Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
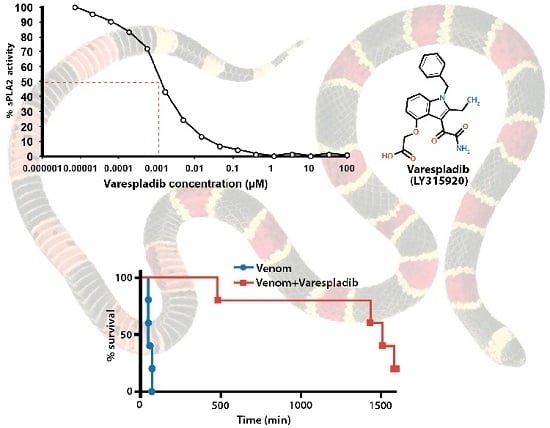
2.1. Inhibition of sPLA2 Activities in Vitro
2.2. Mouse in Vivo Pilot Experiments
2.2.1. Pretreatment with Varespladib in an Elapid Envenomation Model
2.2.2. Coinjection and Rescue against Vipera berus Venom
2.3. Rat in Vivo Modeling
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. In Vitro Experiments
5.2. Animal in Vivo Studies
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| svMP | Snake venom metalloprotease |
| SC | Subcutaneous |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| sPLA2 | secretory Phospholipase A2 |
References
- Mohapatra, B.; Warrell, D.A.; Suraweera, W.; Bhatia, P.; Dhingra, N.; Jotkar, R.M.; Rodriguez, P.S.; Mishra, K.; Whitaker, R.; Jha, P.; et al. Snakebite mortality in India: A nationally representative mortality survey. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Engmark, M.; Milbo, C.; Johannesen, J.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lohse, B. From Fangs to Pharmacology: The Future of Snakebite Envenoming Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Chappuis, F.; Jha, N.; Bovier, P.A.; Loutan, L.; Koirala, S. Impact of snake bites and determinants of fatal outcomes in southeastern Nepal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Wüster, W.; Cook, D.A.; Bolton, F.M.; King, S.I.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Harrison, R.A. Medically important differences in snake venom composition are dictated by distinct postgenomic mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9205–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, A.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Vargas, M.; Uscanga-Reynell, A.; de León-Rosales, S.P.; Jiménez-Corona, M.E.; Reta-Mares, J.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; León, G. Venom of Bothrops asper from Mexico and Costa Rica: Intraspecific variation and cross-neutralization by antivenoms. Toxicon 2012, 59, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; Maduwage, K.; Saiao, A.; Buckley, N.A.; Jayamanne, S.F.; Seyed, S.; Mohamed, F.; Chathuranga, U.; Mendes, A.; Abeysinghe, C.; et al. Population pharmacokinetics of an Indian F(ab’)2 snake antivenom in patients with Russell’s Viper (Daboia russelii) bites. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, R.J.; Monteiro, H.S.; Gonçalves-Machado, L.; Guarnieri, M.C.; Ximenes, R.M.; Borges-Nojosa, D.M.; Karla, P.D.; Zingali, R.B.; Corrêa-Netto, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops erythromelas from five geographic populations within the Caatinga ecoregion of northeastern Brazil. J. Proteom. 2015, 114, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alirol, E.; Lechevalier, P.; Zamatto, F.; Chappuis, F.; Alcoba, G.; Potet, J. Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming: What Is in the Research Pipeline? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.N.; Sahni, A.L.; Chacko, K.A.; Vijay, K. Neostigmine in the treatment of Elapidae bites. J. Assoc. Phys. India 1972, 20, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, G.; Theakston, R.D.; Hayes, C.G.; Yambao, M.L.; Sangalang, R.; Ranoa, C.P.; Alquizalas, E.; Warrell, D.A. Positive response to edrophonium in patients with neurotoxic envenoming by cobras (Naja naja philippinensis). A placebo-controlled study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, B.; Fitzmaurice, M.; Oakley, J. Resolution of neurotoxicity with anticholinesterase therapy in death-adder envenomation. Med. J. Aust. 1988, 148, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Theakston, R.D.; Phillips, R.E.; Warrell, D.A.; Galagedera, Y.; Abeysekera, D.T.; Dissanayaka, P.; de Silva, A.; Aloysius, D.J. Envenoming by the common krait (Bungarus caeruleus) and Sri Lankan cobra (Naja naja naja): Efficacy and complications of therapy with Haffkine antivenom. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 84, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranawaka, U.K.