Electrochemotherapy of Deep-Seated Tumors: State of Art and Perspectives as Possible “EPR Effect Enhancer” to Improve Cancer Nanomedicine Efficacy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
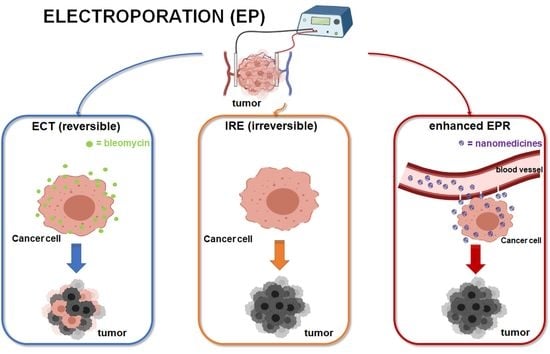
2. Electroporation-Based Therapies
3. Drugs Used in Electroporation-Based Therapies
3.1. Bleomycin
3.2. Cisplatin
4. EP as a Potential “EPR Enhancer” for the Administration of Nanomedicines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR Effect: Unique Features of Tumor Blood Vessels for Drug Delivery, Factors Involved, and Limitations and Augmentation of the Effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A New Concept for Macromolecular Therapeutics in Cancer Chemotherapy: Mechanism of Tumoritropic Accumulation of Proteins and the Antitumor Agent Smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. Tumor-Selective Delivery of Macromolecular Drugs via the EPR Effect: Background and Future Prospects. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Islam, W.; Maeda, H. Exploiting the Dynamics of the EPR Effect and Strategies to Improve the Therapeutic Effects of Nanomedicines by Using EPR Effect Enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 157, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freidus, L.G.; Kumar, P.; Marimuthu, T.; Pradeep, P.; Choonara, Y.E. Theranostic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded With a Curcumin-Naphthoquinone Conjugate for Potential Cancer Intervention. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Maestri, M.; Giunchedi, P. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Therapy and Theranostics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver-Targeting. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, N.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Kamaly, N.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanotechnology: The impact of passive and active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Zhou, S.; Gao, W. What went wrong with Anticancer Nanomedicine Design and how to Make it Right. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12281–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, J.; Henriquez, G.; Narayan, M. Enhancing the Delivery of Chemotherapeutics: Role of Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles. Molecules 2018, 23, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, D.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Xie, J.; Ju, S. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanoplatforms for Cancer Therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 707319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obinu, A.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Maestri, M.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Giunchedi, P. Nanoparticles in Detection and Treatment of Lymph node Metastases: An Update from the Point of View of Administration Routes. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Nanotechnology Based Therapeutic Application in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. 3 Biotech. 2019, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Porcu, E.P.; Fancello, S.; Obinu, A.; Senes, N.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, S.; Fu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, B. Intratumoral Administration of Thermosensitive Hydrogel Co-Loaded with Norcantharidin Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 4073–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfand, R.; Tomalia, D.A. Poly (amidoamine) (PAMAM) Dendrimers: From Biomimicry to Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Drug Discov. Today 2001, 6, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, R.; Cao, X.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Encapsulation of 2-Methoxyestradiol within Multifunctional Poly (Amidoamine) Dendrimers for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3322–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obinu, A.; Burrai, G.P.; Cavalli, R.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Antuofermo, E.; Rassu, G.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Transmucosal Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Improve Genistein Absorption Via Intestinal Lymphatic Transport. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palliyage, G.H.; Hussein, N.; Mimlitz, M.; Weeder, C.; Alnasser, M.H.A.; Singh, S.; Ekpenyong, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Chauhan, H. Novel Curcumin-Resveratrol Solid Nanoparticles Synergistically Inhibit Proliferation of Melanoma Cells. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Cheng, M.-H.; Lin, C.-H. From Nanoparticles to Cancer Nanomedicine: Old Problems with New Solutions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Pavan, B.; Mandracchia, D.; Tripodo, G.; Botti, G.; Dalpiaz, A.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Polymeric Nanomicelles Based on Inulin D α-Tocopherol Succinate for the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, W.; Kimura, S.; Islam, R.; Harada, A.; Ono, K.; Fang, J.; Niidome, T.; Sawa, T.; Maeda, H. EPR-Effect Enhancers Strongly Potentiate Tumor-Targeted Delivery of Nanomedicines to Advanced Cancers: Further Extension to Enhancement of the Therapeutic Effect. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Niu, P.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; An, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Investigating the EPR Effect of Nanomedicines in Human Renal Tumors via ex Vivo Perfusion Strategy. Nano Today 2020, 35, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Wilhelm, S.; Ding, D.; Syed, A.M.; Sindhwani, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; MacMillan, P.; Chan, W.C.W. Quantifying the Ligand-Coated Nanoparticle Delivery to Cancer Cells in Solid Tumors. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8423–8435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Since the EPR Effect Fails in the Clinic, What is the Future of Nanomedicine? J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K. The Beginning of the End of the Nanomedicine Hype. J. Control. Release 2019, 305, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; van der Meel, R.; Chen, X.; Lammer, T. The EPR effect and beyond: Strategies to improve tumor targeting and cancer nanomedicine treatment efficacy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7921–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, T.; Kiessling, F.; Hennink, W.E.; Storm, G. Drug Targeting to Tumors: Principles, Pitfalls and (pre-) Clinical Progress. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, G.H.; Alzghari, S.K.; Chee, W.; Sankari, S.S.; La-Beck, N.M. Meta-analysis of Clinical and Preclinical Studies Comparing the Anticancer Efficacy of Liposomal Versus Conventional Non-liposomal Doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A.; Zheng, G. Improving Accessibility of EPR-insensitive Tumor Phenotypes Using EPR-adaptive Strategies: Designing a New Perspective in Nanomedicine Delivery. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8091–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamitsu, A.; Greish, K.; Maeda, H. Elevating Blood Pressure as a Strategy to Increase Tumor-Targeted Delivery of Macromolecular Drug Smancs: Cases of Advanced Solid Tumors. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 39, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jordan, B.F.; Misson, P.; Demeure, R.; Baudelet, C.; Beghein, N.; Gallez, B. Changes intumor oxygenation/perfusion induced by the no donor, isosorbide dinitrate, in comparison with carbogen: Monitoring by EPR and MRI. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Fang, J.; Liao, L.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. Styrene-maleic Acid Copolymer Encapsulated CORM2, a Water-soluble carbon Monoxide (CO) Donor with a Constant CO-releasing Property, Exhibits Therapeutic Potential for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geboers, B.; Scheffer, H.J.; Graybill, P.M.; Ruarus, A.H.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Puijk, R.S.; van den Tol, P.M.; Davalos, R.V.; Rubinsky, B.; de Gruijl, T.D.; et al. High-Voltage Electrical Pulses in Oncology: Irreversible Electroporation, Electrochemotherapy, Gene Electrotransfer, Electrofusion, and Electroimmunotherapy. Radiology 2020, 295, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djokic, M.; Cemazar, M.; Popovic, P.; Kos, B.; Dezman, R.; Bosnjak, M.; Niksic Zakelj, M.; Miklavcic, D.; Potrc, S.; Stabuc, B.; et al. Electrochemotherapy as Treatment Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a Prospective Pilot Study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edhemovic, I.; Brecelj, E.; Cemazar, M.; Boc, N.; Trotovsek, B.; Djokic, M.; Dezman, R.; Ivanecz, A.; Potrc, S.; Bosnjak, M.; et al. Intraoperative Electrochemotherapy of Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Prospective Phase II Study. Europ. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, N.; Lee, S.R.; Arellano, R.S. Postloco-Regional Therapy Imaging of the Liver. Semin. Roentgenol. 2016, 51, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Qin, Z.; Tao, H.; Shi, J.; Fang, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, K.; Zeng, J.; et al. The Safety of Irreversible Electroporation on Nerves Adjacent to Treated Tumors. World Neurosurg. 2017, 108, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Kim, M.-D.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, W.W.; Kahlid, S.A. Effects of Irreversible Electroporation on Femoral Nerves in a Rabbit Model. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; Wang, X.; Su, Z.; Shangguan, J.; Sun, C.; Figini, M.; Wang, J.; Yaghmai, V.; Larson, A.C.; Zhang, Z. Irreversible Electroporation in Primary and Metastatic Hepatic Malignancies: A Review. Medicine 2017, 96, e6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, J.; White, S.A.; French, J.J.; Littler, P.; Manas, D.M. Systematic Review of Irreversible Electroporation in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Procissi, D.; Tyler, P.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. Rapid Dramatic Alterations to the Tumor Microstructure in Pancreatic Cancer following Irreversible Electroporation Ablation. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.-G.; Chen, X.-H.; Yu, Z.-J.; Lv, J.; Ren, Z.-G. Recent Progress in Pulsed Electric Field Ablation for Liver Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yin, S.; Chai, W.; Zhao, Q.; Tian, G.; Xu, D.; Jiang, T. Irreversible Electroporation in Patients with Liver Tumours: Treated-area Patterns with Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-Y.; Yang, P.-C.; Li, X.; Huang, K.-W. Clinical impact of irreversible electroporation ablation for unresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, E.; Klein, N.; Zapf, S.; Weil, S.; Schlosser, C.; Rubinsky, B.; Stehling, M.K. Prostate Cancer Treatment with Irreversible Electroporation (IRE): Safety, Efficacy and Clinical Experience in 471 Treatments. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, W.V.D.; Scheltema, M.J.; Siriwardana, A.R.; Kalsbeek, A.M.; Thompson, J.E.; Ting, F.; Böhm, M.; Haynes, A.-M.; Shnier, R.; Delprado, W.; et al. Focal irreversible electroporation as primary treatment for localized prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2018, 121, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sersa, G.; Miklavcic, D.; Cemazar, M.; Rudolf, Z.; Pucihar, G.; Snoj, M. Electrochemotherapy in treatment of tumours. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 34, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mir, L.M. Bases and Rationale of the Electrochemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2006, 4, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.L.; Dean, D.A. Electroporation-Mediated Gene Delivery. Adv. Genet. 2015, 89, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xie, J. A Review on Electroporation-Based Intracellular Delivery. Molecules 2018, 23, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Probst, U.; Fuhrmann, I.; Beyer, L.; Wiggermann, P. Electrochemotherapy as a New Modality in Interventional Oncology: A Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mir, L.M.; Orlowski, S.; Belehradek, J., Jr.; Paoletti, C. Electrochemotherapy Potentiation of Antitumour effect of Bleomycin by Local Electric Pulses. Eur. J. Cancer 1991, 27, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełbik, A.; Szlasa, W.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Electroporation-Based Treatments in Urology. Cancers 2020, 12, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvet, C.Y.; Famin, D.; André, F.M.; Mir, L.M. Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin induces hallmarks of immunogenic cell death in murine colon cancer cells. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e28131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brloznik, M.; Boc, N.; Sersa, G.; Zmuc, J.; Gasljevic, G.; Seliskar, A.; Dezman, R.; Edhemovic, I.; Milevoj, N.; Plavec, T.; et al. Radiological Findings of Porcine Liver after Electrochemotherapy with Bleomycin. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marty, M.; Sersa, G.; Garbay, J.; Gehl, J.; Collins, C.G.; Snoj, M.; Billard, V.; Geertsen, P.F.; Larkin, J.O.; Miklavcic, D.; et al. Electrochemotherapy—an Easy, Highly Effective and Safe Treatment of Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Metastases: Results of ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy) Study. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2006, 4, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehl, J.; Sersa, G.; Matthiessen, L.W.; Muir, T.; Soden, D.; Occhini, A.; Quaglino, P.; Curatolo, P.; Campana, L.G.; Kunte, C.; et al. Updated Standard Operating Procedures for Electrochemotherapy of Cutaneous Tumours and Skin Metastases. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavcic, D.; Snoj, M.; Zupanic, A.; Kos, B.; Cemazar, M.; Kropivnik, M.; Bracko, M.; Pecnik, T.; Gadzijev, E.; Sersa, G. Towards treatment planning and treatment of deep-seated solid tumors by electrochemotherapy. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edhemovic, I.; Gadzijev, E.M.; Brecelj, E.; Miklavcic, D.; Kos, B.; Zupanic, A.; Mali, B.; Jarm, T.; Pavliha, D.; Marcan, M.; et al. Electrochemotherapy: A New Technological Approach in Treatment of Metastases in the Liver. Technol. Canc. Res. Treat. 2011, 10, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edhemovic, I.; Brecelj, E.; Gasljevic, G.; Marolt Music, M.; Gorjup, V.; Mali, B.; Jarm, T.; Kos, B.; Pavliha, D.; Kuzmanov, B.G.; et al. Intraoperative Electrochemotherapy of Colorectal Liver Metastases. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djokic, M.; Cemazar, M.; Bosnjak, M.; Dezman, R.; Badovinac, D.; Miklavcic, D.; Kos, B.; Stabuc, M.; Stabuc, B.; Jansa, R.; et al. A Prospective Phase II Study Evaluating Intraoperative Electrochemotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, T.; Uemura, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Ohta, S.; Ishiguro, H.; Kubota, Y. Antitumour effect of electrochemotherapy with bleomycin on human prostate cancer xenograft. BJU Int. 2008, 102, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, L.; Busto, G.; Nasto, A.; Nasto, R.A.; Tarantino, P.; Fristachi, R.; Cacace, L.; Bortone, S. Electrochemotherapy of cholangiocellular carcinoma at hepatic hilum: A feasibility study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Campanacci, L.; Ronchetti, M.; Donati, D. Electrochemotherapy in the Treatment of Bone Metastases: A Phase II Trial. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 3088–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunha, R.M.C.; Lavalle, G.E.; Reis, D.C.; Horta, R.S.; Teixeira, S.V.; Ramirez, J.A.; Araújo, R.B. Assessment of Electrochemotherapy Effects on the Development of Ehrlich Solid Tumor in Swiss Mice Using a Novel Electroporator Device. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2017, 69, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrone, A.M.; Galuppi, A.; Cima, S.; Pozzati, F.; Arcelli, A.; Cortesi, A.; Procaccini, M.; Pellegrini, A.; Zamagni, C.; De Iaco, P. Electrochemotherapy can be Used as Palliative Treatment in Patients with Repeated Loco-regional Recurrence of Squamous Vulvar Cancer: A Preliminary Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 130, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrone, A.M.; Ferioli, M.; Galuppi, A.; Coe, M.; De Terlizzi, F.; Tesei, M.; Dondi, G.; De Palma, A.; Morganti, A.G.; De Iaco, P. Palliative Treatment with Electrochemotherapy in Recurrent or Metastatic Vaginal Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, L.G.; Edhemovic, I.; Soden, D.; Perrone, A.M.; Scarpa, M.; Campanacci, L.; Cemazar, M.; Valpione, S.; Miklavčič, D.; Mocellin, S.; et al. Electrochemotherapy–Emerging Applications Technical Advances, New Indications, Combined Approaches, and Multi-institutional Collaboration. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2019, 45, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferioli, M.; Perrone, A.M.; Buwenge, M.; Arcelli, A.; Zamagni, A.; Macchia, G.; Deodato, F.; Cilla, S.; Tagliaferri, L.; De Terlizzi, F.; et al. Electrochemotherapy of Skin Metastases from Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2021, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Bruners, P.; Isfort, P.; Barabasch, A.; Pfeffer, J.; Schmitz, J.; Pedersoli, F.; Baumann, M. Electroporation of the Liver: More Than 2 Concurrently Active, Curved Electrodes Allow New Concepts for Irreversible Electroporation and Electrochemotherapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mir, L.M.; Tounekti, O.; Orlowski, S. Bleomycin: Revival of an Old Drug. Gen. Pharmacol. 1996, 27, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanauskas, N.; Novell, A.; Escoffre, J.-M.; Venslauskas, M.; Šatkauskas, S.; Bouakaz, A. Bleomycin delivery into cancer cells in vitro with ultrasound and SonoVueor BR14 microbubbles. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pron, G.; Mahrour, N.; Orlowski, S.; Tounekti, O.; Poddevin, B.; Belehradek, J., Jr.; Mir, L.M. Internalisation of the Bleomycin Molecules Responsible for Bleomycin Toxicity: A Receptor-mediated Endocytosis Mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 57, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddevin, B.; Orlowski, S.; Belehradek, J., Jr.; Mir, L.M. Very High Cytotoxicity of Bleomycin Introduced into the Cytosol of Cells in Culture. Biochem. Pharmac. 1991, 42, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffre, J.M.; Rols, M.P. Electrochemotherapy: Progress and Prospects. Curr. Pharm. 2012, 18, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cemazar, M.; Milacic, R.; Miklavcic, D.; Dolzan, V.; Sersa, G. Intratumoral Cisplatin Administration in Electrochemotherapy: Antitumor Effectiveness, Sequence Dependence and Platinum Content. Anti-Cancer Drugs 1998, 9, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuertes, M.; Castilla, J.; Alonso, C.; Pérez, J. Cisplatin Biochemical Mechanism of Action: From Cytotoxicity to Induction of Cell Death through Interconnections between Apoptotic and Necrotic Pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 10, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sersa, G.; Cemazar, M.; Miklavcic, D. Antitumor Effectiveness of Electrochemotherapy with Cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) in Mice. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3450–3455. [Google Scholar]
- Serša, G.; Štabuc, B.; Čemažar, M.; Miklavčič, D.; Rudolf, Z. Electrochemotherapy with Cisplatin: The Systemic Antitumour Effectiveness of Cisplatin can be Potentiated Locally by the Application of Electric Pulses in the Treatment of Malignant Melanoma Skin Metastases. Melanoma Res. 2000, 10, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sersa, G.; Stabuc, B.; Cemazar, M.; Miklavcic, D.; Rudolf, Z. Electrochemotherapy with Cisplatin: Clinical Experience in Malignant Melanoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perrone, A.M.; Ravegnini, G.; Miglietta, S.; Argnani, L.; Ferioli, M.; De Crescenzo, E.; Tesei, M.; Di Stanislao, M.; Girolimetti, G.; Gasparre, G.; et al. Electrochemotherapy in Vulvar Cancer and Cisplatin Combined with Electroporation. Systematic Review and In Vitro Studies. Cancers 2021, 13, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sersa, G.; Cemazar, M.; Parkins, C.S.; Chaplin, D.J. Tumour Blood Flow Changes Induced by Application of Electric Pulses. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sersa, G.; Krzic, M.; Sentjurc, M.; Ivanusa, T.; Beravs, K.; Kotnik, V.; Coer, A.; Swartz, H.M.; Cemazar, M. Reduced Blood Flow and Oxygenation in SA-1 Tumours after Electrochemotherapy with Cisplatin. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gehl, J.; Skovsgaard, T.; Mir, L.M. Vascular Reactions to In Vivo Electroporation: Characterization and Consequences for Drug and Gene Delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1569, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellard, E.; Markelc, B.; Pelofy, S.; Le Guerroué, F.; Sersa, G.; Teissié, J.; Cemazar, M.; Muriel Golzio, M. Intravital Microscopy at the Single Vessel Level Brings New Insights of Vascular Modification Mechanisms Induced by Electropermeabilization. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markelc, B.; Sersa, G.; Cemazar, M. Differential Mechanisms Associated with Vascular Disrupting Action of Electrochemotherapy: Intravital Microscopy on the Level of Single Normal and Tumor Blood Vessels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srimathveeravalli, G.; Abdel-Atti, D.; Pérez-Medina, C.; Takaki, H.; Solomon, S.B.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Reiner, T. Reversible Electroporation–mediated Liposomal Doxorubicin Delivery to Tumors can be Monitored with 89Zr-labeled Reporter Nanoparticles. Mol. Imaging 2018, 17, 1536012117749726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, H.; Shamay, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Shah, J.; Solomon, S.B.; Heller, D.; Srimathveeravalli, G. Electroporation-induced Changes in Tumor Vasculature and Microenvironment can Promote the Delivery and Increase the Efficacy of Sorafenib Nanoparticles. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 130, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbacka, J.; Pucek, A.; Kotulska, M.; Dubińska-Magiera, M.; Rossowska, J.; Rols, M.-P.; Wilk, K.A. Electroporation and Lipid Nanoparticles with Cyanine IR-780 and Flavonoids as Efficient Vectors to Enhanced Drug Delivery in Colon Cancer. Bioelectrochemistry 2016, 110, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-Y.; Cooper, C.; Camarillo, I.; Reece, L.M.; Clah, L.; Natarajan, A.; Campana, L.G.; Sundararajan, R. The Effectiveness of Electroporation based Nanocurcumin and Curcumin Treatments on Human Breast Cancer Cells. In Proceedings of the ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics, Notre Dame, IN, USA, 17–19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Phonesouk, E.; Lechevallier, S.; Ferrand, A.; Rols, M.-P.; Bezombes, C.; Verelst, M.; Golzio, M. Increasing Uptake of Silica Nanoparticles with Electroporation: From Cellular Characterization to Potential Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.A.; Choi, S.; Jeon, S.M.; Yu, J. Silica Nanoparticle Stability in Biological Media Revisited. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Recent Development of Silica Nanoparticles as Delivery Vectors for Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Kind of Technique | Enhancer | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacological co-treatment | Angiotensin II-induced hypertension | [31] |
| Pharmacological co-treatment | NO-generating agents | [32] |
| Pharmacological co-treatment | CO generating agents | [33] |
| Physical co-treatment | Ultrasound | [30] |
| Physical co-treatment | Radiation | [30] |
| Physical co-treatment | Hyperthermia | [30] |
| Physical co-treatment | Photodynamic therapy | [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonferoni, M.C.; Rassu, G.; Gavini, E.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Torre, M.L.; Perteghella, S.; Ansaloni, L.; Maestri, M.; Giunchedi, P. Electrochemotherapy of Deep-Seated Tumors: State of Art and Perspectives as Possible “EPR Effect Enhancer” to Improve Cancer Nanomedicine Efficacy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174437
Bonferoni MC, Rassu G, Gavini E, Sorrenti M, Catenacci L, Torre ML, Perteghella S, Ansaloni L, Maestri M, Giunchedi P. Electrochemotherapy of Deep-Seated Tumors: State of Art and Perspectives as Possible “EPR Effect Enhancer” to Improve Cancer Nanomedicine Efficacy. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174437
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonferoni, Maria Cristina, Giovanna Rassu, Elisabetta Gavini, Milena Sorrenti, Laura Catenacci, Maria Luisa Torre, Sara Perteghella, Luca Ansaloni, Marcello Maestri, and Paolo Giunchedi. 2021. "Electrochemotherapy of Deep-Seated Tumors: State of Art and Perspectives as Possible “EPR Effect Enhancer” to Improve Cancer Nanomedicine Efficacy" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174437
APA StyleBonferoni, M. C., Rassu, G., Gavini, E., Sorrenti, M., Catenacci, L., Torre, M. L., Perteghella, S., Ansaloni, L., Maestri, M., & Giunchedi, P. (2021). Electrochemotherapy of Deep-Seated Tumors: State of Art and Perspectives as Possible “EPR Effect Enhancer” to Improve Cancer Nanomedicine Efficacy. Cancers, 13(17), 4437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174437