Three-Dimensional Tumor Spheroids as a Tool for Reliable Investigation of Combined Gold Nanoparticle and Docetaxel Treatment
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis, Surface Modification, and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles
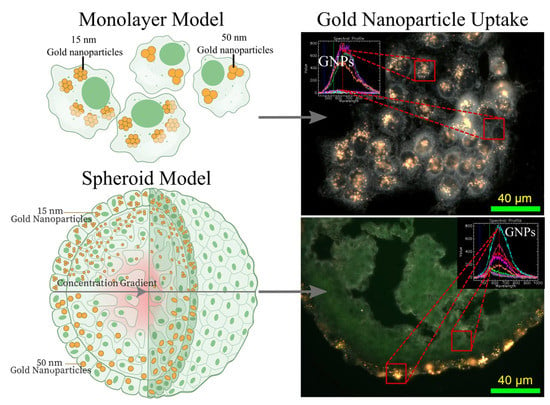
2.2. Cell Culture and Growth of Spheroids
2.3. Proliferation Assay of Docetaxel in Monolayer and Spheroids
2.4. Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticle Complex
2.5. Preparation of Cells for Imaging Using Darkfield and Hyper Spectral Imaging
2.6. Cell Cycle Analysis of Docetaxel Using Flow Cytometry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haume, K.; Rosa, S.; Grellet, S.; Śmiałek, M.A.; Butterworth, K.T.; Solov’yov, A.V.; Prise, K.M.; Golding, J.; Mason, N.J. Gold nanoparticles for cancer radiotherapy: A review. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikjoo, H.; O’Neill, P.; Wilson, W.E.; Goodhead, D.T. Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation. In Proceedings of the Radiation Research. Radiat. Res. Soc. 2001, 156, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffray, D.A.; Gospodarowicz, M.K. Radiation Therapy for Cancer. In Disease Control Priorities, Cancer, 3rd ed.; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Volume 3, pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Delaney, G.P.; Barton, M.B. Evidence-based Estimates of the Demand for Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, S. Is it time for a new paradigm for systemic cancer treatment? Lessons from a century of cancer chemotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baba, A.I.; Câtoi, C. Principles of Anticancer Therapy; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, M.J. Principles of systemic anticancer therapy. Medicine 2020, 48, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, E. Curative Cancer Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 2924–2930. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Jenrow, K.A.; Brown, S.L. Mechanisms of radiation-induced normal tissue toxicity and implications for future clinical trials. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2014, 32, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Rodriguez-Torres, M.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Xue, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Q.; Zhu, J.; Tian, X. Metal-Based Hybrid Nanoparticles as Radiosensitizers in Cancer Therapy. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2018, 23, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W. Applications of gold nanoparticles in cancer nanotechnology. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2008, 1, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Liang, X. Progress in research on gold nanoparticles in cancer management. Medicine 2019, 98, e15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.A.; Razak, K.A.; Geso, M.; Abdullah, R.; Dollah, N.; Rahman, W.N. Radiobiological Characterization of the Radiosensitization Effects by Gold Nanoparticles for Megavoltage Clinical Radiotherapy Beams. Bionanoscience 2018, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, F.; Vallis, K.A.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Bandla, A.; Yukun, D.; Carlisle, R. Megavoltage radiosensitization of gold nanoparticles on a glioblastoma cancer cell line using a clinical platform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Coulter, J.A.; Hounsell, A.R.; Butterworth, K.T.; McMahon, S.J.; Hyland, W.B.; Muir, M.F.; Dickson, G.R.; Prise, K.M.; Currell, F.J.; et al. Cell-Specific Radiosensitization by gold nanoparticles at megavoltage radiation energies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngwa, W.; Kumar, R.; Sridhar, S.; Korideck, H.; Zygmanski, P.; Cormack, R.A.; Berbeco, R.; Makrigiorgos, G.M. Targeted radiotherapy with gold nanoparticles: Current status and future perspectives. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libutti, S.K.; Paciotti, G.F.; Byrnes, A.A.; Alexander, H.R.; Gannon, W.E.; Walker, M.; Seidel, G.D.; Yuldasheva, N.; Tamarkin, L. Phase I and pharmacokinetic studies of CYT-6091, a novel PEGylated colloidal gold-rhTNF nanomedicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6139–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, M.U.; Novosad, V.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Wali, H.; Ali, A.; Fateh, A.A.; Neogi, P.B.; Neogi, A.; Wang, Z. Gold Nanoparticles-enabled Efficient Dual Delivery of Anticancer Therapeutics to HeLa Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Liao, J.; Shao, X.; Li, Q.; Lin, Y. The Effect of shape on Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles in the forms of Stars, Rods, and Triangles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankayala, R.; Huang, Y.