Cloning a Chymotrypsin-Like 1 (CTRL-1) Protease cDNA from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Specific Substrate of Crude N. nomurai Nematocyst Extract
2.2. N. nomurai CTRL-1 cDNA Cloning and Sequence Analysis
2.3. Evolutionary Relationships of the N. nomurai CTRL-1 Gene
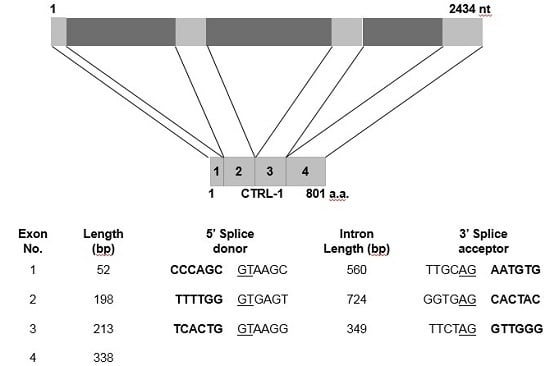
2.4. Genomic Structure of N. nomurai CTRL-1
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Procedures
4.1. Materials
4.2. Nematocyst Isolation and Venom Extraction
4.3. Amidolytic Activity Assay of N. nomurai Venom
4.4. Total RNA Extraction and Full-Length cDNA Sequence Determination
4.5. 3′- and 5′-RACE and cDNA Sequencing
4.6. Genomic DNA Extraction and PCR
4.7. Phylogenetic and Nucleotide Sequence Analysis of CTRL1
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedstrom, L. Serine protease mechanism and specificity. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4501–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krem, M.M.; Cera, E.D. Evolution of enzyme cascades from embryonic development to bold coagulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Evolutionary families of peptidases. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petra, O.; Saskia, L.; Peter, V.; Wim, D. The emergine roles of serine protease cascades in the epidermis. Cell 2009, 34, 453–463. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, B.K.; Haard, H.F. Cold-adapted enzymes from fish. In Food Biotechnology; Knorr, D., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: Quebec, QC, Cannada, 2013; pp. 495–528. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.E. Noncaspase proteases in apoptosis. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, K.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Kaplan, A.P. Activation of the kinin-forming cascade on the surface of endothelial cells. Biol. Chem. 2001, 382, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, C.; Crosby, J.A.; Moreno, R.D. Early steps of sperm-egg interactions during mammalian fertilization. Cell Biol. Int. 1996, 20, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, S.R. Thrombin signaling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 2000, 407, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essam, K. Purification and partial characterization of a chymotrypsin-like serine fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FCF-11 using corn husk as a novel substrate. Wrold J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Hanen, L.; Nacim, Z.; Nabil, M.; Youssef, G. A new chymotrypsin-like serine protease involved in dietary protein digestion in a primitive animal, Scorpio maurus: Purification and biochemical characterization. Lipids health Dis. 2011, 10, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, Z.S.; Xiao, F.Z.; Jin, X.W. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of chymotrypsin-like serine protease from the Chinese shrimp, Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Laura, G.; Massimo, A.; Bella, G. Biologically active polypeptides in the venom of the jellyfish Rhopilema nomadica. Toxicon 1997, 5, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Clemetson, J.M.; Clemetson, K.J. Snake venoms and hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.R.; El-Choufani, S.E.; Smith, M. M.; Groot, H. D. Occupational allergy to bumblebees: Allergens of Bombus terrestris. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uye, S. Blooms of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai: A threat to the fisheries sustainability of the East Asian marginal Seas. Plank. Benth. Res. 2008, 3, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Munawir, A.; Cha, M.; Sohn, E.; Lee, H. Cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity of jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, H.; Cha, M.; Sohn, E.T. Target organ identification of jellyfish envenomation using systemic and integrative analyses in anesthetized dogs. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2011, 64, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Yoon, W.; Lim, D.; Hart, A.J.; Hodgson, W.C. Cardiovascular effects of Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) jellyfish venom in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 167, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, D.; Keesing, J. Jellyfish blooms in China: Dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, R.; Kirkness, E.F.; Barker, S.C. The single mitochondrial chromosome typical of animals has evolved into 18 minichromosomes in the human body louse, Pediculus humanus. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayal, E.; Lavrov, D.V. The mitochondrial genome of Hydra oligactis (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) sheds new light on animal mtDNA evolution and cnidarian phylogeny. Gene 2008, 410, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, O.; Erpenbeck, D.; Worheide, G. A fragmented metazoan organellar genome: the two mitochondrial chromosomes of Hydra magnipapillata. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- David, R.S.; Ehsan, K.; Angel, A.Y.; Allen, G.C.; Stacy, P.; Patrick, J.K. First Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence from a Box Jellyfish Reveals a Highly Fragmented Linear Architecture and Insights into Telomere Evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2011, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitaka, I.; Yoshihiro, Y. Purification, characterization and cDNA cloning of a novel lectin from the jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 156, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chymotrypsin. Available online: http://www.altmd.com/Articles/Chymotrypsin--Encyclopedia-of-Alternative-Medicine (accessed on 30 June 2016).
