The Response of Selected Triticum spp. Genotypes with Different Ploidy Levels to Head Blight Caused by Fusarium culmorum (W.G.Smith) Sacc.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Weather Conditions
2.2. Yield Components
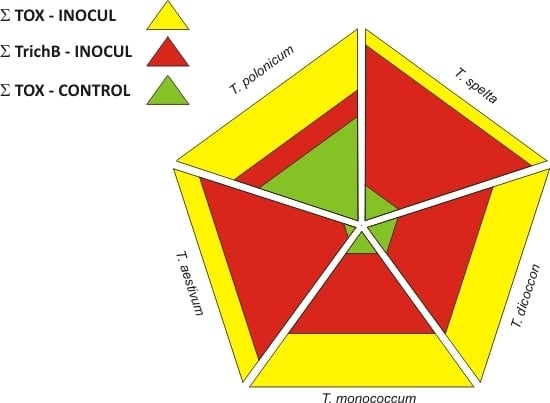
2.3. Mycotoxin Concentrations in Grain
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Material
5.2. Field Experiment
5.3. Determination of Mycotoxins in Grain
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FHB | Fusarium head blight |
| OKW | one kernel weight |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| d.m. | dry matter |
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| D3G | deoxynivalenol-3-β-d-glucopyranoside |
| NIV | nivalenol |
| 3-AcDON | 3-acetyl-deoxynivalenol |
| Deepoxy-DON | de-epoxy-deoxynivalenol |
| ZEA | zearalenone |
| ZEA-4 | sulfate-zearalenone 4-sulfate |
| MON | moniliformin |
| AOH | alternariol |
| AME | alternariol monomethyl ether |
| AUF | aurofusarin |
| BUT | butenolide |
References
- Ward, J.L.; Poutanen, K.; Gebruers, K.; Piironen, V.; Lampi, A.-M.; Nyström, L.; Andersson, A.A.M.; Åman, P.; Boros, D.; Rakszegi, M.; et al. The HEALTHGRAIN cereal diversity screen: Concept, results, and prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9699–9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.A.; Edmeades, G.O. Breeding and cereal yield progress. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, S85–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; D’Ovidio, R.; Lafiandra, D.; Jenkins, J.A. Wheat grain proteins. In Wheat: Chemistry and Technology, 4th ed.; Khan, P.K., Shewry, P., Eds.; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009; pp. 223–298. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.S.; Zhao, F.J.; Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Poulton, P.R.; Dunham, S.J.; McGrath, S.P. Evidence of decreasing mineral density in wheat grain over the last 160 years. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2008, 22, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stępień, Ł.; Chełkowski, J. Fusarium head blight of wheat: Pathogenic species and their mycotoxins. World Mycotoxin J. 2010, 3, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromadzka, K.; Lenc, L.; Sadowski, C.; Baturo-Ciesniewska, A.; Chełkowski, J.; Goliński, P.; Bocianowski, J. Effects of fungicidal protection programs on the development of Fusarium head blight and the accumulation of mycotoxins in winter wheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 2012, 40, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menniti, A.M.; Pancaldi, D.; Maccaferri, M.; Casalini, L. Effect of fungicides on Fusarium head blight and deoxynivalenol content in durum wheat grain. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2003, 109, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, M.; Haidukowski, M.; Pascale, M.; Plizzari, L.; Scudellari, D.; Reyneri, A. Integrated strategies for the control of Fusarium head blight and deoxynivalenol contamination in winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachowska, U.; Kucharska, K.; Jędryczka, M.; Lobik, N. Microorganisms as biological control agents against Fusarium pathogens in winter wheat. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner, B.H.; Munich, M.; Kleijer, G.; Mascher, F. Characterisation of kernel resistance against Fusarium infection in spring wheat by baking quality and mycotoxin assessments. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2008, 120, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowiak, H.; Packa, D.; Wiwart, M.; Perkowski, J. Scanning electron microscopy of Fusarium damaged kernels of spring wheat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 98, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoušková, L.; Capouchová, I.; Kostelanská, M.; Škeříkova, A.; Prokinová, E.; Hajšlová, J.; Salava, J.; Faměra, O. Changes in baking quality of winter wheat with different intensity of Fusarium spp. contamination detected by means of new rheological system mixolab. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 420–429. [Google Scholar]
- Buerstmayr, H.; Ban, T.; Anderson, J.A. QTL mapping and marker-assisted selection for Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat: A review. Plant Breed. 2009, 128, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-C.; Kolb, F.L.; Bai, G.-H.; Domier, L.L.; Yao, J.-B. Effect of individual Sumai 3 chromosomes on resistance to scab spread within spikes and deoxynivalenol accumulation within kernels in wheat. Hereditas 2002, 137, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, B.; Lemmens, M.; Griesser, M.; Scholz, U.; Schondelmaier, J.; Buerstmayr, H. Molecular mapping of resistance to Fusarium head blight in the spring wheat cultivar Frontana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-B.; Bai, G.-H.; Cai, S.-B.; Dong, Y.-H.; Ban, T. New Fusarium head blight-resistant sources from Asian wheat germplasm. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konvalina, P.; Capouchová, I.; Stehno, Z. Agronomically important traits of emmer wheat. Plant Soil Environ. 2012, 58, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Hucl, P.; Sosulski, F.W. Compositional and nutritional characteristics of spring einkorn and spelt wheats. Cereal Chem. 1995, 72, 621–624. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, R.E.; Cai, X.; Friesen, T.L.; Halley, S.; Stack, R.W.; Xu, S.S. Evaluation of Fusarium head blight resistance in tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum L.). Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchowilska, E.; Kandler, W.; Sulyok, M.; Wiwart, M.; Krska, R. Mycotoxin profiles in the grain of Triticum monococcum, Triticum dicoccum and Triticum spelta after head infection with Fusarium culmorum. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garvin, F.D.; Stack, R.W.; Hansen, J.M. Quantitative trait locus mapping of increased Fusarium head blight susceptibility associated with a wild emmer wheat chromosome. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortinovis, C.; Pizzo, F.; Spicer, L.J.; Caloni, F. Fusarium mycotoxins: Effects on reproductive function in domestic animals—A review. Theriogenology 2013, 80, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggert, K.; Wieser, H.; Pawelzik, E. The influence of Fusarium infection and growing location on the quantitative protein composition of (part I) emmer (Triticum dicoccum). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopahnke, D.; Miedaner, T.; Brunsbach, G.; Lind, V.; Schliephake, E.; Ordon, F. Screening of Triticum monococcum and T. dicoccum for resistance to Fusarium. Cereal Res. Commun. 