Real Life Prospective Evaluation of New Drug-Eluting Platform for Chemoembolization of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: PARIS Registry
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
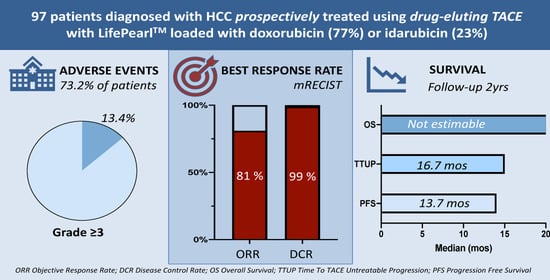
2. Results
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Safety and Toxicity
2.4. Hepatobiliary Toxicities
2.5. Tumour Response and Progression-Free Survival
2.6. Overall Survival
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Outcome Measures
4.2. Patient Treatment
4.3. Follow-Up and Assessments
4.4. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; London, W.T. Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: An emphasis on demographic and regional variability. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 19, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokdad, A.A.; Hester, C.A.; Singal, A.G.; Yopp, A.C. Management of hepatocellular in the United States. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Reig, M.; Sherman, M. Evidence-Based Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; Bolondi, L.; Cheung, T.T.; Kloeckner, R.; de Baere, T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Deschamps, F.; Aho, S.; Munck, F.; Dromain, C.; Boige, V.; Malka, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Ducreux, M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Liver/biliary injuries following chemoembolisation of endocrine tumours and hepatocellular carcinoma: Lipiodol vs. drug-eluting beads. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, A.; Guiu, B.; Duran, R.; Aho, S.; Bize, P.; Deltenre, P.; Dunet, V.; Denys, A. Liver and biliary damages following transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison between drug-eluting beads and lipiodol emulsion. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Plotkin, S.; Yu, R.; Sutter, A.; Wu, Y.; Cruise, G.M. An In Vitro Evaluation of Four Types of Drug-Eluting Microspheres Loaded with Doxorubicin. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aliberti, C.; Carandina, R.; Lonardi, S.; Dadduzio, V.; Vitale, A.; Gringeri, E.; Zanus, G.; Cillo, U. Transarterial Chemoembolization with Small Drug-Eluting Beads in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Experience from a Cohort of 421 Patients at an Italian Center. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.V.; Oliveira, J.A.; Correia, M.T.; Costa, N.V.; Abrantes, J.; Torres, D.; Pereira, P.; Ferreira, A.I.; Luz, J.H.; Spaepen, E.; et al. Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Drug-Eluting Polyethylene Glycol Embolic Agents: Single-Center Retrospective Analysis in 302 Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorentini, G.; Sarti, D.; Carandina, R.; Mulazzani, L.; Mincarelli, C.; Candelari, R.; Argirò, R.; Fiorentini, C.; Aliberti, C. A review discussing the use of polyethylene glycol microspheres in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucatelli, P.; Corradini, L.G.; De Rubeis, G.; Rocco, B.; Basilico, F.; Cannavale, A.; Nardis, P.G.; Corona, M.; Saba, L.; Catalano, C.; et al. Balloon-Occluded Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (b-TACE) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Performed with Polyethylene-Glycol Epirubicin-Loaded Drug-Eluting Embolics: Safety and Preliminary Results. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aliberti, C.; Carandina, R.; Sarti, D.; Mulazzani, L.; Catalano, V.; Felicioli, A.; Coschiera, P.; Fiorentini, G. Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Polyethylene Glycol Drug-eluting Beads for Primary and Metastatic Liver Cancer Therapy. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 3515–3521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aliberti, C.; Carandina, R.; Sarti, D.; Mulazzani, L.; Pizzirani, E.; Guadagni, S.; Fiorentini, G. Chemoembolization Adopting Polyethylene Glycol Drug-Eluting Embolics Loaded With Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulin, M.; Hillon, P.; Cercueil, J.P.; Bonnetain, F.; Dabakuyo, S.; Minello, A.; Jouve, J.L.; Lepage, C.; Bardou, M.; Wendremaire, M.; et al. Idarubicin-loaded beads for chemoembolisation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of the IDASPHERE phase I trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiu, B.; Colombat, S.; Piron, L.; Hermida, M.; Allimant, C.; Pierredon-Foulogne, M.-A.; Belgour, A.; Escal, L.; Cassinotto, C.; Boulin, M. Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Idarubicin-Loaded Tandem Drug-Eluting Embolics. Cancers 2019, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lammer, J.; On Behalf of the PRECISION V Investigators; Malagari, K.; Vogl, T.; Pilleul, F.; Denys, A.; Watkinson, A.; Pitton, M.; Sergent, G.; Pfammatter, T.; et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golfieri, R.; on behalf of the PRECISION ITALIA STUDY GROUP; Giampalma, E.; Renzulli, M.; Cioni, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bartolozzi, C.; Breatta, A.D.; Gandini, G.; Nani, R.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montaña, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Solà, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-M.; Ngan, H.; Tso, W.-K.; Liu, C.-L.; Lam, C.-M.; Poon, R.T.-P.; Fan, S.T.; Wong, J. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Citterio, D.; Bhoori, S.; Bongini, M.; Miceli, R.; De Carlis, L.; Colledan, M.; Salizzoni, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Antonelli, B.; et al. Liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma after tumour downstaging (XXL): A randomised, controlled, phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joskin, J.; De Baere, T.; Auperin, A.; Tselikas, L.; Guiu, B.; Farouil, G.; Boige, V.; Malka, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Ducreux, M.; et al. Predisposing factors of liver necrosis after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumor. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 38, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, S.; Allard, M.-A.; Lewin, M.; Awad, S.; Dahbi, N.; Nitta, H.; Cunha, A.S.; Castaing, D.; Vibert, E.; Cherqui, D.; et al. Ischemic Cholangiopathy Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Hepatectomy: An Underestimated and Devastating Complication. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrel, M.; Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Barrufet, M.; De Lope, C.R.; Tremosini, S.; Ayuso, C.; Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Bruix, J. Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) using Drug Eluting Beads. Implications for clinical practice and trial design. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Arai, Y.; Park, S.J.; Takeuchi, Y.; Anai, H.; Kim, J.K.; Inaba, Y.; Aramaki, T.; Kwon, S.H.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Prospective study of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: An Asian cooperative study between Japan and Korea. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aal, A.K.A.; Moawad, S.; Lune, P.V.; El Khudari, H.; Hanaoka, M.M.; AboulDahab, N.; Gunn, A.J.; White, J.; Shoreibah, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Survival Outcomes of Very Small Drug-Eluting Beads Used in Chemoembolization of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1325–1334.