2019. "The Spodoptera exigua ABCC2 Acts as a Cry1A Receptor Independently of its Nucleotide Binding Domain II" Toxins 11, no. 3: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030172
APA StylePinos, D., Martínez-Solís, M., Herrero, S., Ferré, J., & Hernández-Martínez, P. (2019). The Spodoptera exigua ABCC2 Acts as a Cry1A Receptor Independently of its Nucleotide Binding Domain II. Toxins, 11(3), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030172