Pharmacogenetics of the Central Nervous System—Toxicity and Relapse Affecting the CNS in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
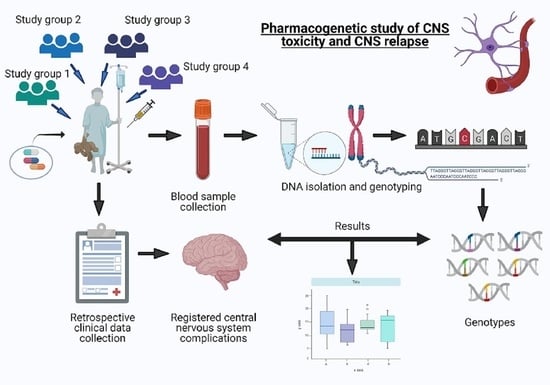
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design, Overview
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Laboratory Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemotherapy Related Adverse Neurological Symptoms
3.1.1. Case-Control Analyses
3.1.2. Survival Analyses on the Neurotoxicity Case-Control Cohorts
3.2. Central Nervous System Relapse
3.3. Inverse Association of SNPs with Chemotherapy Related Adverse Neurological Events and CNS Relapse
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filbin, M.; Monje, M. Developmental origins and emerging therapeutic opportunities for childhood cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.; Pei, D.; Campana, D.; Cheng, C.; Sandlund, J.; Bowman, W.; Hudson, M.; Ribeiro, R.; Raimondi, S.; Jeha, S.; et al. A Revised Definition for Cure of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2336–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coleman, J.J.; Pontefract, S.K. Adverse drug reactions. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearns, G.L.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M.; Alander, S.W.; Blowey, D.L.; Leeder, J.S.; Kauffman, R.E. Developmental pharmacology - Drug disposition, action, and therapy in infants and children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Ceccarelli, R.; Lu, C.Y. Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in US FDA-Approved Drug Labels (2000–2020). J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.; Aplenc, R. Pharmacogenetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment response. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2007, 8, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stary, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Campbell, M.; Castillo, L.; Dibar, E.; Donska, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Izraeli, S.; Janic, D.; Jazbec, J.; et al. Intensive chemotherapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of the randomized intercontinental trial ALL IC-BFM 2002. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchiano, R.D.M.; Sante, G.D.; Piro, G.; Carbone, C.; Tortora, G.; Boldrini, L.; Pietragalla, A.; Daniele, G.; Tredicine, M.; Cesario, A.; et al. Translational Research in the Era of Precision Medicine: Where We Are and Where We Will Go. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.H.; Howard, S.C. Current management and challenges of malignant disease in the CNS in paediatric leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasole, R.; Petruzziello, F.; Menna, G.; Mangione, A.; Cianciulli, E.; Buffardi, S.; Marchese, L.; Nastro, A.; Misuraca, A.; Poggi, V. Central nervous system complications during treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a single pediatric institution. Leuk. Lymphoma 2010, 51, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembhavi, S.A.; Somvanshi, S.; Banavali, S.; Kurkure, P.; Arora, B. Pictorial essay: Acute neurological complications in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2012, 22, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magge, R.S.; De Angelis, L.M. The double-edged sword: Neurotoxicity of chemotherapy. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vagace, J.M.; de la Maya, M.D.; Caceres-Marzal, C.; Gonzalez de Murillo, S.; Gervasini, G. Central nervous system chemotoxicity during treatment of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 84, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, D.C.; Wanderley, A.V.; dos Santos, A.M.R.; Fernandes, M.R.; Cohen Lima de Castro, A.d.N.; Leitão, L.P.C.; de Carvalho, J.A.N.; de Souza, T.P.; Khayat, A.S.; dos Santos, S.E.B.; et al. Pharmacogenomics and variations in the risk of toxicity during the consolidation/maintenance phases of the treatment of pediatric B-cell leukemia patients from an admixed population in the Brazilian Amazon. Leuk. Res. 2018, 74, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanulla, M.; Schäffeler, E.; Arens, S.; Rathmann, A.; Schrauder, A.; Welte, K.; Eichelbaum, M.; Zanger, U.M.; Schrappe, M.; Schwabb, M. GSTP1 and MDR1 genotypes and central nervous system relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2005, 81, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeo, K.M.; Dhall, G.; Panigrahy, A.; Lastra, C.; Ettinger, L.J. Subacute methotrexate neurotoxicity and cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a 12-year old with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism: Homocysteine-mediated methotrexate neurotoxicity via direct endothelial injury. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 27, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbelakin, A.; Ferguson, M.; MacGill, E.; Lehmann, A.; Topletz, A.; Quinney, S.; Li, L.; McCammack, K.; Hall, S.; Renbarger, J. Increased risk of vincristine neurotoxicity associated with low CYP3A5 expression genotype in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froklage, F.E.; Reijneveld, J.C.; Heimans, J.J. Central neurotoxicity in cancer chemotherapy: Pharmacogenetic insights. Pharmacogenomics 2011, 12, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, S.; Cheng, C.; French, D.; Pei, D.; Das, S.; Cook, E.H.; Hijiya, N.; Rizzari, C.; Rosner, G.L.; Frudakis, T.; et al. Ancestry and pharm acogenetics of antileukemic drug toxicity. Blood 2007, 109, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdilyi, D.J.; Kámory, E.; Csókay, B.; Andrikovics, H.; Tordai, A.; Kiss, C.; Filni-Semsei, A.; Janszky, I.; Zalka, A.; Fekete, G.; et al. Synergistic interaction of ABCB1 and ABCG2 polymorphisms predicts the prevalence of toxic encephalopathy during anticancer chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics J. 2008, 8, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talaat, R.M.; El-Kelliny, M.Y.K.; El-Akhras, B.A.; Bakry, R.M.; Riad, K.F.; Guirgis, A.A. Association of C3435T, C1236T and C4125A polymorphisms of the MDR-1 Gene in Egyptian children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceppi, F.; Langlois-pelletier, C.; Gagné, V.; Rousseau, J.; Lorenzo, S.D.; Kevin, K.M.; Cijov, D.; Sallan, S.E.; Lewis, B. Polymorphisms of the vincristine pathway and response to treatment in children with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, P.D.; Beckwith, K.A.; Vijayanathan, V.; Roychowdhury, S.; Smith, A.K.; Kamen, B.A. Folate Homeostasis in Cerebrospinal Fluid During Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 40, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özütemiz, C.; Roshan, S.K.; Kroll, N.J.; Benson, J.C.; Rykken, J.B.; Oswood, M.C.; Zhang, L.; McKinney, A.M. Acute toxic leukoencephalopathy: Etiologies, imaging findings, and outcomes in 101 patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beitinjaneh, A.; McKinney, A.M.; Cao, Q.; Weisdorf, D.J. Toxic Leukoencephalopathy following Fludarabine-Associated Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011, 17, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmiegelow, K.; Attarbaschi, A.; Barzilai, S.; Escherich, G.; Frandsen, T.L.; Halsey, C.; Hough, R.; Jeha, S.; Kato, M.; Liang, D.C.; et al. Consensus definitions of 14 severe acute toxic effects for childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia treatment: A Delphi consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e231–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulbright, J.M.; Raman, S.; McClellan, W.S.; August, K.J. Late effects of childhood leukemia therapy. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2011, 6, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasopoulou, S.; Eriksson, M.A.; Heyman, M.; Wang, C.; Niinimäki, R.; Mikkel, S.; Vaitkevičienė, G.E.; Johannsdottir, I.M.; Myrberg, I.H.; Jonsson, O.G.; et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Clinical characteristics, risk factors, course, and outcome of disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasopoulou, S.; Heyman, M.; Eriksson, M.A.; Niinimäki, R.; Taskinen, M.; Mikkel, S.; Vaitkeviciene, G.E.; Johannsdottir, I.M.; Myrberg, I.H.; Jonsson, O.G.; et al. Seizures during treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 27, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos-Jiménez, R.; Díaz-Carrasco, M.S.; Galera-Miñarro, A.; Pascual-Gazquez, J.F.; Espuny-Miró, A. Evaluation of standardized triple intrathecal therapy toxicity in oncohematological pediatric patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 39, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.K.; Marshall, G.M.; Barbaro, P.M.; Quinn, M.C.; George, C.; Mayoh, C.; Sutton, R.; Revesz, T.; Giles, J.E.; Barbaric, D.; et al. Methotrexate-related central neurotoxicity: Clinical characteristics, risk factors and genome-wide association study in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchey, A.K.; Pollock, B.H.; Lauer, S.J.; Andejeski, Y.; Buchanan, G.R. Improved survival of children with isolated CNS relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A pediatric oncology group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 3745–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurusawa, M.; Yumura-Yagi, K.; Ohara, A.; Hara, J.; Katano, N.; Tsuchida, M. Survival outcome after the first central nervous system relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A retrospective analysis of 79 patients in a joint program involving the experience of three Japanese study groups. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 85, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frishman-Levy, L.; Izraeli, S. Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of CNS acutelymphoblastic leukaemia and potential for therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 176, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Wade, R.; Moorman, A.V.; Mitchell, C.; Kinsey, S.E.; Eden, T.O.B.; Parker, C.; Vora, A.; Richards, S.; Saha, V. Temporal changes in the incidence and pattern of central nervous system relapses in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated on four consecutive Medical Research Council trials, 1985–2001. Leukemia 2010, 24, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, R.W.; Dusenbery, K.E.; Cao, Q.; Smith, A.R.; Yuan, J. Augmenting Total Body Irradiation with a Cranial Boost before Stem Cell Transplantation Protects Against Post-Transplant Central Nervous System Relapse in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukano, R.; Nishimura, M.; Ito, N.; Nakashima, K.; Kodama, Y.; Okamura, J.; Inagaki, J. Efficacy of prophylactic additional cranial irradiation and intrathecal chemotherapy for the prevention of CNS relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for childhood ALL. Pediatr. Transplant. 2014, 18, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laver, J.H.; Barredo, J.C.; Amylon, M.; Schwenn, M.; Kurtzberg, J.; Camitta, B.M.; Pullen, J.; Link, M.P.; Borowitz, M.; Ravindranath, Y.; et al. Effects of cranial radiation in children with high risk T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A Pediatric Oncology Group report. Leukemia 2000, 14, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piette, C.; Suciu, S.; Bertrand, Y.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Vandecruys, E.; Plat, G.; Paillard, C.; Pluchart, C.; Sirvent, N.; Maurus, R.; et al. Long-term outcome evaluation of medium/high risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia children treated with or without cranial radiotherapy in the EORTC 58832 randomized study. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastaniah, W.; Elimam, N.; Abdalla, K.; AlAzmi, A.A.; Algamal, A.; Felimban, S. Intrathecal dose intensification by CNS status at diagnosis in the treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology 2019, 24, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pui, C.H.; Mahmoud, H.H.; Rivera, G.K.; Hancock, M.L.; Sandlund, J.T.; Behm, F.G.; Head, D.R.; Relling, M.V.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; et al. Early intensification of intrathecal chemotherapy virtually eliminates central nervous system relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1998, 92, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ito, M.; Miyajima, T.; Fujii, T.; Okuno, T. Successful management of intractable epilepsy with intravenous lidocaine and lidocaine tapes. Pediatr. Neurol. 