On AC-Field-Induced Nonlinear Electroosmosis next to the Sharp Corner-Field-Singularity of Leaky Dielectric Blocks and Its Application in on-Chip Micro-Mixing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
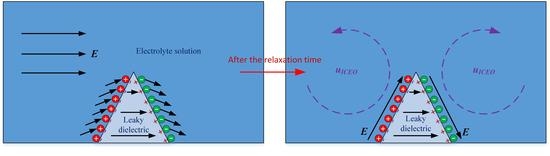
2.1. Design of the Chip Structure for Studying ICEO Next to Leaky Dielectric Block
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.3. Numerical Simulation
2.4. Impedance Analysis
2.5. Mixing Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vortex Streaming of Induce-Charge Electroosmosis Next to a Leaky Dielectric Block
3.1.1. Effect of Solid Block Conductivity
3.1.2. Effect of Solution Conductivity
3.1.3. Effect of Permittivity of Leaky Dielectric Obstruction
3.2. Microfluidic Mixing with High-Frequency ICEO
3.2.1. Effect of the AC Voltage Signal on ICEO Fluid Motion
3.2.2. ICEO Micromixer with Sharp Protrusions of Leaky Dielectric Blocks
Mixer with One Pair of Solid Obstacles
A. Optimization of Block Width
B. Inter-Block Separation
C. Effect of Voltage Amplitude and Inlet Flow Rate on Sample Mixing
Design of Integrated Microfluidic Mixers
Mixing with Smaller Voltages
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ai, Y.; Beskok, A.; Gauthier, D.T.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S. Dc electrokinetic transport of cylindrical cells in straight microchannels. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 044110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Thornton, K.; Ajdari, A. Diffuse-charge dynamics in electrochemical systems. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 021506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.J.; Kim, D.; Erickson, D. Electrokinetic microfluidic devices for rapid, low power drug delivery in autonomous microsystems. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, X.; Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, H. A simplified microfluidic device for particle separation with two consecutive steps: Induced charge electro-osmotic prefocusing and dielectrophoretic separation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9583–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ory, S.; Ehud, Y. The Taylor-Melcher leaky dielectric model as a macroscale electrokinetic description. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 773, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Helmholtz, H. Studien über electrische Grenzschichten. Ann. Der Phys. 1879, 243, 337–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A. Electrokinetics and Electrohydrodynamics in Microsystems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 530. [Google Scholar]
- Yariv, E. “Force-free” electrophoresis? Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 031702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, S.C. Capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shao, J.; Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y. Trapping and chaining self-assembly of colloidal polystyrene particles over a floating electrode by using combined induced-charge electroosmosis and attractive dipole–dipole interactions. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8105–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C. Advances in electrokinetics and their applications in micro/nano fluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 179–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, V.; Hopkins, B.J.; Schieke, J. Electro-osmosis: A new concept for high-speed liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1974, 99, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Li, D. Multiscale phenomena in microfluidics and nanofluidics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, T.M. Induced-charge electrokinetics: Fundamental challenges and opportunities. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yariv, E.; Miloh, T. Electro-convection about conducting particles. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 595, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yossifon, G.; Frankel, I.; Miloh, T. Macro-scale description of transient electro-kinetic phenomena over polarizable dielectric solids. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 620, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canpolat, C.; Zhang, M.; Rosen, W.; Qian, S.; Beskok, A. Induced-charge electroosmosis around touching metal rods. J. Fluids Eng. 2013, 135, 021103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Lazo, I.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Induced-charge electro-osmosis around metal and janus spheres in water: Patterns of flow and breaking symmetries. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boymelgreen, A.; Yossifon, G. Observing electrokinetic Janus particle–channel wall interaction using microparticle image velocimetry. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8243–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, N.G.; Ramos, A.; González, A.; Morgan, H.; Castellanos, A. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. I. Experimental measurements. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.G.; Ramos, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Morgan, H.; Castellanos, A. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. III. Observation of streamlines and numerical simulation. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 026305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Ramos, A.; Green, N.G.; Castellanos, A.; Morgan, H. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. II. A linear double-layer analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdari, A. Pumping liquids using asymmetric electrode arrays. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, L.H.; Bruus, H.; Ajdari, A. Ac electrokinetic micropumps: The effect of geometrical confinement, faradaic current injection, and nonlinear surface capacitance. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 056313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ben, Y.; Battigelli, D.; Chang, H.