Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients under 16 Years Old: A Single-Institution Case Series
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
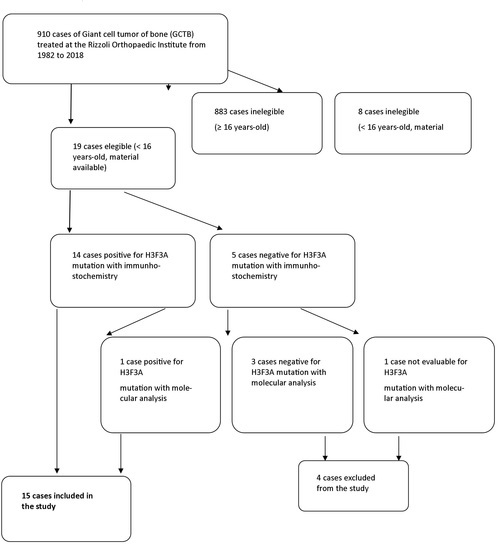
2. Materials and Methods
- Age <16 years old;
- Sufficient clinical information available;
- Histological slides and histological material suitable for immunohistochemistry or genetic analysis for H3F3A gene mutations available.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forsyth, R.; Jundt, G. Giant cell lesion of the small bones. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone; Fletcher, C.D.M., Bridge, J.A., Hogendoorn, P.C.W., Mertens, F., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2013; 320p. [Google Scholar]
- Campanacci, M.; Baldini, N.; Boriani, S.; Sudanese, A. Giant-cell tumor of bone. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1987, 69, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, A.M.; Larousserie, F.; O’Donnel, P.G.; Yoshida, A. Giant cell tumor of bone. In WHO Classification of Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2020; pp. 440–446. ISBN 9789283245025. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ibraheemi, A.; Inwards, C.Y.; Zreik, R.T.; Wenger, D.E.; Jenkins, S.M.; Carter, J.M.; Boland, J.M.; Rose, P.S.; Jin, L.; Oliveira, A.M.; et al. Histologic spectrum of Giant Cell Tumor (GCT) of bone in patients 18 years of age and below. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, D.C.; Cupps, R.E.; Johnson, E.W., Jr. Giant cell tumor: A study of 195 cases. Cancer 1970, 25, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strøm, T.M.; Skeie, A.T.; Lobmaier, I.K.; Zaikova, O. Giant cell tumor: A rare condition in the immature skeleton—A retrospective study of symptoms, treatment, and outcome in 16 children. Sarcoma 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, A.; Agarwal, M.G.; Shah, M.; Jambhekar, N.A.; Anchan, C.; Behle, S. Giant cell tumor of bone in children and adolescents. J. Pediatric Orthop. 2007, 27, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydlik, C.; Dürr, H.R.; Bechtold-Dalla Pozza, S.; Weißenbacher, C.; Roeb, J.; Schmidt, H. Hypercalcaemia after treatment with denosumab in children: Bisphosphonates as an option for therapy and prevention? World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picci, P.I.; Manfrini, M.A.; Zucchi, V.I.; Gherlinzoni, F.R.; Rock, M.I.; Bertoni, F.R.; Neff, J.R. Giant-cell tumor of bone in skeletally immature patients. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1983, 65, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanacci, M.; Enneking, W.F. Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors: Clinical Features, Imaging, Pathology, and Treatment, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Dumford, K.; Moore, T.; Walker, C.; Jaksha, J. Multifocal, metachronous, giant cell tumor of the lower limb. Skeletalradiology 2003, 32, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, D.; Gennari, L.; de Filippo, G.; Merlotti, D.; de Campora, E.; Fazioli, F.; Scarano, G.; Nuti, R.; Strazzullo, P.; Mossetti, G. Evidence for increased clinical severity of familial and sporadic Paget’s disease of bone in Campania, Southern Italy. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divisato, G.; Formicola, D.; Esposito, T.; Merlotti, D.; Pazzaglia, L.; del Fattore, A.; Siris, E.; Orcel, P.; Brown, J.P.; Nuti, R.; et al. ZNF687 mutations in severe Paget disease of bone associated with giant cell tumor. Am. J. Human Genet. 2016, 98, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzer-Kuntschik, M. Differential diagnosis of giant cell tumor of bone. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Pathol. 1998, 82, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Murphey, M.D.; Nomikos, G.C.; Flemming, D.J.; Gannon, F.H.; Temple, H.T.; Kransdorf, M.J. Imaging of giant cell tumor and giant cell reparative granuloma of bone: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2001, 21, 1283–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, L.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.; Sajdik, C.; Tian, X.; Niu, X.; Huang, X. Histological and clinical characteristics of malignant giant cell tumor of bone. Virchows Arch. 2012, 460, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, A.G.; Huvos, A.G.; Marcove, R.C. Primary malignant giant cell tumor of bone: A study of eight cases and review of the literature. Cancer 1979, 44, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominkus, M.; Ruggieri, P.; Bertoni, F.; Briccoli, A.; Picci, P.; Rocca, M.; Mercuri, M. Histologically verified lung metastases in benign giant cell tumours—14 cases from a single institution. Int. Orthop. 2006, 30, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behjati, S.; Tarpey, P.S.; Presneau, N.; Scheipl, S.; Pillay, N.; van Loo, P.; Wedge, D.C.; Cooke, S.L.; Gundem, G.; Davies, H.; et al. Distinct H3F3A and H3F3B driver mutations define chondroblastoma and giant cell tumor of bone. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righi, A.; Mancini, I.; Gambarotti, M.; Picci, P.; Gamberi, G.; Marraccini, C.; dei Tos, A.P.; Simi, L.; Pinzani, P.; Franchi, A. Histone 3.3 mutations in giant cell tumor and giant cell-rich sarcomas of bone. Human Pathol. 2017, 68, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amary, F.; Berisha, F.; Ye, H.; Gupta, M.; Gutteridge, A.; Baumhoer, D.; Gibbons, R.; Tirabosco, R.; O’Donnell, P.; Flanagan, A.M. H3F3A (Histone 3.3) G34W immunohistochemistry: A reliable marker defining benign and malignant giant cell tumor of bone. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Iwasaki, T.; Yamada, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Yoshimoto, M.; Kohashi, K.; Taguchi, K.; Yokoyama, R.; Nakashima, Y.; et al. Diagnostic utility of histone H3.3 G34W, G34R, and G34V mutant-specific antibodies for giant cell tumors of bone. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, I.; Righi, A.; Gambarotti, M.; Picci, P.; dei Tos, A.P.; Steven, D.; Billings, L.S.; Franchi, A. Phenotypic and molecular differences between giant-cell tumour of soft tissue and its bone counterpart. Histopathology 2017, 71, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolami, I.; Mancini, I.; Simoni, A.; Baldi, G.G.; Simi, L.; Campanacci, D.; Beltrami, G.; Scoccianti, G.; D’Arienzo, A.; Capanna, R.; et al. Denosumab treated giant cell tumour of bone: A morphological, immunohistochemical and molecular analysis of a series. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberi, G.; Morandi, L.; Benini, S.; Resca, A.; Cocchi, S.; Magagnoli, G.; Donati, D.M.; Righi, A.; Gambarotti, M. Detection ofH3F3Ap.G35W and p.G35R in giant cell tumor of bone byAllele specific locked nucleic acid quantitative PCR (ASLNAqPCR). Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, C.T.; Lin, E.I.; Olson, M.T.; Eshleman, J.R. Fundamentals of pyrosequencing. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, F.; Bacchini, P.; Staals, E.L. Malignancy in giant cell tumor of bone. Cancer 2003, 97, 2520–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| N° | Sex | Age | Site | Status of Growth Plate | Size (Major Axis) | IHC H3F3A G34W | IHC H3F3A G34R | IHC H3F3A G34V | Molecular Analysis | Surgery | LR | Complications | Last FU (Months) | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 8 | Tibia, proximal central metaphysis | open | 5 | + | - | - | na | curettage and cement (+bone grafts) | yes—8 months | Leg length discrepancy | 48 | ned |