1999, 21, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOPHO Participating Institutions. Available online: https://www.nopho.org/organization/treating_clinics/Participating%20Clinics%202019.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- NIH. Common terminology criteria for adverse events v4.0. NIH Publ. 2009, 2009, 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zaliova, M.; Stuchly, J.; Winkowska, L.; Musilova, A.; Fiser, K.; Slamova, M.; Starkova, J.; Vaskova, M.; Hrusak, O.; Sramkova, L.; et al. Genomic landscape of pediatric B-other acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a consecutive European cohort. Haematologica 2019, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sági, J.C.; Egyed, B.; Kelemen, A.; Kutszegi, N.; Hegyi, M.; Gézsi, A.; Herlitschke, M.A.; Rzepiel, A.; Fodor, L.E.; Ottóffy, G.; et al. Possible roles of genetic variations in chemotherapy related cardiotoxicity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and osteosarcoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolthers, B.O.; Frandsen, T.L.; Abrahamsson, J.; Albertsen, B.K.; Helt, L.R.; Heyman, M.; Jónsson, G.; Kõrgvee, L.T.; Lund, B.; Raja, R.A.; et al. Asparaginase-associated pancreatitis: A study on phenotype and genotype in the NOPHO ALL2008 protocol. Leukemia 2017, 31, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Højfeldt, S.G.; Wolthers, B.O.; Tulstrup, M.; Abrahamsson, J.; Gupta, R.; Harila-Saari, A.; Heyman, M.; Henriksen, L.T.; Jónsson, Ò.G.; Lähteenmäki, P.M.; et al. Genetic predisposition to PEG-asparaginase hypersensitivity in children treated according to NOPHO ALL2008. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storey, J.D. A direct approach to false discovery rates. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2002, 64, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. R package version 3.2-7; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stoer, N.C.; Samuelsen, S.O. Weighted Cox-Regression for Nested Case-Control Data. R package version 1.2-2; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Arakawa, Y.; Oguma, E.; Uehara, T.; Yanagi, M.; Oyama, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Isobe, K.; Mori, M.; et al. Characteristics of methotrexate-induced stroke-like neurotoxicity. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 108, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.K.; Relling, M.V.; Pui, C.H.; Christensen, M.L.; Evans, W.E.; Rodman, J.H. Increased teniposide clearance with concomitant anticonvulsant therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 10, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrøder, H.; Østergaard, J.R. Interference of high-dose methotrexate in the metabolism of valproate? Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1994, 11, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, R.E.; Kirkwood, A.A.; Samarasinghe, S.; Rowntree, C.J.; Goulden, N.J.; Vora, A. Major Deviations in the Delivery of Induction Chemotherapy Are Associated with an Increased Risk of Relapse in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Results from UKALL2003. Blood 2019, 134, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberuyi, N.; Rahgozar, S.; Pourabutaleb, E.; Ghaedi, K. Selective dysregulation of ABC transporters in methotrexate-resistant leukemia T-cells can confer cross-resistance to cytarabine, vincristine and dexamethasone, but not doxorubicin. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2020, 69, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Peñafiel, C.; Olarte-Carrillo, I.; Maldonado, R.C.; de la Cruz Rosas, A.; Collazo-Jaloma, J.; Martínez-Tovar, A. Association of three factors (ABCB1 gene expression, steroid response, early response at day + 8) on the response to induction in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2629–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarte Carrillo, I.; Ramos Peñafiel, C.; Miranda Peralta, E.; Rozen Fuller, E.; Kassack Ipiña, J.J.; Centeno Cruz, F.; Garrido Guerrero, E.; Collazo Jaloma, J.; Nacho Vargas, K.; Martínez Tovar, A. Clinical significance of the ABCB1 and ABCG2 gene expression levels in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology 2017, 22, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ankathil, R. ABCB1 genetic variants in leukemias: Current insights into treatment outcomes. Pharmgenomics. Pers. Med. 2017, 10, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.X.; Sun, Y.H.; Wang, H.Y. ABCB1 polymorphisms correlate with susceptibility to adult acute leukemia and response to high-dose methotrexate. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 7599–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Pacheco, A.; Moreno-Guerrero, S.; Alamillo, I.; Medina-Sanson, A.; Lopez, B.; Moreno-Galván, M. Mexican Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Pilot Study of the MDR1 and MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms and Their Associations with Clinical Outcomes. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 2016, 20, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.P.; Yang, X.Y. Genetic polymorphism in MDR1 C3435T is a determinant of methotrexate cerebrospinal fluid concentrations in Chinese children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 58, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, E.; Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Astigarraga, I.; Navajas, A.; Echebarria-Barona, A.; Garcia-Miguel, P.; Garcia De Andoin, N.; Lobo, C.; Guerra-Merino, I.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; et al. Vincristine pharmacokinetics pathway and neurotoxicity during early phases of treatment in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics 2016, 17, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.A.; Stewart, R.K.; Smith, G.B.J.; Massey, T.E.; Bell, D.A. Human glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphisms: Relationship to lung tissue enzyme activity and population frequency distribution. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krull, K.R.; Bhojwani, D.; Conklin, H.M.; Pei, D.; Cheng, C.; Reddick, W.E.; Sandlund, J.T.; Pui, C.H. Genetic mediators of neurocognitive outcomes in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonardi, D.B.; Abbate, M.; Riccheri, M.C.; Nuñez, M.; Alfonso, G.; Gueron, G.; De Siervi, A.; Vazquez, E.; Cotignola, J. Improving risk stratification of patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Glutathione-S-Transferases polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of relapse. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krajinovic, M.; Labuda, D.; Sinnett, D. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Genetic determinants of susceptibility and disease outcome. Rev. Environ. Health 2001, 16, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderer, G.; Schrappe, M.; Brechlin, A.M.; Lauten, M.; Muti, P.; Welte, K.; Stanulla, M. Polymorphisms within glutathione S-transferase genes and initial response to glucocorticoids in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Pharmacogenetics 2000, 10, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajinovic, M.; Labuda, D.; Sinnett, D. Glutathione S-transferase P1 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Pharmacogenetics 2002, 12, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study Cohort | Hungarian | Austrian | Czech | NOPHO 4 | Combined | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joined Validation Cohort | |||||||
| Non-matched | Matched | Matched | Matched | ||||
| Phenotype | AE | ATE | ATE | ATE | ATE | ||
| Number of patients n | 626 | 580 | 108 | 62 | 119 | 137 | 426 |
| ATE Cases/controls n (%) | 82/544 | 36/544 | 36/72 | 21/41 | 39/80 | 47/90 | 143/283 |
| (13/87) | (6/94) | (33/67) | (34/66) | (49/51) | (34/66) | (34/66) | |
| Seizure only n | 21 | 20 | 20 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 44 |
| SLS 1 n | 6 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 20 |
| Toxic PRES 2 n | 3 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 18 | 33 | 66 |
| Gender n (%) | 339 | 317 | 52 | 26 | 53 | 74 | 205 |
| Male | (54) | (55) | (48) | (42) | (45) | (54) | (48) |
| Period of ALL diagnosis y | 1990–2015 | 1990–2015 | 1992–2015 | 2010–2018 | 2003–2017 | 2008–2015 | 1992–2018 |
| Age at diagnosis n (%) | 104 | 88 | 35 | 30 | 42 | 29 | 136 |
