Bioreactor Study Employing Bacteria with Enhanced Activity toward Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins
Abstract
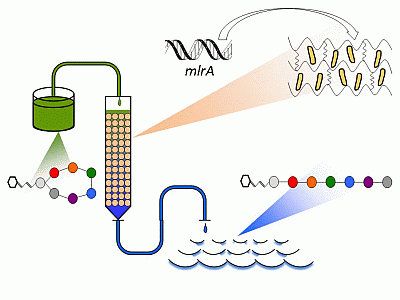
:1. Introduction

2. Results


| Heading | Initial MC-LR concentration (µg L−1) | Type of system | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch bioreactor (closed) | Column (open) | ||||||||||
| time (min) | 5 | 20 | 60 | 120 | 180 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 120 | 180 | |
| volume of carrier 2.23 mL | |||||||||||
| concentration of toxin (µg L−1) | 10 | 8.77 ± 0.28 | 8.21 ± 0.43 | 4.81 ± 0.79 | 2.26 ± 0.44 | 1.16 ± 0.61 | 5.11 ± 0.58 | 4.94 ± 0.82 | 4.81 ± 1.07 | 5.10 ± 0.26 | 5.06 ± 0.51 |
| total degraded toxin (µg) | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.62 | |
| rate of degradation (µg h−1 L−1) | 207.7 | 78.3 | 74.5 | 55.2 | 31.4 | 35.5 | 34.3 | 33.4 | 35.4 | 35.1 | |
| volume of carrier 8.46 mL | |||||||||||
| concentration of toxin (µg L−1) | 10 | 7.94 ± 0.41 | 5.31 ± 0.38 | 1.29 ± 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.92 ± 0.49 | 1.34 ± 0.08 | 1.53 ± 0.25 | 1.29 ± 0.19 | 1.29 ± 0.40 |
| total degraded toxin (µg) | 0.12 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.52 | 1.04 | |
| rate of degradation (µg h−1 L−1) | 175.1 | 99.9 | 61.8 | 35.5 | 17.8 | 32.2 | 30.8 | 30.1 | 30.1 | 30.9 | |
| volume of carrier 8.46 mL | |||||||||||
| concentration of toxin (µg L−1) | 35 | 20.64 ± 0.42 | 7.46 ± 0.38 | 1.43 ± 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5.64 ± 0.62 | 7.40 ± 0.59 | 6.99 ± 0.37 | 4.40 ± 0.16 | 5.06 ± 0.02 |
| total degraded toxin (µg) | 0.25 | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 0.84 | 1.84 | 3.31 | |
| rate of degradation (µg h−1 L−1) | 349.5 | 167.6 | 68.1 | 35.9 | 18.0 | 104.2 | 98.0 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 108.6 | |

