Development of a Biosensor to Detect Venom of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Examination of B. candidus Antivenom Specificity
2.1.1. Dot Blot Hybridization and Indirect ELISA for B. candidus Venom Detection
2.1.2. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) and Western Blotting
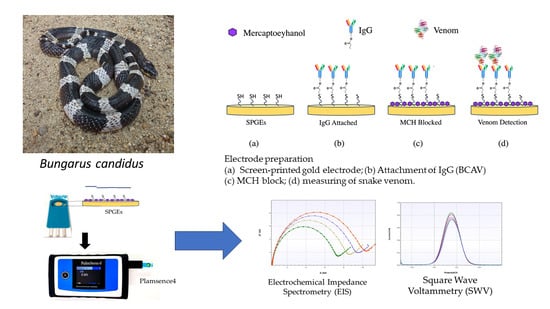
2.2. EIS Measurement for B. candidus Venom Detection under SPGE Biosensor
2.3. SWV Analysis of B. candidus Venom Concentration in Plasma from Non-Envenomed Rats
2.4. SWV Analysis of B. candidus Venom Concentration in Plasma from Envenomed Rats
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Venom Preparation and Antivenom
5.2. Animal Ethics and Care
5.3. Anesthetized Rat Preparation and Blood Sample Collection
5.4. Dot Blot Hybridization and Indirect ELISA for Snake Venom Antigen Detection
5.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE)
5.6. Western Immunoblotting
5.7. Invention of Gold Electrode Biosensor for Measuring B. candidus Venom Concentration
5.8. Electrochemical Analysis
5.9. Characterization of the Electrochemical Biosensor by EIS
5.10. Data Analysis and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chippaux, J.P. Snakebite envenomation turns again into a neglected tropical disease! J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Koudou, G.B.; Bagot, M.; Drabo, F.; Bougma, W.R.; Pulford, C.; Bockarie, M.; Harrison, R.A. Health and economic burden estimates of snakebite management upon health facilities in three regions of southern Burkina Faso. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanhome, L.; Cox, M.J.; Wilde, H.; Jintakoon, P.; Chaiyabutr, N.; Sitprija, V. Venomous Snakebite in Thailand I: Medically Important Snakes. Mil. Med. 1998, 163, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Venomous snakes of the South-East Asia Region, their venoms and pathophysiology of human envenoming. In Guidelines for the Management of Snake-Bites, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Management of Snake-Bites. In Guidelines for the Management of Snake-Bites; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Viravan, C.; Looareesuwan, S.; Kosakarn, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; McCarthy, C.J.; Stimson, A.F.; Bunnag, D.; Harinasuta, T.; Warrell, D.A. A national hospital-based survey of snakes responsible for bites in Thailand. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1992, 86, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.H.; Poh, C.H.; Tan, C.S. The lethal and biochemical properties of Bungarus candidus (Malayan krait) venom and venom fractions. Toxicon 1989, 27, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A.; Looareesuwan, S.; White, N.J.; Theakston, R.D.; Warrell, M.J.; Kosakarn, W.; Reid, H.A. Severe neurotoxic envenoming by the Malayan krait Bungarus candidus (Linnaeus): Response to antivenom and anticholinesterase. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1983, 286, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmili, M.R.; Yee, T.T.; Mustafa, M.R.; Hodgson, W.C.; Othman, I. Proteomic characterization and comparison of Malaysian Bungarus candidus and Bungarus fasciatus venoms. J. Proteom. 2014, 110, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmili, M.R.A.; Othman, I.; Abidin, S.A.Z.; Yusof, F.A.; Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Chanhome, L.; Hodgson, W.C.; Chaisakul, J. Variations in neurotoxicity and proteome profile of Malayan krait (Bungarus candidus) venoms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0227122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khow, O.; Chanhome, L.; Omori-Satoh, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Yanoshita, R.; Samejima, Y.; Kuch, U.; Mebs, D.; Sitprija, V. Isolation, toxicity and amino terminal sequences of three major neurotoxins in the venom of Malayan krait (Bungarus candidus) from Thailand. J. Biochem. 2003, 134, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanhome, L.; Sitprija, V.; Chaiyabutr, N. Effect of Bungarus candidus (Malayan krait) venom on general circulation and renal hemodynamics in experimental animals. Asian Biomed. 2010, 4, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.X.; Khac, Q.L.; Trinh, L.X.; Warrell, D.A. Hyponatraemia, rhabdomyolysis, alterations in blood pressure and persistent mydriasis in patients envenomed by Malayan kraits (Bungarus candidus) in southern Viet Nam. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Rusmili, M.R.; Hodgson, W.C.; Hatthachote, P.; Suwan, K.; Inchan, A.; Chanhome, L.; Othman, I.; Chootip, K. A Pharmacological Examination of the Cardiovascular Effects of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus) Venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongpoo, A.; Sriapha, C.; Pradoo, A.; Udomsubpayakul, U.; Srisuma, S.; Wananukul, W.; Trakulsrichai, S. Krait envenomation in Thailand. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojnuckarin, P.; Suteparak, S.; Sibunruang, S. Diagnosis and management of venomous snakebites in Southeast Asia. Asian Biomed. 2012, 6, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Koirala, S.; Dahal, G. Krait bite requiring high dose antivenom: A case report. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2002, 33, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.P.; Yu, Y.J.; Hung, D.Z. Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Taiwan cobra venom. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2002, 44, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Dong le, V.; Eng, K.H.; Quyen le, K.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Optical immunoassay for snake venom detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong le, V.; Selvanayagam, Z.E.