The Draft Genome Sequence of the Yersinia entomophaga Entomopathogenic Type Strain MH96T
Abstract
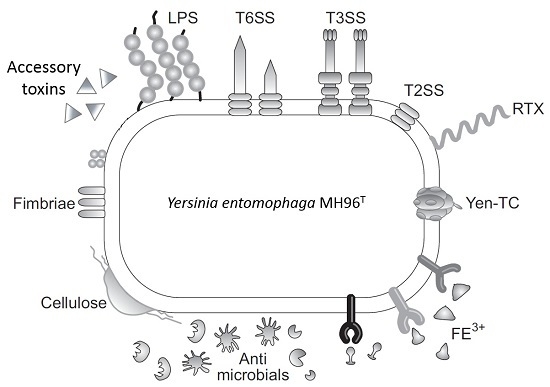
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Yersinia entomophaga Genome Summary
2.2. Putative Virulence Clusters
2.3. Rhs and Type VI-Associated Regions
2.4. Type II and III Secretion Systems
2.5. Accessory Virulence Determinants
2.6. Iron Acquisition
2.7. Proteolytic Enzymes
2.8. Cell Adhesins
2.9. Host Defense and Microbial Competition Systems
3. Discussion
3.1. Multi-Component Toxin Delivery Systems
3.2. Co-Location of Cell Adhesins or Lytic Enzymes with Virulence Determinants
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Genomic DNA Isolation
4.2. Genome Sequencing
4.3. Genome Assembly
4.4. Genome Annotation
4.5. Genome Atlas and Genome–Genome DNA Identity Comparison
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woese, C.R.; Fox, G.E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 74, 5088–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.D.; Fetherston, J.D. Yersinia pestis—Etiologic agent of plague. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ewing, W.H.A.; Ross, A.J.; Brenner, D.J.; Fanning, G.R. Yersinia ruckeri sp. nov., the redmouth (RM) bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1978, 28, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulakvelidze, A. Yersiniae other than Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. pestis: The ignored species. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Connor, T.; Barquist, L.; Walker, D.; Feltwell, T.; Harris, S.; Fookes, M.; Hall, M.; Petty, N.; Fuchs, T.; et al. Parallel independent evolution of pathogenicity within the genus Yersinia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6768–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murros-Kontiainen, A.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Korkeala, H.; Johansson, P.; Rahkila, R.; Björkroth, J. Yersinia nurmii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 61, 2368–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.A.; Imori, P.F.; Falcão, J.P. Multilocus sequence analysis and 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveal that Yersinia frederiksenii genospecies 2 is Yersinia massiliensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 3124–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, A.; Thomson, N.R.; Reuter, S.; Wren, B.W. Add, stir and reduce: Yersinia spp. as model bacteria for pathogen evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, L.; Méndez, J.; Guijarro, J.A. Molecular virulence mechanisms of the fish pathogen Yersinia ruckeri. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 125, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottone, E.J.; Bercovier, H.; Mollaret, H.H. Genus. XLI. Yersinia. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Garrity, G.M., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA; 2005; Volume 2, pp. 838–848. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; Becher, S.A.; Young, S.D.; Nelson, T.L.; Glare, T.R. Yersinia entomophaga sp. nov. isolated from the New Zealand grass grub Costelytra zealandica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 61, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, M.R.; van Koten, C.; Jackson, T.A. Pathology of Yersinia entomophaga MH96 towards Costelytra zealandica (Coleoptera; Scarabaeidae) larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 115, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; Beattie, A.; Jones, S.; Hsu, P.-C.; Calder, J.; van Koten, C. Galleria mellonella mortality as a result of Yersinia entomophaga infection is temperature-dependent. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6404–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; Jones, S.A.; Tan, B.; Harper, L.A.; Glare, T.R. The main virulence determinant of Yersinia entomophaga MH96 is a broad-host-range toxin complex active against insects. J. Bact. 2011, 193, 1966–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsberg, M.J.; Jones, S.A.; Rothnagel, R.; Busby, J.N.; Marshall, S.D.G.; Simpson, R.M.; Lott, J.S.; Hankamer, B.; Hurst, M.R.H. 3D structure of the Yersinia entomophaga toxin complex and implications for insecticidal activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 108, 20544–20549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.W.; Sandt, C.H.; Vlazny, D.A. Rhs elements of Escherichia coli: A family of genetic composites each encoding a large mosaic protein. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 12, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busby, J.N.; Landsberg, M.J.; Simpson, R.; Jones, S.A.; Hankamer, B.; Hurst, M.R.; Lott, J.S. Structural analysis of chi1 chitinase from Yen-Tc: The multisubunit insecticidal ABC toxin complex of yersinia entomophaga. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 3, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskiniemi, S.; Lamoureux, J.G.; Nikolakakis, K.C.; de Roodenbeke, C.T.; Kaplan, M.D.; Low, D.A.; Hayes, C.S. Rhs proteins from diverse bacteria mediate intercellular competition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7032–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskiniemi, S.; Garza-Sánchez, F.; Sandegren, L.; Webb, J.S.; Braaten, B.A.; Poole, S.J.; Andersson, D.I.; Hayes, C.S.; Low, D.A. Selection of orphan Rhs toxin expression in evolved Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, S.D.G.; Hares, M.C.; Jones, S.A.; Harper, L.A.; James, V.R.; Harland, D.P.; Jackson, T.A.; Hurst, M.R.H. Histolopathological effects of the Yen-Tc toxin complex from Yersina entomophaga MH96 (Enterobacteriaceae) on the midgut of Costelytra zealandica (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) larvae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4835–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects-diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Gely, I.; Lemaitre, B.; Boccard, F. Bacterial strategies to overcome insect defences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.F. The Insects: Structure and Function, 5th ed.; Simpson, S.J., Douglas, A.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge, C.; Dover, L.G. Iron metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 881–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaar, E.P. The battle for iron between bacterial pathogens and their vertebrate hosts. PLoS Pathog. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Ciche, T.; Clarke, D. Photorhabdus and a host of hosts. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen-LeRoux, C.; Gaudriault, S.; Ramarao, N.; Lereclus, D.; Givaudan, A. How the insect pathogen bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis and Xenorhabdus/Photorhabdus occupy their hosts. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.; Rocheleau, T.A.; Blackburn, M.; Andreev, O.; Golubeva, E.; Bhartia, R.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Insecticidal toxins from the bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Science 1998, 280, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchaud, E.; Rusniok, C.; Frangeul, L.; Buchrieser, C.; Givaudan, A.; Taourit, S.; Bocs, S.; Boursaux-Eude, C.; Chandler, M.; Charles, J.-F.; et al. The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.; Kamita, S.G.; Hammock, B.D.; Ffrench-Constant, R. The Photorhabdus Pir toxins are similar to a developmentally regulated insect protein but show no juvenile hormone esterase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 245, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daborn, P.J.; Waterfield, N.R.; Silva, C.P.; Au, C.P.; Sharma, S.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. A single Photorhabdus gene, makes caterpillars floppy (mcf), allows Escherichia coli to persist within and kill insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 88, 10742–10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, A.J.; Daborn, P.J.; Waterfield, N.R.; Wang, P.; Streuli, C.H.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. The insecticidal toxin Makes caterpillars floppy (Mcf) promotes apoptosis in mammalian cells. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S.A.; Brachmann, A.O.; Glazer, I.; Lango, L.; Schwär, G.; Clarke, D.J.; Bode, H.B. Bacterial biosynthesis of a multipotent stilbene. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 1942–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.J.; Seo, S.; Shrestha, S.; Kim, Y. Bacterial metabolites of an entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, inhibit a catalytic activity of phenoloxidase of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abergel, C.; Monchois, V.; Byrne, D.; Chenivesse, S.; Lembo, F.; Lazzaroni, J.C.; Claverie, J.M. Structure and evolution of the Ivy protein family, unexpected lysozyme inhibitors in Gram-negative bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6394–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckers, D.; Masschalck, B.; Aertsen, A.; Callewaert, L.; van Tiggelen, C.G.; Atanassova, M.; Michiels, C.W. Periplasmic lysozyme inhibitor contributes to lysozyme resistance in Escherichia coli. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Daborn, P.J.; ffrench-Constant, R.H. Genomic islands in Photorhabdus. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasukira, A.; Tayebwa, J.; Thwaites, R.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Aritua, V.; Kubiriba, J.; Smith, J.; Grant, M.; Studholme, D.J. Genome-wide sequencing reveals two major sub-lineages in the genetically monomorphic pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. Musacearum. Genes. 2012, 3, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurst, M.R.; Beard, S.S.; Jackson, T.A.; Jones, S.M. Isolation and characterization of the Serratia entomophila antifeeding prophage. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 270, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.-T.; Tyler, B.M.; Setubal, J.C. Protein secretion systems in bacterial-host associations, and their description in the Gene Ontology. BMC. Microbiol. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, P. Functional domains and motifs of bacterial type III effector proteins and their roles in infection. FEMS. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 1100–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foultier, B.; Troisfontaines, P.; Müller, S.; Opperdoes, F.R.; Cornelis, G.R. Characterization of the ysa pathogenicity locus in the chromosome of Yersinia enterocolitica and phylogeny analysis of type III secretion systems. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 55, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, J.C.; Skurnik, M. Adhesins of human pathogens from the genus Yersinia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 715, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.A.; Miller, V.L. Regulation of the Ysa type III secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica by YsaE/SycB and YsrS/YsrR. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 4056–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.R.; Felisberto-Rodrigues, C.; Meir, A.; Prevost, M.S.; Redzej, A.; Trokter, M.; Waksman, G. Secretion systems in Gram-negative bacteria: Structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotkov, K.V.; Sandkvist, M.; Hol, W.G. The type II secretion system: Biogenesis, molecular architecture and mechanism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, E.T.; Hill, R.B.; Kieba, I.R.; Korostoff, J. The interaction between RTX toxins and target cells. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Schauer, D.B.; Fox, J.G. In vivo virulence properties of bacterial cytolethal-distending toxin. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, L.; Cortes-Bratti, X.; Guidi, R.; Frisan, T. The biology of the cytolethal distending toxins. Toxins 2011, 3, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: An overview of their biocidal activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, G.W. Vegetative insecticidal proteins: Novel proteins for control of corn pests. In Advances in Insect Control: The Role of Transgenic Plants; Carozzi, N.B., Koziel, M.G., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1997; pp. 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Craig, J.A.; Putnam, C.D.; Carozzi, N.B.; Tainer, J.A. Evolution and mechanism from structures of an ADP-ribosylating toxin and NAD complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1999, 6, 932–936. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.-J.; Guo, Q. The adenylyl cyclase activity of anthrax edema factor. Mol. Aspects Med. 2009, 30, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, M.J.; Ching, K.H.; Heffron, F. Salmonella SsrB activates a global regulon of horizontally acquired genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jank, T.; Eckerle, S.; Steinemann, M.; Trillhaase, C.; Schimpl, M.; Wiese, S.; van Aalten, D.M.; Driever, W.; Aktories, K. Tyrosine glycosylation of Rho by Yersinia toxin impairs blastomere cell behaviour in zebrafish embryos. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, M.S.; Virdi, J.S. Strategies used by Yersinia enterocolitica to evade killing by the host: Thinking beyond Yops. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlenkamp, M.; Oberhettinger, P.; Leo, J.C.; Linke, D.; Schütz, M.S. Yersinia adhesin A (YadA)-beauty & beast. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Opota, O.; Vallet-Gély, I.; Vincentelli, R.; Kellenberger, C.; Iacovache, I.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Roussel, A.; van der Goot, F.-G.; Lemaitre, B. Monalysin, a novel β-pore-forming toxin from the Drosophila pathogen Pseudomonas entomophila, contributes to host intestinal damage and lethality. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; Glare, T.R.; Jackson, T.A. Cloning Serratia entomophila anti-feeding genes—A putative defective prophage active against the grass grub Costelytra zealandica. J. Bact. 2004, 186, 5116–5128. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneux, F.F.; Zumbihl, R.; Jubelin, G.; Ribeiro, C.; Poncet, J.; Baghdiguian, S.; Givaudan, A.; Brehélin, M. The xaxAB Genes encoding a new apoptotic toxin from the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus nematophila are present in plant and human pathogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.E.; Cao, A.T.; Dobson, P.; Hines, E.R.; Akhurst, R.J.; East, P.D. Txp40, a ubiquitous insecticidal toxin protein from Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, B.; Sekirov, I.; Finlay, B.B. Type III secretion systems and disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Young, G.M. Proteomic and functional analysis of the suite of Ysp proteins exported by the Ysa type III secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica Biovar 1B. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauvarque, M.O.; Bergeret, E.; Chabert, J.; Daucheux, D.; Satre, M.; Attree, I. Role and activation of type III secretion system genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced Drosophila killing. Microb. Pathog. 