Micro-Electromechanical Acoustic Resonator Coated with Polyethyleneimine Nanofibers for the Detection of Formaldehyde Vapor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Device Configuration and Fabrication
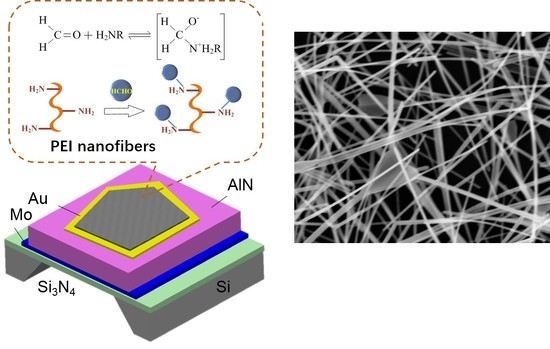
2.1. Schematic Structure and Sensing Mechanism
2.2. Fabrication of Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator (FBAR) Device
2.3. Electrospinning Deposition of Polyethyleneimine (PEI) Nanofibers
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Resonator
3.2. Effect of Deposition Time on the Formaldehyde Response
3.3. Sensitive Performance of the Optimized Sensor
3.4. Influence of Relative Humidity
3.5. Selectivity of the Sensors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, M.E.; Blicharz, A.P.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F.; Garshick, E.; Smith, T.J. Occupational exposure to volatile organic compounds and aldehydes in the U.S. trucking industry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7152–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marć, M.; Zabiegała, B.; Namieśnik, J. Testing and sampling devices for monitoring volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds in indoor air. TrAC Trends in Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, J.; Choi, N.J.; Song, H.; Lee, D.S. Nonstoichiometric Co-rich ZnCo2O4 hollow nanospheres for high performance formaldehyde detection at ppb levels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3233–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Han, N.; Zhang, D.; Ho, J.C.; Chen, Y. Highly formaldehyde-sensitive, transition-metal doped ZnO nanorods prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 169, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, P. Formaldehyde sensing properties of electrospun NiO-doped SnO2 nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 156, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosefian, M.; Raissi, H.; Mola, A. The hybrid of Pd and SWCNT (Pd loaded on SWCNT) as an efficient sensor for the formaldehyde molecule detection: A DFT study. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 212, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Shi, K.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xie, H. Fabrication and characterization of amino group functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) formaldehyde gas sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Sheng, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J. Multi-wall carbon nanotube gas sensors modified with amino-group to detect low concentration of formaldehyde. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 168, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Boampong, S.; Peng, J.S.; Carlan, J.; Belbruno, J.J. A molecularly imprinted fluoral-p/polyaniline double layer sensor system for selective sensing of formaldehyde. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppel, C.C.W. Acoustic wave filter technology-A review. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2017, 64, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.Y. Radio frequency bulk acoustic wave filters: Current status and future prospective. IEEE Trans. Electron. Inf. Syst. 2013, 133, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, C.; Merugu, S.; Singh, N.; Gu, Y. A High Coupling Coefficient 2.3-GHz AlN Resonator for High Band LTE Filtering Application. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1344–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Gan, Y.; Sun, X.; Jin, Y. High sensitive self-assembled monolayer modified solid mounted resonator for organophosphate vapor detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4365–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ashley, G.M.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Jin, H.; Luo, J.; Flewitt, A.J.; Lu, J.R. Protein functionalized ZnO thin film bulk acoustic resonator as an odorant biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 163, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.J.; Li, D.H.; Xu, Y. Hydrogen sensor based on Pd-functionalized film bulk acoustic resonator. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 159, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Tang, N.; Qu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Pang, W.; Duan, X. Detection of volatile organic compounds by self-assembled monolayer coated sSensor array with concentration-independent fingerprints. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pan, F.; Ashley, G.M.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Luo, J.; Flewitt, A.J.; Milne, W.I.; Lu, J.R. Label-free detection of human prostate-specific antigen (HPSA) using film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs). Sens. Actuators B 2014, 190, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J. Real-time monitoring of human blood clotting using a lateral excited film bulk acoustic resonator. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiculescu, I.; Nordin, A.N. Acoustic wave based MEMS devices for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Song, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q. Micro-electromechanical film bulk acoustic sensor for plasma and whole blood coagulation monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, W.; Zhao, H.; Kim, E.S.; Zhang, H.; Yuc, H.; Hu, X. Piezoelectric microelectromechanical resonant sensors for chemical and biological detection. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, D. A pure shear mode ZnO film resonator for the detection of organophosphorous pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 171–172, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, W. ZnO Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator for the Kinetics Study of Human Blood Coagulation. Sensors 2017, 17, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, Q. A poly(vinylidene fluoride)-coated ZnO film bulk acoustic resonator for nerve gas detection. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 085017–085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Liu, W.-H.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.-Y. A micro-machined thin film electro-acoustic biosensor for detection of pesticide residuals. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. C-Comput. Electron. 2014, 15, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Cui, W.; Pang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Duan, X. Kinetic studies of microfabricated biosensors using local adsorption strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W. Label-free immunosensor based on micromachined bulk acoustic resonator for the detection of trace pesticide residues. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 190, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Gu, H. A biosensor based on a film bulk acoustic resonator and biotin-avidin system for the detection of the epithelial tumor marker mucin 1. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 66355–66359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.; Jiménez, C.; Trigo, C.; Ibarra, P.; Rana, D.; Thiruganesh, R.; Ramalingam, M.; Haidar, Z.S. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring: A powerful tool for bionanoscience and drug discovery. J. Bionanosci. 2015, 9, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, Y.; Quan, W.; Liu, B. Enhanced sensitivity of ammonia sensor using graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 178, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khassaf, H.; Khakpash, N.; Sun, F.; Sbrockey, N.M.; Tompa, G.S.; Kalkur, T.S.; Alpay, S.P. Strain engineered barium strontium titanate for tunable thin film resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 202902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Highly sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides by acetylcholinesterase-coated thin film bulk acoustic resonator mass-loading sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Highly sensitive lateral field excited piezoelectric film acoustic enzyme biosensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Tang, N.; Qu, H.; Liu, J.; Pang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Duan, X. Detection of volatile organic compounds using microfabricated resonator array functionalized with supramolecular monolayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17893–17903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Solidly mounted resonators operated in thickness shear mode based on c-axis oriented AlN films. Sens. Actuators A 2011, 165, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingjing, W.; Da, Z.; Ke, W.; Weiwei, H. The detection of formaldehyde using microelectromechanical acoustic resonator with multiwalled carbon nanotubes-polyethyleneimine composite coating. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 015003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Pan, N. Nanoporous polystyrene fibers functionalized by polyethyleneimine for enhanced formaldehyde sensing. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 152, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Sun, M.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Nanofibrous polyethyleneimine membranes as sensitive coatings for quartz crystal microbalance-based formaldehyde sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 144, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, F.; Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Functionalized nanoporous TiO2 fibers on quartz crystal microbalance platform for formaldehyde sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 171–172, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, H.; Bao, X.; He, Y.; Du, X.; Xie, G.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced formaldehyde-sensing performances of mixed polyethyleneimine-multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite films on quartz crystal microbalance. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiang, Y.; Shang, Y. Basic Origanic Chemistry; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 350–351. ISBN 9787302186571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Marma, M.S.; Kim, E.S.; McKenna, C.E. Thompson, M.E. A film bulk acoustic resonator in liquid environments. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 1911–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, P.; Liu, W. Sensing characteristics of pure-shear film bulk acoustic resonator in viscous liquids. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 31, 1750086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, J.; Dai, W.; Cernigliaro, G.; Sun, H. Ultrasensitive quartz crystal microbalance enabled by micropillar structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, J.; Su, C.F.; Dai, W.; Cernigliaro, G.; Sun, H. An ultrasensitive quartz crystal microbalance-micropillars based sensor for humidity detection. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 224501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.R.; Tzeng, C.T.; Ke, M.T.; Lee, C.Y. Formaldehyde gas sensors: A review. Sensors 2013, 13, 4468–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramod, N.G.; Pandey, S.N.; Sahay, P.P. Sn-doped In2O3 nanocrystalline thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis: Microstructural, optical, electrical, and formaldehyde-sensing characteristics. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, G.D. Theory of high overtone bulk acoustic wave resonator as a gas sensor. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar and Wireless Communications, MIKON 2000, Wroclaw, Poland, 22–24 May 2000; pp. 469–472. [Google Scholar]
- Cranston, E.D.; Eita, M.; Johansson, E.; Netrval, J.; Salajková, M.; Arwin, H.; Wagberg, L. Determination of Young’s modulus for nanofibrillated cellulose multilayer thin films using buckling mechanics. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penza, M.; Aversa, P.; Cassano, G.; Suriano, D.; Wlodarski, W.; Benetti, M.; Cannatà, D.; Pietrantonio, F.D.; Verona, E. Thin-film bulk-acoustic-resonator gas sensor functionalized with a nanocomposite langmuir-blodgett layer of carbon nanotubes. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2008, 55, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, Y. Solvent effects on vibrational spectra of hydrogen-bonded complexes of formaldehyde and water: An ab initio study. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 1997, 391, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Yang, L.; Yu, W.; Wu, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Micro-Electromechanical Acoustic Resonator Coated with Polyethyleneimine Nanofibers for the Detection of Formaldehyde Vapor. Micromachines 2018, 9, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020062
Chen D, Yang L, Yu W, Wu M, Wang W, Wang H. Micro-Electromechanical Acoustic Resonator Coated with Polyethyleneimine Nanofibers for the Detection of Formaldehyde Vapor. Micromachines. 2018; 9(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Da, Lei Yang, Wenhua Yu, Maozeng Wu, Wei Wang, and Hongfei Wang. 2018. "Micro-Electromechanical Acoustic Resonator Coated with Polyethyleneimine Nanofibers for the Detection of Formaldehyde Vapor" Micromachines 9, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020062
APA StyleChen, D., Yang, L., Yu, W., Wu, M., Wang, W., & Wang, H. (2018). Micro-Electromechanical Acoustic Resonator Coated with Polyethyleneimine Nanofibers for the Detection of Formaldehyde Vapor. Micromachines, 9(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9020062