3. Discussion
3.1. Biodegradation of MCs as a Promising Alternative
3.2. MlrA Location
3.3. Efficiency of Bioreactors
| Cited work | Type of reactor | Initial MC concentration (µg L−1) | Calculated parameters of MC removal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate of degradation (µg h−1 L−1) | Efficiency (%) | |||
| [26] | Slow sand filter with Sphingomonas MJ-PV strain inoculated in column | 50 | 1.3 | 80 |
| [27] | Cells of B-9 strain immobilized on polyester pieces in closed container | 200 | 7.5 | 90 |
| [8] | Morgan WTP filter sand packed in column colonized by bacteria with mlrA gene | 20 | 40 | 100 |
| [28] | Photocatalytic degradation in continuous treatment system | 5 | 225.0 a | 85 |
| present work | Column filled with alginate beads, BL21(DE3)-mlrA cells immobilized in gel | 10 | 30.5 | 86 |
| 35 | 105.5 | 85 | ||
| 100 | 219.9 | 62 | ||
| 35 | 3.8 b | − | ||
3.4. Stability of Designed System
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Expression of Recombinant MlrA
4.3. Location of MlrA Activity in Cellular Fractions
4.4. Immobilization of E. coli BL21-mlrA on Alginate
4.5. Activity of Alginate Beads with Entrapped E. coli BL21-mlrA
4.6. Degradation of MC-LR in the Bioreactors
4.7. HPLC Assays
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welker, M.; Steinberg, C. Rates of humic substance photosensitized degradation of microcystin-LR in natural waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3415–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Fang, T.; Xu, X.Q. Study on photodegradation of cyanobacterial toxin in blooms of Dianchi Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2001, 21, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, K.; Lyck, S.; Winding, A. Microbial activity and bacterial community structure during degradation of microcystins. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 27, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Uptake of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR by aquatic macrophytes. J. Appl. Bot. 1998, 72, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, K.; Masui, H.; Uemura, H.; Mori, Y.; Harada, K.I. Analysis of microcystins in sediments using MMPB method. Toxicon 2001, 39, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, T.; Jorgensen, N.O.G.; Jorgensen, C.; Johansen, A. Degradation of microcystin in sediments at oxic and anoxic, denitrifying conditions. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4748–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Wasylewski, M.; Wladyka, B.; Nybom, S.; Meriluoto, J. Microbial degradation of microcystins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Meyn, T.; Keegan, A.; Hoefel, D.; Brookes, J.; Saint, C.P.; Newcombe, G. Bacterial degradation of microcystin toxins within a biologically active sand filter. Water Res. 2006, 40, 768–774. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, L.; Newcombe, G. Evaluating the adsorption of microcystin toxins using granular activated carbon (GAC). J. Water. Supply. Res. Technol. 2007, 56, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ho, L.; Lewis, D.M.; Brookes, J.D.; Newcombe, G. Discriminating and assessing adsorption and biodegradation removal mechanisms during granular activated carbon filtration of microcystin toxins. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4262–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.P.; Lua, X.W.; Li, X.N.; Pu, J.P. Biological degradation of algae and microcystins by microbial enrichment on artificial media. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumino, T.; Ogasawara, T.; Park, H.D. Method and Equipment for Treating Microcystin-Containing Water. U.S. Patent 7.425.267, 16 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dziga, D.; Sworzen, M.; Wladyka, B.; Wasylewski, M. Genetically engineered bacteria immobilized in alginate as an option of cyanotoxins removal. Intern. J. Environ. Sci. Develop. 2013, 4, 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Eleuterio, L.; Batista, F.R. Biodegradation studies and sequencing of microcystin-LR degrading bacteria isolated from a drinking water biofilter and a fresh water lake. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Gaudieux, A.L.; Fanok, S.; Newcombe, G.; Humpage, A.R. Bacterial degradation of microcystin toxins in drinking water eliminates their toxicity. Toxicon 2007, 50, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayler, G.S.; Ripp, S. Field applications of genetically engineered microorganisms for bioremediation processes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, Ch.; Raina, V.; Pal, R.; Suar, M.; Lal, S.; Gartemann, K.H.; Holliger, Ch.; van der Meer, J.; Lal, R. Organization of lin genes and IS6100 among different strains of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas paucimobilis. Evidence for horizontal gene transfer. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, R.; Cui, Z.; He, J.; Gu, L.; Li, S. Parameters controlling the gene-targeting frequencyat the Sphingomonas species rrn site and expression of the methyl parathion hydrolase gene. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 102, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, R.J.; Li, R.; Gu, J.; Li, S. Simultaneous biodegradation of methyl parathion and carbofuran by a genetically engineered microorganism constructed by mini-Tn5 transposon. Biodegradation 2007, 18, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hong, Q.; Xu, J.K.; Jun, W.; Li, S.P. Construction of a genetically engineered microorganism for degrading organophosphate and carbamate pesticides. Intern. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2006, 58, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Dziga, D.; Wladyka, B.; Zielińska, G.; Meriluoto, J.; Wasylewski, M. Heterologous expression and characterisation of microcystinase. Toxicon 2012, 59, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Wasylewski, M.; Szettla, A.; Bocheńska, O.; Wladyka, B. Verification of the role of MlrC in microcystin biodegradation by studies using a heterologously expressed enzyme. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1192–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Okano, K.; Kurashima, T.; Kawauchi, Y.; Xue, Q.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Enzymatic pathway for biodegrading microcystin LR in Sphingopyxis sp. C-1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wie, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Characterization of the first step involved in enzymatic pathway for microcystin-RR biodegraded by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Garrido, I. Microalgae immobilization: Current techniques and uses. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3949–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Blakeley, R.L.; Riddles, P.; Jones, G.J. Biodegradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR in natural water and biologically active slow sand filters. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, K.; Asakawa, M.; Anzai, Y.; Sumino, T.; Harada, K. Degradation of microcystins using immobilized microorganism isolated in an eutrophic lake. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, L.C.; Peralta-Zamora, P.; Campos, F.R.; Pontarolo, R. Photocatalytic degradation of microcystin-LR in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdek, P.; Lechowski, Z.; Dziga, D.; Bialczyk, J. Detoxification of microcystin-LR using Fenton reagent. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2003, 12, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Meriluoto, J.; Spoof, L. Analysis of Microcystins by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode-Array Detection. In TOXIC: Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; Meriluoto, J., Codd, G.A., Eds.; Åbo Akademi University Press: Turku, Finland, 2005; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dziga, D.; Lisznianska, M.; Wladyka, B. Bioreactor Study Employing Bacteria with Enhanced Activity toward Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins. Toxins 2014, 6, 2379-2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082379
Dziga D, Lisznianska M, Wladyka B. Bioreactor Study Employing Bacteria with Enhanced Activity toward Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins. Toxins. 2014; 6(8):2379-2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082379
Chicago/Turabian StyleDziga, Dariusz, Magdalena Lisznianska, and Benedykt Wladyka. 2014. "Bioreactor Study Employing Bacteria with Enhanced Activity toward Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins" Toxins 6, no. 8: 2379-2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082379
APA StyleDziga, D., Lisznianska, M., & Wladyka, B. (2014). Bioreactor Study Employing Bacteria with Enhanced Activity toward Cyanobacterial Toxins Microcystins. Toxins, 6(8), 2379-2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6082379