2002, 32, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Martins, B.M.; Rösch, P.; Wöhrl, B.M. Crystal structure of the human transcription elongation factor DSIF hSpt4 subunit in complex with the hSpt5 dimerization interface. Biochem. J. 2009, 425, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugirard-Ricaud, K.; Duchaud, E.; Givaudan, A.; Girard, P.A.; Kunst, F.; Boemare, N.; Brehélin, M.; Zumbihl, R. Site-specific antiphagocytic function of the Photorhabdus luminescens type III secretion system during insect colonization. Cell Microbiol. 2005, 7, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivaskumar, M.; Francetic, O. Type II secretion system: A magic beanstalk or a protein escalator. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederiksen, R.F.; Yoshimura, Y.; Storgaard, B.G.; Paspaliari, D.K.; Petersen, B.O.; Chen, K.; Larsen, T.; Duus, J.O.; Ingmer, H.; Bovin, N.V.; et al. A diverse range of bacterial and eukaryotic chitinases hydrolyzes the LacNAc (Galβ1-4GlcNAc) and LacdiNAc (GalNAcβ1-4GlcNAc) motifs found on vertebrate and insect cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5354–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, K.G.; LaRock, C.N.; D’Argenio, D.A.; Berg, C.A.; Collins, C.M. Metalloprotease secreted by the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens induces melanization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7622–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Adachi, T.; Hara, T.; Hamamoto, H.; Sekimizu, K. Identification of a Serratia marcescens virulence factor that promotes hemolymph bleeding in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 117, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaoud, M.K.; Marokházi, J.; Venekei, I. Enzymatic characterization of a serralysin-like metalloprotease from the entomopathogen bacterium, Xenorhabdus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Prot. Proteom. 2011, 1814, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Białas, N.; Kasperkiewicz, K.; Radziejewska-Lebrecht, J.; Skurnik, N. Bacterial cell surface structures in Yersinia enterocolitica. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2012, 60, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan-Miklos, S.; Rahme, L.G.; Ausubel, F.M. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms of bacterial virulence using non-mammalian hosts. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahme, L.G.; Stevens, E.J.; Wolfort, S.F.; Shao, J.; Tompkins, R.G.; Ausubel, F.M. Common virulence factors for bacterial pathogenicity in plants and animals. Science 1995, 268, 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahme, L.G.; Ausubel, F.M.; Cao, H.; Drenkard, E.; Goumnerov, B.C.; Lau, G.W.; Mahajan-Miklos, S.; Plotnikova, J.; Tan, M.W.; Tsongalis, J.; et al. Plants and animals share functionally common bacterial virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8815–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Wren, B.W.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H. Invertebrates as a source of emerging human pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heermann, R.; Fuchs, T.M. Comparative analysis of the Photorhabdus luminescens and the Yersinia enterocolitica genomes: Uncovering candidate genes involved in insect pathogenicity. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K.; Schwan, C.; Papatheodorou, P.; Lang, A.E. Bidirectional attack on the actin cytoskeleton. Bacterial protein toxins causing polymerization or depolymerization of actin. Toxicon 2012, 60, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; van der Goot, F.G. The bacterial toxin toolkit. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 2, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Dowling, A.J.; Gerike, U.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Waterfield, N.R. Photorhabdus virulence cassettes confer injectable insecticidal activity against the wax moth. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2254–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemichez, E.; Flatau, G.; Bruzzone, M.; Boquet, P.; Gauthier, M. Molecular localization of the Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor CNF1 cell-binding and catalytic domains. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owuama, C.I. Entomopathogenic symbiotic bacteria, Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus of nematodes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.P.; Peterson, D.A.; Biggs, P.J. SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crusoe, M.R.; Alameldin, H.F.; Awad, S.; Boucher, E.; Caldwell, A.; Cartwright, R.; Charbonneau, A.; Constantinides, B.; Edvenson, G.; Fay, S.; et al. The khmer software package: Enabling efficient nucleotide sequence analysis. F1000Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulies, M.; Egholm, M.; Altman, W.E.; Attiya, S.; Bader, J.S.; Bemben, L.A.; Berka, J.; Braverman, M.S.