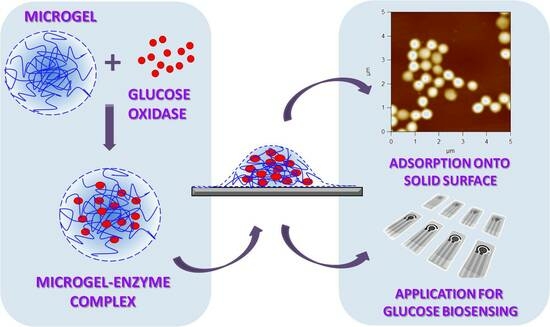
Adsorption of Preformed Microgel–Enzyme Complexes as a Novel Strategy toward Engineering Microgel-Based Enzymatic Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Microgel–Enzyme Complexes
2.3. Potentiometric Titration
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering and Laser Microelectrophoresis
2.5. Fabrication of Electrochemical Microgel–Enzyme Constructs
2.6. Electrochemical Assay
2.7. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D)
2.8. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanefeld, U.; Gardossi, L.; Magner, E. Understanding enzyme immobilisation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.; Meyer, L.E.; Kara, S. Enzyme immobilization in hydrogels: A perfect liaison for efficient and sustainable biocatalysis. Eng. Life Sci. 2022, 22, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehipour, M.; Rezaei, S.; Yazdani, M.; Mogharabi-Manzari, M. Recent advances in preparation of polymer hydrogel composites and their applications in enzyme immobilization. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 5861–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, N.C.; Gaur, D.; Tripathi, B.P. Responsive microgels and microgel assemblies in biocatalytic applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguruma, H. Biosensors: Enzyme Immobilization Chemistry. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry: Surface Science and Electrochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Enzyme immobilization: The quest for optimum performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1289–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Abetxuko, A.; Sánchez-deAlcázar, D.; Muñumer, P.; Beloqui, A. Tunable Polymeric Scaffolds for Enzyme Immobilization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H.; Winnik, F.M. Non-ionic thermoresponsive polymers in water. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 242, 29–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Responsive polymers for biosensing and protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2444–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberg, A.; Yu, X.; Kuckling, D. Responsive polymers as smart carriers in tunable catalytic processes. In Smart Polymer Catalysts and Tunable Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Huck, W.T.S.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M.; et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pich, A.; Richtering, W. Microgels by Precipitation Polymerization: Synthesis, Characterization, and Functionalization. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2010, 234, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertle, Y.; Hellweg, T. Thermoresponsive copolymer microgels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5874–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Functional Microgels and Microgel Systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Agrawal, R. Functional Microgels: Recent Advances in Their Biomedical Applications. Small 2018, 14, 1801724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.; Pich, A.; Hellweg, T.; Hoare, T.; Lyon, A.L.; Crassous, J.; Suzuki, D.; Gumerov, R.A.; Schneider, S.; Potemkin, I.I.; et al. Nanogels and Microgels: From Model Colloids to Applications, Recent Developments, and Future Trends. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6231–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijitta, J.; Schurtenberger, P. Responsive hydrogel colloids: Structure, interactions, phase behavior, and equilibrium and nonequilibrium transitions of microgel dispersions. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface. Sci. 2019, 40, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Avais, M.; Chattopadhyay, S. Microgels as Smart Polymer Colloids for Sensing and Environmental Remediation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 1626–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Gladyr, S.Y.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Mergel, O.; Pergushov, D.V.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Dual-stimuli-sensitive microgels as a tool for stimulated spongelike adsorption of biomaterials for biosensor applications. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Mergel, O.; Evtushenko, E.G.; Gladyr, S.Y.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Pergushov, D.V.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Engineering Systems with Spatially Separated Enzymes via Dual-Stimuli-Sensitive Properties of Microgels. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13029–13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Pergushov, D.V.; Oelmann, M.; Schwarz, S.; Brugnoni, M.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Plamper, F.A.; Fery, A.; Richtering, W. Surface functionalization by stimuli-sensitive microgels for effective enzyme uptake and rational design of biosensor setups. Polymers 2018, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Pergushov, D.V.; Gladyr, S.Y.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Richtering, W. Microgels in Tandem with Enzymes: Tuning Adsorption of a pH- and Thermoresponsive Microgel for Improved Design of Enzymatic Biosensors. Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 2022, 9, 2200310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Gladyr, S.Y.; Mergel, O.