- Seppa, H. The role of chymotrypsin-like protease of rat mast cells in inflammatory vasopermeability and fibrinolysis. Inflammation 1980, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, F.S., Jr. Snake Venom Fibrinogenolytic and fibrinolytic enzymes: An Updated Inventory. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 79, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.S.; Georgieva, D.; Genov, N.; Murakami, M.T.; Sinha, M.; Kumar, R.P.; Kaur, P.; Kumar, S.; Dey, S.; Sharma, S.; Vrielink, A.; Betzel, C.; Takeda, S.; Arni, R.K.; Singh, T.P.; Kini, R.M. Enzymatic toxins from snake venom: structural characterization and mechanism of catalysis. FEBS. J. 2011, 278, 4544–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breathnach, R.; Benoist, C.; O’hare, K.; Gannon, F.; Chambon, P. Ovalbumin gene: Evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 10, 4853–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breathnach, R.; Chambon, P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1981, 50, 349–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yum, S.; Shin, K.; Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology, Geoje, Korea. Whole transcriptome information in medusa of N. nomurai. Unpublished work. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- NCBI BLAST program. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ (accessed on 25 May2016).
- InterProScan search tool program. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/InterProScan/ (accessed on 30 June 2016).
- SignalP 4.1 program. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/ (accessed on 30 June 2016).
- Deduced amino acid sequence analysis program. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/emboss/align/ (accessed on 30 June 2016).






| Class | Species | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Scyphozoa | Aurelia aurita | 42 |
| Hydrozoa | Hydra vulgaris | 42 |
| Actinopterygii | Danio rerio | 48 |
| Poecilia reticulate | 43 | |
| Stegastes partitus | 43 | |
| Salmon salar | 41 | |
| Takifugu rubripes | 44 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, Y.; Kwon, Y.C.; Bae, S.K.; Hwang, D.; Yang, H.R.; Choudhary, I.; Lee, H.; Yum, S.; Shin, K.; Yoon, W.D.; et al. Cloning a Chymotrypsin-Like 1 (CTRL-1) Protease cDNA from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Toxins 2016, 8, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070205
Heo Y, Kwon YC, Bae SK, Hwang D, Yang HR, Choudhary I, Lee H, Yum S, Shin K, Yoon WD, et al. Cloning a Chymotrypsin-Like 1 (CTRL-1) Protease cDNA from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Toxins. 2016; 8(7):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070205
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Yunwi, Young Chul Kwon, Seong Kyeong Bae, Duhyeon Hwang, Hye Ryeon Yang, Indu Choudhary, Hyunkyoung Lee, Seungshic Yum, Kyoungsoon Shin, Won Duk Yoon, and et al. 2016. "Cloning a Chymotrypsin-Like 1 (CTRL-1) Protease cDNA from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai" Toxins 8, no. 7: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070205
APA StyleHeo, Y., Kwon, Y. C., Bae, S. K., Hwang, D., Yang, H. R., Choudhary, I., Lee, H., Yum, S., Shin, K., Yoon, W. D., Kang, C., & Kim, E. (2016). Cloning a Chymotrypsin-Like 1 (CTRL-1) Protease cDNA from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Toxins, 8(7), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070205