| 2 | F | 10 | Femur, left central metaphysis | open | 6 | + | - | - | na | chondrodiastasis and intercalar | NO | none | 112 | ned |
| 3 | F | 11 | Tibia, eccentric distal, meta-epiphysis | closed | 4 | + | - | - | na | curettage and cement (+bone grafts) | NO | none | lost | na |
| 4 | F | 12 | Tibia, eccentric distal, meta-epiphysis | closed | 4 | + | - | - | na | curettage and bone grafts | NO | none | 123 | ned |
| 5 | F | 13 | Femur, distal meta-epiphysis | closed | 9 | + | - | - | na | curettage and cement | NO | none | 90 | ned |
| 6 | F | 13 | Tibia, distal meta-epiphysis, | closed | 5 | + | - | - | na | massive grafting | NO | graft obturation, revision with fibula | 42 | ned |
| 7 | F | 13 | Radius, distal, meta-epiphysis | na | na | + | - | - | na | osteoarticular resection and grafting | NO | graft failure, revision in arthrodesis | 204 | ned |
| 8 | F | 13 | Tibia, central proximal metaphysis | na | na | + | - | - | na | na | yes—12 months | none | 14 | ned |
| 9 | F | 14 | Sacrum | indeterminate | 8 | + | - | - | na | none, treated with denosumab | never operated on and in remission | na | 96 | awd |
| 10 | F | 14 | Radius, distal epiphysis | na | na | + | - | - | na | curettage and bone grafts | NO | none | 120 | ned |
| 11 | F | 15 | T12 vertebra | na | na | - | - | - | + | vertebrectomy and reconstruction | NO | infection | 180 | ned |
| 12 | F | 14 | Tibia, proximal meta-epiphysis | closed | 5 | + | - | - | na | curettage and cement | NO | none | lost | na |
| 13 | F | 13 | Tibia, proximal eccentric, meta-epiphysis | closed | 4 | + | - | - | na | curettage and cement | NO | none | 12 | ned |
| 14 | F | 14 | Distal femur, pathological fracture | na | na | + | - | - | na | resection and prosthesis | NO | none | 144 | ned |
| 15 | M | 15 | Tibia, distal, eccentric, meta-epiphysis | closed | 6 | + | - | - | na | curettage and cement | NO | none | 6 | ned |
| Publication | Range of Time Cases | Sex Age | Bone | Status of Growth Plate | Location | Treatment | Note | Molecular Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ajay Puri et al., 2007 [7] | January 2000 to December 2005 17 patients | 14 F (82%) 3 M (18%) 10–18 years | lower end of the femur (n = 5, 29%) | all open (17–100%) | 13 (76.5%) epiphysiometaphyseal in location | 14 IIC intralesional curettage | 2 local recurrences | |
| the upper end of the tibia (n = 4, 24%) | ||||||||
| the upper end of the fibula (n = 2) | 2 lower end-radius | |||||||
| distal end of radius (n = 2) | 2 not applicable | 3 wide excisions | 1 pulmonary nodule | |||||
| patient each of the upper end of the humerus, metacarpal, clavicle, and cuboid (n = 1) | ||||||||
| ThaleM. Asp Strøm et al., 2016 [6] | 1984 to 2015 16 patients | 12 F (75%) 4 M (25%) 6–15 years | tibia (n = 4, 25%) | all open (16–100%) | 4 (25%) epiphysiometaphyseal distal | 15 curettage 1 excision | 2 local recurrences | |
| fibula (n = 3, 18.75%) | 3 (18.75%) epiphysiometaphyseal proximal | |||||||
| clavicula (n = 3, 18.75%) | 1 (6.25%) proximal epiphysis | |||||||
| III metatarsal (n = 2, 12.5%) | 3 (18.75%) proximal (short bones) | 1 multicentric disease | ||||||
| sacrum (n = 2, 12.5%) | ||||||||
| scapula (n = 1, 6.25%) | 2 (12.5%) distal (short bones) | |||||||
| radius (n = 1, 6.25%) | ||||||||
| David C. Dahli et al., 1969 [5] | 1910 to 1969 21 patients (75%) 7 patients (25%) | 21 F (75%) 15–20 years | uk | no malignant transformation | ||||