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 2005, 437, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 228, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angiuoli, S.V.; Gussman, A.; Klimke, W.; Cochrane, G.; Field, D.; Garrity, G.; Kodira, C.D.; Kyrpides, N.; Madupu, R.; Markowitz, V.; et al. Toward an online repository of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for (meta)genomic annotation. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2008, 12, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, D.M.; Kannan, L.; Coleman, M.K.; Wolf, Y.I.; Sorokin, A.; Koonin, E.V.; Mushegian, A. A low-polynomial algorithm for assembling clusters of orthologous groups from intergenomic symmetric best matches. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altermann, E.; Klaenhammer, T.R. GAMOLA: A new local solution for sequence annotation and analyzing draft and finished prokaryotic genomes. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2003, 7, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.G.; Jensen, L.J.; Brunak, S.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Ussery, D.W. A DNA structural atlas for Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 299, 907–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.S. Improved Pairwise Alignment of Genomic DNA. Ph.D. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]







| Code | Value | % of Total | COG Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 0.05 | RNA processing and modification |
| B | 0 | 0.0 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| C | 197 | 4.7 | Energy production and conversion |
| D | 32 | 0.7 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| E | 324 | 7.6 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 88 | 2.1 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| G | 238 | 5.6 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| H | 157 | 3.7 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 91 | 2.2 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| J | 180 | 4.2 | Translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis |
| K | 250 | 5.9 | Transcription |
| L | 161 | 3.8 | Replication, recombination, and repair |
| M | 208 | 4.9 | Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis |
| N | 105 | 2.5 | Cell motility |
| O | 129 | 3 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| P | 239 | 5.7 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 71 | 1.7 | Secondary metabolite biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism |
| R | 359 | 8.5 | General function prediction only |
| S | 325 | 7.7 | Function unknown |
| T | 193 | 4.5 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| U | 130 | 3.1 | Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport |
| V | 43 | 1 | Defense mechanisms |
| - | 703 | 16.6 | Not in COGs |
| Total | 4225 | - | - |
| Putative Toxin or Toxin Encoding Gene Cluster | Locus (Putative Virulence-Associated Region) 1 | Predicted Function |
|---|---|---|
| Rhs1 (Yen-TC) | PL78_03740-03770 | orally active toxin complex |
| Rhs2 (LopT) | PL78_18780 (PL78_18715-18790) | Hemoceolic active toxin |
| Rhs3 (Spt4) | PL78_00990 (PL78_00895-01045) | T6SS, hemoceolic active toxin |
| Rhs4 (T3SS, T6SS) | PL78_12135 (PL78_12045-12170) | Hemoceolic active toxin |
| Rhs5 | PL78_15070 (PL78_15035-15075) | Effector island |
| YenT (Yst) | PL78_03785 | Heat-stable enterotoxin |
| PirAB | PL78_09590-09595 | Hemoceolic active toxin |
| CdtAB | PL78_18444-18445 | Hemoceolic active toxin |
| RTX | PL78_16910 | Repeats in toxin |
| adenylate cyclase | PL78_08395 | Hemoceolic active toxin |
| Vip2 | PL78_16145 | Hemoceolic active toxin |
| LopT | PL78_18760 | T3SS effector, hemoceolic active toxin |
| T3SS1 | PL78_18075-18225 | Type three secretion system |
| T3SS2 | PL78_14485-14620 | Type three secretion system |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurst, M.R.H.; Beattie, A.; Altermann, E.; Moraga, R.M.; Harper, L.A.; Calder, J.; Laugraud, A. The Draft Genome Sequence of the Yersinia entomophaga Entomopathogenic Type Strain MH96T. Toxins 2016, 8, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050143
Hurst MRH, Beattie A, Altermann E, Moraga RM, Harper LA, Calder J, Laugraud A. The Draft Genome Sequence of the Yersinia entomophaga Entomopathogenic Type Strain MH96T. Toxins. 2016; 8(5):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050143
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurst, Mark R. H., Amy Beattie, Eric Altermann, Roger M. Moraga, Lincoln A. Harper, Joanne Calder, and Aurelie Laugraud. 2016. "The Draft Genome Sequence of the Yersinia entomophaga Entomopathogenic Type Strain MH96T" Toxins 8, no. 5: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050143
APA StyleHurst, M. R. H., Beattie, A., Altermann, E., Moraga, R. M., Harper, L. A., Calder, J., & Laugraud, A. (2016). The Draft Genome Sequence of the Yersinia entomophaga Entomopathogenic Type Strain MH96T. Toxins, 8(5), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050143