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.U.; Echevarria-Uraga, J.J.; Ciampi-Dopazo, J.J.; Sánchez-Corral, J.A.; Alonso, J.C.; Anton-Ladislao, A.; Peña-Baranda, B.; Nacarino-Mejias, V.; González-Costero, R.; Ruiz-Canela, J.J.M.; et al. Multicentre prospective study of drug-eluting bead chemoembolisation safety using tightly calibrated small microspheres in non-resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 126, 108966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-J.; Lin, Y.-X.; Ye, H.; Xiong, X.-Z.; Li, F.-Y.; Cheng, N.-S. Prognostic value of alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and lactate dehydrogenase in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with liver resection. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 36, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Wang, E.Q.; Lam, M.G.E.H.; Abdelmaksoud, M.H.; Louie, J.D.; Hwang, G.L.; Kothary, N.; Kuo, W.T.; Hofmann, L.V.; Sze, D.Y. Superselective Chemoembolization of HCC: Comparison of Short-term Safety and Efficacy between Drug-eluting LC Beads, QuadraSpheres, and Conventional Ethiodized Oil Emulsion. Radiology 2016, 278, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guiu, B.; Chevallier, P.; Assenat, E.; Barbier, E.; Merle, P.; Bouvier, A.; Dumortier, J.; Nguyen-Khac, E.; Gugenheim, J.; Rode, A.; et al. Idarubicin-loaded Beads for Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The IDASPHERE II Single-Arm Phase II Trial. Radiology 2019, 291, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.S.; Teyssier, Y.; Abousalihac, M.; Seigneurin, A.; Ghelfi, J.; Sengel, C.; Decaens, T. Idarubicin vs doxorubicin in transarterial chemoembolization of intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; De Baere, T.; Burrel, M.; Caridi, J.G.; Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Martin, R.C.G.; O’Grady, E.; Real, M.I.; Vogl, T.J.; et al. Transcatheter treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with Doxorubicin-loaded DC Bead (DEBDOX): Technical recommendations. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Type of Drug | BCLC Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Total Population (N = 97) | Doxorubicin (N = 75) | Idarubicin (N = 22) | p | BCLC 0&A (N = 46) | BCLC B&C (N = 51) | p |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 65.9 ± 10.6 | 66.3 ± 10.1 | 64.7 ± 12.3 | 0.62 | 65.2 ± 11.3 | 66.6 ± 9.9 | 0.42 |
| Gender, Male (%) | 92.8% | 93.3% | 90.9% | 0.70 | 87.0% | 98.0% | 0.04 |
| Cirrhosis (%) | 84.0% | 91.7% | 59.1% | <0.001 | 88.9% | 79.6% | 0.40 |
| Child Pugh Score * | |||||||
| A | 90.9% | 91.8% | 83.3% | 0.69 | 91.67% | 94.3% | 0.79 |
| B | 7.3% | 6.1% | 16.7% | 5.56% | 5.7% | ||
| C | 1.8% | 2.0% | 0.0% | 2.78% | 0.0% | ||
| Ascites | 16.5% | 4.6% | 20.0% | 0.08 | 23.9% | 9.8% | 0.06 |
| BCLC stage | |||||||
| BCLC 0 | 7.2% | 9.3% | 0.0% | 0.14 | 15.2% | 0.0% | 0.004 |
| BCLC A | 40.2% | 42.7% | 31.8% | 0.36 | 84.8% | 0.0% | <0.001 |
| BCLC B | 46.4% | 41.3% | 63.6% | 0.07 | 0.0% | 88.2% | <0.001 |
| BCLC C | 6.2% | 6.7% | 4.6% | 0.72 | 0.0% | 11.8% | 0.017 |
| Laboratory values | |||||||
| Alpha-feto protein | 279.2 ± 938.9 | 325.9 ± 1015 | 22.4 ± 20.9 | 0.74 | 43.0 ± 90.4 | 481 ± 1,251 | 0.15 |
| AST (IU/L) | 52.1 ± 33.8 | 53.7 ± 35.6 | 42.4 ± 18.1 | 0.41 | 42.8 ± 18.0 | 61.5 ± 42.7 | 0.02 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 45.8 ± 39.5 | 46.9 ± 41.1 | 39.4 ± 28.1 | 0.52 | 37.3 ± 26.6 | 54.5 ± 48.1 | 0.06 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) | 127.9 ± 58.8 | 130.0 ± 61.3 | 116.5 ± 43.3 | 0.57 | 116.2 ± 52.2 | 141.3 ± 63.7 | 0.074 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.20 ± 0.49 | 4.20 ± 0.49 | 4.20 ± 0.49 | 0.88 | 4.11 ± 0.57 | 4.29 ± 0.38 | 0.08 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 139.1 ± 3.6 | 139.1 ± 3.6 | 139.2 ± 4.1 | 0.93 | 139.8 ± 3.9 | 138.4 ± 3.3 | 0.02 |
| Tumor characteristics | |||||||