-C. Long-range ac electroosmotic trapping and detection of bioparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Squires, T.M. Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena: Theory and microfluidic applications. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 066101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, T.M.; Bazant, M.Z. Induced-charge electro-osmosis. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 509, 217–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Ben, Y. Theoretical prediction of fast 3D AC electro-osmotic pumps. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.; Smith, C.; Rennie, A. Pumping of water with ac electric fields applied to asymmetric pairs of microelectrodes. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 63, 016305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.; Morgan, H.; Green, N.G.; González, A.; Castellanos, A. Pumping of liquids with traveling-wave electroosmosis. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 084906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Ramos, A.; García-Sánchez, P.; Castellanos, A. Effect of the combined action of faradaic currents and mobility differences in ac electro-osmosis. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 016320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, B.P.; Heyderman, L.J.; Gobrecht, J.; Stemmer, A. Electro-osmotic streaming on application of traveling-wave electric fields. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 036305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.K.; Morganti, D.; Jiang, H.Y.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. Electrorotation of metallic microspheres. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2128–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sánchez, P.; Ren, Y.; Arcenegui, J.J.; Morgan, H.; Ramos, A. Alternating current electrokinetic properties of gold-coated microspheres. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13861–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q. On traveling-wave field-effect flow control for simultaneous induced-charge electroosmotic pumping and mixing in microfluidics: Physical perspectives and theoretical analyzes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascall, A.J.; Squires, T.M. Induced charge electro-osmosis over controllably contaminated electrodes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 088301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Tao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Hou, L.; Li, W.; Jiang, H. Flexible particle flow-focusing in microchannel driven by droplet-directed induced-charge electroosmosis. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Q.; Ren, Y.; Cui, P.; Yao, B.; Li, Y.; Hui, M.; Jiang, T.; Bai, L. On the bipolar dc flow field-effect-transistor for multifunctional sample handing in microfluidics: A theoretical analysis under the debye–huckel limit. Micromachines 2018, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Lang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Hou, L.; Jiang, H. Scaled particle focusing in a microfluidic device with asymmetric electrodes utilizing induced-charge electroosmosis. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canpolat, C. Induced-charge electro-osmotic flow around cylinders with various orientations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 231, 4057–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canpolat, C.; Qian, S.; Beskok, A. Micro-PIV measurements of induced-charge electro-osmosis around a metal rod. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2013, 14, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canpolat, C.; Qian, S.; Beskok, A. Induced-charge electro-osmosis of polymer-containing fluid around a metallic rod. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 16, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.L.; Yang, C. Ac field induced-charge electroosmosis over leaky dielectric blocks embedded in a microchannel. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzer, O.; Frankel, I.; Yariv, E. Electrokinetic flows about conducting drops. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 722, 394–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yossifon, G.; Frankel, I.; Miloh, T. On electro-osmotic flows through microchannel junctions. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 117108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, Y.; Yossifon, G.; Seifert, A.; Miloh, T. Nonlinear electrokinetic phenomena around nearly insulated sharp tips in microflows. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzer, O.; Yariv, E. Induced-charge electro-osmosis beyond weak fields. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 061506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, R.A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Hu, G.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Xuan, X. Induced charge effects on electrokinetic entry flow. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Yang, H.; Sivagnanam, V.; Gijs, M.A. Microfluidic protein preconcentrator using a microchannel-integrated Nafion strip: Experiment and modeling. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9989–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.M.; Andersen, M.B.; Mani, A. Chaotic induced-charge electro-osmosis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 128302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Yao, B.; Liu, N.; Wu, Q. A universal design of field-effect-tunable microfluidic ion diode based on a gating cation-exchange nanoporous membrane. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Han, J. Direct seawater desalination by ion concentration polarization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, Z.; Yeh, L.H.; Chou, T.H.; Qian, S. Tunable Donnan potential and electrokinetic flow in a biomimetic gated nanochannel with pH-regulated polyelectrolyte brushes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19806–19813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.H.; Xue, S.; Sang, W.J.; Qian, S.; Hsu, J.P. Field effect control of surface charge property and electroosmotic flow in nanofluidics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4209–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, S.E.; Sharma, A.; Qian, S.; Joo, S.W.; Baysal, O. Manipulating particles in microfluidics by floating electrodes. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Lang, Q.; Jiang, H. Enhanced particle trapping performance of induced charge electroosmosis. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Shao, J.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, H. Induced-charge electroosmotic trapping of particles. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Shao, J.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.; Jiang, H.; Ding, Y. Effects of discrete-electrode arrangement on traveling-wave electroosmotic pumping. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 095003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Kitamori, T.; Kim, H.B. Fluid mixing using ac electrothermal flow on meandering electrodes in a microchannel. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimsa, J.; Wachner, D. A unified resistor-capacitor model for impedance, dielectrophoresis, electrorotation, and induced transmembrane potential. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimsa, J.; Stubbe, M.; Gimsa, U. A short tutorial contribution to impedance and ac-electrokinetic characterization and manipulation of cells and media: Are electric methods more versatile than acoustic and laser methods? J. Electr. Bioimpedance 2014, 5, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, M.; Staroske, W.; Jaeger, M.S.; Schwille, P.; Duschl, C. Accumulation and filtering of nanoparticles in microchannels using electrohydrodynamically induced vortical flows. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbe, M.; Gyurova, A.; Gimsa, J. Experimental verification of an equivalent circuit for the characterization of electrothermal micropumps: High pumping velocities induced by the external inductance at driving voltages below 5 V. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.J. Enhanced electrothermal pumping with thin film resistive heaters. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, B.; Hui, M.; Bai, L. Control of two-phase flow in microfluidics using out-of-phase electroconvective streaming. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, H. On controlling the flow behavior driven by induction electrohydrodynamics in microfluidic channels. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Ren, Y.; Jia, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, X.; Jiang, H. Continuously electrotriggered core coalescence of double-emulsion drops for microreactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12282–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Hou, L.; Tao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, H. Electrocoalescence of paired droplets encapsulated in double-emulsion drops. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4313–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Shao, J.; Jiang, H.; Ding, Y. A theoretical and numerical investigation of travelling wave induction microfluidic pumping in a temperature gradient. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 075501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shao, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ding, Y. On utilizing alternating current-flow field effect transistor for flexibly manipulating particles in microfluidics and nanofluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Tao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, H. Particle rotational trapping on a floating electrode by rotating induced-charge electroosmosis. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Controllable rotating behavior of individual dielectric microrod in a rotating electric field. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Ren, Y.; Hou, L.; Liu, W.; Deng, X.; Jiang, H. Sequential coalescence enabled two-step microreactions in triple-core double-emulsion droplets triggered by an electric field. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, H. Simulation analysis of improving microfluidic heterogeneous immunoassay using induced charge electroosmosis on a floating gate. Micromachines 2017, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Yao, B.; Li, Y. Simulation analysis of rectifying microfluidic mixing with field-effect-tunable electrothermal induced flow. Electrophoresis 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Tao, Y.; Hui, M.; Wu, Q. On AC-Field-Induced Nonlinear Electroosmosis next to the Sharp Corner-Field-Singularity of Leaky Dielectric Blocks and Its Application in on-Chip Micro-Mixing. Micromachines 2018, 9, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030102
Ren Y, Liu W, Tao Y, Hui M, Wu Q. On AC-Field-Induced Nonlinear Electroosmosis next to the Sharp Corner-Field-Singularity of Leaky Dielectric Blocks and Its Application in on-Chip Micro-Mixing. Micromachines. 2018; 9(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030102
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Yukun, Weiyu Liu, Ye Tao, Meng Hui, and Qisheng Wu. 2018. "On AC-Field-Induced Nonlinear Electroosmosis next to the Sharp Corner-Field-Singularity of Leaky Dielectric Blocks and Its Application in on-Chip Micro-Mixing" Micromachines 9, no. 3: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030102
APA StyleRen, Y., Liu, W., Tao, Y., Hui, M., & Wu, Q. (2018). On AC-Field-Induced Nonlinear Electroosmosis next to the Sharp Corner-Field-Singularity of Leaky Dielectric Blocks and Its Application in on-Chip Micro-Mixing. Micromachines, 9(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030102