Assessment of Inheritance and Fitness Costs Associated with Field-Evolved Resistance to Cry3Bb1 Maize by Western Corn Rootworm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
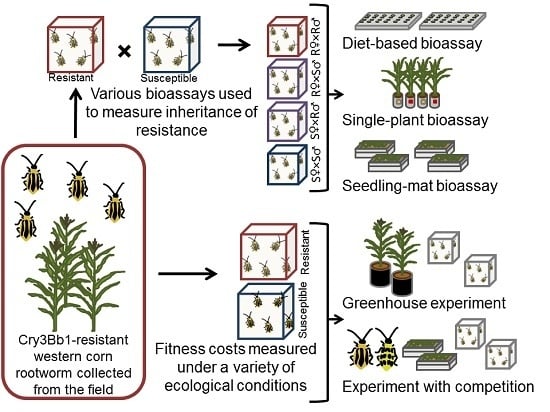
2.1. Quantifying Inheritance of Resistance to Cry3Bb1
2.2. Greenhouse Assessment of Fitness Costs
2.3. Effect of Competition on Fitness Costs
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Rootworm Strains
4.2. Strain Rearing
4.3. Quantifying Inheritance of Resistance to Cry3Bb1
4.4. Greenhouse Experiment Testing for Fitness Costs
4.5. Competition Experiment Testing for Fitness Costs
4.6. Data Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, M.E.; Sappington, T.W.; Miller, N.J.; Moeser, J.; Bohn, M.O. Adaptation and invasiveness of western corn rootworm: Intensifying research on a worsening pest. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahler, A.L.; Olness, A.E.; Sutter, G.R.; Dybing, C.D.; Devine, O.J. Root damage by western corn rootworm and nutrient content in maize. Agron. J. 1985, 77, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, Z.; Mitchell, P.D.; Agosti, M. Estimating Diabrotica virgifera virgifera damage functions with field trial data: Applying an unbalanced nested error component model. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, H.J.; Weekman, G.T. Insecticide resistance in the adult western corn rootworm in Nebraska. J. Econ. Entomol. 1962, 55, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinke, L.J.; Siegfried, B.D.; Wright, R.J.; Chandler, L.D. Adult susceptibility of Nebraska western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) populations to selected insecticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 1998, 91, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.E.; Wang, H.; Zukoff, S.N.; Meinke, L.J.; French, B.W.; Siegfried, B.D. Evidence of field-evolved resistance to bifenthrin in western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte) populations in western Nebraska and Kansas. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, E.; Spencer, J.L.; Isard, S.A.; Onstad, D.W.; Gray, M.E. Adaptation of the western corn rootworm to crop rotation: Evolution of a new strain in response to a management practice. Am. Entomol. 2002, 48, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Petzold-Maxwell, J.L.; Keweshan, R.S.; Dunbar, M.W. Field-evolved resistance to Bt maize by western corn rootworm. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Petzold-Maxwell, J.L.; Keweshan, R.S.; Dunbar, M.W. Western corn rootworm and Bt maize: Challenges of pest resistance in the field. GM Crops Food 2012, 3, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Petzold-Maxwell, J.L.; Clifton, E.H.; Dunbar, M.W.; Hoffmann, A.M.; Ingber, D.A.; Keweshan, R.S. Field-evolved resistance by western corn rootworm to multiple Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in transgenic maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5141–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangila, D.S.; Gassmann, A.J.; Petzold-Maxwell, J.L.; French, B.W.; Meinke, L.J. Susceptibility of Nebraska western corn rootworm populations (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) populations to Bt corn events. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakka, S.R.K.; Shrestha, R.B.; Gassmann, A.J. Broad-spectrum resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins by western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biopesticides Registration Action Document: Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Bb1 Protein and the Genetic Material Necessary for Its Production (Vector PV-ZMIR13L) in MON 863 Corn (OECD Unique Identifier: MON-ØØ863-5). Available online: http://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/pip/cry3bb1-brad.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2017).
