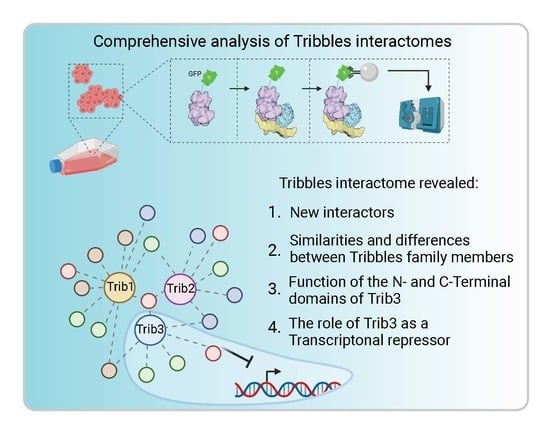
Comprehensive Profiling of Mammalian Tribbles Interactomes Implicates TRIB3 in Gene Repression
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Plasmids
2.4. Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Immunoprecipitation
2.7. Confocal Microscopy
2.8. Mass Spectrometry
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of TRIB1, TRIB2 and TRIB3 Interactomes in HEK293T Cells Using AP-MS
3.2. Contribution of the Different Domains to the TRIB3 Interactome
3.3. TRIB3 Function as a Transcriptional Repressor
3.4. Comparison of TRIB1 and TRIB3 Interactomes in MCF7 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fabbro, D.; Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Moebitz, H. Ten things you should know about protein kinases: IUPHAR Review 14. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2675–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, P.; Cross, D.; Jänne, P.A. Kinase drug discovery 20 years after imatinib: Progress and future directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D.P.; Foulkes, D.M.; Eyers, P.A. Pseudokinases: Update on their functions and evaluation as new drug targets. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, L.; Keeshan, K. Pseudokinases: A tribble-edged sword. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4170–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyers, P.A.; Keeshan, K.; Kannan, N. Tribbles in the 21st Century: The Evolving Roles of Tribbles Pseudokinases in Biology and Disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss-Toth, E.; Velasco, G.; Pear, W.S. Tribbles at the cross-roads. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 1049–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubeyrand, S.; Martinuk, A.; Lau, P.; McPherson, R. TRIB1 Is Regulated Post-Transcriptionally by Proteasomal and Non-Proteasomal Pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, W.; Qiao, Y.; Ma, L.; Xiao, W.; Yu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Sun, F. Impaired phosphorylation and ubiquitination by p70 S6 kinase (p70S6K) and Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1) promote tribbles homolog 2 (TRIB2) stability and carcinogenic property in liver cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33667–33681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, J.; Nakatani, Y.; Jamieson, S.A.; Dai, W.; Lucet, I.S.; Mace, P.D. Molecular Mechanism of CCAAT-Enhancer Binding Protein Recruitment by the TRIB1 Pseudokinase. Structure 2015, 23, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kanno, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takahara, T.; Miyata, S.; Nakamura, T. Trib1 links the MEK1/ERK pathway in myeloid leukemogenesis. Blood 2010, 116, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durzynska, I.; Xu, X.; Adelmant, G.; Ficarro, S.B.; Marto, J.A.; Sliz, P.; Uljon, S.; Blacklow, S.C. STK40 Is a Pseudokinase that Binds the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase COP1. Structure 2017, 25, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; He, K.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Gu, J.; Zhou, C.; Lu, R.; Jin, Y. Stk40 represses adipogenesis through translational control of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, T.; Nakamura, T. Tribbles in disease: Signaling pathways important for cellular function and neoplastic transformation. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Sebo, Z.; Pence, L.; Dobens, L.L. Drosophila tribbles antagonizes insulin signaling-mediated growth and metabolism via interactions with Akt kinase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, J.; Kong, L.; Zhang, H. Tribbles homolog 2 promotes hepatic fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis through phosphatase 1A-Mediated stabilization of yes-associated protein. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.I.; Santos, B.; Link, W.; De Sousa-Coelho, A.L. Tribbles pseudokinases in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobens, L.L.; Bouyain, S. Developmental roles of tribbles protein family members. Dev. Dyn. 2012, 241, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, J.E.; Jura, N. The pseudokinase TRIB 1 toggles an intramolecular switch to regulate COP 1 nuclear export. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e99708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-J.; Zhou, D.-D.; Yang, X.-X.; Cui, B.; Tan, F.-W.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Shang, S.; Zhang, C.; Lv, X.-X.; et al. TRIB3-EGFR interaction promotes lung cancer progression and defines a therapeutic target. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrouzi, P.; Astobiza, I.; Cortazar, A.R.; Torrano, V.; Macchia, A.; Flores, J.M.; Niespolo, C.; Mendizabal, I.; Caloto, R.; Ercilla, A.; et al. Genomic and Functional Regulation of TRIB1 Contributes to Prostate Cancer Pathogenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Johnston, J.; Felipe, F.J.C.; Hamby, S.; Castillo-Lluva, S.; Consortium, T.C.; Goodall, A.H.; Velasco, G.; Ocana, A.; Muthana, M.; et al. TRIB1 regulates tumour growth via controlling tumour-associated macrophage phenotypes and is associated with breast cancer survival and treatment response. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovska, B.; André, F.; Fromigué, O. Tribbles Pseudokinase 3 Regulation and Contribution to Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton-Chess, J.; Giral, M.; Mengel, M.; Renaudin, K.; Foucher, Y.; Gwinner, W.; Braud, C.; Dugast, E.; Quillard, T.; Thebault, P.; et al. Tribbles-1 as a novel biomarker of chronic antibody-mediated rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Han, Z.-D.; He, H.-C.; Ling, X.-H.; Fu, X.; Dai, Q.-S.; Cai, C.; Chen, J.-H.; et al. MicroRNA-224 inhibits progression of human prostate cancer by downregulating TRIB1. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wu, F.; Wei, X.; Qi, G.; Liang, X.; Tang, F.; et al. Inhibition of tribbles protein-1 attenuates radioresistance in human glioma cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gendelman, R.; Xing, H.; Mirzoeva, O.K.; Sarde, P.; Curtis, C.; Feiler, H.S.; McDonagh, P.; Gray, J.W.; Khalil, I.; Korn, W.M. Bayesian network inference modeling identifies TRIB1 as a novel regulator of cell-cycle progression and survival in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grandinetti, K.B.; A Stevens, T.; Ha, S.; Salamone, R.J.; Walker, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Agarwalla, S.; Tenen, D.; Peters, E.C.; Reddy, A.V. Overexpression of TRIB2 in human lung cancers contributes to tumorigenesis through downregulation of C/EBPα. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3328–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, R.; Kalathur, R.K.R.; Colaço, L.; Brandão, R.; Ugurel, S.; Futschik, M.; Link, W. TRIB2 as a biomarker for diagnosis and progression of melanoma. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-M.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.-H.; Liang, X.; Hua, F.; Li, K.; Lv, X.-X.; Zhang, X.-W.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yu, J.-J.; et al. TRIB3 supports breast cancer stemness by suppressing FOXO1 degradation and enhancing SOX2 transcription. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, F.; Shang, S.; Yang, Y.W.; Zhang, H.Z.; Xu, T.L.; Yu, J.J.; Zhou, D.D.; Cui, B.; Li, K.; Lv, X.X.; et al. TRIB3 Interacts with β-Catenin and TCF4 to Increase Stem Cell Features of Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells and Tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 708.e15–721.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, H.; Shuaib, A.; De Leon, D.D.; Angyal, A.; Salazar, M.; Velasco, G.; Holcombe, M.; Dower, S.K.; Kiss-Toth, E. Competition between members of the tribbles pseudokinase protein family shapes their interactions with mitogen activated protein kinase pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smits, A.H.; Vermeulen, M. Characterizing Protein-Protein Interactions Using Mass Spectrometry: Challenges and Opportunities. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, A.H.; Vermeulen, M. Quantitative liver proteomics identifies FGF19 targets that couple metabolism and proliferation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, R.; Vos, H.; Van Es, R.M.; Chen, J.; Burgering, B.M.; Westendorp, B.; De Bruin, A. Chk1 and 14-3-3 proteins inhibit atypical E2Fs to prevent a permanent cell cycle arrest. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nuland, R.; Smits, A.H.; Pallaki, P.; Jansen, P.W.T.C.; Vermeulen, M.; Timmers, H.T.M. Quantitative dissection and stoichiometry determination of the human SET1/MLL histone methyltransferase complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalkhoven, E.; Teunissen, H.; Houweling, A.; Verrijzer, C.P.; Zantema, A. The PHD type zinc finger is an integral part of the CBP acetyltransferase domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeninga, E.H.; Van Beekum, O.; van Dijk, A.-J.; Hamers, N.; Hendriks-Stegeman, B.I.; Bonvin, A.M.; Berger, R.; Kalkhoven, E. Impaired peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma function through mutation of a conserved salt bridge (R425C) in familial partial lipodystrophy. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baymaz, H.I.; Spruijt, C.G.; Vermeulen, M. Identifying Nuclear Protein–Protein Interactions Using GFP Affinity Purification and SILAC-Based Quantitative Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1188, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Sullivan, J.A.; Komatsu, S.; Gusmaroli, G.; Suzuki, G.; Yin, J.; Ishibashi, T.; Saijo, Y.; Rubio, V.; Kimura, S.; et al. Arabidopsis COP10 forms a complex with DDB1 and DET1 in vivo and enhances the activity of ubiquitin conjugating enzymes. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guruharsha, K.; Rual, J.-F.; Zhai, B.; Mintseris, J.; Vaidya, P.; Vaidya, N.; Beekman, C.; Wong, C.; Rhee, D.; Cenaj, O.; et al. A protein complex network of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 2011, 147, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jousse, C.; Deval, C.; Maurin, A.-C.; Parry, L.; Cherasse, Y.; Chaveroux, C.; Lefloch, R.; Lenormand, P.; Bruhat, A.; Fafournoux, P. TRB3 inhibits the transcriptional activation of stress-regulated genes by a negative feedback on the ATF4 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15851–15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayoral-Varo, V.; Jiménez, L.; Link, W. The critical role of trib2 in cancer and therapy resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.; Madureira, P.A.; Ferreira, B.; Baptista, I.; Machado, S.; Colaço, L.; dos Santos, M.; Liu, N.; Dopazo, A.; Ugurel, S.; et al. TRIB2 confers resistance to anti-cancer therapy by activating the serine/threonine protein kinase AKT. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.F.; Hofmann, S.; Neupert, W.; Brunner, M. Protein translocation into mitochondria: The role of TIM complexes. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, S.A.; Ruan, Z.; Burgess, A.E.; Curry, J.R.; McMillan, H.D.; Brewster, J.L.; Dunbier, A.K.; Axtman, A.D.; Kannan, N.; Mace, P.D. Substrate binding allosterically relieves autoinhibition of the pseudokinase TRIB1. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaau0597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al Dhaheri, N.; Wu, N.; Zhao, S.; Wu, Z.; Blank, R.D.; Zhang, J.; Raggio, C.; Halanski, M.; Shen, J.; Noonan, K.; et al. KIAA1217: A novel candidate gene associated with isolated and syndromic vertebral malformations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davuluri, G.; Song, P.; Liu, Z.; Wald, D.; Sakaguchi, T.F.; Green, M.R.; Devireddy, L. Inactivation of 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 2 delays zebrafish erythroid maturation by conferring premature mitophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1460–E1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kume, K.; Iizumi, Y.; Shimada, M.; Ito, Y.; Kishi, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Handa, H. Role of N-end rule ubiquitin ligases UBR1 and UBR2 in regulating the leucine-mTOR signaling pathway. Genes Cells 2010, 15, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Jing, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. Usp16 regulates kinetochore localization of Plk1 to promote proper chromosome alignment in mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 210, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, W.; Baird, D.; Feng, Q.; Cerione, R.A. Identification of a DOCK180-related guanine nucleotide exchange factor that is capable of mediating a positive feedback activation of Cdc42. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35253–35262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Tyagi, S. Diverse roles of WDR5-RbBP5-ASH2L-DPY30 (WRAD) complex in the functions of the SET1 histone methyltransferase family. J. Biosci. 2017, 42, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdon, J.-C.; Surget, S.; Khoury, M.P. Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: A clinical perspective. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2013, 7, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bech-Otschir, D.; Kraft, R.; Huang, X.; Henklein, P.; Kapelari, B.; Pollmann, C.; Dubiel, W. COP9 signalosome-specific phosphorylation targets p53 to degradation by the ubiquitin system. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalkhoven, E. CBP and p300: HATs for different occasions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyoshi, M.; Schwabe, J.W.R. A conserved structural motif reveals the essential transcriptional repression function of Spen proteins and their role in developmental signaling. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, F.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, H.; Wang, W.; Jin, L.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.-C. Novel human BTB/POZ domain-containing zinc finger protein ZBTB1 inhibits transcriptional activities of CRE. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 357, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.W.; Fang, M.; Park, S.M.; Hutchinson, L.; Green, M.R. A KRAS-directed transcriptional silencing pathway that mediates the CpG island methylator phenotype. Elife 2014, 3, e02313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Dejsuphong, D.; Adelmant, G.; Ceccaldi, R.; Yang, K.; Marto, J.A.; D’Andrea, A.D. Transcriptional repressor ZBTB1 promotes chromatin remodeling and translesion DNA synthesis. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matic, I.; Schimmel, J.; Hendriks, I.A.; van Santen, M.A.; van de Rijke, F.; van Dam, H.; Gnad, F.; Mann, M.; Vertegaal, A.C.O. Site-specific identification of SUMO-2 targets in cells reveals an inverted SUMOylation motif and a hydrophobic cluster SUMOylation motif. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmann, P.; Georgiev, O.; Le Douarin, B.; Bourquin, J.P.; Schaffner, W. Transcriptional repression by RING finger protein TIF1 beta that interacts with the KRAB repressor domain of KOX1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 4859–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wennemers, M.; Bussink, J.; Scheijen, B.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; van Laarhoven, H.W.; A Raleigh, J.; A Varia, M.; Heuvel, J.J.; Rouschop, K.M.; Sweep, F.C.; et al. Tribbles homolog 3 denotes a poor prognosis in breast cancer and is involved in hypoxia response. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orea-Soufi, A.; Castillo-Lluva, S.; Salvador-Tormo, N.; Martín-Cabrera, P.; Recuero, S.; Gabicagogeascoa, E.; Moreno-valladares, M.; Mendiburu-Eliçabe, M.; Blanco-Gómez, A.; Ramos-Pittol, J.M.; et al. The Pseudokinase TRIB3 Negatively Regulates the HER2 Receptor Pathway and Is a Biomarker of Good Prognosis in Luminal Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. Cell Cycle Regulation and Apoptosis1. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 60, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, J.; Curado, S.; Ephrussi, A.; Rorth, P. Tribbles Coordinates Mitosis and Morphogenesis in Drosophila by Regulating String/CDC25 Proteolysis. Cell 2000, 101, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flavin, R.; Peluso, S.; Nguyen, P.L.; Loda, M. Fatty acid synthase as a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, R.C.; Sasaki, M.; Cohen, D.M.; Cui, J.; Smith, M.A.; Yenilmez, B.O.; Steger, D.J.; Rader, D.J. Tribbles-1 regulates hepatic lipogenesis through posttranscriptional regulation of C/EBPα. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 3809–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Aldana-Masangkay, G.I. The role of HDAC6 in cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 875824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupo, A.; Cesaro, E.; Montano, G.; Zurlo, D.; Izzo, P.; Costanzo, P. KRAB-Zinc Finger Proteins: A Repressor Family Displaying Multiple Biological Functions. Curr. Genomics 2013, 14, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Qian, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Cao, S.; et al. A novel tumor suppressor ZBTB1 regulates tamoxifen resistance and aerobic glycolysis through suppressing HER2 expression in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14140–14152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Jian, Y.; Dai, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhao, L.; et al. TRIB3 confers radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by stabilizing TAZ. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3710–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chuang, G.C.; Hill, H.S.; Tian, L.; Fu, Y.; Moellering, D.R.; Garvey, W.T. Role of TRIB3 in regulation of insulin sensitivity and nutrient metabolism during short-term fasting and nutrient excess. Am. J. Physiol.—Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Wang, F.; Cao, W.-B.; Lv, X.-X.; Hua, F.; Cui, B.; Yu, J.-J.; Zhang, X.-W.; Shang, S.; Liu, S.-S.; et al. TRIB3 Promotes APL Progression through Stabilization of the Oncoprotein PML-RARα and Inhibition of p53-Mediated Senescence. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 697.e7–710.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, C.A.; Luo, X.; He, Q.; Jiang, C.; Huang, Y.; Sheikh, M.S. Genotoxic and endoplasmic reticulum stresses differentially regulate TRB3 expression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandoth, C.; McLellan, M.D.; Vandin, F.; Ye, K.; Niu, B.; Lu, C.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; McMichael, J.F.; Wyczalkowski, M.A.; et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature 2013, 502, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. p21 in cancer: Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fhu, C.W.; Ali, A. Fatty Acid Synthase: An Emerging Target in Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prudente, S.; Hribal, M.L.; Flex, E.; Turchi, F.; Morini, E.; De Cosmo, S.; Bacci, S.; Tassi, V.; Cardellini, M.; Lauro, R.; et al. The functional Q84R polymorphism of mammalian Tribbles homolog TRB3 is associated with insulin resistance and related cardiovascular risk in Caucasians from Italy. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2807–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Gene Name | -Log (p-Value) | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change * | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNAJC10 | 6.4354 | 6.18 × 10−5 | 7.300 | DnaJ Heat Shock Protein Family Member C10 |
| DDB1 | 5.8200 | 0.04 | 4.678 | Damage Specific DNA Binding Protein 1 |
| TRIB1 | 5.7117 | 8.17 × 10−7 | 2.567 | Tribbles Pseudokinase 1 |
| PPM1G | 5.2926 | 0.02 | 6.113 | Protein Phosphatase Mg2+ Dependent 1G |
| PSMA1 | 5.2130 | 5.29 × 10−5 | 4.699 | Proteosome 20S subunit Alpha 1 |
| PSMA2 | 5.0433 | 0.0002 | 3.443 | Proteosome 20S subunit Alpha 2 |