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Noyong, M.; Simon, U.; Pergushov, D.V.; Kurochkin, I.N.; Plamper, F.A.; Richtering, W. Easy-Preparable Butyrylcholinesterase/Microgel Construct for Facilitated Organophosphate Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigolaeva, L.V.; Efremova, O.V.; Pergushov, D.V. Temperature behavior of glucose oxidase immobilized into surface-attached stimuli-sensitive copolymer microgel. Mendeleev Commun. 2023, 33, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergel, O.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Wünnemann, P.; Böker, A.; Simon, U.; Plamper, F.A. Selective Packaging of Ferricyanide within Thermoresponsive Microgels. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 26199–26211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dontsova, E.A.; Zeifman, Y.S.; Budashov, I.A.; Eremenko, A.V.; Kalnov, S.L.; Kurochkin, I.N. Screen-printed carbon electrode for choline based on MnO2 nanoparticles and choline oxidase/polyelectrolyte layers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 159, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Akhtar, S.; Bhakuni, V. Monovalent cation-induced conformational change in glucose oxidase leading to stabilization of the enzyme. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pergushov, D.V.; Sigolaeva, L.V.; Balabushevich, N.G.; Sharifullin, T.Z.; Noyong, M.; Richtering, W. Loading of doxorubicin into surface-attached stimuli-responsive microgels and its subsequent release under different conditions. Polymer 2021, 213, 123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juska, V.B.; Pemble, M.E. A critical review of electrochemical glucose sensing: Evolution of biosensor platforms based on advanced nanosystems. Sensors 2020, 20, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.; Vyas, C.; Grieve, B.; Bartolo, P. Recent advances in enzymatic and non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Ahiabu, A.; Serpe, M.J. Sequential and controlled release of small molecules from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel-based reservoir devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5144–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walta, S.; Pergushov, D.V.; Oppermann, A.; Steinschulte, A.A.; Geisel, K.; Sigolaeva, L.V.; Plamper, F.A.; Wöll, D.; Richtering, W. Microgels enable capacious uptake and controlled release of architecturally complex macromolecular species. Polymer 2017, 119, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelissen, A.P.H.; Scotti, A.; Turnhoff, S.K.; Janssen, C.; Radulescu, A.; Pich, A.; Rudov, A.A.; Potemkin, I.I.; Richtering, W. An anionic shell shields a cationic core allowing for uptake and release of polyelectrolytes within core-shell responsive microgels. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 4287–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Sample | Dh, nm | μE, (μm × cm)/(V × s) | ζ-Potential, mV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microgel | 710 ± 10 | +1.249 ± 0.036 | +16.0 ± 0.4 |
| Microgel–enzyme complex [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:80 | 790 ± 70 | +1.287 ± 0.051 | +16.4 ± 0.7 |
| Microgel–enzyme complex [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:40 | 1370 ± 300 | +0.297 ± 0.078 | +3.8 ± 1.0 |
| Sample | Number of Objects Per Scan (1) | Object Height, nm (2) | Object Diameter, nm (2),(3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microgel | 2 ± 1 | 44 ± 7 (n = 6) | 675 ± 24 (n = 6) |
| Microgel–enzyme complex [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:80 | 8 ± 2 | 84 ± 16 (n = 30) | 614 ± 54 (n = 30) |
| Microgel–enzyme complex [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:40 | 37 ± 7 | 133 ± 13 (n = 35) | 593 ± 33 (n = 35) |
| Way 1 | Way 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SPE/MnO2/Microgel (pH 7)/GO | 120 ± 30 | SPE/MnO2/Microgel-GO [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:80 | 250 ± 65 |
| SPE/MnO2/Microgel (pH 9.5)/GO | 380 ± 55 | SPE/MnO2/Microgel-GO [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:40 | 550 ± 110 |
| Analytical Parameter | System | |
|---|---|---|
| SPE/MnO2/Microgel (pH 9.5)/GO | SPE/MnO2/Microgel-GO [GO]:[DMAPMA] = 1:80 | |
| Sensitivity, A/(M × cm2) | 0.0162 | 0.00746 |
| Linear range, μM | 0.5–1000 | 1.0–2000 |
| Limit of detection (S/N = 3), μM | 0.5 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sigolaeva, L.V.; Shalybkova, A.A.; Sharifullin, T.Z.; Pergushov, D.V. Adsorption of Preformed Microgel–Enzyme Complexes as a Novel Strategy toward Engineering Microgel-Based Enzymatic Biosensors. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081629
Sigolaeva LV, Shalybkova AA, Sharifullin TZ, Pergushov DV. Adsorption of Preformed Microgel–Enzyme Complexes as a Novel Strategy toward Engineering Microgel-Based Enzymatic Biosensors. Micromachines. 2023; 14(8):1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081629
Chicago/Turabian StyleSigolaeva, Larisa V., Anna A. Shalybkova, Timur Z. Sharifullin, and Dmitry V. Pergushov. 2023. "Adsorption of Preformed Microgel–Enzyme Complexes as a Novel Strategy toward Engineering Microgel-Based Enzymatic Biosensors" Micromachines 14, no. 8: 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081629
APA StyleSigolaeva, L. V., Shalybkova, A. A., Sharifullin, T. Z., & Pergushov, D. V. (2023). Adsorption of Preformed Microgel–Enzyme Complexes as a Novel Strategy toward Engineering Microgel-Based Enzymatic Biosensors. Micromachines, 14(8), 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081629