- Oswald, K.J.; French, B.W.; Nielson, C.; Bagley, M. Selection for Cry3Bb1 resistance in a genetically diverse population of nondiapausing western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitloff, J.; Dunbar, M.W.; Ingber, D.A.; Hibbard, B.E.; Gassmann, A.J. Effects of refuges on the evolution of resistance to transgenic corn by the western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meihls, L.N.; Higdon, M.L.; Siegfried, B.D.; Miller, N.J.; Sappington, T.W.; Ellersieck, M.R.; Spencer, T.A.; Hibbard, B.E. Increased survival of western corn rootworm on transgenic corn within three generations of on-plant greenhouse selection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19177–19182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Shrestha, R.B.; Jakka, S.R.K.; Dunbar, M.W.; Clifton, E.H.; Paolino, A.R.; Ingber, D.A.; French, B.W.; Masloski, K.E.; Doudna, J.W.; et al. Evidence of resistance to Cry34/35Ab1 corn by western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): Root injury in the field and larval survival in plant-based bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1872–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zukoff, S.N.; Ostlie, K.R.; Potter, B.; Meihls, L.N.; Zukoff, A.L.; French, L.; Ellersieck, M.R.; French, B.W.; Hibbard, B.E. Multiple assays indicate varying levels of cross resistance in Cry3Bb1-selected field populations of the western corn rootworm to mCry3A, eCry3.1Ab, and Cry34/35Ab1. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwick, D.C.; Meihls, L.N.; Ostlie, K.R.; Potter, B.D.; French, L.; Hibbard, B.E. Minnesota field population of western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) shows incomplete resistance to Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 and Cry3Bb1. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, P.M.; Estes, R.E.; Tinsley, N.A.; Gassmann, A.J.; Gray, M.E. Evaluation of adult emergence and larval root injury for Cry3Bb1-resistant populations of the western corn rootworm. J. Appl. Entomol. 2016, 141, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Current and Previously Registered Section 3 Plant-Incorporated Protectant (PIP) Registrations. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/current-previously-registered-section-3-plant-incorporated (accessed on 21 March 2017).
- Gould, F. Sustainability of transgenic insecticidal cultivars: Integrating pest genetics and ecology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 701–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, A.J. Field-evolved resistance to Bt maize by western corn rootworm: Predictions from the laboratory and effects in the field. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Brevault, T.; Carriere, Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: Lessons from the first billion acres. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Carrière, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E. Fitness costs of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, D.W.; Carrière, Y. Comparing the refuge strategy for managing the evolution of resistance under different reproductive strategies. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 261, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janmaat, A.F.; Myers, J. The cost of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis varies with the host plant of Trichoplusia ni. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. Ser. B 2005, 272, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, L.J.; Akhurst, R.J. Effects of host plant species on fitness costs of Bt resistance in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biol. Control 2007, 40, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, Y.; Ellers-Kirk, C.; Biggs, R.; Degain, B.; Holley, D.; Yafuso, C.; Evans, P.; Dennehy, T.J.; Tabashnik, B.E. Effects of cotton cultivar on fitness costs associated with resistance of pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) to Bt cotton. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, B.; Sayyed, A.H.; Hails, R.S.; Wright, D.J. Exploiting pathogens and their impact on fitness costs to manage the evolution of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Stock, S.P.; Carrière, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E. Effect of entomopathogenic nematodes on the fitness cost of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 105, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Stock, S.P.; Sisterson, M.S.; Carrière, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E. Synergism between entomopathogenic nematodes and Bacillus thuringiensis crops: Integrating biological control and resistance management. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, B.; Sayyed, A.H.; Wright, D.J. Genes and environment interact to determine the fitness costs of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. Ser. B 2005, 272, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meihls, L.N.; Higdon, M.L.; Ellersieck, M.R.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Hibbard, B.E. Greenhouse-selected resistance to Cry3Bb1-producing corn in three western corn rootworm populations. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, K.J.; French, B.W.; Nielson, C.; Bagley, M. Assessment of fitness costs in Cry3Bb1-resistant and susceptible western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) laboratory colonies. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 136, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold-Maxwell, J.L.; Cibils-Stewart, X.; French, B.W.; Gassmann, A.J. Adaptation by western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) to Bt maize: Inheritance, fitness costs, and feeding preference. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.M.; French, B.W.; Hellmich, R.L.; Lauter, N.; Gassmann, A.J. Fitness costs of resistance to Cry3Bb1 maize by western corn rootworm. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 139, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.M.; French, B.W.; Jaronski, S.T.; Gassmann, A.J. Effects of entomopathogens on mortality of western corn rootworm and fitness costs of resistance to Cry3Bb1 maize. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingber, D.A.; Gassmann, A.J. Inheritance and fitness costs of resistance to Cry3Bb1 corn by western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Gassmann, A.J.; Crowder, D.W.; Carrière, Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: Evidence versus theory. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Final Report of the FIFRA Scientific Advisory Panel Subpanel on Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Plant-Pesticides and Resistance Management. Available online: http://archive.epa.gov/scipoly/sap/meetings/web/pdf/finalfeb.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2017).
