Development and Validation of an Automated Magneto-Controlled Pretreatment for Chromatography-Free Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Cereals and Oils through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
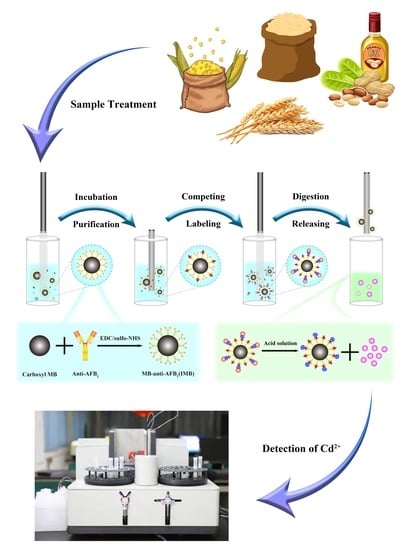
2.1. Method Principle
2.2. Optimization of Experimental Parameters
2.2.1. Extraction Solution
2.2.2. Nonspecific Adsorption
2.2.3. Digestion Conditions
2.2.4. Atomic Absorption Conditions
2.3. Establishment and Specificity of Standard Curves in a Standard Solution and Four Types of Matrix Fluids
2.4. Accuracy, Repeatability, and Reproducibility of the AAS Method
2.5. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Immunomagnetic Beads (IMB)
4.3. Synthesis of Aflatoxin Haptens (AFB1-CMO)
4.4. Synthesis of Aflatoxin Complete Antigen (AFB1-BSA)
4.5. Coupling of Pegylated Quantum Dots with Complete Antigen AFB1-BSA
4.6. Sample Automatic Processing
4.7. Atomic Absorption Detection
4.8. Method Verification
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, A.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Luan, Y. An aptamer affinity column for purification and enrichment of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin B2 in agro-products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, F.; Roshanfekr, H.; Peyman, H. Ultra-sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for label-free detection of Aflatoxin B1 in wheat flour sample using factorial design experiments. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S. Purification and identification of an aflatoxin B1 degradation enzyme from Pantoea sp. T6. Toxicon 2019, 157, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, A.M.; Ruan, D.; El-Senousey, H.K.; Chen, W.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, C. Harmful effects and control strategies of aflatoxin b1 produced by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus strains on poultry. Toxins 2019, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.; Xie, Y.; Ma, W. Research progress on the protection and detoxification of phytochemicals against aflatoxin B1-Induced liver toxicity. Toxicon 2021, 195, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Q.; Ji, C.; Zhao, L. Transcriptional profiling of aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response in macrophages. Toxins 2021, 13, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Khan, M.Z.; Khan, A.; Javed, I.; Saleemi, M.K.; Mahmood, S.; Asi, M.R. Residues of aflatoxin B1 in broiler meat: Effect of age and dietary aflatoxin B1 levels. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3304–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Jia, N. Highly sensitive electrochemical impedance spectroscopy immunosensor for the detection of AFB1 in olive oil. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Rasheed, H.; Routledge, M.N.; Wu, H.; Gong, Y.Y. Super-Sensitive LC-MS Analyses of Exposure Biomarkers for Multiple Mycotoxins in a Rural Pakistan Population. Toxins 2022, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Ye, J.; Li, L.; Tian, W.; Wang, S. Reliable and disposable quantum dot–based electrochemical immunosensor for aflatoxin B1 simplified analysis with automated magneto-controlled pretreatment system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7615–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S. An automated and high-throughput immunoaffinity magnetic bead-based sample clean-up platform for the determination of aflatoxins in grains and oils using UPLC-FLD. Toxins 2019, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Xuan, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. Development and validation of a rapid and efficient method for simultaneous determination of mycotoxins in coix seed using one-step extraction and UHPLC-HRMS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egner, P.A.; Groopman, J.D.; Wang, J.-S.; Kensler, T.W.; Friesen, M.D. Quantification of aflatoxin-b1-n 7-guanine in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography and isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry1. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er Demirhan, B.; Demirhan, B. Investigation of Twelve Significant Mycotoxin Contamination in Nut-Based Products by the LC–MS/MS Method. Metabolites 2022, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwat, A.; Rauf, W.; Majeed, S.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Iqbal, M. LC-MS/MS based appraisal of multi-mycotoxin co-occurrence in poultry feeds from different regions of Punjab, Pakistan. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2022, 15, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudumija, N.; Vulić, A.; Lešić, T.; Vahčić, N.; Pleadin, J. Aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in dry-fermented sausages in Croatia, by LC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2020, 13, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Ananthanarayan, L. Standardization and validation of a high-performance thin-layer chromatography method for the quantification of aflatoxin B1 and its application in surveillance of contamination level in marketed food commodities from the Mumbai region. JPC–J. Planar Chromatogr.–Mod. TLC 2020, 33, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Vargas, E.A. Determining aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in maize using florisil clean up with thin layer chromatography and visual and densitometric quantification. Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 21, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, L.-L.; Jia, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Duan, L.; Yang, G.; Han, C.-Q.; Li, H. Thin layer chromatography combined with surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for rapid sensing aflatoxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1579, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Thin-layer chromatography of mycotoxins and comparison with other chromatographic methods. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 815, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroka, J.; Anklam, E. Development of a simplified densitometer for the determination of aflatoxins by thin-layer chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 904, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojinrin, T.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Cui, D.; J Byrne, H.; Curtin, J.F.; Tian, F. Developing gold nanoparticles-conjugated aflatoxin B1 antifungal strips. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, Q.-m.; Liu, J.-m.; Shi, G.-Q. A “green” method to detect aflatoxin B 1 residue in plant oil based on a colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masinde, L.A.; Sheng, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Kennedy, I.R.; Wang, S. Colloidal gold based immunochromatographic strip for the simple and sensitive determination of aflatoxin B1 and B2 in corn and rice. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Lu, S.S.; Sun, Q.; Yang, J.C.; Shi, G.Q. Development of a Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for the Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Food Samples; Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1279–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.A.; Wang, S.; Allan, R.D.; Kennedy, I.R. A rapid aflatoxin B1 ELISA: Development and validation with reduced matrix effects for peanuts, corn, pistachio, and soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oplatowska-Stachowiak, M.; Sajic, N.; Xu, Y.; Haughey, S.A.; Mooney, M.H.; Gong, Y.Y.; Verheijen, R.; Elliott, C.T. Fast and sensitive aflatoxin B1 and total aflatoxins ELISAs for analysis of peanuts, maize and feed ingredients. Food Control 2016, 63, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, M.; Mashak, Z.; Heshmati, A.; Shokrzadeh, M.; Mozaffari Nejad, A.S. Determination of aflatoxin B1 levels in Iranian rice by ELISA method. Toxin Rev. 2015, 34, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, J.P.; Cerveira, C.; Miceli, T.M.; Moraes, D.P.; Mesko, M.F.; Pereira, J.S. Evaluation of sample preparation methods for cereal digestion for subsequent As, Cd, Hg and Pb determination by AAS-based techniques. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Merkoçi, A. Electrochemical coding technology for simultaneous detection of multiple DNA targets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3214–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.A.; Wang, J.; Kawde, A.-N.; Xiang, Y.; Gothelf, K.V.; Collins, G. Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2228–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, M.J. Principles, mechanisms, and application of carbon quantum dots in sensors: A review. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Marco, F.M.; Martínez-Peinado, P.; Mora, J.; Grindlay, G. Evaluation of different competitive immunoassays for aflatoxin M1 determination in milk samples by means of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1049, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xuan, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, S. One-step automatic sample pretreatment for rapid, simple, sensitive, and efficient determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk by immunomagnetic beads coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2022, 137, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Ye, J.; Wang, S. Copper Oxide Nanoparticle-Based Immunosensor for Zearalenone Analysis by Combining Automated Sample Pre-Processing and High-Throughput Terminal Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xuan, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Xie, G.; Wang, S. Automated analysis of ochratoxin A in cereals and oil by immunoaffinity magnetic beads coupled to UPLC-FLD. Food Control 2019, 104, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lu, M.; Wang, S.; Xin, Y.