2008, 36, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Buerstmayr, H.; Stierschneider, M.; Steiner, B.; Lemmens, M.; Griesser, M.; Nevo, E.; Fahima, T. Variation for resistance to head blight caused by Fusarium graminearum in wild emmer (Triticum dicoccoides) originating from Israel. Euphytica 2003, 130, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, N.; Buerstmayr, M.; Steiner, B.; Robert, O.; Buerstmayr, H. Current knowledge on resistance to Fusarium head blight in tetraploid wheat. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedaner, T.; Longin, C.F.H. Genetic variation for resistance to Fusarium head blight in winter durum material. Crop Pasture Sci. 2014, 65, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talas, F.; Longin, F.; Miedaner, T. Sources of resistance to Fusarium head blight within Syrian durum wheat landraces. Plant Breed. 2011, 130, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, R.W.; Elias, E.M.; Mitchell Fetch, J.; Miller, J.D.; Joppa, L.R. Fusarium head blight reaction of Langdon durum-Triticum dicoccoides chromosome substitution lines. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, L.E.; Stein, J.M. Epidemiology of Fusarium head blight on small-grain cereals. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bueren, E.T.L.; Struik, P.C.; Jacobsen, E. Ecological concepts in organic farming and their consequences for an organic crop ideotype. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 50, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.-L.; Wie, Y.-M.; Cao, W.; Lan, X.-J.; Yu, M.; Chen, Z.-M.; Chen, G.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-L. Confirmation of the relationship between plant height and Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by QTL meta-analysis. Euphytica 2010, 174, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.D.; Kianian, S.F.; Elias, E.M.; Stack, R.W.; Joppa, L.R. Genetic dissection of a major Fusarium head blight QTL in tetraploid wheat. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Faris, J.D.; Hu, J.; Stack, R.W.; Adhikari, T.; Elias, E.M.; Kianian, S.F.; Cai, X. Saturation and comparative mapping of a major Fusarium head blight resistance QTL in tetraploid wheat. Mol. Breed. 2007, 19, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.; Thrane, U. Food-borne fungi in fruit and cereals and their production of mycotoxins. In Advances in Food Mycology; Hocking, A.D., Pitt, J.I., Samson, R.A., Thrane, U., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1126/2007 of 28 September 2007 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards Fusarium toxins in maize and maize products. Off. J. Eur. Union 2007, 50, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmens, M.; Scholz, U.; Berthiller, F.; Dall’Asta, C.; Koutnik, A.; Schuhmacher, R.; Adam, G.; Buerstmayr, H.; Mesterházy, A.; Krska, R.; et al. The ability to detoxify the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol colocalizes with a major QTL for Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthiller, F.; Crews, C.; Dall’Asta, C.; de Saeger, S.; Haesaert, G.; Karlovsky, P.; Oswald, I.P.; Seefelder, W.; Speijers, G.; Stroka, J. Masked mycotoxins: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gacek, E.S. List of Agriculture Cultivars; Research Center for Cultivar Testing: Słupia Wielka, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, J.F.; Summerrell, B.A. The Fusarium Laboratory Manual; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Stępień, Ł.; Popiel, D.; Koczyk, G.; Chełkowski, J. Wheat-infecting Fusarium species in Poland—Their chemotypes and frequencies revealed by PCR assay. J. Appl. Genet. 