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. Neurotoxicity in snakebite-the limits of our knowledge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Harrison, R.A.; Bicknell, A.B.; Gibbins, J.M.; Hutchinson, G. Purification and functional characterisation of rhinocerase, a novel serine protease from the venom of Bitis gabonica rhinoceros. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Harrison, R.A.; Gibbins, J.M.; Hutchinson, E.G. Evolutionary analysis of novel serine proteases in the venom gland transcriptome of Bitis gabonica rhinoceros. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Thiyagarajan, N.; Hutchinson, E.G.; Gibbins, J.M. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of viper venom serine proteases. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, J.M.; Theakston, R.D.; Laing, G.D. Neutralization of the haemorrhagic activities of viperine snake venoms and venom metalloproteinases using synthetic peptide inhibitors and chelators. Toxicon 2007, 49, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnasamy, S.; Chinnasamy, S.; Nagamani, S.; Muthusamy, K. Identification of potent inhibitors against snake venom metalloproteinase (SVMP) using molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 33, 1516–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urs, A.N.; Yariswamy, M.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Joshi, V.; Suvilesh, K.N.; Savitha, M.N.; Velmurugan, D.; Vishwanath, B.S. Inhibitory potential of three zinc chelating agents against the proteolytic, hemorrhagic, and myotoxic activities of Echis carinatus venom. Toxicon 2015, 93, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Gutierrez, J.M. Effect of the metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat in the systemic toxicity induced by Bothrops asper snake venom: Understanding the role of metalloproteinases in envenomation. Toxicon 2004, 43, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paes Leme, A.F.; Escalante, T.; Pereira, J.G.; Oliveira, A.K.; Sanchez, E.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Serrano, S.M.; Fox, J.W. High resolution analysis of snake venom metalloproteinase (SVMP) peptide bond cleavage specificity using proteome based peptide libraries and mass spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.A.; Cardoso, F.F.; Cavalcante, W.G.; Soares, A.M.; Dal-Pai, M.; Gallacci, M.; Fontes, M.R. Structural Basis for the Inhibition of a Phospholipase A2-Like Toxin by Caffeic and Aristolochic Acids. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatehi, M.; Rowan, E.G.; Harvey, A.L. The effects of two phospholipase A2 inhibitors on the neuromuscular blocking activities of homologous phospholipases A2 from the venom of Pseudechis australis, the Australian king brown snake. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcussi, S.; Sant’Ana, C.D.; Oliveira, C.Z.; Quintero Rueda, A.; Menaldo, D.L.; Beleboni, R.O.; Stabeli, R.G.; Giglio, J.R.; Fontes, M.; Marcos, R.; et al. Snake venom phospholipase A2 inhibitors: Medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendra Sharath Chandra, J.N.; Ponnappa, K.C.; Sadashiva, C.T.; Priya, B.S.; Nanda, B.L.; Veerabasappa Gowda, T.; Vishwanath, B.S.; Rangappa, K.S. Chemistry and structural evaluation of different phospholipase A2 inhibitors in arachidonic acid pathway mediated inflammation and snake venom toxicity. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaramakrishnan, V.; Ilamathi, M.; Ghosh, K.S.; Sathish, S.; Gowda, T.V.; Vishwanath, B.S.; Rangappa, K.S.; Dhananjaya, B.L. Virtual analysis of structurally diverse synthetic analogs as inhibitors of snake venom secretory phospholipase A2. J. Mol. Recognit. 2016, 29, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K. Snakebite doesn’t cause disseminated intravascular coagulation: Coagulopathy and thrombotic microangiopathy in snake envenoming. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Fernández, J.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Segura, Á.; León, G.; Angulo, Y.; Paiva, O.