Molecular Cloning and Functional Studies of Two Kazal-Type Serine Protease Inhibitors Specifically Expressed by Nasonia vitripennis Venom Apparatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Molecular Characterization of NvKSPI-1 and NvKSPI-2




2.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant NvKSPI-1 and NvKSPI-2

2.3. Transcriptional Profiles of NvKSPI-1 and NvKSPI-2 in Different Tissues and Developmental Stages


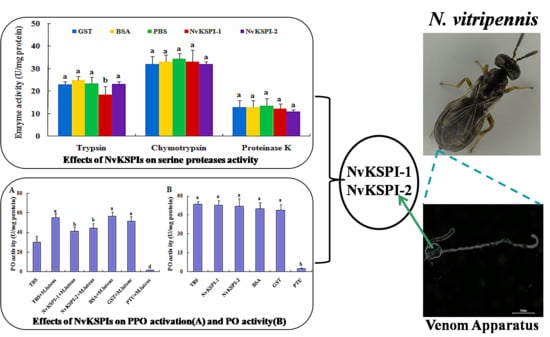
2.4. Serine Protease Inhibition Activity of NvKSPIs

2.5. Effects of NvKSPIs on Prophenoloxidase (PPO) Activation and Phenoloxidase (PO) Activity

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Cloning
| Primers Function | Primer Name | Primer Sequence(5ʹ-3ʹ) |
|---|---|---|
| Gene cloning | NvKSPI-1-F | TTGAGACGTGTCACCGAACA |
| NvKSPI -1-R | ACTTGGCAATGGTAAGTTCTTG | |
| NvKSPI -2-F | ATGAAGTTAACCGTATTCCTCTTC | |
| NvKSPI -2-R | TTAAACAAGTCCGAAGTTTGCATC | |
| RT-qPCR | RT-NvKSPI-1-F | ACTACCAACCAGTATGTGAC |
| RT-NvKSPI-1-R | TCACTGTACTTGGCAATGGT | |
| RT-NvKSPI-2-F | CGGACGATTATGAAGAAGAAG | |
| RT-NvKSPI-2-R | ACTTGATAGCTTCCTCGTTAG | |
| RT-18S-F | TGGGCCGGTACGTTTACTTT | |
| RT-18S-R | CACCTCTAACGTCGCAATAC | |
| Recombinant expression | NvKSPI-1-F-B | CGCGGATCCTGCATTTGTCCAAGAAACTACC |
| NvKSPI-1-R-E | CCGGAATTCTTAACATTCACTGTACTTGGCAATG | |
| NvKSPI-2-F-B | CGCGGATCCCAACTTGAATCGGACGATTATGAAG | |
| NvKSPI-2-R-E | CCGGAATTCTTAAACAAGTCCGAAGTTTGCATCG |
4.4. Sequence Analysis
4.5. Protein Expression, Purification, and Antibody Preparation
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Serine Protease Inhibition Assays
4.8. Prophenoloxidase (PPO) Activation and Phenoloxidase (PO) Activity Assays
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazal, L.A.; Spicer, D.S.; Brahinsky, R.A. Isolation of a crystalline trypsin inhibitor-anticoagulant protein from pancreas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, M., Jr.; Kato, I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 593–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, T.; Kroger, B.; Bialojan, S.; Lemaire, H.G.; Hoffken, H.W.; Reuschenbach, P.; Otte, M.; Dodt, J. A Kazal-type inhibitor with thrombin specificity from Rhodnius prolixus. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 16216–16222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.W.; Keyser, P.; Soderhall, K. Purification and cDNA cloning of a four-domain Kazal proteinase inhibitor from crayfish blood cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 223, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerhoff, C.P.; Sollner, C.; Mentele, R.; Piechottka, G.P.; Auerswald, E.A.; Fritz, H. A Kazal-type inhibitor of human mast cell tryptase: Isolation from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis, characterization, and sequence analysis. Biol. Chem. Hoppe. Seyler. 1994, 375, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Albores, F.; Villalpando, E. A new type of Kazal proteinase inhibitor related to shrimp Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Vega, F.; Vargas-Albores, F. A four-Kazal domain protein in Litopenaeus vannamei hemocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, Y.; Pons, T.; Gil, J.; Besada, V.; Alonso-del-Rivero, M.; Tanaka, A.S.; Araujo, M.S.; Chávez, M.A. Characterization and comparative 3D modeling of CmPI-II, a novel “non-classical” Kazal-type inhibitor from the marine snail Cenchritis muricatus (Mollusca). Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Characterization, kinetics, and possible function of Kazal-type proteinase inhibitors of Chinese white shrimp, Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visetnan, S.; Donpudsa, S.; Supungul, P.; Tassanakajon, A.; Rimphanitchayakit, V. Domain 2 of a Kazal serine proteinase inhibitor SPIPm2 from Penaeus monodon possesses antiviral activity against WSSV. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.L.; Chen, J.; Nie, Z.M.; Lv, Z.B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.Z. Expression, purification and characterization of a three-domain Kazal-type inhibitor from silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 146, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillard-Bourdet, M.; Hamdaoui, A.; Hajjar, E.; Boudier, C.; Reuter, N.; Ehret-Sabatier, L.; Bieth, J.G.; Gauthier, F. A novel locust (Schistocerca gregaria) serine protease inhibitor with a high affinity for neutrophil elastase. Biochem. J. 2006, 400, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krowarsch, D.; Cierpicki, T.; Jelen, F.; Otlewski, J. Canonical protein inhibitors of serine proteases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 2427–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christeller, J.T. Evolutionary mechanisms acting on proteinase inhibitor variability. FEBS. J. 2005, 272, 5710–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Tassanakajon, A. Structure and function of invertebrate Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitors. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Song, L.; Chang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, L. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of a novel serine proteinase inhibitor gene in bay scallops (Argopecten irradians, Lamarck 1819). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanost, M.R. Serine proteinase inhibitors in arthropod immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.R. The clip-domain family of serine proteinases in arthropods. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cera, E. Serine proteases. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, I.T.; Amino, R.; Sampaio, C.A.; Auerswald, E.A.; Friedrich, T.; Lemaire, H.G.; Schenkman, S.; Tanaka, A.S. Infestin, a thrombin inhibitor presents in Triatoma infestans midgut, a Chagas disease vector: Gene cloning, expression and characterization of the inhibitor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.T.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Tanaka, A.S. Identification and characterization of a novel factor XIIa inhibitor in the hematophagous insect, Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). FEBS Lett. 2004, 577, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovato, D.V.; de Campos, I.T.N.; Amino, R.; Tanaka, A.S. The full-length cDNA of anticoagulant protein infestin revealed a novel releasable Kazal domain, a neutrophil elastase inhibitor lacking anticoagulant activity. Biochimie 2006, 88, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiser, C.K.; Piechura, H.; Werner, T.; Dittmeyer-Schäfer, S.; Meyer, H.E.; Warscheid, B.; Schaub, G.A.; Balczun, C. Kazal-type inhibitors in the stomach of Panstrongylus megistus (Triatominae, Reduviidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Ye, G.Y.; Fang, Q.; Wu, M.L.; Hu, C. A pathogenic picorna-like from the endoparasitoid wasp, Pteromalus puparum: Initial discovery and partial genomic characterization. Virus Res. 2008, 138, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.Z.; Ye, G.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Hu, C.; Liu, S. Vitellin of Pteromalus puparum (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae), a pupal endoparasitoid of Pieris rapae (Lepidoptera: Pieridae): Biochemical characterization, temporal patterns of production and degradation. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.Z.; Ye, G.Y.; Hu, C. Roles of Ecdysteroid and juvenile hormone in vitellogenesis in an endoparasitic wasp, Pteromalus puparum (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Gen. Comp. Endoc. 2009, 160, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivers, D.B.; Uçkan, F.; Ergin, E.; Keefer, D.A. Pathological and ultrastructural changes in cultured cells induced by venom from the ectoparasitic wasp Nasonia vitripennis (Walker) (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ye, G.Y.; Cai, J.; Hu, C. Comparative venom toxicity between Pteromalus puparum and Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) toward the hemocytes of their natural hosts, non-target insects and cultured insect cells. Toxicon 2005, 46, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.Z.; Ye, G.Y.; Yao, P.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, X.X.; Shen, Z.C.; Hu, C. Effects of starvation on the vitellogenesis, ovarian development and fecundity in the ectoparasitoid, Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Insect Sci. 2008, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, D.C.; Aerts, M.; Brunain, M.; Desjardins, C.A.; Jacobs, F.J.; Werren, J.H.; Devreese, B. Insight into the venom composition of the ectoparasitoid wasp Nasonia vitripennis from bioinformatics and proteomic studies. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C. Identification of Venom Proteins from Nasonia vitripennis and Functional Analysis of Pacifastin and Kazal Type Genes. Ph. D. Dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shuker, D.; Lynch, J.; Peire Morais, A. Moving from model to non-model organisms? Lessons from Nasonia wasps. Bioessays 2003, 25, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurm, Y.; Keller, L. Parasitoid wasps: from natural history to genomic studies. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R242–R244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werren, J.H.; Richards, S.; Desjardins, C.A.; Niehuis, O.; Gadau, J.; Colbourne, J.K.; Desplan, C.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Elsik, C.G.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.; et al. Functional and evolutionary insights from the genomes of three parasitoid Nasonia species. Science 2010, 327, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Apostol, I.; Qasim, M.A.; Warne, N.; Wynn, R.; Zhang, W.L.; Anderson, S.; Chiang, Y.W.; Ogin, E.; Rothberg, I.; et al. Binding of amino acid side-chains to S1 cavities of serine proteinases. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 266, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoef, V.; Breugelmans, B.; Spit, J.; Simonet, G.; Zels, S.; Vanden, B.J. Phylogenetic distribution of protease inhibitors of the Kazal-family within the Arthropoda. Peptides 2013, 41, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, J.; Jiang, S. Molecular characterization, expression and function analysis of a five-domain Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitor from pearl oyster Pinctada fucata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 37, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Aguayo, W.; Núñez-Acuña, G.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Chávez-Mardones, J.