2008, 49, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzenberger, A.; Hack, H.; van den Boom, T. Erläuterungen zum BBCH-Dezimal-Code für die Entwicklungsstadien des Getreides—Mit Abbildungen. Gesunde Pflanz. 1989, 41, 384–388. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), Version 10, 2011. Available online: http://www.statsoft.com (accessed on 3 February 2016).




| Species | Treatment | Weight of One Spike (g) | Number of Kernels per Spike | One Kernel Weight (mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | ||
| T. monococcum | C | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 19.7 | 20.6 | 14.3 | 30.0 | 29.3 | 38.6 |
| I | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 17.2 | 20.6 | 10.5 | 28.4 | 25.3 | 35.0 | |
| 1 − (I/C) (%) | 0 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 0 | 26.6 | 5.3 | 13.7 | 9.3 | |
| T. dicoccon | C | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 32.9 | 38.4 | 25.3 | 31.8 | 33.6 | 47.9 |
| I | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 30.1 | 39.7 | 21.1 | 31.9 | 30.2 | 41.1 | |
| 1 − (I/C) (%) | 5.9 | 5.3 | 21.1 | 8.5 | −3.4 | 16.6 | −0.3 | 10.1 | 14.2 | |
| T. spelta | C | 2.3 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 31.4 | 33.1 | 22.1 | 44.8 | 40.2 | 57.2 |
| I | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 28.5 | 34.1 | 22.4 | 40.5 | 37.2 | 55.0 | |
| 1 − (I/C) (%) | 8.7 | 0 | 5.6 | 9.2 | −3.0 | −1.4 | 9.6 | 7.5 | 3.8 | |
| T. polonicum | C | 1.8 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 21.2 | 29.3 | 20.9 | 50.1 | 54.6 | 72.9 |
| I | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 15.4 | 27.1 | 21.6 | 43.5 | 48.3 | 69.1 | |
| 1 − (I/C) (%) | 16.7 | 8.7 | 8.0 | 27.4 | 7.5 | −3.3 | 13.2 | 11.5 | 5.2 | |
| T. aestivum | C | 1.6 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 34.3 | 41.1 | 30.6 | 35.9 | 38.4 | 56.5 |
| I | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 31.6 | 35.4 | 28.6 | 28.1 | 33.9 | 49.8 | |
| 1 − (I/C) (%) | 18.8 | 20.0 | 17.4 | 7.9 | 13.9 | 6.5 | 21.7 | 11.7 | 11.9 | |
| Source of Variation | Weight of One Spike (g) | Number of Kernels per Spike | One Kernel Weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype (G) | F (13, 168) = 30.4, p < 0.00001 | F (13, 168) = 2,085.2, p < 0.00001 | F (13, 168) = 4,497, p < 0.00001 |
| Inoculation (I) | F (1, 168) = 3.8, p = 0.04925 | F (1, 168) = 785.7, p < 0.00001 | F (1, 168) = 307, p < 0.00001 |
| Year (Y) | F (2, 168) = 1.1, NS | F (2, 168) = 6,389.4, p < 0.00001 | F (2, 168) = 1,893, p < 0.00001 |
| G × I | F (13, 168) = 0.29, NS | F (13, 168) = 38.7, p < 0.00001 | F (13, 168) = 24, p < 0.00001 |
| G × Y | F (26, 168) = 0.79, NS | F (26, 168) = 183.2, p < 0.00001 | F (26, 168) = 78, p < 0.00001 |
| I × Y | F (2, 168) = 9.2, p = 0.0002 | F (2, 168) = 164.8, p < 0.00001 | F (2, 168) = 17,085, p < 0.00001 |
| G × I × Y | F (26, 168) = 3.4, p < 0.00001 | F (26, 168) = 49.0, p < 0.00001 | F (26, 168) = 292, p < 0.00001 |
| Species | Treatment | Measure | DON (8) | D-3G (1) | 3-Ac DON (2) | Deepoxy-DON (15) | NIV (5) | ZEA (2) | ZEA-4 Sulfate (1) | MON (20) | Apicidin (0.04) | Tentoxin (0.2) | AOH (30) | AME (0.8) | AUF (24) | Hexadepsipeptides † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. monococcum | C | mean | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 9 | <LOD | <LOD | 59 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 184 |