| PSMD4 | 5.0242 | 0.0004 | 3.112 | Proteasome 26S Subunit Ubiquitin receptor 4 |
| HDAC6 | 4.9461 | 0.03 | 4.223 | Histone Deacetylase 6 |
| PSMC6 | 4.5066 | 3.12 × 10−5 | 4.667 | Proteosome 26S subunit ATPase 6 |
| ADRM1 | 4.4064 | 0.0004 | 5.600 | 26S Proteosome Ubiquitin Receptor |
| PSMC2 | 4.3112 | 4.68 × 10−5 | 2.554 | Proteosome 26S subunit ATPase 2 |
| PSMB6 | 4.1668 | 0.006 | 6.433 | Proteosome 20S subunit Beta 7 |
| STIP1 | 3.9432 | 0.01 | 4.001 | Stress induced Phosphoprotein 1 |
| PSMB2 | 3.9126 | 1.70 × 10−5 | 3.333 | Proteosome 20S subunit Beta 2 |
| STUB1 | 3.8218 | 0.05 | 5.677 | STIP1 Homology and U-Box Containing Protein 1 |
| PSMC1 | 3.7980 | 9.63 × 10−6 | 3.655 | Proteosome 20S subunit Beta 7 |
| HSPH1 | 3.6860 | 0.004 | 5.911 | Heat Shock Protein Family H Member 1 |
| KPNA4 | 3.6243 | 0.001 | 3.770 | Karyopherin Subunit Alpha 4 |
| DET1 | 3.5614 | 5.29 × 10−5 | 3.190 | DET 1 Partner of COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| HSPA4L | 3.4984 | 0.003 | 4.675 | Heat Shock Protein Family A Member 4 Like |
| RFWD2 | 3.3768 | 0.0004 | 9.453 | COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| PSMA5 | 3.3478 | 0.0004 | 2.724 | Proteosome 20S subunit Alpha 5 |
| HSPA4 | 3.0482 | 1.30 × 10−5 | 5.119 | Heat Shock Protein A Member 4 |
| PSMA7 | 3.0482 | 0.003 | 3.880 | Proteosome 20S subunit Alpha 7 |
| KPNA3 | 2.7785 | 0.001 | 4.654 | Karyopherin Subunit Alpha 3 |
| Gene Name | -Log (p-Value) | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change * | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIB1 | 5.771 | 2.76 × 10−5 | 12.364 | Tribbles Pseudokinase 1 |
| USP11 | 5.541 | 0.001 | 4.356 | Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 11 |
| ISCA1 | 5.391 | 0.0002 | 6.115 | IRON-Sulfur Cluster Assembly 1 |
| BDH2 | 4.951 | 3.90 × 10−6 | 8.657 | 3-Hydroxybutyrate Dehtdrogenase 2 |
| ZKSCAN1 | 4.945 | 0.0001 | 6.503 | Zinc Finger with KRAB and SCAN Domains 1 |
| DET1 | 4.885 | 3.4 × 10−5 | 7.812 | DET 1 Partner of COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| DDB1 | 4.523 | 0.001 | 4.456 | Damage Specific DNA Binding Protein 1 |
| AIFM1 | 4.274 | 3.27 × 10−5 | 4.898 | Apoptosis inducing Factor Mitochondrial Associated 1 |
| FECH | 4.262 | 2.76 × 10−5 | 5.878 | Ferrochelatase |
| WDR37 | 4.007 | 0.001 | 7.058 | WD Repeat Domain 37 |
| KIAA1217 | 3.789 | 0.001 | 9.837 | Sickle tail Protein Homolog |
| KCTD21 | 3.751 | 0.002 | 3.573 | BTB/POZ Domain-Containing Protein KCTD21 |
| CDC42EP1 | 3.686 | 0.0003 | 3.082 | CDC42 Effector Protein 1 |
| MLF2 | 3.471 | 0.0003 | 4.887 | Myeloid Leukemia factor 1 |
| STK40 | 3.231 | 0.0001 | 7.644 | Serine/Threonine Kinase 40 |
| RAB3GAP1 | 3.218 | 0.0002 | 3.543 | RAB3 GTPase Activating Protein Catalytic Subunit 1 |
| EMD | 3.153 | 0.01 | 4.316 | Emerin |
| RFWD2 | 3.034 | 0.002 | 10.620 | COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| RPTOR | 2.864 | 0.002 | 2.346 | Regulatory Associated Protein of MTOR Complex 1 |
| FKBP4 | 2.841 | 0.01 | 4.293 | FKBP Prolyl Isomerase 4 |
| SRCIN1 | 2.762 | 0.0004 | 4.617 | SRC Kinase Signaling Inhibitor 1 |
| PKP2 | 2.646 | 0.0004 | 4.004 | Plakophilin 2 |
| TBC1D4 | 2.634 | 0.001 | 2.375 | TBC1 Domain Family Member 4 |
| HAUS8 | 2.163 | 0.002 | 3.115 | HAUS Augmin Like Complex Subunit 8 |
| RICTOR | 1.999 | 0.001 | 2.706 | RPTOR Independent Companion of MTOR Complex 2 |
| Gene Name | -Log (p-Value) | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change * | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIMM13 | 7.1286 | 0.0002 | 12.187 | Translocase of Inner Mitochondrial Membrane 13 |
| TRIM37 | 6.9472 | 0.006 | 6.961 | Tripartite Motif Containing 37 |
| DDB1 | 6.2442 | 0.005 | 5.187 | Damage Specific DNA Binding Protein 1 |
| KCMF1 | 5.7442 | 0.007 | 5.885 | Potassium Channel Modulatory Factor 1 |
| ATF4 | 5.7130 | 0.01 | 1.345 | Activating Transcription factor 4 |
| STUB1 | 5.4533 | 0.03 | 5.972 | STIP1 Homology and U-Box Containing Protein 1 |
| MLLT11 | 5.0745 | 0.002 | 6.917 | MLLT11 Transcription factor 7 Cofactor |
