Three-Dimensional Reservoir-Based Dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for Enhanced Particle Enrichment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
3. Theory and Simulation
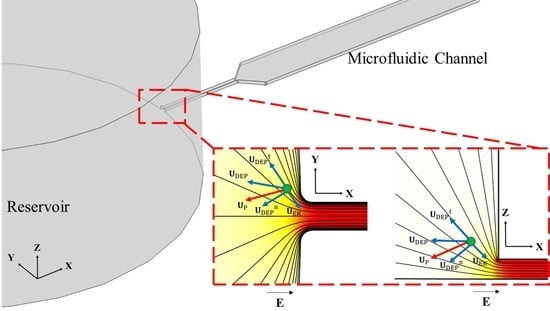
3.1. Working Principle
3.2. Numerical Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Focusing Ability of the Two Devices
4.2. Comparison of the Trapping Ability of the Two Devices
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maheux, A.F.; Bissonnette, L.; Boissinot, M.; Bernier, J.-L.T.; Huppe, V.; Picard, F.J.; Berube, E.; Bergeron, M.G. Rapid concentration and molecular enrichment approach for sensitive detection of escherichia coli and shigella species in potable water samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6199–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; O’Rorke, R.D.; Kale, A.; Rimsa, R.; Tomlinson, M.J.; Kirkham, J.; Davies, A.G.; Walti, C.; Wood, C.D. Rapid cell separation with minimal manipulation for autologous cell therapies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaltis, D.; Quake, S.R.; Yang, C. Developing optofluidic technology through the fusion of microfluidics and optics. Nature 2006, 442, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, P.; Edwards, T.; Fu, E.; Helton, K.; Nelson, K.; Tam, M.R.; Weigl, B.H. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 2006, 442, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, E.D.; Huang, C.; Hawkins, B.G.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Kirby, B.J. Rare cell capture in microfluidic devices. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Yazai, S.; Ardekani, A.M. Review of cell and particle trapping in microfluidic systems. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, D.; Haeberle, S.; Roth, G.; von Stetten, F.; Zengerle, R. Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip platforms: Requirements, characteristics and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1153–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velve-Casquillas, G.; Berre, M.L.; Piel, M.; Tran, P.T. Microfluidic tools for cell biological research. Nano Today 2010, 5, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyawahare, S.; Griffiths, A.D.; Merten, C. Miniaturization and parallelization of biological and chemical assays in microfluidic devices. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamme, N. Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijs, M.A.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbansky, A.; Lenshof, A.; Dykes, J.; Laurell, T.; Scheding, S. Affinity-bead-mediated enrichment of CD8+ lymphocytes from peripheral blood progenitor cell products using acoustophoresis. Micromachines 2016, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurell, T.; Petersson, F.; Nilsson, A. Chip integrated strategies for acoustic separation and manipulation of cells and particles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, A.; Spittler, A.; Brandhoff, L.; Zirath, H.; Puchberger-Enengl, D.; Keplinger, F.; Vellekoop, M.J. Microfluidic vortex enhancement for on-chip sample preparation. Micromachines 2015, 6, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, G. High-throughput particle manipulation based on hydrodynamic effects in microchannels. Micromachines 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, S.; Dong, Z.; Lee, G.-B.; Li, W.J. Optical spectrum and electric field waveform dependent optically-induced dielectrophoretic (ODEP) micro-manipulation. Micromachines 2012, 3, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Tu, E.; Raymond, D.E.; Yang, J.M.; Zhang, H.; Hagen, N.; Dees, B.; Mercer, E.M.; Forster, A.H.; Kariv, I.; et al. Microfluidic sorting of mammalian cells by optical force switching. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, A.; Sanghavi, B.J.; Salahi, A.; Liao, K.T.; Chou, C.-F.; Swami, N.S. Frequency-selective electrokinetic enrichment of biomolecules in physiological media based on electrical double-layer polarization. Nanoscale 2017, 33, 12124–12131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Verbridge, S.S. Microfluidic Methods for Molecular Biology, 1st ed.; Springer: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, H.A. Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Fields (Cambridge Monographs on Physics); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, H.A. The motion and precipitation of suspensoids in divergent electric fields. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R. Dielectrophoresis: An assessment of its potential to aid the research and practice of drug discovery and delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, R.E.; Rohani, A.; Farmehini, V.; Swami, N.S. Review: Microbial analysis in dielectrophoretic microfluidic systems. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 966, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.Y.; Madou, M.J. 3-D electrode designs for flow-through dielectrophoretic systems. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3745–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Beskok, A. Alternating current electrokinetic motion of colloidal particles on interdigitated microelectrodes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demierre, N.; Braschler, T.; Linderholm, P.; Seger, U.; van Lintel, H.; Renaud, P. Characterization and optimization of liquid electrodes for lateral dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natu, R.; Martinez-Duarte, R. Numerical model of streaming DEP for stem cell sorting. Micromachines 2016, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.; Hughes, M.P.; Green, N.G. Separation of submicron bioparticles by dielectrophoresis. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Soffe, R.; Nahavandi, S.; Shukla, R.; Khoshmanesh, K. High resolution scanning electron microscopy of cells using dielectrophoresis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Baratchi, S.; Nasabi, M.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Khoshmanesh, K. Modifying dielectrophoretic response of nonviable yeas.t cells by ionic surfactant treatment. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6364–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, C.; Zhu, J.; Xuan, X. Negative dielectrophoresis-based particle separation by size in a serpentine microchannel. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Xuan, X. Curvature-induced dielectrophoresis for continuous separation of particles by charge in spiral microchannels. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 024111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubose, J.; Zhu, J.; Patel, S.; Lu, X.; Tupper, N.; Stonaker, J.M.; Xuan, X. Electrokinetic particle separation in a single-spiral microchannel. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Davalos, R.V.; Simmons, B.A.; Cummings, E.B.; Fintschenko, Y. An insulator-based (electrodeless) dielectrophoretic concentrator for microbes in water. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 62, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Kang, Y.; Xuan, X.; Li, D. Continuous separation of microparticles by size with DC-dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, B.G.; Smith, A.E.; Syed, Y.A.; Kirby, B.J. Continuous-flow particle separation by 3D insulative dielectrophoresis using coherently shaped, DC-biased, AC electric fields. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7291–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Qian, S.; Liu, S.; Joo, S.W. Dielectrophoretic choking phenomenon in a converging-diverging microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 013201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Creel, M.F.; Goodrich, E.; Polniak, D.V.; Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. Assessment of sub-micron particles by exploiting charge differences with dielectrophoresis. Micromachines 2017, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braff, W.A.; Pignier, A.; Buie, C.R. High sensitivity three-dimensional insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Lawrence, R.M.; Jones, P.V.; Hogue, B.G.; Hayes, M.A. Concentration of Sindbis virus with optimized gradient insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Analyst 2016, 141, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.P.; Pacheco, J.R.; Hayes, M.A.; Staton, S.J.R. Insulator-based dielectrophoretic separation of small particles in a sawtooth channel. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, B.G.; Chao, T.C.; Kupitz, C.; Fromme, P.; Ros, A. Dielectrophoretic sorting of membrane protein nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9129–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.V.; Salmon, G.L.; Ros, A. Continuous separation of DNA molecules by size using insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, B.J.; Varhue, W.; Rohani, A.; Liao, K.T.; Bazydlo, L.A.L.; Chou, C.-F.; Swami, N.S. Ultrafast immunoassays by coupling dielectrophoretic biomarker enrichment in nanoslit channel with electrochemical detection on graphene. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zellner, P.; Shake, T.; Hosseini, Y.; Nakidde, D.; Riquelme, L.V.; Sahari, A.; Pruden, A.; Behkam, B.; Agah, M. 3D insulator-based dielectrophoresis using DC-biased, AC electric fields for selective bacterial trapping. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S.; Chen, X.; Bai, F.; Song, S.; Fu, J. Dielectrophoresis-based protein enrichment for a highly sensitive immunoassay using Ag/SiO2 nanorod arrays. Small 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, A. Joule Heating Effects in Insulator-Based Dielectrophoresis Microdevices. Ph.D. Thesis, Clemson University, Clemson, SC, USA, 7 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, X. Joule heating in electrokinetic flow. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, B.J.; Kirby, B.J. Electrothermal flow effects in insulating (electrodeless) dielectrophoresis systems. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3622–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, S.; Zhu, J.; Hu, G.; Xuan, X. Joule heating effects on electroosmotic flow in insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, A.; Patel, S.; Hu, G.; Xuan, X. Numerical modeling of Joule heating effects in insulator-based dielectrophoresis microdevices. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo-Villanueva, R.C.; Sano, M.B.; Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Davalos, R.V. Joule heating effects on particle immobilization in insulator-based dielectrophoretic devices. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, G.; Xuan, X. Electrokinetic particle entry into microchannels. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Showers, D.; Vedantam, P.; Tzeng, T.; Qian, S.; Xuan, X. Microfluidic separation of live and dead yeast cells using reservoir-based dielectrophoresis (rDEP). Biomicrofluids 2012, 6, 034102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, A.; Patel, S.; Qian, S.; Hu, G.; Xuan, X. Joule heating effects on reservoir-based dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2014, 36, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Qian, S.; Xuan, X. Reservoir-based dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for microfluidic particle separation by charge. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Patel, S.H.; Johnson, M.; Kale, A.; Raval, Y.; Tzeng, T.-R.; Xuan, X. Enhanced throughput for electrokinetic manipulation of particles and cells in a stacked microfluidic device. Micromachines 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Lu, X.; Patel, S.; Xuan, X. Continuous flow dielectrophoretic trapping and patterning of colloidal particles in a ratchet microchannel. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 075007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Patel, S.; Zhang, M.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S.; Ogale, A.; Xuan, X. An unexpected particle oscillation for electrophoresis in viscoelastic fluids through a microchannel constriction. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 021802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.-S. Formula for the viscosity of a glycerol-water mixture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3285–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Electroosmotic pumps and their applications in microfluidic systems. Microfluids Nanofluids 2009, 6, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.F.; Ye, W.; Peng, W.K.; Hou, H.W.; Marcos; Preiser, P.R.; Ngyuen, N.-T.; Han, J. Enhancing malaria diagnosis through microfluidic cell enrichment and magnetic resonance relaxometry detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonogi, A.; Terao, K.; Okitsu, T.; Suzuki, T.; Yokokawa, R.; Ohoka, M.; Kotera, H. Development of simple microfluidic cell culturing system toward observation of cell-to-cell communication. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, Groningen, The Netherlands, 3–7 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, A.; Ramos, A.; Gonz´alez, A.; Green, N.G.; Morgan, H. Electrohydrodynamics and dielectrophoresis in microsystems: Scaling laws. J. Phys. D 2003, 36, 2584–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurey, V.; Rohani, A.; Su, Y.H.; Liao, K.T.; Chou, C.F.; Swami, N.S. Scaling down constriction-based (electrodeless) dielectrophoresis devices for trapping nanoscale bioparticles in physiological media of high-conductivity. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kale, A.; Patel, S.; Xuan, X. Three-Dimensional Reservoir-Based Dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for Enhanced Particle Enrichment. Micromachines 2018, 9, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030123
Kale A, Patel S, Xuan X. Three-Dimensional Reservoir-Based Dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for Enhanced Particle Enrichment. Micromachines. 2018; 9(3):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030123
Chicago/Turabian StyleKale, Akshay, Saurin Patel, and Xiangchun Xuan. 2018. "Three-Dimensional Reservoir-Based Dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for Enhanced Particle Enrichment" Micromachines 9, no. 3: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030123
APA StyleKale, A., Patel, S., & Xuan, X. (2018). Three-Dimensional Reservoir-Based Dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for Enhanced Particle Enrichment. Micromachines, 9(3), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9030123