- Gassmann, A.J. Resistance to Bt maize by western corn rootworm: Insights from the laboratory and the field. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 15, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andow, D.A.; Pueppke, S.G.; Schaafsma, A.W.; Gassmann, A.J.; Sappington, T.W.; Meinke, L.J.; Mitchell, P.D.; Hurley, T.M.; Hellmich, R.L.; Porter, R.P. Early detection and mitigation of resistance to Bt maize by western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comins, H.N. The development of insecticide resistance in the presence of migration. J. Theor. Biol. 1977, 64, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E. Reversing insect adaptation to transgenic insecticidal plants. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. Ser. B 2001, 268, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toepfer, S.; Kuhlmann, U. Natural mortality factors acting on western corn rootworm: A comparison between the United States and Central Europe. In Western Corn Rootworm: Ecology and Management; Vidal, S., Kuhlmann, U., Edwards, C.R., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2005; pp. 95–120. [Google Scholar]
- Carrière, Y.; Ellers-Kirk, C.; Patin, A.L.; Sims, M.A.; Meyer, S.; Liu, Y.-B.; Dennehy, T.J.; Tabashnik, B.E. Overwintering cost associated with resistance to transgenic cotton in the pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Finson, N.; Groeters, F.R.; Moar, W.J.; Johnson, M.W.; Lou, K.; Adang, M.J. Reversal of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in Plutella xylostella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4120–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrière, Y.; Crowder, D.W.; Tabashnik, B.E. Evolutionary ecology of insect adaptation to Bt crops. Evol. Appl. 2010, 3, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.N.; Andow, D.A.; Buschman, L.L. Success of the high-dose/refuge resistance management strategy after 15 years of Bt crop use in North America. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 140, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, N.P.; Babcock, J.M.; Schlenz, M.; Meade, T.; Thompson, G.D.; Bing, J.W.; Huchaba, R.M. Discovery and characterization of field resistance to Bt maize: Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Puerto Rico. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rensburg, J.B.J. Evaluation of Bt-transgenic maize for resistance to the stem borers Busseola fusca (Fuller) and Chilo partellus (Swinhoe) in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 1999, 16, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensburg, J.B.J. First report of field resistance by stem borer, Busseola fusca (Fuller) to Bt-transgenic maize. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2007, 24, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, C.; Bernardi, O.; Salmeron, E.; Sorgatto, R.J.; Dourado, P.M.; Crivellari, A.; Carvalho, R.A.; Willse, A.; Martinelli, S.; Head, G.P. Field-evolved resistance to Cry1Ab maize by Spodoptera frugiperda in Brazil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branson, T.F. The selection of a non-diapausing strain of Diabrotica virgifera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1976, 19, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; French, B.W.; Sumerford, D.V.; Sappington, T.W. Genetic diversity in laboratory colonies of western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), including a nondiapausing colony. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.J. Rearing and handling of Diabrotica virgifera virgifera and Diabrotica umdecimpunctata howardi. In Methods for the Study of Pest Diabrotica; Krysan, J.L., Miller, T.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hammack, L.; French, B.W. Sexual dimorphism of basitarsi in pest species of Diabrotica and Cerotoma (Coleoptera : Chrysomelidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2007, 100, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, B.D.; Vaughn, T.T.; Spencer, T. Baseline susceptibility of western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) to Cry3Bb1 Bacillus thuringiensis toxin. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.H.; Musick, G.J.; Fairchild, M.L. Apparatus and procedure for separation of corn rootworm eggs from soil. J. Econ. Entomol. 1966, 59, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, R.C.; Milliken, G.A.; Stroup, W.W.; Wolfinger, R.D. SAS System for Linear Models; SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, G.P.; Keough, M.J. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Tabashnik, B.E. Inheritance of resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1C in the diamondback moth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




| Experiment | Effect | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elma seedling mat a | Strain | 3,117 | 26.86 | <0.0001 |
| Hybrid | 1,117 | 366.08 | <0.0001 | |
| Strain × Hybrid | 3,117 | 27.92 | <0.0001 | |
| Monona seedling mat b | Strain | 2,13 | 6.98 | 0.0087 |
| Hybrid | 1,11 | 41.05 | <0.0001 | |
| Strain × Hybrid | 2,13 | 10.32 | 0.0021 | |
| Monona single plant c | Strain | 2,135 | 3.72 | 0.0268 |
| Hybrid | 1,135 | 30.14 | <0.0001 | |
| Strain × Hybrid | 2,135 | 4.11 | 0.0185 |
| Strain | df | χ2 | p | LC50 a (95% FL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible | 3 | 1.57 | 0.6653 | 6.09 (2.22 to 10.01) |
| Heterozygote | 3 | 2.93 | 0.4022 | 32.90 (19.53 to 49.74) |
| Monona | 3 | 8.08 | 0.0443 | >341.60 |
| Analysis | Effect | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development rate | Strain | 1,58 | 0.03 | 0.8651 |
| Sex | 1,58 | 11.14 | 0.0015 | |
| Strain × Sex | 1,58 | 0.03 | 0.8537 | |
| Survival | Strain | 1,30 | 0.18 | 0.6713 |
| Size | Strain | 1,58 | 0.69 | 0.6913 |
| Sex | 1,58 | 0.02 | 0.9018 | |
| Strain × Sex | 1,58 | 0.25 | 0.6186 | |
| Adult lifespan | Strain | 1,58 | 0.52 | 0.4746 |
| Sex | 1,58 | 3.02 | 0.0877 | |
| Strain × Sex | 1,58 | 0.70 | 0.4059 | |
| Egg viability | Strain | 1,30 | 0.71 | 0.4072 |
| Experiment | Effect | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible vs. Monona | Strain | 1,30 | 0.62 | 0.4370 |
| Week | 8,227 | 78.74 | <0.0001 | |
| Strain × Week | 8,227 | 1.21 | 0.3720 | |
| Susceptible vs. Elma | Strain | 1,37 | 0.03 | 0.8681 |
| FA a | 1,37 | 8.51 | 0.0060 | |
| SCR b | 1,37 | 1.58 | 0.2164 | |
| Strain × FA | 1,37 | 1.40 | 0.2438 | |
| Strain × SCR | 1,37 | 0.70 | 0.4083 | |
| FA × SCR | 1,37 | 1.17 | 0.2863 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR | 1,37 | 0.07 | 0.7965 | |
| Week | 6,169 | 30.67 | <0.0001 | |
| Strain × Week | 6,169 | 0.43 | 0.8577 | |
| FA × Week | 6,169 | 5.97 | <0.0001 | |
| SCR × Week | 6,169 | 1.32 | 0.2505 | |
| Strain × FA × Week | 5,169 | 1.53 | 0.1839 | |
| Strain × SCR × Week | 6,169 | 1.10 | 0.3655 | |
| FA × SCR × Week | 5,169 | 0.63 | 0.6764 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR × Week | 5,169 | 0.15 | 0.9788 |
| Analysis | Effect | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development Rate | Strain | 1,78 | 7.73 | 0.0068 |