| RSD (%) | 100 | 120 | 100 | |||||||||||||
| #>LOD | 1 | 1 | - | |||||||||||||
| I | mean | 9.7 × 103 | 0.9 × 103 | 334 | 31 | 15 | 7 | 3 | 43 | <LOD | 2 | <LOD | <LOD | 1.1 × 103 | 86 | |
| RSD (%) | 67 | 50 | 74 | 107 | 10 | 81 | 116 | 110 | 132 | 40 | 30 | |||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | - | |||||
| T. dicoccon | C | mean | 248 | 32 | <LOD | <LOD | 6 | <LOD | <LOD | 14 | 0.1 | 0.4 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 76 |
| RSD (%) | 85 | 96 | 101 | 51 | 130 | 133 | 123 | |||||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | |||||||||
| I | mean | 10.8 × 103 | 0.9 × 103 | 251 | <LOD | 11 | 5 | 3 | <LOD | 0.4 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.8 × 103 | 40 | |
| RSD (%) | 65 | 74 | 52 | 113 | 65 | 80 | 165 | 76 | 25 | |||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | - | |||||||
| T. spelta | C | mean | 135 | 31 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 20 | <LOD | 1.7 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 150 |
| RSD (%) | 168 | 170 | 88 | 97 | 126 | |||||||||||
| #>LOD | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | |||||||||||
| I | mean | 7.0 × 103 | 1.4 × 103 | 186 | <LOD | 12 | 9 | 2 | 27 | <LOD | 2 | <LOD | <LOD | 1.7 × 103 | 83 | |
| RSD (%) | 45 | 24 | 53 | 47 | 143 | 88 | 25 | 99 | 117 | 89 | ||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | ||||||
| T. polonicum | C | mean | 225 | 64 | <LOD | <LOD | 55 | 1 | <LOD | 3.7 × 103 | 28.2 | 0.4 | <LOD | <LOD | 41.4 × 103 | 12.9 × 103 |
| RSD (%) | 128 | 158 | 86 | 43 | 32 | 91 | 130 | 65 | 41 | |||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | - | |||||||
| I | mean | 52.6 × 103 | 5.7 × 103 | 594 | 261 | 434 | 266 | 157 | 1.5 × 103 | 3 | 5 | 23 | 27 | 73.4 × 103 | 3.4 × 103 | |
| RSD (%) | 73 | 34 | 93 | 88 | 131 | 39 | 38 | 58 | 84 | 155 | 60 | 171 | 38 | 64 | ||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | ||
| T. aestivum | C | mean | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 7 | <LOD | <LOD | 93 | 1.3 | 3.7 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 71 |
| RSD (%) | 94 | 126 | 107 | 138 | 101 | |||||||||||
| #>LOD | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | |||||||||||
| I | mean | 35.8 × 103 | 3.4 × 103 | 2.2 × 103 | 165 | 305 | 247 | 32 | 64 | 8.0 | 0.9 | <LOD | <LOD | 15.1 × 103 | 121 | |
| RSD (%) | 128 | 106 | 138 | 135 | 131 | 134 | 137 | 54 | 141 | 126 | 135 | 81 | ||||
| #>LOD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - |
| Species | Treatmnet | Measure | DON | D-3G | 3-Ac DON | BUT | NIV | ZEA | ZEA-4 Sulfate | MON | Apicidin | Equisetin | Emodin | Tentoxin | Culmorin | 15-Hydroxy-Culmorin | 5-Hydroxy-Culmorin | AUF | Chlamydo- sporol | Avenacein Y | Hexadepsi-peptides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (8) | (1) | (2) | (25) | (5) | (2) | (1) | (20) | (0.04) | (5) | (0.50) | (0.2) | (10) | (10) | (30) | (24) | (1.5) | (15) | - | |||
| T. monococcum | C | Mean | 0.26 × 103 | 10 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 67 | 5.9 | 21 | 2 | 0.6 | 11 | 28 | <LOD | 37 | 9 | <LOD | 164 |
| RSD (%) | 36 | 11 | 37 | 79 | 124 | 152 | 73 | 50 | 30 | 22 | 82 | 56 | |||||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | |||||||||
