Does Deoxynivalenol Affect Amoxicillin and Doxycycline Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract? Ex Vivo Study on Swine Jejunum Mucosa Explants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effect of Deoxynivalenol on the Viability, Integrity, and Permeability of Jejunum Mucosa Explants
2.2. The Effect of Amoxicillin and Doxycycline on the Viability, Integrity, and Permeability of Jejunum Mucosa Explants
2.3. The Effect of Combined Exposure to Deoxynivalenol and Amoxicillin or Doxycycline on the Viability, Integrity, and Permeability of Jejunum Mucosa Explants
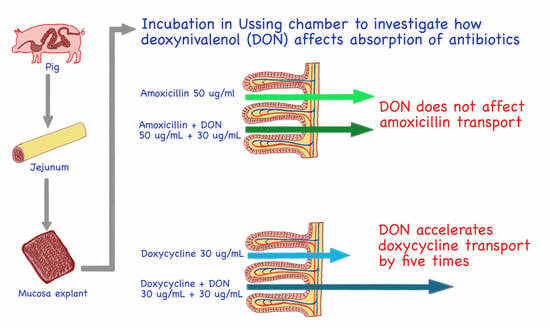
2.4. The Effect of Deoxynivalenol on Amoxicillin and Doxycycline Penetration across Swine Jejunum Explants
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals
5.2. Tissue Preparation
5.3. Measurement of the Viability, Integrity, and Permeability of Mucosa Explants
5.4. Ex Vivo Exposure of Swine Jejunum to Deoxynivalenol and Antibiotics
5.5. Analyses
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global Mycotoxin Occurrence in Feed: A Ten-Year Survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khodaei, D.; Javanmardi, F.; Khaneghah, A.M. The global overview of the occurrence of mycotoxins in cereals: A three-year survey. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, R.; Crisci, A.; Venâncio, A.; Cortiñas Abrahantes, J.; Dorne, J.-L.; Battilani, P.; Toscano, P. Occurrence and Co-Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Cereal-Based Feed and Food. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos Pereira, C.; Cunha, C.S.; Fernandes, J.O. Prevalent Mycotoxins in Animal Feed: Occurrence and Analytical Methods. Toxins 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munkvold, G.P.; Arias, S.; Taschl, I.; Gruber-Dorninger, C. Mycotoxins in Corn: Occurrence, Impacts, and Management. In Corn. Chemistry and Technology, 3rd ed.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O., Ed.; Elsevier Inc. in Cooperation with AACC International: Duxford, UK, 2019; pp. 235–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiuk, L.; Jedziniak, P.; Pietruszka, K.; Piatkowska, M.; Bocian, L. Frequency and levels of regulated and emerging mycotoxins in silage in Poland. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Weng, C.F.; Chen, B.J.; Chang, M.H. Toxicity of different Fusarium mycotoxins on growth performance, immune responses and efficacy of a mycotoxin degrading enzyme in pigs. Anim Res. 2006, 55, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, G.; Diéguez, S.N.; Fernández Paggi, M.B.; Riccio, M.B.; Pérez Gaudio, D.S.; Rodríguez, E.; Amanto, F.A.; Tapia, M.O.; Soraci, A.L. Effect of fosfomycin, Cynara scolymus extract, deoxynivalenol and their combinations on intestinal health of weaned piglets. Animal Nutr. 2019, 5, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, P.; Accensi, F.; Beauchamp, E.; Cossalter, A.M.; Callu, P.; Grosjean, F.; Oswald, I.P. Ingestion of deoxynivalenol (DON) contaminated feed alters the pig vaccinal immune responses. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 177, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, B.A. Toxicology of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, P.; Nougayrede, J.P.; del Rio, J.C.; Moreno, C.; Marin, D.; Ferrier, L.; Barcarense, A.P.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P. The food contaminant, deoxynivalenol, decreases intestinal barrier function and reduces claudin expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pestka, J.J.; Zhou, H.R.; Moon, Y.; Chung, Y.J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms for immune modulation by deoxynivalenol and other trichothecenes: Unraveling a paradox. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, J.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Pasmans, F.; De Baere, S.; Devreese, M.; Osselaere, A.; Verbrugghe, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Saeger, S.; Eeckhout, M.; et al. Influence of Mycotoxins and a Mycotoxin Adsorbing Agent on the Oral Bioavailability of Commonly Used Antibiotics in Pigs. Toxins 2012, 4, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, T.H.; Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Oswald, I.P.; Pinton, P. Analysis of the interactions between environmental and food contaminants, cadmium and deoxynivalenol, in different target organs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, M.; Mahfoud, R.; Garmy, N.; Fantini, J. The mycotoxin deoxynivalenol affects nutrient absorption in human intestinal epithelial cells. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez, G.; Perez, D.S.; Soraci, A.L.; Tapia, M.O. Penetration of Fosfomycin into IPEC-J2 Cells in the Presence or Absence of Deoxynivalenol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, E.; Weil, D.E.; Raviglionea MNakatania, H. World Health Organization World Health Day Antimicrobial Resistance Technical Working Group. The WHO policy package to combat antimicrobial resistance. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Ge, F.; Huang, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, R. Occurrence of veterinary antibiotics in animal wastewater and surface water around farms in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungemach, F.R.; Muller-Bahrdt, D.; Abraham, G. Guidelines for prudent use of antimicrobials and their implications on antibiotic usage in veterinary medicine. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296 (Suppl. S41), 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, P.; Braber, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Verheijden, K.A.T.; Schoterman, M.H.C.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Garssen, J.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Galacto-oligosaccharides protect the Intestinal Barrier by Maintaining the Tight Junction Network and Modulating the Inflammatory Responses after a Challenge with the Mycotoxin Deoxynivalenol in Human Caco-2 Cell Monolayers and B6C3F1 Mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawa, A.; Dänicke, S.; Kersten, S.; Breves, G. Effects of deoxynivalenol and lipopolysaccharide on electrophysiological parameters in growing pigs. Mycotoxin Res. 2012, 28, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.R.; Payros, D.; Pinton, P.; Dogi, C.A.; Laffitte, J.; Neves, M.; González Pereyra, M.L.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Oswald, I.P. Intestinal toxicity of deoxynivalenol is limited by Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007 in pig jejunum explants. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, M.; Karlik, W.; Chłopecka, M. The impact of chlorophyllin on deoxynivalenol transport across jejunum mucosa explants obtained from adult pigs. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EMA/CVMP/CHMP/682198/2017; Categorisation of Antibiotics in the European Union. European Medicinces Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 12 December 2019.
- Baert, K.; Croubels, S.; Gasthuys, F.; de Busser, J.; de Backer, P. Pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of a doxycycline formulation (DOXYCYCLINE 75%) in nonfasted young pigs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 23, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousquet, E.; Nouws, J.; Terlouw, P.; de Kleyne, S. Pharmacokinetics of doxycycline in pigs following oral administration in feed. Vet. Res. BioMed. Cent. 1998, 29, 475–485. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00902540 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Prats, C.; El Korchi, G.; Giralt, M.; Cristofol, C.; Pena, J.; Zorrilla, I.; Saborit, J.; Perez, B. PK and PK/PD of doxycycline in drinking water after therapeutic use in pigs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 28, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.; Gicquel, M.; Hurtaud, D.; Chapel, A.M.; Gaudiche, C.; Bousquet, E. Absolute bioavailability of doxycycline after oral administration in medicated feed to pigs. In Proceedings of the International Pig Veterinary Society 14th Congress, Bologna, Italy, 7–10 July 1996; p. 663. [Google Scholar]
- Papaich, M.G.; Rivere, J.E. β-lactam antibiotics: Penicillins, cephalosporins, and related drugs. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 9th ed.; Riviere, J.E., Papich, M.G., Adams, H.R., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 865–893. [Google Scholar]