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of the venom of the taipan snake, Oxyuranus scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia: Role of neurotoxic and procoagulant effects in venom toxicity. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, A.; Isbister, G.K.; Duffull, S.B. Effect of Australian elapid venoms on blood coagulation: Australian Snakebite Project (ASP-17). Toxicon 2013, 61, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, K.M.; Correlje, E.; Martin, C.L.; Robertson, J.D.; Isbister, G.K. Point-of-care derived INR does not reliably detect significant coagulopathy following Australian snakebite. Thromb. Res. 2013, 132, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, G.; Meade, B.D.; Theakston, R.D.; Padre, L.P.; Tuazon, M.L.; Calubaquib, C.; Santiago, E.; Ranoa, C.P. Comparison of Tensilon® and antivenom for the treatment of cobra-bite paralysis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 83, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce-Bejarano, R.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M. Intravascular hemolysis induced by the venom of the Eastern coral snake, Micrurus fulvius, in a mouse model: Identification of directly hemolytic phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2014, 90, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Suarez, P.; Nunez, V.; Fernandez, J.; Lomonte, B. Integrative characterization of the venom of the coral snake Micrurus dumerilii (Elapidae) from Colombia: Proteome, toxicity, and cross-neutralization by antivenom. J. Proteom. 2016, 136, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, I.; Castillo, E.Y.; Romero-Piña, M.E.; Torres-Viquez, I.; Paniagua, D.; Boyer, L.V.; Alagón, A.; Medina, L.A. Biodistribution and Lymphatic Tracking of the Main Neurotoxin of Micrurus fulvius Venom by Molecular Imaging. Toxins 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reading, C.J. Incidence, pathology, and treatment of adder (Vipera berus L.) bites in man. J. Accid. Emerg. Med. 1996, 13, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary, T.; Prüller, F.; Froehlich, H.; Werner, S.; Hafner, F.; Brodmann, M. Proximal lower limb vein thrombosis following Vipera berus hand bite. VASA Z. Gefasskrankh. 2010, 39, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lervik, J.B.; Lilliehook, I.; Frendin, J.H. Clinical and biochemical changes in 53 Swedish dogs bitten by the European adder—Vipera berus. Acta Vet. Scand. 2010, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, T.; Krecsak, L.; Jelić, D.; Maretić, T.; Toth, T.; Šiško, M.; Pandak, N. First clinical experiences about the neurotoxic envenomings inflicted by lowland populations of the Balkan adder, Vipera berus bosniensis. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honge, B.L.; Hedegaard, S.K.; Cederstrom, S.; Nielsen, H. Hospital Contacts after Bite by the European Adder (Vipera berus). Dan. Med. J. 2015, 61. Available online: http://www.danmedj.dk/portal/pls/portal/!PORTAL.wwpob_page.show?_docname=10693350.PDF (accessed on 22 August 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Palgan, K.; Kuzminski, A.; Janik, A.; Gotz-Zbikowska, M.; Bartuzi, Z. Snake (Vipera berus) bite: The cause of severe anaphylactic shock and hepatocellular injury. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anlen, K.G. Effects of bites by the European adder (Vipera berus) in seven Swedish horses. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, M.R. Envenomation Therapies and Related Pharmaceutical Compositions, Systems and Kits: USPTO: PCT/US2015/061834; Ophirex, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Katkar, G.D.; Sundaram, M.S.; NaveenKumar, S.K.; Swethakumar, B.; Sharma, R.D.; Paul, M.; Vishalakshi, G.J.; Devaraja, S.; Girish, K.S.; Kemparaju, K. NETosis and lack of DNase activity are key factors in Echis carinatus venom-induced tissue destruction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varespladib. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2011, 11, 137–143.
