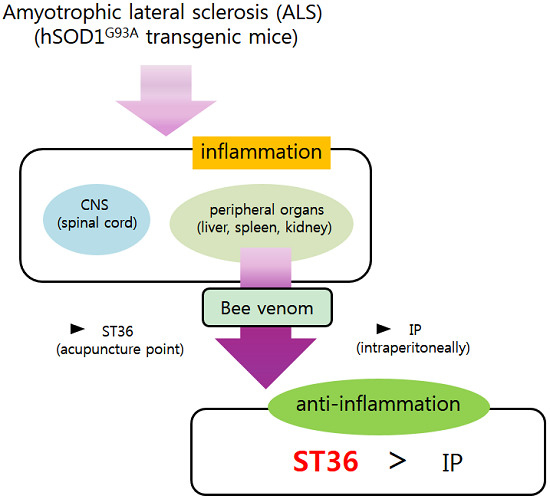
Bee Venom Acupuncture Augments Anti-Inflammation in the Peripheral Organs of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BV Treatment at ST36 Reduces Inflammatory Proteins in the Liver of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice

2.2. BV Treatment at ST36 Reduces Inflammation in the Spleen of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice


2.3. BV Treatment at ST36 Downregulates Inflammation in the Kidney of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Bee Venom Treatment
4.3. Tissue Preparation and Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, R.G.; Mitchell, J.D.; Moore, D.H. Riluzole for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)/motor neuron disease (MND). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 3, CD001447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, M.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Lee, S.D.; Kim, M.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, C.H. Effects of bee venom on protease activities and free radical damages in synovial fluid from type II collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis rats. Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 20, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, D.H.; Kwon, Y.B.; Kim, H.W.; Ham, T.W.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Han, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.H. Acupoint stimulation with diluted bee venom (apipuncture) alleviates thermal hyperalgesia in a rodent neuropathic pain model: Involvement of spinal alpha 2-adrenoceptors. J. Pain 2004, 5, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.K.; Park, K.K. Anti-allergic effect of bee venom in an allergic rhinitis mouse model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Noelker, C.; Vulinović, F.; Grünewald, A.; Chevarin, C.; Klein, C.; Oertel, W.H.; Hirsch, E.C.; Michel, P.P.; Hartmann, A. Bee venom and its component apamin as neuroprotective agents in a Parkinson disease mouse model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doo, A.R.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, S.N.; Moon, W.; Yin, C.S.; Chae, Y.; Park, H.K.; Lee, H.; Park, H.J. Neuroprotective effects of bee venom pharmaceutical acupuncture in acute 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Res. 2010, 32, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.J.; Jiang, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, S.C.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, M.S.; Choi, S.M. Bee venom attenuates neuroinflammatory events and extends survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis models. J. Neuroinflammation 2010, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, S.; Garbelli, S.; Pasini, A.; Alimonti, D.; Perotti, C.; Melazzini, M.; Bendotti, C.; Mora, G. Immune system alterations in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients suggest an ongoing neuroinflammatory process. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 210, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipnis, J.; Avidan, H.; Caspi, R.R.; Schwartz, M. Dual effect of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in neurodegeneration: A dialogue with microglia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14663–14669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phani, S.; Re, D.B.; Przedborski, S. The Role of the Innate Immune System in ALS. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.H.; Yang, E.J.; Baek, M.G.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.M.; Choi, S.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of electroacupuncture in the respiratory system of a symptomatic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis animal model. Neurodegener. Dis. 2011, 8, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.M.; Yang, E.J. Melittin ameliorates the inflammation of organs in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis animal model. Exp. Neurobiol. 2014, 23, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, A.; Kunis, G.; Seksenyan, A.; Ronen, A.; Berkutzki, T.; Azoulay, D.; Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Schwartz, M. Abnormal changes in NKT cells, the IGF-1 axis, and liver pathology in an animal model of ALS. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.L.; McGeer, E.G. Inflammatory processes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2002, 26, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, P.A.; Bergemalm, D.; Andersen, P.M.; Gredal, O.; Brännström, T.; Marklund, S.L. Inclusions of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked superoxide dismutase in ventral horns, liver, and kidney. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, D.R.; Siddique, T.; Patterson, D.; Figlewicz, D.A.; Sapp, P.; Hentati, A.; Donaldson, D.; Goto, J.; O’Regan, J.P.; Deng, H.X.; et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 1993, 362, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.S.; Jeong, H.S.; Park, H.J.; Baik, Y.; Yoon, M.H.; Choi, C.B.; Koh, H.G. A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 84, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Choi, S.-M.; Yang, E.J. Bee Venom Acupuncture Augments Anti-Inflammation in the Peripheral Organs of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice. Toxins 2015, 7, 2835-2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082835
Lee S-H, Choi S-M, Yang EJ. Bee Venom Acupuncture Augments Anti-Inflammation in the Peripheral Organs of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice. Toxins. 2015; 7(8):2835-2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sun-Hwa, Sun-Mi Choi, and Eun Jin Yang. 2015. "Bee Venom Acupuncture Augments Anti-Inflammation in the Peripheral Organs of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice" Toxins 7, no. 8: 2835-2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082835
APA StyleLee, S. -H., Choi, S. -M., & Yang, E. J. (2015). Bee Venom Acupuncture Augments Anti-Inflammation in the Peripheral Organs of hSOD1G93A Transgenic Mice. Toxins, 7(8), 2835-2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082835