| 7 M (75%) 12–14 years | ||||||||
| Alyaa Al-Ibraheemi et al., 2016 * [4] | all curettage and resection; all specimens of primary “GCT of bone” from patients 18 years old or younger | 43 F (68%) 20 M (32%) 8–18 years | tibia (n = 16, 25%) | radiologic images (n = 15): 7 patients with open physes (47%); 8 patients with closed growth plates (53%) | 7 (21%) cases involved the metaphysis without extension into the epiphysis | curettage and resection | 1 multifocal | 4 patients G34W 1 patient G34L |
| femur (n = 14, 22%) | 21 local recurrences (38%) | |||||||
| vertebral body (n = 13, 21%) | 23 (70%) cases involved the epiphysis and metaphysis | 2 (4%) pulmonary metastases 15 and 20 months after the diagnosis | ||||||
| radius (n = 4, 6%) | ||||||||
| humerus (n = 4, 6%) | ||||||||
| metacarp (n = 3, 5%) | ||||||||
| fibula (n = 2, 3%) | 5-year progression-free survival was observed in 57% (95% confidence interval, 43–71%) | |||||||
| patella (n = 2, 3%) | ||||||||
| calcaneus (n = 1, 2%) | ||||||||
| navicular (n = 1, 2%) | ||||||||
| phalanx (n = 1, 2%) | 3 (9%) cases were confined to the epiphysis | |||||||
| pelvis (n = 1, 2%) | ||||||||
| ulna (n = 1, 2%) | ||||||||
| Carmen Sydlik et al., 2020 [8] | children underwent therapy with denosumab between September 2011 and December 2014 4 patients | 1 F (25%) 3 M (75%) 6–13 years | solid variant of ABC in the left os sacrum (n = 1, 25%) | uk | children with severe hypercalcemia after treatment with denosumab for unresectable giant cell tumors of bone and for aneurysmal bone cysts | 1 patient developed pulmonary metastasis | ||
| a giant cell tumor in lumbosacral spine (L5/S1) (n = 1, 25%) | ||||||||
| left thigh and aneurismal | ||||||||
| bone cyst with typical osteoclast-like giant cells and intense vascularization (n = 1, 25%) | ||||||||
| a giant cell tumor localized in Th2 | ||||||||
| Picci Piero et al., 1983 [9] | giant-cell tumor of bone in skeletally immature patients 6 patients | 5 F (90%) 1 M (10%) 10–14 years | proximal fibula (n = 1; 10%) | 6 patients with open physes (100%) | epiphyseal plate involvement (n = 5/6; 83%) | marginal resection (n = 1; 10%) | ||
| distal femur (n = 4; 80%) | wide resection (n = 2; 40%) | |||||||
| proximal tibia (n = 1; 10%) | curettage (n = 3; 60%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ambrosi, F.; Righi, A.; Benini, S.; Magagnoli, G.; Chiaramonte, I.; Manfrini, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Frisoni, T.; Gambarotti, M. Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients under 16 Years Old: A Single-Institution Case Series. Cancers 2021, 13, 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112585
Ambrosi F, Righi A, Benini S, Magagnoli G, Chiaramonte I, Manfrini M, Gasbarrini A, Frisoni T, Gambarotti M. Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients under 16 Years Old: A Single-Institution Case Series. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112585
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmbrosi, Francesca, Alberto Righi, Stefania Benini, Giovanna Magagnoli, Ilaria Chiaramonte, Marco Manfrini, Alessandro Gasbarrini, Tommaso Frisoni, and Marco Gambarotti. 2021. "Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients under 16 Years Old: A Single-Institution Case Series" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112585
APA StyleAmbrosi, F., Righi, A., Benini, S., Magagnoli, G., Chiaramonte, I., Manfrini, M., Gasbarrini, A., Frisoni, T., & Gambarotti, M. (2021). Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients under 16 Years Old: A Single-Institution Case Series. Cancers, 13(11), 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112585