Influence of Asymmetry and Driving Forces on the Propulsion of Bubble-Propelled Catalytic Micromotors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Setup
2.2. Numerical Simulation and Numerical Model
3. Results and Discussion
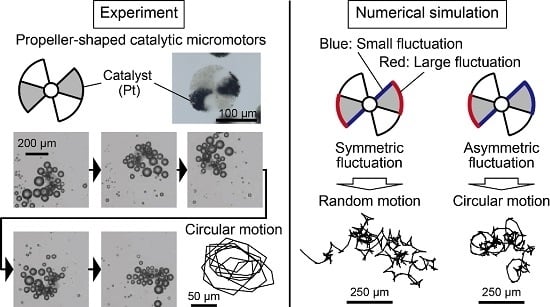
3.1. Experimental Observation of Bubble-Propelled Motions of Propeller-Shaped Micromotors
3.2. Numerical Analyses of Bubble-Propelled Motions of Propeller-Shaped Micromotors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howse, J.R.; Jones, R.A.L.; Ryan, A.J.; Gough, T.; Vafabakhsh, R.; Golestanian, R. Self-motile colloidal particles: From directed propulsion to random Walk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 048102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, R.J.; Campbell, A.I.; Ebbens, S.J. Glancing angle metal evaporation synthesis of catalytic swimming Janus colloids with well defined angular velocity. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 6872–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxton, W.F.; Kistler, K.C.; Olmeda, C.C.; Sen, A.; St. Angelo, S.K.; Cao, Y.; Mallouk, T.E.; Lammert, P.E.; Crespi, V.H. Catalytic nanomotors: Autonomous movement of striped nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13424–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, D.; Mukai, A.; Okita, N.; Yoshikawa, K.; Shioi, A. Catalytic micromotor generating self-propelled regular motion through random fluctuation. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 034705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, D.; Takada, T.; Tachibana, M.; Iijima, Y.; Shioi, A.; Yoshikawa, K. Micromotors working in water through artificial aerobic metabolism. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13186–13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fei, S.; Byun, Y.-M.; Lammert, P.E.; Crespi, V.H.; Sen, A.; Mallouk, T.E. Dynamic interactions between fast microscale rotors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9926–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jewell, E.L.; Wang, W.; Mallouk, T.E. Catalytically driven assembly of trisegmented metallic nanorods and polystyrene tracer particles. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2501–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Duan, W.; Sen, A.; Mallouk, T.E. Catalytically powered dynamic assembly of rod-shaped nanomotors and passive tracer particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17744–17749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y. Designing catalytic nanomotors by dynamic shadowing growth. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, G.; Pumera, M. Beyond platinum: Bubble-propelled micromotors based on Ag and MnO2 catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2719–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Pei, A.; Wang, J. Water-driven micromotors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8432–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, M.; Itkonen, T.; Janis, J. Bubble-propelled trimetallic microcaps as functional catalytic micromotors. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13171–13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Orozco, J.; Wang, J. Highly efficient catalytic microengines: Template electrosynthesis of polyaniline/platinum microtubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11862–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Pumera, M. Geometric asymmetry driven Janus micromotors. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11177–11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Leong, Y.J.; Rozen, I.; Qu, X.; Dong, R.; Wu, Z.; Gao, W.; Chung, P.H.; Wang, J.; et al. 3D-printed artificial microfish. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4411–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golestanian, R.; Liverpool, T.B.; Ajdari, A. Propulsion of a molecular machine by asymmetric distribution of reaction products. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 220801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbens, S.; Jones, R.A.L.; Ryan, A.J.; Golestanian, R.; Howse, J.R. Self-assembled autonomous runners and tumblers. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 015304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, U.; Soler, L.; Gibbs, J.G.; Sanchez, S.; Fischer, P. Surface roughness-induced speed increase for active Janus micromotors. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8660–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theurkauff, I.; Cottin-Bizonne, C.; Palacci, J.; Ybert, C.; Bocquet, L. Dynamic clustering in active colloidal suspensions with chemical signaling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 268303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Qian, S.; Zhao, Y.; Qiao, R. Self-diffusiophoresis of Janus catalytic micromotors in confined geometries. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5580–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbens, S.; Tu, M.-H.; Howse, J.R.; Golestanian, R. Size dependence of the propulsion velocity for catalytic Janus-sphere swimmers. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 020401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjare, M.; Yang, B.; Zhao, Y.-P. Bubble driven quasioscillatory translational motion of catalytic micromotors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 128305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, N. Selecting the swimming mechanisms of colloidal particles: Bubble propulsion versus self-diffusiophoresis. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, J.G.; Zhao, Y.-P. Autonomously motile catalytic nanomotors by bubble propulsion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 163104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Wang, J. Catalytically propelled micro-/nanomotors: How fast can they move? Chem. Rec. 2012, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Wang, J. The environmental impact of micro/nanomachines: A review. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3170–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovev, A.A.; Sanchez, S.; Pumera, M.; Mei, Y.F.; Schmidt, O.G. Magnetic control of tubular catalytic microbots for the transport, assembly, and delivery of micro-objects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lin, X.; He, Q.; Li, J. Autonomous movement of controllable assembled Janus capsule motors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10910–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovev, A.A.; Xi, W.; Gracias, D.H.; Harazim, S.M.; Deneke, C.; Sanchez, S.; Schmidt, O.G. Self-propelled nanotools. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, D.A.; Campbell, A.I.; Ebbens, S.J. Effect of catalyst distribution on spherical bubble swimmer trajectories. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 15339–15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, G.; Pumera, M. Crucial role of surfactants in bubble-propelled microengines. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5268–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.; Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Wagner, G.; Gao, W.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Galarnyk, M.; Cortés, A.; Saintillan, D.; Wang, J. Bubble-propelled micromotors for enhanced transport of passive tracers. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5082–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.; Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Escarpa, A.; Wang, J. Template electrosynthesis of high-performance graphene microengines. Small 2015, 11, 3568–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quéré, D. Wetting and roughness. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Moo, J.G.S.; Pumera, M. From nanomotors to micromotors: The influence of the size of an autonomous bubble-propelled device upon its motion. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5041–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilan, B.; Gao, W.; Pei, A.; Rozen, I.; Dong, R.; Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Wang, J.; Saintillan, D. Motion-based threat detection using microrods: Experiments and numerical simulations. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7833–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, M.; Onoe, H.; Nagai, K.H.; Takinoue, M. Complex-shaped three-dimensional multi-compartmental microparticles generated by diffusional and Marangoni microflows in centrifugally discharged droplets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Onoe, H.; Takinoue, M.; Takeuchi, S. Controlled synthesis of 3D multi-compartmental particles with centrifuge-based microdroplet formation from a multi-barrelled capillary. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylis, J.R.; Yeon, J.H.; Thomson, M.H.; Kazerooni, A.; Wang, X.; St. John, A.E.; Lim, E.B.; Chien, D.; Lee, A.; Zhang, J.Q.; et al. Self-propelled particles that transport cargo through flowing blood and halt hemorrhage. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Dong, R.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Li, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Artificial micromotors in the mouse’s stomach: A step toward in vivo use of synthetic motors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayakawa, M.; Onoe, H.; Nagai, K.H.; Takinoue, M. Influence of Asymmetry and Driving Forces on the Propulsion of Bubble-Propelled Catalytic Micromotors. Micromachines 2016, 7, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7120229
Hayakawa M, Onoe H, Nagai KH, Takinoue M. Influence of Asymmetry and Driving Forces on the Propulsion of Bubble-Propelled Catalytic Micromotors. Micromachines. 2016; 7(12):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7120229
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayakawa, Masayuki, Hiroaki Onoe, Ken H. Nagai, and Masahiro Takinoue. 2016. "Influence of Asymmetry and Driving Forces on the Propulsion of Bubble-Propelled Catalytic Micromotors" Micromachines 7, no. 12: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7120229
APA StyleHayakawa, M., Onoe, H., Nagai, K. H., & Takinoue, M. (2016). Influence of Asymmetry and Driving Forces on the Propulsion of Bubble-Propelled Catalytic Micromotors. Micromachines, 7(12), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7120229