Sampling, Logistics, and Analytics of Urine for RT-qPCR-based Diagnostics
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
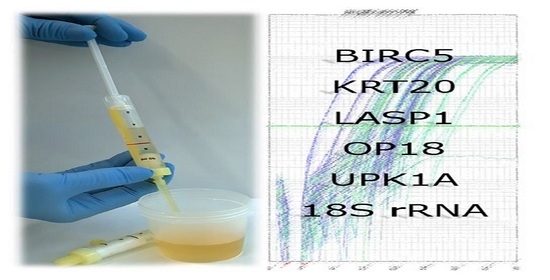
2.1. Clinical Sampling of Urine
2.2. Shipping Urine Samples
2.3. Laboratory Handling, Storage, and Thawing Samples
2.4. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. Primer Design for PCR
2.6. qPCR-Based Detection of RNA Sequences
2.7. Marker Ratio—Evaluation of Data
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. RNA Isolation
3.2. cDNA Synthesis
3.3. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brezgyte, G.; Shah, V.; Jach, D.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Earlier Detection of Pancreatic Cancer-A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, S.; et al. A urine-based DNA methylation assay to facilitate early detection and risk stratification of bladder cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laugsand, E.A.; Brenne, S.S.; Skorpen, F. DNA methylation markers detected in blood, stool, urine, and tissue in colorectal cancer: A systematic review of paired samples. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2021, 36, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeurickx, E.; Hendrix, A. Targets, pitfalls and reference materials for liquid biopsy tests in cancer diagnostics. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 72, 100828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goričar, K.; Dolžan, V.; Lenassi, M. Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Tool Facilitating Personalized Medicine and Pharmacogenomics in Oncology. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrano, V.; Royo, F.; Peinado, H.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Unda, M.; Falcón-Perez, J.M.; Carracedo, A. Vesicle-MaNiA: Extracellular vesicles in liquid biopsy and cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biggs, C.N.; Siddiqui, K.M.; Al-Zahrani, A.A.; Pardhan, S.; Brett, S.I.; Guo, Q.Q.; Yang, J.; Wolf, P.; Power, N.E.; Durfee, P.N.; et al. Prostate extracellular vesicles in patient plasma as a liquid biopsy platform for prostate cancer using nanoscale flow cytometry. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8839–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yazarlou, F.; Modarressi, M.H.; Mowla, S.J.; Oskooei, V.K.; Motevaseli, E.; Farhady Tooli, L.F.; Nekoohesh, L.; Eghbali, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Afsharpad, M. Urinary exosomal expression of long non-coding RNAs as diagnostic marker in bladder cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6357–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Du, J.; Jin, B.; Pang, L.; Duan, N.; Huang, C.; Hou, J.; Yu, W.; Hao, H.; Li, H. Combination of Urine Exosomal mRNAs and lncRNAs as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 667212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.; Constâncio, V.; Henrique, R.; Carvalho, A.; Jerónimo, C. Urinary Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for Urologic Cancers: An Overview of Current Methods and Advances. Cancers 2021, 13, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshi, M.; Murthy, V.; Takahashi, H.; Huyser, M.; Okano, M.; Tokumaru, Y.; Rashid, O.M.; Matsuyama, R.; Endo, I.; Takabe, K. Urine as a Source of Liquid Biopsy for Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das Gupta, A.; Krawczynska, N.; Nelson, E.R. Extracellular Vesicles-The Next Frontier in Endocrinology. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithraprabhu, S.; Chen, M.; Savvidou, I.; Reale, A.; Spencer, A. Liquid biopsy: An evolving paradigm for the biological characterisation of plasma cell disorders. Leukemia 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drees, E.E.E.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Groenewegen, N.J.; Perez-Boza, J.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Prins, L.I.; Verkuijlen, S.A.W.M.; Tran, X.M.; Driessen, J.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; et al. Extracellular vesicle miRNA predict FDG-PET status in patients with classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelizzaro, F.; Cardin, R.; Penzo, B.; Pinto, E.; Vitale, A.; Cillo, U.; Russo, F.P.; Farinati, F. Liquid Biopsy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Where Are We Now? Cancers 2021, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryzgunova, O.E.; Laktionov, P.P. Extracellular Nucleic Acids in Urine: Sources, Structure, Diagnostic Potential. Acta Nat. 2015, 7, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitale, S.R.; Helmijr, J.A.; Gerritsen, M.; Coban, H.; van Dessel, L.F.; Beije, N.; van der Vlugt-Daane, M.; Vigneri, P.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Dits, N.; et al. Detection of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in plasma from patients with solid cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykova, E.Y.; Skvortsova, T.E.; Laktionov, P.P.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Bryzgunova, O.E.; Starikov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, N.P.; Kolomiets, S.A.; Sevostianova, N.V.; Vlassov, V.V. Investigation of Tumor-Derived Extracellular DNA in Blood of Cancer Patients by Methylation-Specific PCR. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Fan, X.; Zaleta-Rivera, K.; Nguyen, T.C.