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Molecular characterization of two Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitor genes in the surf clam Mesodesma donacium exposed to Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horita, S.; Ishibashi, J.; Nagata, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Tanokura, M. Isolation, cDNA cloning, and structure-based functional characterization of oryctin, a hemolymph protein from the coconut rhinoceros beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros, as a novel serine protease inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30150–30158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, K.; Petoukhova, O.; Koulitchkova, V.; Schaub, G.A.; Lange, U.; Kaufmann, R.; Nowak, G. Dipetalogastin, a potent thrombin inhibitor from the blood-sucking insect. Dipetalogaster maximus cDNA cloning, expression and characterization. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 266, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.M.; Soares, T.S.; Morais-Zani, K.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Maciel, C.; Capurro, M.L.; Torquato, R.J.; Tanaka, A.S. A novel trypsin Kazal-type inhibitor from Aedes aegypti with thrombin coagulant inhibitory activity. Biochimie 2010, 92, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Zou, F.M.; Wan, H.; Choi, Y.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Kwon, H.W.; Je, Y.H.; Jin, B.R. Antimicrobial activity of a honeybee (Apis cerana) venom Kazal-type serine protease inhibitor. Toxicon 2013, 76, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckage, N.E.; Gelman, D.B. Wasp parasitoid disruption of host development: Implications for new biologically based strategies for insect control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 299–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, S. Venom proteins from polydnavirus-producing endoparasitoids: Their role in host-parasite interactions. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 61, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abt, M.; Rivers, D.B. Characterization of phenoloxidase activity in venom from the ectoparasitoid Nasonia vitripennis (Walker) (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2007, 94, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerenius, L.; Lee, B.L.; Soderhall, K. The proPO-system: pros and cons for its role in invertebrate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerenius, L.; Soderhall, K. The prophenoloxidase-activating system in invertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.R. Identification of plasma proteases inhibited by Manduca sexta serpin-4 and serpin-5 and their association with components of the prophenol oxidase activation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14932–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Kanost, M.R. Manduca sexta serpin-4 and serpin-5 inhibit the prophenol oxidase activation pathway: cDNA cloning, protein expression, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14923–14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gorman, M.J.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.R. Manduca sexta serpin-3 regulates prophenoloxidase activation in response to infection by inhibiting prophenoloxidase-activating proteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46556–46564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.Y.; Dong, S.Z.; Dong, H.; Hu, C.; Shen, Z.C.; Cheng, J.A. Effects of host (Boettcherisca peregrina) copper exposure on development, reproduction and vitellogenesis of the ectoparasitic wasp, Nasonia vitripennis. Insect Sci. 2009, 16, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. Available online: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 30 July 2015).
- CBS: Center of Biological Sequence Analysis. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/ (accessed on 30 July 2015).
- ClustalW2. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/ (accessed on 30 July 2015).
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, E.J.; Rao, X.J.; Ao, J.Q.; Yu, X.Q. Purification and characterization of a small cationic protein from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, C.; Fang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ye, G.-Y. Molecular Cloning and Functional Studies of Two Kazal-Type Serine Protease Inhibitors Specifically Expressed by Nasonia vitripennis Venom Apparatus. Toxins 2015, 7, 2888-2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082888
Qian C, Fang Q, Wang L, Ye G-Y. Molecular Cloning and Functional Studies of Two Kazal-Type Serine Protease Inhibitors Specifically Expressed by Nasonia vitripennis Venom Apparatus. Toxins. 2015; 7(8):2888-2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082888
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Cen, Qi Fang, Lei Wang, and Gong-Yin Ye. 2015. "Molecular Cloning and Functional Studies of Two Kazal-Type Serine Protease Inhibitors Specifically Expressed by Nasonia vitripennis Venom Apparatus" Toxins 7, no. 8: 2888-2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082888
APA StyleQian, C., Fang, Q., Wang, L., & Ye, G. -Y. (2015). Molecular Cloning and Functional Studies of Two Kazal-Type Serine Protease Inhibitors Specifically Expressed by Nasonia vitripennis Venom Apparatus. Toxins, 7(8), 2888-2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7082888