- Abraham, E.; Naum, C.; Bandi, V.; Gervich, D.; Lowry, S.F.; Wunderink, R.; Schein, R.M.; Macias, W.; Skerjanec, S.; Dmitrienko, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of LY315920Na/S-5920, a selective inhibitor of 14-kDa group IIA secretory phospholipase A2, in patients with suspected sepsis and organ failure. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiher, B.G.; Steingrub, J.; Laterre, P.F.; Dmitrienko, A.; Fukiishi, Y.; Abraham, E. LY315920NA/S-5920, a selective inhibitor of group IIA secretory phospholipase A2, fails to improve clinical outcome for patients with severe sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Fraser, H.; Goulder, M.A.; Hislop, C. Anti-inflammatory effects of varespladib methyl in diabetic patients with acute coronary syndrome. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2011, 25, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Kastelein, J.J.; Schwartz, G.G.; Bash, D.; Rosenson, R.S.; Cavender, M.A.; Brennan, D.M.; Koenig, W.; Jukema, J.W.; Nambi, V.; et al. Varespladib and cardiovascular events in patients with an acute coronary syndrome: The VISTA-16 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, M.; Lamorde, M.; Dalhat, M.M.; Habib, Z.G.; Kuznik, A. Cost-Effectiveness of Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming in 16 Countries in West Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzel, B. Snakebite in Southern India: A Threshold Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Master’s Thesis, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The toxicogenomic multiverse: Convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijon, M.A.; Perez, C.; Mendez, E.; Sanchez Crespo, M. Phospholipase A2 from plasma of patients with septic shock is associated with high-density lipoproteins and C3 anaphylatoxin: Some implications for its functional role. Biochem. J. 1995, 306 Pt 1, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.H.; Ponnudurai, G. The biological properties of venoms of some American coral snakes (Genus micrurus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Comp. Biochem. 1992, 101, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucaretchi, F.; Hyslop, S.; Vieira, R.J.; Toledo, A.S.; Madureira, P.R.; Capitani, E.M. Bites by coral snakes (Micrurus spp.) in Campinas, State of Sao Paulo, Southeastern Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2006, 48, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, G.D.; Furtado Mde, F.; Portaro, F.C.; Sant’Anna, O.A.; Tambourgi, D.V. Diversity of Micrurus snake species related to their venom toxic effects and the prospective of antivenom neutralization. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, G.D.; Pidde-Queiroz, G.; de Fatima, D.F.M.; van den Berg, C.; Tambourgi, D.V. Micrurus snake venoms activate human complement system and generate anaphylatoxins. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, B.R.; da Silva, N.J.; Seebart, C.; Silva, L.L.; Schmidt, J.J.; Kaiser, I.I. Toxins isolated from the venom of the Brazilian coral snake (Micrurus frontalis frontalis) include hemorrhagic type phospholipases A2 and postsynaptic neurotoxins. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, R.; Mukherjee, A.K. Purification and characterization of an anticoagulant phospholipase A(2) from Indian monocled cobra (Naja kaouthia) venom. Toxicon 2003, 41, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Urs, N.; Hiremath, V.; Vishwanath, B.S.; Doley, R. Biochemical and biological characterization of Naja kaouthia venom from North-East India and its neutralization by polyvalent antivenom. J. Venom Res. 2013, 4, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warrell, D.A.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Williams, D. New approaches & technologies of venomics to meet the challenge of human envenoming by snakebites in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, L.V.; Pla, D.; Herrera, M.; Chippaux, J.P.; Calvete, J.