| I | mean | 30.1 × 103 | 1.3 × 103 | 245 | 2469 | 33 | 121 | 17 | 122 | 6.9 | 33 | 14 | 0.7 | 1,409 | 2,056 | 538 | 3.7 × 103 | 12 | <LOD | 245 | |
| RSD (%) | 14 | 11 | 29 | 44 | 11 | 41 | 23 | 55 | 100 | 67 | 139 | 83 | 24 | 31 | 73 | 39 | 163 | 95 | |||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | - | |||
| T. dicoccum | C | mean | 0.52 × 103 | 30 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 16 | 1.1 | <LOD | 8 | 0.7 | 12 | <LOD | <LOD | 64 | <LOD | <LOD | 65 |
| RSD (%) | 94 | 135 | 67 | 64 | 168 | 57 | 100 | 72 | 73 | ||||||||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | ||||||||||||
| I | mean | 20.5 × 103 | 1.1 × 103 | 217 | 769 | 12 | 21 | 3 | 23 | 4.2 | 23 | 2 | 0.5 | 418 | 932 | 153 | 0.8 × 103 | <LOD | <LOD | 36 | |
| RSD (%) | 54 | 40 | 40 | 68 | 37 | 79 | 35 | 98 | 17 | 94 | 144 | 76 | 68 | 49 | 51 | 36 | 94 | ||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | ||||
| T. spelta | C | mean | 76 | 9 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 30 | 5.1 | 20 | 3 | 0.6 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 71 | 3 | <LOD | 100 |
| RSD (%) | 112 | 90 | 71 | 76 | 134 | 88 | 73 | 38 | 129 | 54 | |||||||||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | |||||||||||
| I | mean | 9.2 × 103 | 0.9 × 103 | 141 | 755 | 4 | 26 | 3 | 33 | 2.1 | 34 | 2 | <LOD | 327 | 609 | 136 | 0.9 × 103 | 3 | <LOD | 62 | |
| RSD (%) | 37 | 23 | 45 | 20 | 70 | 47 | 75 | 66 | 80 | 84 | 144 | 23 | 44 | 50 | 53 | 131 | 54 | ||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | - | ||||
| T. polonicum | C | mean | 1.5 × 103 | 0.1 × 103 | <LOD | 233 | 42 | 32 | 1 | 1507 | 14.3 | 275 | 82 | 1.6 | 37 | <LOD | <LOD | 2.0 × 103 | 148 | 1,563 | 3,570 |
| RSD (%) | 15 | 44 | 85 | 65 | 137 | 108 | 82 | 108 | 150 | 115 | 93 | 47 | 82 | 76 | 23 | 72 | |||||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | - | |||||
| I | mean | 56.1 × 103 | 4.8 × 103 | 342 | 4,168 | 121 | 1,451 | 103 | 853 | 37.3 | 499 | 20 | 1.2 | 1,875 | 4,675 | 909 | 9.0 × 103 | 110 | 479 | 2,045 | |
| RSD (%) | 25 | 18 | 15 | 50 | 54 | 28 | 34 | 48 | 55 | 88 | 64 | 36 | 45 | 49 | 45 | 29 | 42 | 42 | 53 | ||
| #>LOD | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - | ||
| T. aestivum | C | mean | 0.1 × 103 | 29 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 53 | 1.3 | 251 | 2 | 1.1 | 11 | <LOD | <LOD | 56 | 11 | <LOD | 176 |
| RSD (%) | 31 | 10 | 19 | 74 | 138 | 123 | 7 | 79 | 111 | 132 | 73 | ||||||||||
| #>LOD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | ||||||||||
| I | mean | 10.5 × 103 | 1.3 × 103 | 189 | 888 | 14 | 104 | 5 | 35 | 4.2 | 21 | 10 | 0.5 | 309 | 994 | 346 | 0.7 × 103 | 7 | 263 | 183 | |
| RSD (%) | 86 | 50 | 98 | 51 | 19 | 66 | 28 | 101 | 27 | 100 | 18 | 110 | 92 | 89 | 122 | 35 | 126 | 137 | 119 | ||
| #>LOD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Year | Treatment | 2010 | 2011 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Σ Tox | Including | Trich. B/Σ Tox (%) | Σ Tox | Including | Trich. B/Σ Tox (%) | ||||
| Trich. B | other | Trich. B | other | |||||||
| T. monococcum | C | 275 | 25 | 250 | 9.1 | 659 | 277 | 382 | 42.1 | |
| I | 14.1 × 103 | 12.8 × 103 | 1.2 × 103 | 91.1 | 42.4 × 103 | 31.7 × 103 | 10.7 × 103 | 74.7 | ||
| T. dicoccon | C | 407 | 300 | 107 | 73.7 | 785 | 557 | 228 | 71.0 | |
| I | 13.9 × 103 | 12.0 × 103 | 1.9 × 103 | 86.4 | 25.1 × 103 | 21.9 × 103 | 3.2 × 103 | 87.3 | ||