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y.; Gao, J.; Fang, R.H.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Z.B.; et al. Natural display of nuclear-encoded RNA on the cell surface and its impact on cell interaction. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veziroglu, E.M.; Mias, G.I. Characterizing Extracellular Vesicles and Their Diverse RNA Contents. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, M.; Kausch, I.; Dahmen, G.; Jocham, D.; Warnecke, J.M. Detailed Technical Analysis of Urine RNA-Based Tumor Diagnostics Reveals ETS2/Urokinase Plasminogen Activator to Be a Novel Marker for Bladder Cancer. Clin Chem. 2007, 53, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, M.; Hoefig, K.; Merz, H.; Feller, A.C.; Kausch, I.; Jocham, D.; Warnecke, J.M.; Sczakiel, G. A robust methodology to study urine microRNA as tumor marker: microRNA-126 and microRNA-182 are related to urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2010, 28, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, T.B.; Warnecke, J.M. Improved Conditions for Isolation and Quantification of RNA in Urine Specimens. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1022, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, M.; Dubois, J.; Kausch, I.; Petkovic, S.; Sczakiel, G. Oncoprotein 18 is necessary for malignant cell proliferation in bladder cancer cells and serves as a G3-specific non-invasive diagnostic marker candidate in urinary RNA. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, J.; Rueger, J.; Haubold, B.; Kretschmer-Kazemi Far, R.; Sczakiel, G. Transcriptome analyses of urine RNA reveal tumor markers for human bladder cancer: Validated amplicons for RT-qPCR-based. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.; Ritch, C.R. Urinary biomarkers in bladder cancer: Where do we stand? Curr. Opin. Urol. 2019, 29, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, M.; Bedke, J.; Stenzl, A.; Todenhöfer, T. Can urinary biomarkers replace cystoscopy? World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.; Meehan, K.; Pereira, M.R.; Mirzai, B.; Lim, S.H.; Leslie, C.; Clark, M.; Sader, C.; Friedland, P.; Lindsay, A.; et al. A comparative study of extracellular vesicle-associated and cell-free DNA and RNA for HPV detection in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryzgunova, O.E.; Zaripov, M.M.; Skvortsova, T.E.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Zaporozhchenko, I.A.; Morozkin, E.S.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Yurchenko, Y.B.; Voitsitskiy, V.E.; et al. Comparative Study of Extracellular Vesicles from the Urine of Healthy Individuals and Prostate Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.L.; Li, H.; Ng, P.L.A.; Kong, S.T.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Tai, W.C.S.; Yu, A.C.S.; Yim, A.K.Y.; Tsang, H.F.; et al. The potential of circulating exosomal RNA biomarkers in cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Health Status | KRT20 | LASP1 | OP18 | UPK1A | BIRC5 | 18S rRNA | Luciferase | No. of Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 282 | 1.946 | 193 | 406 | 9 | 616,126 | 1001 | 41 |
| A2 | 138 | 410 | 38 | 1.206 | 4 | 307,401 | 1349 | 40 |
| A3 | 8263 | 6321 | 5605 | 26,517 | 1022 | 2,791,914 | 1852 | 66 |
| B1 | 777 | 18,784 | 109 | 530 | 6 | 4,300,097 | 2287 | 49 |
| B2 | 12 | 754 | 157 | 1717 | 21 | 423,152 | 1308 | 4 |
| B3 | 5 | 707 | 5 | 91 | 0 | 72,451 | 722 | 3 |
| B4 | 20 | 68 | 6 | 157 | 0 | 39,717 | 587 | 12 |
| C | 89 | 328 | 63 | 533 | 6 | 207,231 | 1328 | 47 |
| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) Upper Line: Forward Lower Line: Reverse | Amplicon (bp) | Standard Plasmid |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIRC5 | GACCACCGCATCTCTACATTCA CAAGTCTGGCTCGTTCTCAGT | 117 | pCRII-BIRC5P2P1 |
| KRT20 | AGCTGCGAAGTCAGATTAAGGA GAAGTCCTCAGCAGCCAGTT | 89 | pCRII-KRT20P1P1 |
| LASP1 | CTCGGAACCATGAACCCCA ATGCCAGAACTTATCCAGACAGT | 87 | pCRII-LASP1P1 |
| OP18 | AAAGACGCAAGTCCCATGAAG AGCTTCCATTTTGTGGGTCAG | 146 | pCRII-OP18 |
| UPK1A | CGGAAGGCTGACGTGAAGT CGTCATGATTGAGCAAGAATGC | 72 | pcDNA-UPK1A |
| Luciferase | GAACATCACGTACGCGGAATAC TTTCACTGCATACGACGATTCTG | 152 | pCRII-Topo-18S |
| 18S rRNA | CACATCCAAGGAAGGCAGCAG GACTTGCCCTCCAATGGATCC | 152 | pCRII-Topo-18S |
| Gene | Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| OP18 | FAM-GCAGCTGGCTGAGAAACGAGAGCA-BHQ-1 |
| UPK1A | FAM-TGGCACATCTGGTCCCATGGA-BHQ-1 |
| Luciferase | FAM-TCGAAATGTCCGTTCGGTTGGCA-BHQ-1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kretschmer-Kazemi Far, R.; Frank, K.; Sczakiel, G. Sampling, Logistics, and Analytics of Urine for RT-qPCR-based Diagnostics. Cancers 2021, 13, 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174381
Kretschmer-Kazemi Far R, Frank K, Sczakiel G. Sampling, Logistics, and Analytics of Urine for RT-qPCR-based Diagnostics. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174381
Chicago/Turabian StyleKretschmer-Kazemi Far, Rosel, Kirsten Frank, and Georg Sczakiel. 2021. "Sampling, Logistics, and Analytics of Urine for RT-qPCR-based Diagnostics" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174381
APA StyleKretschmer-Kazemi Far, R., Frank, K., & Sczakiel, G. (2021). Sampling, Logistics, and Analytics of Urine for RT-qPCR-based Diagnostics. Cancers, 13(17), 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174381