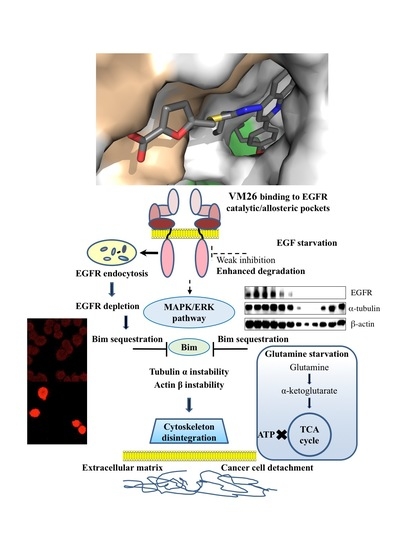
Targeting Degradation of EGFR through the Allosteric Site Leads to Cancer Cell Detachment-Promoted Death
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of Polyfunctionalized Heterocyclic Compounds
2.2. Identification of Compounds That Decrease EGFR Levels in Cancer Cells
2.3. Small Compounds Activate Endocytosis of EGFR
2.4. Small Compounds Promote Cancer Cell Detachment
2.5. Bim Expression is Temporarily Up-Regulated in Starved Cancer Cells upon Exposure to VM26
2.6. Glutamine Starvation Enhances Small Compound-Promoted Sequestration of Bim
2.7. Compound VM26 Weakly Inhibits EGFR Phosphorylation
2.8. Binding of Small Compounds Results in Dynamic Structural Rearrangements in EGFR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Cell Detachment Assay
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. siRNA Interference Knockdown of EGFR
4.7. Confocal Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.8. Molecular Docking
4.9. Molecular Dynamics
4.10. Statistical Information
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlessinger, J. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Legacy of the first two decades. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a008912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Baselga, J. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Fukuoka, M.; Baselga, J. Gefitinib—A novel targeted approach to treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.F.; Eiseman, I.A.; Fry, D.W.; Lenehan, P.F. CI-1033, an irreversible pan-erbB receptor inhibitor and its potential application for the treatment of breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Nair, S.K.; Murray, B.W. Recent progress on third generation covalent EGFR inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Goldstein, D.; Crowe, P.J.; Yang, J.-L. Next-generation EGFR/HER tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: A review of the evidence. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 5461–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.S.; Kang, S.W.; Seo, M.S.; Baines, I.C.; Takle, E.; Chock, P.B.; Rhee, S.G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced generation of hydrogen peroxide. Role in EGF receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, C.E.; Truong, T.H.; Garcia, F.J.; Homann, A.; Gupta, V.; Leonard, S.E.; Carroll, K.S. Peroxide-dependent sulfenylation of the EGFR catalytic site enhances kinase activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.H.; Ung, P.M.-U.; Palde, P.B.; Paulsen, C.E.; Schlessinger, A.; Carroll, K.S. Molecular Basis for Redox Activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Kinase. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, E.; Tinti, M.; Costa, S.; Corallino, S.; Nardozza, A.P.; Chatraryamontri, A.; Ceol, A.; Cesareni, G.; Castagnoli, L. Identification of New Substrates of the Protein-tyrosine Phosphatase PTP1B by Bayesian Integration of Proteome Evidence. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 4173–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Ramsey, T.T.; Shawver, L.K.; Guyer, C.A. Unliganded epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization induced by direct interaction of quinazolines with the ATP binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23247–23254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdick, A.D.; Davis, J.W., II; Liu, K.J.; Hudson, L.G.; Shi, H.; Monske, M.L.; Burchiel, S.W. Benzo(a)pyrene Quinones Increase Cell Proliferation, Generate Reactive Oxygen Species, and Transactivate the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Breast Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7825–7833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakanyan, V.; Hulin, P.; Alves de Sousa, R.; Silva, V.A.O.; Hambardzumyan, A.; Nedellec, S.; Tomasoni, C.; Loge, C.; Pineau, C.; Roussakis, C.; et al. Activation of EGFR by small compounds through coupling the generation of hydrogen peroxide to stable dimerization of Cu/Zn SOD1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakanyan, V. Reactive Chemicals and Electrophilic Stress in Cancer: A Minireview. High Throughput 2018, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Pascual, C.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy: Machinery and regulation. Microb. Cell 2016, 3, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, L.K.; Sorkin, A. Endocytosis of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a017459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Algisi, V.; Nappo, G.; Conte, A.; Pascolutti, R.; Cuomo, A.; Bonaldi, T.; Argenzio, E.; Verhoef, L.G.G.C.; Maspero, E.; et al. Threshold-controlled ubiquitination of the EGFR directs receptor fate. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2140–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, Y.; Bereczky, B.; Ono, M. The EGFR inhibitor gefitinib suppresses ligand-stimulated endocytosis of EGFR via the early/late endocytic pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 127, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Moriya, S.; Kazama, H.; Hirasawa, K.; Miyahara, K.; Kokuba, H.; Hino, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Takano, N.; Hiramoto, M.; et al. Amino acid starvation culture condition sensitizes EGFR-expressing cancer cell lines to gefitinib-mediated cytotoxicity by inducing atypical necroptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahakis, A.; Debnath, J. The Interconnections between Autophagy and Integrin-Mediated Cell Adhesion. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionov, R.V.; Granot, Z.; Vlahopoulos, S.A. Regulation of Bim in Health and Disease. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23058–23134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, S.M.; Francis, H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.-J.; Wildey, G.M.; Howe, P.H. Evidence That Ser87 of BimEL Is Phosphorylated by Akt and Regulates BimEL Apoptotic Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ley, R.; Ewings, K.E.; Hadfield, K.; Cook, S.J. Regulatory phosphorylation of Bim: Sorting out the ERK from the JNK. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, C.L.; Angarola, B.L.; Steiner, A.; Weigel, K.J.; Schafer, Z.T. Anoikis evasion in inflammatory breast cancer cells is mediated by Bim-EL sequestration. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iradyan, M.A.; Iradyan, N.S.; Hambardzumyan, A.A.; Minasyan, N.S.; Roussakis, C.; Sakanyan, V.A. Synthesis of furfuryl derivatives of 4-allyl-1-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzyl)-3-[2- (4-alkoxyphenyl)-quinolin-4-yl]-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5-thions and their toxicity in cancer cells. Chem. J. Arm. 2018, 71, 559–570. [Google Scholar]
- Avetyan, S.A.; Azaryan, A.S.; Aroyan, A.A. Quinoline derivatives V. Some derivatives of 2-(4-alkoxyphenyl)quinolin-4-carboxylic acids. Arm. Chem. J. 1973, 26, 763–767. [Google Scholar]
- Iradyan, M.A.; Iradyan, N.S.; Hambardzumyn, A.A.; Panosyan, H.A.; Tamazyan, R.A.; Ayvazyan, A.G.; Hovhannisyan, G.S.; Alves de sousa, R.; Sakanyan, V.A. Selective N-, S-alkylation of 4-allyl-3-[2-(4-alkoxyphenyl)-quinolin-4-yl]-4,5-dihydro-1h-1,2,4-triazole-5-thiones with substituted benzylchlorides. synthesis, docking analysis and cytotoxic action. Chem. J. Arm. 2018, 71, 389–406. [Google Scholar]
- Filmus, J.; Pollak, M.N.; Cailleau, R.; Buick, R.N. MDA-468, a human breast cancer cell line with a high number of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors, has an amplified EGF receptor gene and is growth inhibited by EGF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 128, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabeya, Y.; Mizushima, N.; Ueno, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kirisako, T.; Noda, T.; Kominami, E.; Ohsumi, Y.; Yoshimori, T. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5720–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, D.; Frank, J.; Appl, H.; Schoffl, H.; Pfaller, W.; Gstraunthaler, G. Serum-free cell culture: The serum-free media interactive online database. ALTEX 2010, 27, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Soler, L.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Brunet, J.; Menendez, J.A.; De Llorens, R.; Colomer, R. An update of the mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: Gefitinib (Iressa)-induced changes in the expression and nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of HER-ligands (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, D.; Shaw, K.; Jazayeri, J.; Leedman, P.J. Complex post-transcriptional regulation of EGF-receptor expression by EGF and TGF-α in human prostate cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakita, Y.; Seto, M.; Ohashi, T.; Tamura, T.; Yusa, T.; Miki, H.; Iwata, H.; Kamiguchi, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sogabe, S.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel pyrimido[4,5-b]azepine derivatives as HER2/EGFR dual inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Lelais, G.; DiDonato, M.; Bursulaya, B.; Michellys, P.-Y.; Epple, R.; Marsilje, T.H.; McNeill, M.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. EAI045: The fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor overcoming T790M and C797S resistance. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.; Lock, R.; Gao, S.; Salas, E.; Debnath, J. Induction of autophagy during extracellular matrix detachment promotes cell survival. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginato, M.J.; Mills, K.R.; Paulus, J.K.; Lynch, D.K.; Sgroi, D.C.; Debnath, J.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Brugge, J.S. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.B.; Halmos, B.; Kumar, A.; Schumer, S.T.; Huberman, M.S.; Boggon, T.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, M.S.; Kuroda, J.; Puthalakath, H.; Huang, D.C.S.; Strasser, A. Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, J.; Osterlund, E.J.; Andrews, D.W. BCL-2 family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Keusgen, M.; Salazar, A.; von Hagen, J. Amino acids in the cultivation of mammalian cells. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altman, B.J.; Stine, Z.E.; Dang, C.V. From Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Taylor, P.; Moran, M.F. Proteomic Analysis of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Interactome and Post-translational Modifications Associated with Receptor Endocytosis in Response to EGF and Stress. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 1644–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyata, Y.; Nakamoto, H.; Neckers, L. The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. Cancer cell metabolism: The essential role of the nonessential amino acid, glutamine. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momcilovic, M.; Bailey, S.T.; Lee, J.T.; Fishbein, M.C.; Magyar, C.; Braas, D.; Graeber, T.; Jackson, N.J.; Czernin, J.; Emberley, E.; et al. Targeted Inhibition of EGFR and Glutaminase Induces Metabolic Crisis in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Harari, D.; Shohat, G.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Gan, J.; Lavi, S.; Eisenstein, M.; Kimchi, A.; Wallach, D.; Pietrokovski, S.; et al. Hsp90 Recognizes a Common Surface on Client Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14361–14369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, Z.; Becker, N.; Anderson, M.; Sumpter, R.; Xiao, G.; Kinch, L.; Koduru, P.; Christudass, C.S.; Veltri, R.W.; et al. EGFR-Mediated Beclin 1 Phosphorylation in Autophagy Suppression, Tumor Progression, and Tumor Chemoresistance. Cell 2013, 154, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Shen, A.; Zhang, C.; Song, Z.; Ai, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Ding, J.; Geng, M.; Zhang, A. Development of Heat Shock Protein (Hsp90) Inhibitors To Combat Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors through Hsp90-Kinase Interactions. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5563–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Bogacki, R.; McReynolds, L.; Howley, P.M. Harnessing the ubiquitination machinery to target the degradation of specific cellular proteins. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: Chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burslem, G.M.; Smith, B.E.; Lai, A.C.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; McQuaid, D.C.; Bondeson, D.P.; Toure, M.; Dong, H.; Qian, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. The Advantages of Targeted Protein Degradation Over Inhibition: An RTK Case Study. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 67–77.e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, T.; Dass, C.R.; Choong, P.F.M. Bim-targeted cancer therapy: A link between drug action and underlying molecular changes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 3173–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.-J.; Zhao, P.; Ma, R.; Yan, X.-E.; Yun, C.-H.; Zhu, S.-J.; Zhao, P.; Ma, R.; Yan, X.-E.; Yun, C.-H.; et al. Structural insights into drug development strategy targeting EGFR T790M/C797S. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13652–13665. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ojemuyiwa, M.A.; Madan, R.A.; Dahut, W.L. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of prostate cancer: Taking the next step in clinical development. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2014, 19, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iradyan, M.A.; Iradyan, N.S.; Hambardzumyan, A.A.; Nersesyan, L.E.; Aharonyan, A.S.; Danielyan, I.S.; Muradyan, R.E.; Paronikyan, R.V.; Stepanyan, G.M. Docking analysis and some biological properties of furfuryl derivatives of 4-allyl-5- [2- (4-alkoxyphenyl) quinolin-4-yl] -4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-thiol. Biol. J. Arm. 2018, 70, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Vindelov, L.L. Flow microfluorometric analysis of nuclear DNA in cells from solid tumors and cell suspensions. A new method for rapid isolation and straining of nuclei. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. 1977, 24, 227–242. [Google Scholar]
- Yeretssian, G.; Lecocq, M.; Lebon, G.; Hurst, H.C.; Sakanyan, V. Competition on nitrocellulose-immobilized antibody arrays. From bacterial protein binding assay to protein profiling in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general Amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iradyan, M.; Iradyan, N.; Hulin, P.; Hambardzumyan, A.; Gyulkhandanyan, A.; Alves de Sousa, R.; Hessani, A.; Roussakis, C.; Bollot, G.; Bauvais, C.; et al. Targeting Degradation of EGFR through the Allosteric Site Leads to Cancer Cell Detachment-Promoted Death. Cancers 2019, 11, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081094
Iradyan M, Iradyan N, Hulin P, Hambardzumyan A, Gyulkhandanyan A, Alves de Sousa R, Hessani A, Roussakis C, Bollot G, Bauvais C, et al. Targeting Degradation of EGFR through the Allosteric Site Leads to Cancer Cell Detachment-Promoted Death. Cancers. 2019; 11(8):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081094
Chicago/Turabian StyleIradyan, Melkon, Nina Iradyan, Philippe Hulin, Artur Hambardzumyan, Aram Gyulkhandanyan, Rodolphe Alves de Sousa, Assia Hessani, Christos Roussakis, Guillaume Bollot, Cyril Bauvais, and et al. 2019. "Targeting Degradation of EGFR through the Allosteric Site Leads to Cancer Cell Detachment-Promoted Death" Cancers 11, no. 8: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081094
APA StyleIradyan, M., Iradyan, N., Hulin, P., Hambardzumyan, A., Gyulkhandanyan, A., Alves de Sousa, R., Hessani, A., Roussakis, C., Bollot, G., Bauvais, C., & Sakanyan, V. (2019). Targeting Degradation of EGFR through the Allosteric Site Leads to Cancer Cell Detachment-Promoted Death. Cancers, 11(8), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081094