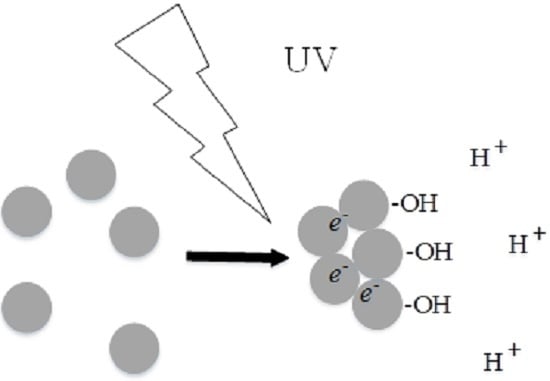
UV Light–Induced Aggregation of Titania Submicron Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Aggregation Experiments
2.2. Particle Mobility Measurement
3. Theory
3.1. Particle Mobility and Zeta Potential
3.2. DLVO Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Aggregation under UV Light
4.2. Particle Mobility
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pak, O.S.; Gao, W.; Wang, J.; Lauga, E. High-speed propulsion of flexible nanowire motors: Theory and experiments. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8169–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mou, F.; Chen, C.; You, M.; Yin, Y.; Xu, L.; Guan, J. Light-controlled bubble propulsion of amorphous TiO2/Au janus micromotors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Si, T.; Gao, W.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; He, Q. Superfast near-infrared light-driven polymer multilayer rockets. Small 2016, 12, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, W.; Pei, A.; Ren, B. Highly efficient light-driven TiO2–Au janus micromotors. ACS Nano 2015, 10, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlick, R.A.; Sengupta, S.; McFadden, T.; Zhang, H.; Sen, A. A polymerization-powered motor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9374–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibele, M.; Mallouk, T.E.; Sen, A. Schooling behavior of light-powered autonomous micromotors in water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3308–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Singh, V.V.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Orozco, J.; Kaufmann, K.; Dong, R.; Gao, W.; Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Fedorak, Y.; Wang, J. Water-driven micromotors for rapid photocatalytic degradation of biological and chemical warfare agents. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11118–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Leung, M.K.; Leung, D.Y.; Sumathy, K. A review and recent developments in photocatalytic water-splitting using TiO2 for hydrogen production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Diaz, M.; Córdova-Figueroa, U.M.; Sen, A. Light-driven titanium-dioxide-based reversible microfireworks and micromotor/micropump systems. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.W.; Zhou, D.; Mielke, R.; Keller, A.A. Photoinduced disaggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles enables transdermal penetration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Bennett, S.W.; Keller, A.A. Increased mobility of metal oxide nanoparticles due to photo and thermal induced disagglomeration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Guo, L.-H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L. UV irradiation induced transformation of TiO2 nanoparticles in water: Aggregation and photoreactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11962–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, X.; Hua, Z.; Ma, W.; Dai, Z.; Huang, X.; Gu, H. Uniformly distributed anatase TiO2 nanoparticles on graphene: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic application. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 599, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhang, J.; Bai, X.; Ye, Z.; Tang, Z.; Liang, L.; Liu, Y. Aggregation of TiO2-graphene nanocomposites in aqueous environment: Influence of environmental factors and UV irradiation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Qi, N.; Ao, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Qian, J. Effect of UV irradiation on the aggregation of TiO2 in an aquatic environment: Influence of humic acid and pH. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandzy, N.; Grulke, E.; Druffel, T. Breakage of TiO2 agglomerates in electrostatically stabilized aqueous dispersions. Powder Technol. 2005, 160, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Romoser, A.; Banerjee, N.; Zebda, R.; Sayes, C.M. The relationship between pH and Zeta potential of ~30 nm metal oxide nanoparticle suspensions relevant to in vitro toxicological evaluations. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, B.J.; Hasselbrink, E.F. Zeta potential of microfluidic substrates: 2. Data for polymers. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, Á.V.; González-Caballero, F.; Hunter, R.; Koopal, L.; Lyklema, J. Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 194–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, H. A simple expression for henry’s function for the retardation effect in electrophoresis of spherical colloidal particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 168, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, J.; Yu, J. New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20382–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, N.; Fujishima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Quantitative evaluation of the photoinduced hydrophilic conversion properties of TiO2 thin film surfaces by the reciprocal of contact angle. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sakai, N.; Fujishima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Studies of surface wettability conversion on TiO2 single-crystal surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.-I.; Nosaka, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A. Time-dependent behavior of active oxygen species formed on photoirradiated TiO2 films in air. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. pH-dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. IV. Update and new approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttiponparnit, K.; Jiang, J.; Sahu, M.; Suvachittanont, S.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Biswas, P. Role of surface area, primary particle size, and crystal phase on titanium dioxide nanoparticle dispersion properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barisik, M.; Atalay, S.; Beskok, A.; Qian, S. Size dependent surface charge properties of silica nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Bashirzadeh, Y.; Bernadowski, T.A.; Zhang, X. UV Light–Induced Aggregation of Titania Submicron Particles. Micromachines 2016, 7, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110203
Zhou C, Bashirzadeh Y, Bernadowski TA, Zhang X. UV Light–Induced Aggregation of Titania Submicron Particles. Micromachines. 2016; 7(11):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Can, Yashar Bashirzadeh, Timothy A. Bernadowski, and Xiaoyu Zhang. 2016. "UV Light–Induced Aggregation of Titania Submicron Particles" Micromachines 7, no. 11: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110203
APA StyleZhou, C., Bashirzadeh, Y., Bernadowski, T. A., & Zhang, X. (2016). UV Light–Induced Aggregation of Titania Submicron Particles. Micromachines, 7(11), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7110203