| Number of tumors (mean ± SD) | 2.3 ± 1.6 | 2.2 ± 1.5 | 2.6 ± 2.1 | 0.83 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 2.8 ± 2.0 | 0.93 |
| Median (range) | 2 (1, 10) | 1 (1, 5) | 2 (2, 10) | <0.001 | 2 (1, 9) | 2 (1, 10) | |
| Sum of tumor diameters, mm (mean ± SD) | 63.0 ± 41.5 | 57.2 ± 35.7 | 84.4 ± 53.9 | 0.02 | 39.1 ± 17.6 | 85.4 ± 45.0 | 0.001 |
| Type of Drug | BCLC Stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Total Population (N = 97) | Doxorubicin (N = 75) | Idarubicin (N = 22) | BCLC 0&A (N = 46) | BCLC B&C (N = 51) |
| N° of procedures per patient, Mean ± SD | 1.93 ± 1.14 | 2.08 ± 1.21 | 1.43 ± 0.60 * | 1.76 ± 0.87 | 2.08 ± 1.32 |
| Median | 2.0 (1.0, 7.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 7.0) | 1.0 (1.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 7.0) |
| Treatment selectivity, % | |||||
| Lobar/selective | 23.7 | 27.7 | 14.3 | 21.7 | 26.5 |
| Super-selective | 52.6 | 48.6 | 61.9 | 56.5 | 56.5 |
| Not reported | 23.7 | 23.6 | 21.7 | 21.7 | 25.5 |
| Bilobar treatment, % | 34.0 | 34.7 | 28.6 | 17.4 | 49.0 * |
| Bead size 100 µm, % | 25.8 | 29.2 | 19.1 | 32.6 | 19.6 |
| Bead size 200 µm, % | 74.2 | 70.8 | 80.9 | 67.4 | 80.4 |
| Time to last imaging FU, months | 7.2 ± 6.5 | 8.2 ± 6.6 | 3.7 ± 4.7 * | 7.8 ± 6.6 | 6.9 ± 6.5 |
| Adverse Events (AE) Type | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| N° AE | N° Patients | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Abdominal pain | 6 | 6 |
| Diarrhea | 2 | 1 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Fatigue | 3 | 3 |
| General health alteration | 1 | 1 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Enterobacter cloacae sepsis | 1 | 1 |
| Urinary infection with Proteus Mirabilis | 1 | 1 |
| Investigations | ||
| Blood bilirubin increased | 1 | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Cutaneous lesions on face | 1 | 1 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Chronic artery occlusion and stenosis of coronary ostium artery | 1 | 1 |
| Hypertension | 3 | 3 |
| False aneurysm of segment V in the liver | 1 | 1 |
| Total general | 21 | 13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Baere, T.; Guiu, B.; Ronot, M.; Chevallier, P.; Sergent, G.; Tancredi, I.; Tselikas, L.; Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Raynaud, L.; Deschamps, F.; et al. Real Life Prospective Evaluation of New Drug-Eluting Platform for Chemoembolization of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: PARIS Registry. Cancers 2020, 12, 3405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113405
de Baere T, Guiu B, Ronot M, Chevallier P, Sergent G, Tancredi I, Tselikas L, Dioguardi Burgio M, Raynaud L, Deschamps F, et al. Real Life Prospective Evaluation of New Drug-Eluting Platform for Chemoembolization of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: PARIS Registry. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113405
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Baere, Thierry, Boris Guiu, Maxime Ronot, Patrick Chevallier, Géraldine Sergent, Illario Tancredi, Lambros Tselikas, Marco Dioguardi Burgio, Lucas Raynaud, Frederic Deschamps, and et al. 2020. "Real Life Prospective Evaluation of New Drug-Eluting Platform for Chemoembolization of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: PARIS Registry" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113405
APA Stylede Baere, T., Guiu, B., Ronot, M., Chevallier, P., Sergent, G., Tancredi, I., Tselikas, L., Dioguardi Burgio, M., Raynaud, L., Deschamps, F., & Verset, G. (2020). Real Life Prospective Evaluation of New Drug-Eluting Platform for Chemoembolization of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: PARIS Registry. Cancers, 12(11), 3405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113405