| >10 yr n | (17) | (15) | (32) | (48) | (35) | (21) | (32) |
| Median (range) yr | 5.0 (1–18) | 5.0 (1–18) | 7.7 (1–18) | 9.9 (1.8–17.7) | 7.1 (1.3–18) | 7.0 (1–16) | 7.6 (1–18) |
| Risk group (HR 3) n | 75 | 69 | 17 | 29 | 15 | 41 | 102 |
| (%) | (12) | (12) | (16) | (47) | (13) | (30) | (24) |
| Study Cohort | Austrian | Czech | Hungarian | NOPHO 2 | Combined |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matched cohorts | |||||
| Number of patients n | 39 | 62 | 18 | 132 | 251 |
| Cases/controls n (%) | 13/26 | 19/43 | 6/12 | 44/88 | 82/169 |
| (33/67) | (31/69) | (33/66) | (33/66) | (33/67) | |
| Gender n (%) | 18 | 43 | 9 | 76 | 146 |
| Male | (46) | (69) | (50) | (58) | (58) |
| Period of ALL diagnosis y | 2010–2017 | 2003–2017 | 1998–2013 | 2008–2015 | 1998–2017 |
| Age at diagnosis n (%) | 14 | 16 | 9 | 23 | 62 |
| >10 yr n | (36) | (26) | (50) | (17) | (25) |
| Median (range) yr | 9.0(1.8–16.9) | 5.68(1.3–14.5) | 10.5(4–15) | 8.0(1–15) | 8.0(1–16.9) |
| Risk group (HR 1) n | 21 | 7 | 3 | 48 | 79 |
| (%) | (54) | (11) | (17) | (36) | (32) |
| Study Cohorts | Austrian | Czech | Hungarian | NOPHO 4 | Combined |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matched cohorts | |||||
| Number of patients n | 8 | 152 | 60 | 100 | 320 |
| Isolated CNS 1 relapse | 1 | 10 | 4 | 19 | 35 |
| Combined CNS relapse | 2 | 26 | 12 | 12 | 51 |
| Isolated BM 2 relapse | 5 | 54 | 16 | 30 | 105 |
| Relapse- free controls | 0 | 62 | 28 | 39 | 129 |
| Gender n (%) | 4 | 102 | 42 | 62 | 210 |
| Male | (50) | (67) | (70) | (62) | (66) |
| Period of ALL diagnosis y | 2010–2014 | 1996–2017 | 1992–2013 | 2008–2015 | 1992–2017 |
| Age at diagnosis n (%) | 3 | 29 | 22 | 24 | 78 |
| >10 yr n | (40) | (19) | (37) | (24) | (24) |
| Median (range) yr | 9.5 (5.8–15.9) | 4.2 (0.1–17.8) | 7.4 (1–17) | 5.0 (1–16) | 4.9 (0.1–17.8) |
| Risk group (HR 3) n | 5 | 38 | 17 | 27 | 87 |
| (%) | (63) | (25) | (28) | (27) | (27) |
| Study Cohorts | Seizure | CNS Relapse Cases vs. Patients without Relapse (n = 86/129) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Cases/Controls) | (n = 44/89) | |||
| Gene | SNP | Comparisons | OR (CI95%) | OR (CI95%) |
| ABCB1 | rs1128503 | TT + CT vs. CC | 2.10 (0.82–5.39) | 0.48 (0.24–0.96) |
| TT vs. CC + CT | 2.49 (0.99–6.26) | 0.74 (0.33–1.64) | ||
| CT vs. CC | 1.67 (0.61–4.52) | 0.48 (0.23–1.01) | ||
| TT vs. CC | 3.50 (1.10–11.12) | 0.46 (0.18–1.16) | ||
| rs2032582 (triallelic) | AG vs. GG | nv | 0.54 (0.10–2.97) | |
| TA vs. GG | 2.16 (0.16–28.70) | nv | ||
| TT vs. GG | 3.71 (1.23–11.17) | 0.59 (0.25–1.40) | ||
| GT vs. GG | 1.37 (0.50–3.75) | 0.41 (0.20–0.87) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sági, J.C.; Gézsi, A.; Egyed, B.; Jakab, Z.; Benedek, N.; Attarbaschi, A.; Köhrer, S.; Sipek, J.; Winkowska, L.; Zaliova, M.; et al. Pharmacogenetics of the Central Nervous System—Toxicity and Relapse Affecting the CNS in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102333
Sági JC, Gézsi A, Egyed B, Jakab Z, Benedek N, Attarbaschi A, Köhrer S, Sipek J, Winkowska L, Zaliova M, et al. Pharmacogenetics of the Central Nervous System—Toxicity and Relapse Affecting the CNS in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers. 2021; 13(10):2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102333
Chicago/Turabian StyleSági, Judit C., András Gézsi, Bálint Egyed, Zsuzsanna Jakab, Noémi Benedek, Andishe Attarbaschi, Stefan Köhrer, Jakub Sipek, Lucie Winkowska, Marketa Zaliova, and et al. 2021. "Pharmacogenetics of the Central Nervous System—Toxicity and Relapse Affecting the CNS in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Cancers 13, no. 10: 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102333
APA StyleSági, J. C., Gézsi, A., Egyed, B., Jakab, Z., Benedek, N., Attarbaschi, A., Köhrer, S., Sipek, J., Winkowska, L., Zaliova, M., Anastasopoulou, S., Wolthers, B. O., Ranta, S., Szalai, C., Kovács, G. T., Semsei, Á. F., & Erdélyi, D. J. (2021). Pharmacogenetics of the Central Nervous System—Toxicity and Relapse Affecting the CNS in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers, 13(10), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102333