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Eng, K.H. A new avidin-biotin optical immunoassay for the detection of beta-bungarotoxin and application in diagnosis of experimental snake envenomation. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 260, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viravan, C.; Veeravat, U.; Warrell, M.J.; Theakston, R.D.; Warrell, D.A. ELISA confirmation of acute and past envenoming by the monocellate Thai cobra (Naja kaouthia). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 35, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Warrell, M.J.; Warrell, D.A.; Bidwell, D.; Voller, A. A critical reappraisal of the use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in the study of snake bite. Toxicon 1986, 24, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulawickrama, S.; O’Leary, M.A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Brown, S.G.; Jacoby, T.; Davern, K.; Isbister, G.K. Development of a sensitive enzyme immunoassay for measuring taipan venom in serum. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Chatterjee, B.; Dhiman, A.; Goel, R.; Khan, E.; Malhotra, A.; Santra, V.; Salvi, N.; Khadilkar, M.V.; Bhatnagar, I.; et al. Complex target SELEX-based identification of DNA aptamers against Bungarus caeruleus venom for the detection of envenomation using a paper-based device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S. Electrochemical biosensors: Perspective on functional nanomaterials for on-site analysis. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Kumar, S.; Jayant, R.D.; Vashist, A.; Brown, A.N.; Li, C.Z.; Nair, M. A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of Zika-virus protein. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, E.; Gilgunn, S.; Sharma, S.; Adamson, K.; Carthy, E.; O’Kennedy, R.; Forster, R.J. Detection of prostate specific antigen based on electrocatalytic platinum nanoparticles conjugated to a recombinant scFv antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oloketuyi, S.; Mazzega, E.; Zavasnik, J.; Pungjunun, K.; Kalcher, K.; de Marco, A.; Mehmeti, E. Electrochemical immunosensor functionalized with nanobodies for the detection of the toxic microalgae Alexandrium minutum using glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 154, 112052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, C. Contemporary voltammetric techniques and its application to pesticide analysis: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeprasert, W.; Kaojarern, S. Specific antivenom for Bungarus candidus. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. = Chotmaihet Thangphaet 2007, 90, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Chanhome, L.; Wongtongkam, N.; Khow, O.; Pakmanee, N.; Omori-Satoh, T.; Sitprija, V. Genus specific neutralization of Bungarus snake venoms by Thai Red Cross banded krait antivenom. J. Nat. Toxins 1999, 8, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Rusmili, M.R.; Yee, T.T.; Mustafa, M.R.; Othman, I.; Hodgson, W.C. In-vitro neurotoxicity of two Malaysian krait species (Bungarus candidus and Bungarus fasciatus) venoms: Neutralization by monovalent and polyvalent antivenoms from Thailand. Toxins 2014, 6, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, P.K.; Sim, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Sumana, K.; Sitprija, V.; Tan, N.H. Cross neutralization of Afro-Asian cobra and Asian krait venoms by a Thai polyvalent snake antivenom (Neuro Polyvalent Snake Antivenom). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Tan, C.H. Venom proteomics and antivenom neutralization for the Chinese eastern Russell’s viper, Daboia siamensis from Guangxi and Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klangprapan, S.; Weng, C.C.; Huang, W.T.; Li, Y.K.; Choowongkomon, K. Selection and characterization of a single-chain variable fragment against porcine circovirus type 2 capsid and impedimetric immunosensor development. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 24233–24243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; O’Leary, M.; Isbister, G.K. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the myotoxic venom of Pseudechis australis (mulga snake) in the anesthetised rat. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, J.E. The application of the cathode ray oscillograph to polarography: Underlying principles. Analyst 1947, 72, 301–304. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choowongkomon, K.; Chaisakul, J.; Seetaha, S.; Vasaruchapong, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Rasri, N.; Chaeksin, K.; Boonchaleaw, S.; Sookprasert, N. Development of a Biosensor to Detect Venom of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus). Toxins 2024, 16, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16010056
Choowongkomon K, Chaisakul J, Seetaha S, Vasaruchapong T, Hodgson WC, Rasri N, Chaeksin K, Boonchaleaw S, Sookprasert N. Development of a Biosensor to Detect Venom of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus). Toxins. 2024; 16(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoowongkomon, Kiattawee, Janeyuth Chaisakul, Supaphorn Seetaha, Taksa Vasaruchapong, Wayne C. Hodgson, Natchaya Rasri, Katechawin Chaeksin, Sattawat Boonchaleaw, and Nattapon Sookprasert. 2024. "Development of a Biosensor to Detect Venom of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus)" Toxins 16, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16010056
APA StyleChoowongkomon, K., Chaisakul, J., Seetaha, S., Vasaruchapong, T., Hodgson, W. C., Rasri, N., Chaeksin, K., Boonchaleaw, S., & Sookprasert, N. (2024). Development of a Biosensor to Detect Venom of Malayan Krait (Bungarus candidus). Toxins, 16(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16010056