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Mariappan, M.; Wang, S. Development and Interlaboratory Study of a Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometric Methodfor the Determination of Multiple Mycotoxins inCereals Using Stable Isotope Dilution. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex, S. STAN 193-1995 General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed; FAO/WHO: Quebec City, QC, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]



| Curve Range (μg/kg) | Curve Coefficient | Linear Range (μg/kg) | Linear Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard solution | 0.08–800 | 0.9986 | 5–240 | 0.9859 |
| Wheat | 0.8–800 | 0.9944 | 2.5–240 | 0.9778 |
| Maize | 0.8–800 | 0.9951 | 2.5–240 | 0.9939 |
| Peanut oil | 0.08–800 | 0.9977 | 2.5–240 | 0.9901 |
| Husked rice | 0.08–800 | 0.9989 | 5–240 | 0.9869 |
| Matrix | Recovery ± RSD (%, n = 3) | Inter-Day RSD (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | ||
| Maize | 99.5 ± 4.2 | 94.9 ± 3.2 | 101.7 ± 1.7 | 6.2 |
| Wheat | 92.9 ± 4.7 | 103.8 ± 2 | 100.3 ± 4.4 | 5.8 |
| Husked rice | 94.7 ± 5.2 | 95.8 ± 0.8 | 92.6 ± 4.8 | 0.6 |
| Peanut oil | 108.7 ± 6.3 | 104.4 ± 1.8 | 101.9 ± 0.7 | 6.9 |
| AFB1 Reference Material | Lot Number | Detected Amount (µg/kg) | Certificate Value (µg/kg) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | GBW(E)100386 | 26.5 | 27 ± 3 |
| Peanut oil | JTZK-007 | 15.2 | 15.8 ± 1.9 |
| Husked rice | JTZK-002 | 25.5 | 26 ± 3.9 |
| Sample | This Method (µg/kg) | LC-MS/MS (µg/kg) | t | df | Sig. (Two-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Husked rice | 31.70 | 31.88 | 0.305 | 2 | 0.789 |
| 32.31 | 32.40 | ||||
| 33.77 | 33.32 | ||||
| Maize | 38.32 | 31.00 | 1.855 | 2 | 0.205 |
| 31.75 | 29.00 | ||||
| 31.75 | 31.00 | ||||
| Rice | 6.90 | 8.60 | 1.095 | 2 | 0.388 |
| 16.69 | 11.30 | ||||
| 14.59 | 11.40 |
| Step | Well | Mixing Time/min | Collection Time/min | Mixing Frequency /Hz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 6.5 |
| Reaction | 1 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| Wash 1 | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 6.5 |
| Competing | 3 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 6.5 |
| Wash 2 | 4 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 6.5 |
| Digestion | 5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 7.5 |
| Collection | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 6.5 |
| Spectrometer Conditions | Heating Program | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Step | Temperature (°C) | Ramp (s) | Hold (s) | Argon | |
| Wavelength (nm) | 228.8 | Drying 1 | 75 | 5 | 2 | ON |
| Bandpass (nm) | 0.8 | Drying 2 | 90 | 5 | 2 | ON |
| sample volume (μL) | 12 | Drying 3 | 110 | 10 | 2 | ON |
| Lamp current (mA) | 4 | Pyrolysis | 300 | 5 | 5 | ON |
| Atomization | 1600 | 2 | 1 | OFF | ||
| Cleaning | 1650 | 1 | 1 | ON | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Zheng, M.; Ma, H.; Xuan, Z.; Tian, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Development and Validation of an Automated Magneto-Controlled Pretreatment for Chromatography-Free Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Cereals and Oils through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Toxins 2022, 14, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070454
Ye J, Zheng M, Ma H, Xuan Z, Tian W, Liu H, Wang S, Zhang Y. Development and Validation of an Automated Magneto-Controlled Pretreatment for Chromatography-Free Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Cereals and Oils through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Toxins. 2022; 14(7):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070454
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jin, Mengyao Zheng, Haihua Ma, Zhihong Xuan, Wei Tian, Hongmei Liu, Songxue Wang, and Yuan Zhang. 2022. "Development and Validation of an Automated Magneto-Controlled Pretreatment for Chromatography-Free Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Cereals and Oils through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy" Toxins 14, no. 7: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070454
APA StyleYe, J., Zheng, M., Ma, H., Xuan, Z., Tian, W., Liu, H., Wang, S., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Development and Validation of an Automated Magneto-Controlled Pretreatment for Chromatography-Free Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Cereals and Oils through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Toxins, 14(7), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070454