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Evaluation of the preclinical efficacy of four antivenoms, distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, to neutralize the venom of the carpet viper, Echis ocellatus, from Mali, Cameroon, and Nigeria. Toxicon 2015, 106, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Arias, A.S.; Rodríguez, Y.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Sánchez, L.V.; Chippaux, J.P.; Pla, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Preclinical evaluation of three polyspecific antivenoms against the venom of Echis ocellatus: Neutralization of toxic activities and antivenomics. Toxicon 2016, 119, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduwage, K.; Buckley, N.A.; de Silva, H.J.; Lalloo, D.G.; Isbister, G.K. Snake antivenom for snake venom induced consumption coagulopathy. Cochrane Database Syste. Rev. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Venom | Geographic Range | Varespladib IC50 µM | Me-Varespladib IC50 µM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bee Venom | Worldwide | 13.25 | * Indeterminate |
| Acanthophis antarcticus (Common death adder) | Australia/PNG | 0.0006 | Not tested |
| Agkistrodon blomhoffii brevicaudus (Mamushi) | SE Asia, Japan | 0.0005 | 0.04 |
| Agkistrodon contortrix (Copperhead) | N. America | 0.0002 | Not tested |
| Agkistrodon piscivorus (Cottonmouth) | N. America | 0.0003 | Not tested |
| Bitis gabonica (Gaboon viper) | Africa | 0.0003 | Not tested |
| Bothrops asper (Fer-de-lance) | S. America | 0.0001 | Not tested |
| Bothrops jararaca (Jararaca) | S. America | 0.0002 | Not tested |
| Bungarus caeruleus (Common krait) | India/Asia | 0.0001 | 0.02 |
| Bungarus fasciatus (Banded krait) | India/Asia | 0.00003 | 0.01 |
| Calloselasma rhodostoma (Malayan pit viper) | SE Asia | 0.002 | Not tested |
| Crotalus adamanteus (Eastern diamondback rattlesnake) | N. America | 0.0002 | 0.02 |
| Crotalus atrox (Western diamondback rattlesnake) | N. America | 0.0003 | 0.04 |
| Crotalus durissus terrificus (South American rattlesnake) | S. America | 0.005 | 0.26 |
| Crotalus scutulatus scutulatus (Mojave green rattlesnake) | N. America | 0.002 | 0.21 |
| Dendroaspis polylepis (Black mamba) | Africa | 0.00003 | 0.02 |
| Echis carinatus (Saw-scaled viper) | India/Pakistan | 0.00006 | 0.009 |
| Laticauda semifasciata (Banded sea krait) | Pacific Ocean | 0.00006 | 0.02 |
| Micrurus fulvius (Eastern coral snake) | N. America | 0.001 | 0.08 |
| Naja naja atra (Chinese cobra) | China/Taiwan | 0.0008 | 0.01 |
| Naja naja kaouthia (Monocled cobra) | India/Asia | 0.00005 | 0.02 |
| Naja naja naja (Spectacled or Indian cobra) | India | 0.001 | 0.02 |
| Notechis scutatus scutatus (Tiger snake) | Australia | 0.00006 | 0.03 |
| Ophiophagus hannah (King cobra) | India/Asia | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Oxyuranus scutellatus (Coastal taipan) | Australia/PNG | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| Pseudechis australis (Mulga snake) | Australia | 0.003 | 0.09 |
| Trimersurus elegans (Elegant pit viper) | SE Asia | 0.0007 | Not tested |
| Vipera berus (Common European adder) | Europe/Asia | 0.00002 | 0.03 |
| Vipera russelli (Russell’s viper) | India/Asia | 0.0006 | 0.02 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090248
Lewin M, Samuel S, Merkel J, Bickler P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins. 2016; 8(9):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewin, Matthew, Stephen Samuel, Janie Merkel, and Philip Bickler. 2016. "Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation" Toxins 8, no. 9: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090248
APA StyleLewin, M., Samuel, S., Merkel, J., & Bickler, P. (2016). Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins, 8(9), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8090248