- Papaich, M.G.; Rivere, J.E. Tetracycline Antibiotics. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 9th ed.; Riviere, J.E., Papich, M.G., Adams, H.R., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 895–913. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, L.; Fæste, C.K.; Solhaug, A. Role of P-glycoprotein in deoxynivalenol-mediated in vitro toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 284, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mu, P.; Wen, J.; Deng, Y. Carrier-Mediated and Energy-Dependent Uptake and Efflux of Deoxynivalenol in Mammalian Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Videmann, B.; Tep, J.; Cavret, S.; Lecoeur, S. Epithelial transport of deoxynivalenol: Involvement of human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (ABCC2). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mealey, K.L.; Barhoumi, R.; Burghardt, R.C.; Safe, S.; Kochevar, D.T. Doxycycline induces expression of P glycoprotein in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agbedanu, P.N.; Anderson, K.L.; Brewer, M.T.; Carlson, S.A. Doxycycline as an inhibitor of p-glycoprotein in the alpaca for the purpose of maintaining avermectins in the CNS during treatment for parelaphostrongylosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskola, M.; Kos, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Hajšlová, J.; Mayar, S.; Krska, R. Worldwide contamination of food-crops with mycotoxins: Validity of the widely cited ‘FAO estimate’ of 25. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2773–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungell, A.L.; Andreasson, A.; Lundin, K.; Utter, L. Effects of enzymatic inhibition and increased paracellular shunting on transport of vasopressin analogues in the rat. J. Pharm. Sci. 1992, 87, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucioli, J.; Pinton, P.; Callu, P.; Laffitte, J.; Grosjean, F.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P.; Bracarense, A.P. The food contaminant deoxynivalenol activates the mitogen activated protein kinases in the intestine: Interest of ex vivo models as an alternative to in vivo experiments. Toxicon 2013, 66, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westerhout, J.; van de Steeg, E.; Grossouw, D.; Zeijedner, E.E.; Krul, C.A.M.; Verwei, M.; Wortelboer, H.M. A new approach to predict human intestinal absorption using porcine intestinal tissue and biorelevant matrices. Eur. J. Parmac. Sci. 2014, 63, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, Å.; Lutz, M.; Tannergren, C.; Wingolf, C.; Borde, A.; Ungell, A.L. Comprehensive study on regional human intestinal permeability and prediction of fraction absorbed of drugs using the Ussing chamber technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Analyte | Parent Ion M + H+ [m/z] | Daughter Ions [m/z] | DP [V] | CE [eV] | Dwell Time [ms] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doxycycline (444.4 g/mol) | 445.4 | 428.0; 154.0 | 60 | 24; 41 | 250 |
| Amoxicillin (365.4 g/mol) | 366.1 | 349.0; 208.0 | 45 | 12; 18 | 250 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendel, M.; Karlik, W.; Latek, U.; Chłopecka, M.; Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Pietruszka, K.; Jedziniak, P. Does Deoxynivalenol Affect Amoxicillin and Doxycycline Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract? Ex Vivo Study on Swine Jejunum Mucosa Explants. Toxins 2022, 14, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110743
Mendel M, Karlik W, Latek U, Chłopecka M, Nowacka-Kozak E, Pietruszka K, Jedziniak P. Does Deoxynivalenol Affect Amoxicillin and Doxycycline Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract? Ex Vivo Study on Swine Jejunum Mucosa Explants. Toxins. 2022; 14(11):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110743
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendel, Marta, Wojciech Karlik, Urszula Latek, Magdalena Chłopecka, Ewelina Nowacka-Kozak, Katarzyna Pietruszka, and Piotr Jedziniak. 2022. "Does Deoxynivalenol Affect Amoxicillin and Doxycycline Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract? Ex Vivo Study on Swine Jejunum Mucosa Explants" Toxins 14, no. 11: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110743
APA StyleMendel, M., Karlik, W., Latek, U., Chłopecka, M., Nowacka-Kozak, E., Pietruszka, K., & Jedziniak, P. (2022). Does Deoxynivalenol Affect Amoxicillin and Doxycycline Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract? Ex Vivo Study on Swine Jejunum Mucosa Explants. Toxins, 14(11), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110743