| RFWD2 | 5.0033 | 0.0006 | 2.489 | COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| PARN | 4.9405 | 0.01 | 7.321 | Poly(A)-Specific Ribonuclease |
| PRKD2 | 4.6601 | 0.001 | 7.015 | Protein kinase D2 |
| PASK | 4.6442 | 0.005 | 8.091 | PAS Domain Containing Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| DPY30 | 4.3027 | 0.04 | 5.462 | Dpy-30 Histone Methyltransferase Complex |
| DET1 | 4.1258 | 0.04 | 5.134 | DET 1 Partner of COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| ZNF24 | 4.0712 | 0.001 | 4.125 | Zinc Finger Protein 24 |
| EP300 | 3.9599 | 0.01 | 6.900 | E1A Binding Protein P300 |
| STIP1 | 3.9000 | 0.020. | 3.582 | Stress induced Phosphoprotein 1 |
| KANK2 | 3.7899 | 0.16 | 6.740 | KN Motif Ankyrin Repeat Domains 2 |
| RBBP8 | 3.7371 | 0.019 | 7.875 | RB Binding Protein 8 |
| ZNF507 | 3.6606 | 0.006 | 7.112 | Zinc Finger Protein 507 |
| PPP6C | 3.5073 | 0.03 | 7.964 | Protein Phosphatase 6 Catalytic Subunit |
| WDR62 | 3.5072 | 0.006 | 7.074 | WD Repeat Domain 62 |
| PPP6R3 | 3.4224 | 0.003 | 7.112 | Protein Phosphatase 6 Regulatory Subunit 3 |
| AKAP8L | 2.7110 | 0.0005 | 8.183 | A-Kinase Anchoring Protein 8 Like |
| ZNF655 | 2.6525 | 0.01 | 6.810 | Zinc Finger Protein 655 |
| TIMM8A | 2.6021 | 3.48 × 10−5 | 12.262 | Translocase of Inner Mitochondrial Membrane 8A |
| Gene Name | -Log (p-Value) | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change * | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIB3-ΔC-Terminal Binding partners | ||||
| RFWD2 | 4.4826 | 4.54 × 10−6 | 5.943 | COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| STK40 | 3.1119 | 0.0002 | 6.370 | Serine/Threonine Kinase 40 |
| DOCK11 | 3.7967 | 0.004 | 3.498 | Dedicator of Cytokinases 11 |
| DET1 | 3.8995 | 1.02 × 10−5 | 4.667 | DET 1 Partner of COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| USP16 | 2.5863 | 0.01 | 3.822 | Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 16 |
| UBR2 | 3.1640 | 0.001 | 2.610 | Ubiquitin Protein Ligase E3 Component N-Recognin 2 |
| DDI2 | 1.8154 | 0.02 | 1.811 | DNA Damage 1 Homolog 2 |
| TRIB3-ΔN-Terminal Binding partners | ||||
| MKNK2 | 6.0395 | 0.007 | 3.525 | MAPK Interacting Serine/Threonine Kinase 2 |
| WDR5 | 5.7443 | 4.38 × 10−7 | 7.841 | WD Repeat Domain 5 |
| COPS8 | 5.6291 | 0.01 | 3.123 | COP9 Signalosome Subunit 8 |
| TP53 | 5.3723 | 3.16 × 10−6 | 2.800 | Tumor Protein P53 |
| PARN | 5.0650 | 4.38 × 10−7 | 6.298 | Poly(A)-Specific Ribonuclease |
| GEN1 | 4.8329 | 1.35 × 10−5 | 4.438 | Gen1 Holliday Junction 5′ Flap Endonuclease |
| SPEN | 3.8986 | 3.87 × 10−6 | 4.154 | SPEN Family Transcriptional Repressor |
| ZNFP24 | 3.8823 | 0.0001 | 1.719 | Zinc Finger Protein 91 |
| NACC1 | 3.7582 | 3.08 × 10−5 | 2.193 | Nucleus Accumbens Associated 1 |
| ZBTB1 | 3.5994 | 8.91 × 10−5 | 4.004 | Zinc Finger And BTB Domain 1 |
| SETD2 | 3.5315 | 0.002 | 1.627 | SET Domain 2 Histone Lysine Methyltranferase |
| DPY30 | 3.4148 | 5.56 × 10−5 | 2.296 | Dpy-30 Histone Methyltranferase Complex Subunit |
| RBBP5 | 3.2480 | 0.0009 | 4.471 | RB Binding Protein 5 |
| MYC | 2.6206 | 0.01 | 2.233 | MYC Proto-Oncogene |
| EP300 | 2.5832 | 0.005 | 4.017 | E1A Binding Protein P300 |
| MKNK1 | 2.5381 | 0.05 | 3.411 | MAPK Interacting Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 |
| ASH2L | 2.4872 | 0.001 | 5.577 | Set1/Ash2 Histone Methyltranferase Complex Subunit |
| AKAP1 | 2.2902 | 0.005 | 2.712 | A-Kinase Anchoring Protein 1 |
| PRKD1 | 1.7714 | 0.03 | 4.106 | Protein kinase D1 |
| NFAT4 | 3.936 | 0.008 | 2.464 | Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells 3 |
| Gene Name | -Log (p-Value) | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIB1 binding partners in MCF7 | ||||
| PFN1 | 6.8434 | 0.007 | 2.550 | Profilin 1 |
| CDKN1A | 6.7563 | 0.0002 | 2.315 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A |
| CCT5 | 6.0523 | 0.0002 | 2.083 | T-complex protein 1 subunit epsilon |
| PDAP1 | 6.0427 | 0.006 | 2.151 | PDGFA Associated Protein 1 |
| PRKDC | 5.8532 | 0.0001 | 2.508 | DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit |
| ERH | 5.8170 | 4.16 × 10−5 | 3.553 | ERH MRNA Splicing and Mitosis Factor |
| RFWD2 | 5.5455 | 1.08 × 10−8 | 6.240 | COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| RNF40 | 5.3754 | 7.73 × 10−6 | 3.083 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1B |
| FASN | 5.3652 | 0.01 | 1.708 | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| MTHFD1 | 5.0852 | 4.23 × 10−5 | 2.525 | C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase |
| STIP1 | 4.9889 | 2.89 × 10−5 | 3.699 | Stress-induced-phosphoprotein 1 |
| DNAJB1 | 4.9816 | 2.18 × 10−7 | 5.567 | DnaJ Heat Shock Protein Family Member B1 |
| STK40 | 4.9431 | 5.94 × 10−6 | 5.105 | Serine/threonine Kinase 40 |
| PLEC | 4.3460 | 0.0006 | 3.183 | Plectin |
| HDAC6 | 4.1498 | 0.01 | 2.356 | Histone Deacetylase 6 |
| PAAF1 | 3.9612 | 0.008 | 2.609 | Proteasomal ATPase Associated Factor 1 |
| EDF1 | 3.8339 | 1.82 × 10−5 | 3.326 | Endothelial Differentiation Related Factor 1 |
| CUX1 | 3.7878 | 0.003 | 2.122 | Cut like Homeobox 1 |
| PRDX2 | 3.7664 | 0.01 | 3.741 | Peroxiredoxin 2 |
| CEBPB | 2.9757 | 0.01 | 1.223 | CCAAT Enhancer Binding Protein Beta |
| TRIB3 binding partners in MCF7 | ||||
| CDKN1A | 7.7691 | 0.0001 | 2.752 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A |
| TRIM37 | 7.6337 | 0.01 | 3.405 | Tripartite Motif Containing 37 |
| ZNF217 | 7.5252 | 2.35 × 10−6 | 2.732 | Zinc Finger Protein 217 |
| TRIB1 | 6.5117 | 0.001 | 2.966 | Tribbles Pseudokinase 1 |
| HIF1A | 6.4611 | 0.0001 | 2.139 | Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 Subunit Alpha |
| PPM1D | 6.4143 | 0.006 | 2.567 | Protein Phosphatase Mg Dependent 1D |
| ZBTB1 | 6.0395 | 0.01 | 1.828 | Zinc Finger And BTB Domain 1 |
| CEBPB | 5.7224 | 0.0001 | 2.463 | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta |
| WDR5 | 5.7100 | 0.001 | 2.372 | WD repeat-containing protein 5 |
| ZNF627 | 5.3262 | 0.003 | 2.866 | Zinc Finger Protein 627 |
| ZNF460 | 5.1982 | 0.002 | 1.775 | Zinc Finger Protein 460 |
| DNAJB1 | 5.1152 | 2.35 × 10−6 | 4.064 | DnaJ homolog subfamily B member 1 |
| PARN | 4.9613 | 2.48 × 10−5 | 3.301 | Poly(A)-specific Ribonuclease |
| RFWD2 | 4.9105 | 5.62 × 10−7 | 3.904 | COP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| FASN | 4.6569 | 0.05 | 1.709 | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| TIMM13 | 3.8986 | 1.92 × 10−5 | 2.370 | Translocase of Inner Mitochondrial Membrane 13 |
| ZNF12 | 3.7582 | 0.01 | 2.602 | Zinc Finger Protein 12 |
| KDM3B | 3.5315 | 0.05 | 2.185 | Lysine-specific demethylase 3B |
| DPY30 | 3.3126 | 0.001 | 2.089 | Dpy-30 Histone Methyltranferase Complex |
| TP53 | 2.3725 | 0.0001 | 2.372 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Quiles, M.; Baak, R.; Borgman, A.; den Haan, S.; Sobrevals Alcaraz, P.; van Es, R.; Kiss-Toth, E.; Vos, H.; Kalkhoven, E. Comprehensive Profiling of Mammalian Tribbles Interactomes Implicates TRIB3 in Gene Repression. Cancers 2021, 13, 6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246318
Hernández-Quiles M, Baak R, Borgman A, den Haan S, Sobrevals Alcaraz P, van Es R, Kiss-Toth E, Vos H, Kalkhoven E. Comprehensive Profiling of Mammalian Tribbles Interactomes Implicates TRIB3 in Gene Repression. Cancers. 2021; 13(24):6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246318
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Quiles, Miguel, Rosalie Baak, Anouska Borgman, Suzanne den Haan, Paula Sobrevals Alcaraz, Robert van Es, Endre Kiss-Toth, Harmjan Vos, and Eric Kalkhoven. 2021. "Comprehensive Profiling of Mammalian Tribbles Interactomes Implicates TRIB3 in Gene Repression" Cancers 13, no. 24: 6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246318
APA StyleHernández-Quiles, M., Baak, R., Borgman, A., den Haan, S., Sobrevals Alcaraz, P., van Es, R., Kiss-Toth, E., Vos, H., & Kalkhoven, E. (2021). Comprehensive Profiling of Mammalian Tribbles Interactomes Implicates TRIB3 in Gene Repression. Cancers, 13(24), 6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246318