-K.; Kalluru, P.; Chiang, C.-S.; Hwang, K.C. First Demonstration of Gold Nanorods-Mediated Photodynamic Therapeutic Destruction of Tumors via Near Infra-Red Light Activation. Small 2014, 10, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrabalak, S.E.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, X.; Au, L.; Cobley, C.M.; Xia, Y. Gold nanocages: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, P.; Han, G.; De, M.; Kim, C.K.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in delivery applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciotti, G.F.; Kingston, D.G.I.; Tamarkin, L. Colloidal gold nanoparticles: A novel nanoparticle platform for developing multifunctional tumor-targeted drug delivery vectors. Drug Dev. Res. 2006, 67, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromma, K.; Chithrani, D.B. Advances in Gold Nanoparticle-Based Combined Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Shi, W.; Freund, L.B. Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Stewart, J.; Allen, C.; Jaffray, D.A. Intracellular uptake, transport, and processing of nanostructures in cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Chan, W.C.W. Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuemann, J.; Bagley, A.A.F.; Berbeco, R.; Bromma, K.; Butterworth, K.T.K.T.; Byrne, H.; Chithrani, D.B.; Cho, S.H.S.H.; Cook, J.R.J.R.; Favaudon, V.; et al. Roadmap for metal nanoparticles in radiation therapy: Current status, translational challenges, and future directions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, T.A.; Dey, P.; Mosca, S.; Salimi, M.; Palombo, F.; Matousek, P.; Stone, N. Smart Gold Nanostructures for Light Mediated Cancer Theranostics: Combining Optical Diagnostics with Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Wu, D.; Shen, X.; Liu, P.-X.; Yang, N.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.-M.; Zhang, L.-A.; Fan, Y.-M. Fan Size-dependent in vivo toxicity of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruje, C.; Yang, C.; Uertz, J.; Van Prooijen, M.; Chithrani, B.D. Optimization of PEG coated nanoscale gold particles for enhanced radiation therapy. RSC Adv. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, S.; Doyle, H.; Blasco, J.; Redmond, G.; Sheehan, D. Oxidative stress and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, Á.M.; da Silva, K.R.M.; Calado, C.M.S.; Saraiva, K.L.A.; Regina, R.C.B.; Leite, A.C.R.; Meneghetti, M.R. Evaluation of gold nanorods toxicity on isolated mitochondria. Toxicology 2019, 413, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, M.W.; Mouw, J.K.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teti, A. Regulation of cellular functions by extracellular matrix. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1992, 2, S83–S87. [Google Scholar]
- Engin, A.B.; Nikitovic, D.; Neagu, M.; Henrich-Noack, P.; Docea, A.O.; Shtilman, M.I.; Golokhvast, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Mechanistic understanding of nanoparticles’ interactions with extracellular matrix: The cell and immune system. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Poh, M.Z.; Insin, N.; Bawendi, M.G.; Fukumura, D.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. Diffusion of particles in the extracellular matrix: The effect of repulsive electrostatic interactions. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-R.; Lin, R.; Li, H.-J.; He, W.; Du, J.-Z.; Wang, J. Strategies to improve tumor penetration of nanomedicines through nanoparticle design. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pluen, A.; Boucher, Y.; Ramanujan, S.; McKee, T.D.; Gohongi, T.; Di Tomaso, E.; Brown, E.B.; Izumi, Y.; Campbell, R.B.; Berk, D.A.; et al. Role of tumor-host interactions in interstitial diffusion of macromolecules: Cranial vs. subcutaneous tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4628–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rane, T.D.; Armani, A.M. Two-Photon Microscopy Analysis of Gold Nanoparticle Uptake in 3D Cell Spheroids. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelobanov, B.; Poletaeva, J.; Epanchintseva, A.; Tupitsyna, A.; Pyshnaya, I.; Ryabchikova, E. Ultrastructural Features of Gold Nanoparticles Interaction with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells in Monolayer and Spheroids. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Su, J.; Mamdooh, R.; Li, Y.; Stenzel, M.H. Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles and Their Movement in 3D Multicellular Tumor Spheroids: Effect of Molecular Weight and Grafting Density of Poly(2-hydroxyl ethyl acrylate). Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 1900221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, V.; Mekky, G.; van der Meer, S.B.; Seeds, M.C.; Atala, A.J.; Epple, M. Transport of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles (2 nm) across the blood–brain barrier in a six-cell brain spheroid model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Huo, S.; Kumar, A.; Wei, T.; Zhang, X.; Jin, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, P.C.; et al. Size-dependent localization and penetration of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in cancer cells, multicellular spheroids, and tumors in vivo. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4483–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, S.; Jin, S.; Ma, X.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Kumar, A.; Wang, P.C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Liang, X.J. Ultrasmall gold nanoparticles as carriers for nucleus-based gene therapy due to size-dependent nuclear entry. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Yan, H.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.J.; Zhang, J. Ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 494–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffle, S.; Pandey, R.N.; Albert, M.; Hegde, R.S. Linking hypoxia, DNA damage and proliferation in multicellular tumor spheroids. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, A.H.; Bromma, K.; Sung, W.; Monica, M.; Cicon, L.; Howard, P.; Chow, R.L.; Schuemann, J.; Chithrani, D.B. Modulation of nanoparticle uptake, intracellular distribution, and retention with docetaxel to enhance radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P. A new paradigm for the treatment of high-risk prostate cancer: Radiosensitization with docetaxel. Rev. Urol. 2003, 5 (Suppl. 3), S71–S77. [Google Scholar]
- Frens, G. Controlled Nucleation for the Regulation of the Particle Size in Monodisperse Gold Suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromma, K.; Cicon, L.; Beckham, W.; Chithrani, D.B.D.B. Gold nanoparticle mediated radiation response among key cell components of the tumour microenvironment for the advancement of cancer nanotechnology. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nativo, P.; Prior, I.A.; Brust, M. Uptake and intracellular fate of surface-modified gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elci, S.G.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, B.; Kim, S.T.; Saha, K.; Moyano, D.F.; Yesilbag Tonga, G.; Jackson, L.C.; Rotello, V.M.; Vachet, R.W. Surface Charge Controls the Suborgan Biodistributions of Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5536–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manson, J.; Kumar, D.; Meenan, B.J.; Dixon, D. Polyethylene glycol functionalized gold nanoparticles: The influence of capping density on stability in various media. Gold Bull. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-H.H.; Onodera, Y.; Ichikawa, Y.; Rankin, E.B.; Giaccia, A.J.; Watanabe, Y.; Qian, W.; Hashimoto, T.; Shirato, H.; Nam, J.-M.M. Targeting integrins with RGD-conjugated gold nanoparticles in radiotherapy decreases the invasive activity of breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 5069–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wuithschick, M.; Birnbaum, A.; Witte, S.; Sztucki, M.; Vainio, U.; Pinna, N.; Rademann, K.; Emmerling, F.; Kraehnert, R.; Polte, J. Turkevich in New Robes: Key Questions Answered for the Most Common Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7052–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Kendall, K.; Toloueinia, P.; Mehrabadi, Y.; Gupta, G.; Newton, J. Aggregation and adhesion of gold nanoparticles in phosphate buffered saline. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.E.; Ho, C.L.; Lin, C.S.; Chen, Y.W. Complete remission in very advanced oral cancer by docetaxel, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil based induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiation. J. Dent. Sci. 2018, 13, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantab, R.; Sivananthan, S.; Tannock, I.F. The penetration of anticancer drugs through tumor tissue as a function of cellular adhesion and packing density of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhail, A.S.; Eetezadi, S.; Allen, C. Multicellular Tumor Spheroids for Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Tumor Growth Inhibitory Effects of Nanomedicines In Vitro: A Comparison of Docetaxel-Loaded Block Copolymer Micelles and Taxotere®. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Abbas, S.; Saxena, A.K.; Tiwari, S.; Sharma, L.K.; Tiwari, M. Critical role of three-dimensional tumorsphere size on experimental outcome. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, M.; Niepel, M.; Chung, M.; Sorger, P.K. Growth rate inhibition metrics correct for confounders in measuring sensitivity to cancer drugs. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riedl, A.; Schlederer, M.; Pudelko, K.; Stadler, M.; Walter, S.; Unterleuthner, D.; Unger, C.; Kramer, N.; Hengstschläger, M.; Kenner, L.; et al. Comparison of cancer cells in 2D vs. 3D culture reveals differences in AKT-mTOR-S6K signaling and drug responses. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.L.; Tian, T.; Nan, K.J.; Zhao, N.; Guo, Y.H.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.G. Survival advantages of multicellular spheroids vs. monolayers of HepG2 cells in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edmondson, R.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Influence of Matrices on 3D-Cultured Prostate Cancer Cells’ Drug Response and Expression of Drug-Action Associated Proteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abyaneh, H.S.; Regenold, M.; McKee, T.D.; Allen, C.; Gauthier, M.A. Towards extracellular matrix normalization for improved treatment of solid tumors. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1960–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fr Brunsvig, P.; Andersen, A.; Aamdal, S.; Kristensen, V.; Olsen, H. Pharmacokinetic analysis of two different docetaxel dose levels in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with docetaxel as monotherapy or with concurrent radiotherapy. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamora-Perez, P.; Tsoutsi, D.; Xu, R.; Rivera-Gil, P. Hyperspectral-enhanced dark field microscopy for single and collective nanoparticle characterization in biological environments. Materials 2018, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- England, C.G.; Huang, J.S.; James, K.T.; Zhang, G.; Gobin, A.; Frieboes, H.B. Detection of phosphatidylcholine-coated gold nanoparticles in orthotopic pancreatic adenocarcinoma using hyperspectral imaging. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, T.M.; Keyomarsi, K. Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuthu, K.; Lubin, B.C.; Bazylevich, A.; Gellerman, G.; Shpilberg, O.; Luboshits, G.; Firer, M.A. Gold nanoparticles stabilize peptide-drug-conjugates for sustained targeted drug delivery to cancer cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, T.; Chatterjee, D.; Lee, J.; Grant, J.D.; Bhattarai, S.; Tailor, R.; Goodrich, G.; Nicolucci, P.; Krishnan, S. Targeted gold nanoparticles enhance sensitization of prostate tumors to megavoltage radiation therapy in vivo. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.L.; Hu, Y.S.; Jackson, M.A.; Lin, A.Y.; Young, J.K.; Langsner, R.J.; Drezek, R.A. Quantifying spectral changes experienced by plasmonic nanoparticles in a cellular environment to inform biomedical nanoparticle design. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Uertz, J.; Yohan, D.; Chithrani, B.D. Peptide modified gold nanoparticles for improved cellular uptake, nuclear transport, and intracellular retention. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12026–12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mó, I.; Sabino, I.J.; De Melo-Diogo, D.; Lima-Sousa, R.; Alves, C.G.; Correia, I.J. The importance of spheroids in analyzing nanomedicine efficacy. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehullah, A.; Tan, S.H.; Barker, N. Organoids as an in vitro model of human development and disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penninckx, S.; Heuskin, A.C.; Michiels, C.; Lucas, S. Gold nanoparticles as a potent radiosensitizer: A transdisciplinary approach from physics to patient. Cancers 2020, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bromma, K.; Alhussan, A.; Perez, M.M.; Howard, P.; Beckham, W.; Chithrani, D.B. Three-Dimensional Tumor Spheroids as a Tool for Reliable Investigation of Combined Gold Nanoparticle and Docetaxel Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061465
Bromma K, Alhussan A, Perez MM, Howard P, Beckham W, Chithrani DB. Three-Dimensional Tumor Spheroids as a Tool for Reliable Investigation of Combined Gold Nanoparticle and Docetaxel Treatment. Cancers. 2021; 13(6):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061465
Chicago/Turabian StyleBromma, Kyle, Abdulaziz Alhussan, Monica Mesa Perez, Perry Howard, Wayne Beckham, and Devika B. Chithrani. 2021. "Three-Dimensional Tumor Spheroids as a Tool for Reliable Investigation of Combined Gold Nanoparticle and Docetaxel Treatment" Cancers 13, no. 6: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061465
APA StyleBromma, K., Alhussan, A., Perez, M. M., Howard, P., Beckham, W., & Chithrani, D. B. (2021). Three-Dimensional Tumor Spheroids as a Tool for Reliable Investigation of Combined Gold Nanoparticle and Docetaxel Treatment. Cancers, 13(6), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061465