| T. spelta | C | 368 | 182 | 186 | 49.5 | 366 | 87 | 279 | 23.9 | |
| I | 10.5 × 103 | 8.7 × 103 | 1.8 × 103 | 82.7 | 13.1 × 103 | 10.3 × 103 | 2.9 × 103 | 78.1 | ||
| T. polonicum | C | 58.4 × 103 | 357 | 58.0 × 103 | 0.6 | 11.2 × 103 | 1,660 | 9,547 | 14.8 | |
| I | 13.8 × 104 | 59.6 × 103 | 78.8 × 103 | 43.1 | 87.6 × 103 | 61.4 × 103 | 26.3 × 103 | 70.0 | ||
| T. aestivum | C | 210 | 25 | 184 | 11.9 | 778 | 169 | 609 | 21.8 | |
| I | 57.5 × 103 | 41.8 × 103 | 15.6 × 103 | 72.8 | 15.9 × 103 | 12.0 × 103 | 3.9 × 103 | 75.6 | ||
| Mean | C | 11.9 × 103 | 178 | 11.7 × 103 | 28.9 | 2.8 × 103 | 550 | 2,209 | 34.7 | |
| I | 57.3 × 103 | 24.7 × 103 | 32.6 × 103 | 75.1 | 36.8 × 103 | 27.5 × 103 | 9.4 × 103 | 77.1 | ||
| Species | Line/Cultivar | Origin |
|---|---|---|
| T. monococcum | K-1 | National Centre for Plant Genetic Resources, Radzików, Poland |
| K-6 | National Centre for Plant Genetic Resources, Radzików, Poland | |
| cv. Terzino | Getreidezüchtung Karl Josef Müller, Darzau, Germany | |
| T. dicoccon | cv. Lamela | Department of Plant Breeding and Seed Production, University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland |
| cv. Bondka | Department of Plant Breeding and Seed Production, University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland | |
| P-3 | National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, USA | |
| T. spelta | K-20 | Leibniz-Institut für Pflanzengenetik und Kulturpflanzenforschung, Gatersleben, Germany |
| UWM-13 | Breeding strain from the Department of Plant Breeding and Seed Production, University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland | |
| cv. Nexon | University of Saskatchewan, Canada | |
| T. polonicum | Pol-11 | National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, USA |
| Pol-19 | National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, USA | |
| cv. Kamut * | Kamut International Ltd., USA | |
| T. aestivum | cv. Torka | Plant Breeding Strzelce Ltd., Poland |
| cv. Sumai-3 | Nanjing Agricultural University, China |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiwart, M.; Suchowilska, E.; Kandler, W.; Sulyok, M.; Wachowska, U.; Krska, R. The Response of Selected Triticum spp. Genotypes with Different Ploidy Levels to Head Blight Caused by Fusarium culmorum (W.G.Smith) Sacc. Toxins 2016, 8, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040112
Wiwart M, Suchowilska E, Kandler W, Sulyok M, Wachowska U, Krska R. The Response of Selected Triticum spp. Genotypes with Different Ploidy Levels to Head Blight Caused by Fusarium culmorum (W.G.Smith) Sacc. Toxins. 2016; 8(4):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040112
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiwart, Marian, Elżbieta Suchowilska, Wolfang Kandler, Michael Sulyok, Urszula Wachowska, and Rudolf Krska. 2016. "The Response of Selected Triticum spp. Genotypes with Different Ploidy Levels to Head Blight Caused by Fusarium culmorum (W.G.Smith) Sacc." Toxins 8, no. 4: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040112
APA StyleWiwart, M., Suchowilska, E., Kandler, W., Sulyok, M., Wachowska, U., & Krska, R. (2016). The Response of Selected Triticum spp. Genotypes with Different Ploidy Levels to Head Blight Caused by Fusarium culmorum (W.G.Smith) Sacc. Toxins, 8(4), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040112