| FA a | 1,78 | 20.89 | <0.0001 | |
| Sex | 1,78 | 15.31 | 0.0002 | |
| SCR b | 1,78 | 1.02 | 0.3149 | |
| Strain × FA | 1,78 | 2.39 | 0.1260 | |
| Strain × Sex | 1,78 | 2.74 | 0.1017 | |
| Strain × SCR | 1,78 | 2.54 | 0.1149 | |
| FA × Sex | 1,78 | 7.59 | 0.0073 | |
| FA × SCR | 1,78 | 0.74 | 0.3938 | |
| Sex × SCR | 1,78 | 3.26 | 0.0749 | |
| Strain × FA × Sex | 1,78 | 0.49 | 0.4861 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR | 1,78 | 0.22 | 0.6434 | |
| Strain × Sex × SCR | 1,78 | 0.25 | 0.6175 | |
| FA × Sex × SCR | 1,78 | 0.00 | 0.9532 | |
| Strain × FA × Sex × SCR | 1,78 | 1.92 | 0.1695 | |
| Survival | Strain | 1,50 | 0.54 | 0.4644 |
| FA | 1,50 | 124.58 | <0.0001 | |
| SCR | 1,50 | 34.2 | <0.0001 | |
| Strain × FA | 1,50 | 0.02 | 0.8831 | |
| Strain × SCR | 1,50 | 0.08 | 0.7827 | |
| FA × SCR | 1,50 | 1.33 | 0.2540 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR | 1,50 | 0.21 | 0.6466 | |
| Size | Strain | 1,73 | 0.04 | 0.8363 |
| FA | 1,73 | 1.25 | 0.2668 | |
| Sex | 1,73 | 1.84 | 0.1792 | |
| SCR | 1,73 | 3.94 | 0.0508 | |
| Strain × FA | 1,73 | 0.08 | 0.7718 | |
| Strain × Sex | 1,73 | 0.00 | 0.9944 | |
| Strain × SCR | 1,73 | 0.41 | 0.5225 | |
| FA × Sex | 1,73 | 1.17 | 0.2830 | |
| FA × SCR | 1,73 | 0.03 | 0.8546 | |
| Sex × SCR | 1,73 | 0.97 | 0.3279 | |
| Strain × FA × Sex | 1,73 | 0.00 | 0.9649 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR | 1,73 | 0.00 | 0.9907 | |
| Strain × Sex × SCR | 1,73 | 0.33 | 0.5677 | |
| FA × Sex × SCR | 1,73 | 0.02 | 0.8918 | |
| Strain × FA × Sex × SCR | 1,73 | 0.33 | 0.5664 | |
| Adult Lifespan | Strain | 1,74 | 0.32 | 0.5732 |
| FA | 1,74 | 2.39 | 0.1261 | |
| Sex | 1,74 | 3.01 | 0.0871 | |
| SCR | 1,74 | 0.47 | 0.4952 | |
| Strain × FA | 1,74 | 0.1 | 0.7563 | |
| Strain × Sex | 1,74 | 0.04 | 0.8405 | |
| Strain × SCR | 1,74 | 0.04 | 0.8369 | |
| FA × Sex | 1,74 | 3.94 | 0.0509 | |
| FA × SCR | 1,74 | 1.24 | 0.2698 | |
| Sex × SCR | 1,74 | 1.47 | 0.2297 | |
| Strain × FA × Sex | 1,74 | 0.01 | 0.9417 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR | 1,74 | 0.36 | 0.5493 | |
| Strain × Sex × SCR | 1,74 | 0.68 | 0.4123 | |
| FA × Sex × SCR | 1,74 | 3.35 | 0.0712 | |
| Strain × FA × Sex × SCR | 1,74 | 0.63 | 0.4304 | |
| Egg Viability | Strain | 1,18 | 0.27 | 0.6111 |
| FA | 1,18 | 0.5 | 0.4891 | |
| SCR | 1,18 | 0.37 | 0.5486 | |
| Strain × FA | 1,18 | 0.26 | 0.6149 | |
| Strain × SCR | 1,18 | 0.16 | 0.6907 | |
| FA × SCR | 1,18 | 0.98 | 0.3349 | |
| Strain × FA × SCR c | - | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paolino, A.R.; Gassmann, A.J. Assessment of Inheritance and Fitness Costs Associated with Field-Evolved Resistance to Cry3Bb1 Maize by Western Corn Rootworm. Toxins 2017, 9, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050159
Paolino AR, Gassmann AJ. Assessment of Inheritance and Fitness Costs Associated with Field-Evolved Resistance to Cry3Bb1 Maize by Western Corn Rootworm. Toxins. 2017; 9(5):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050159
Chicago/Turabian StylePaolino, Aubrey R., and Aaron J. Gassmann. 2017. "Assessment of Inheritance and Fitness Costs Associated with Field-Evolved Resistance to Cry3Bb1 Maize by Western Corn Rootworm" Toxins 9, no. 5: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050159
APA StylePaolino, A. R., & Gassmann, A. J. (2017). Assessment of Inheritance and Fitness Costs Associated with Field-Evolved Resistance to Cry3Bb1 Maize by Western Corn Rootworm. Toxins, 9(5), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050159