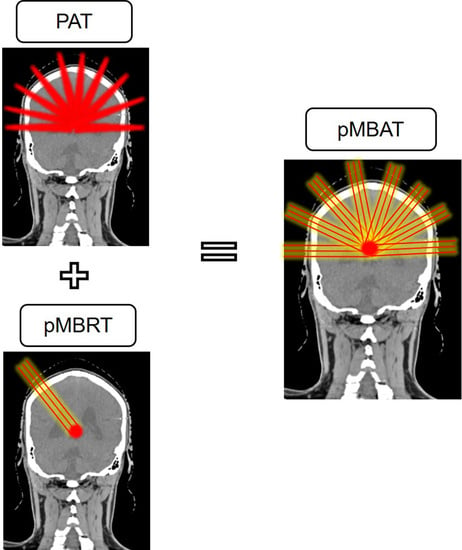
Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy and Arc Therapy: Proof of Concept of a Winning Alliance
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation Geometry and Details
2.2. Treatment Plans
2.2.1. Single-Array pMBRT Treatment
2.2.2. PAT Treatments
2.2.3. pMBAT Treatments
3. Results
3.1. Preservation of the Spatial Modulation of the Dose
3.2. Dose Reduction to Healthy Tissues
3.3. LET Distributions
3.4. Influence of the Plan Parameters in the Dose Reduction in pMBAT
3.4.1. Influence of the Number of Arrays on the Dose Reduction
3.4.2. Influence of the Angular Separation on the Dose Reduction
3.4.3. Centre-To-Centre Distance
3.4.4. PTV Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaspar, L.E.; Ding, M. A review of intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 10, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszak, M.M.; Yan, D.; Grills, I.; Martinez, A. Clinical applications of volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Kang, Y.; Riley, B.; Bilton, S.; Mohan, R.; Komaki, R.; Cox, J.D. Significant reduction of normal tissue dose by proton radiotherapy compared with three-dimensional conformal or intensity-modulated radiation therapy in Stage I or Stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralik, S.F.; Ho, C.Y.; Finke, W.; Buchsbaum, J.C.; Haskins, C.P.; Shih, C.S. Radiation Necrosis in Pediatric Patients with Brain Tumors Treated with Proton Radiotherapy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.M.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Stevens, C.; Yan, D. Spot-Scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) Therapy: The First Robust and Delivery-Efficient Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezado, Y.; Fois, G.R. Proton-minibeam radiation therapy: A proof of concept. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 031712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, J.; Gu, G.; Marcelos, T.; Kooy, H.; Willers, H. Proton arc reduces range uncertainty effects and improves conformality compared with photon volumetric modulated arc therapy in stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, X.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Krauss, D.; Kabolizadeh, P. Have we reached proton beam therapy dosimetric limitations?—A novel robust, delivery-efficient and continuous spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy is to improve the dosimetric outcome in treating prostate cancer. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Blas, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Qin, A.; Chinnaiyan, P.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; et al. Improving dosimetric outcome for hippocampus and cochlea sparing whole brain radiotherapy using spot-scanning proton arc therapy. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Qin, A.; Zheng, W.; Yan, D.; Zhang, S.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Ding, X. Improve the dosimetric outcome in bilateral head and neck cancer (HNC) treatment using spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy: A feasibility study. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Yan, D.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Hong, Y.; Guerrero, T.; Grills, I.; Stevens, C.; Ding, X. Improve dosimetric outcome in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer treatment using spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, L.; Dilworth, J.T.; Zheng, W.; Jawad, S.; Yan, D.; Chen, P.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; et al. Feasibility study: Spot-scanning proton arc therapy (SPArc) for left-sided whole breast radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Bertolet-Reina, A.; Karagounis, I.; Huynh, K.; Dale, R.G. Is there a role for arcing techniques in proton therapy? Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peucelle, C.; Nauraye, C.; Patriarca, A.; Hierso, E.; Fournier-Bidoz, N.; Martínez-Rovira, I.; Prezado, Y. Proton minibeam radiation therapy: Experimental dosimetry evaluation. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 7108–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamirault, C.; Doyère, V.; Juchaux, M.; Pouzoulet, F.; Labiod, D.; Dendale, R.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Le Dudal, M.; Jouvion, G.; et al. Short and long-term evaluation of the impact of proton minibeam radiation therapy on motor, emotional and cognitive functions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezado, Y.; Jouvion, G.; Hardy, D.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Bergs, J.; González, W.; Guardiola, C.; Juchaux, M.; Labiod, D.; et al. Proton minibeam radiation therapy spares normal rat brain: Long-Term Clinical, Radiological and Histopathological Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlobinskaya, O.; Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Hable, V.; Siebenwirth, C.; Walsh, D.W.; Multhoff, G.; Wilkens, J.J.; Schmid, T.E.; Dollinger, G. Reduced side effects by proton microchannel radiotherapy: Study in a human skin model. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2013, 52, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Reindl, J.; Siebenwirth, C.; Zlobinskaya, O.; Walsh, D.W.; Ilicic, K.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Wilkens, J.J.; et al. Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy Reduces Side Effects in an In Vivo Mouse Ear Model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prezado, Y.; Jouvion, G.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Guardiola, C.; Juchaux, M.; Lamirault, C.; Labiod, D.; Jourdain, L.; Sebrie, C.; et al. Proton minibeam radiation therapy widens the therapeutic index for high-grade gliomas. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamirault, C.; Brisebard, E.; Patriarca, A.; Juchaux, M.; Crepin, D.; Labiod, D.; Pouzoulet, F.; Sebrie, C.; Jourdain, L.; Le Dudal, M.; et al. Spatially Modulated Proton Minibeams Results in the Same Increase of Lifespan as a Uniform Target Dose Coverage in F98-Glioma-Bearing Rats. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezado, Y.; Jouvion, G.; Guardiola, C.; Gonzalez, W.; Juchaux, M.; Bergs, J.; Nauraye, C.; Labiod, D.; De Marzi, L.; Pouzoulet, F.; et al. Tumor Control in RG2 Glioma-Bearing Rats: A Comparison Between Proton Minibeam Therapy and Standard Proton Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, J.; Shin, J.; Schümann, J.; Faddegon, B.; Paganetti, H. TOPAS: An innovative proton Monte Carlo platform for research and clinical applications. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 6818–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marzi, L.; Da Fonseca, A.; Moignier, C.; Patriarca, A.; Goudjil, F.; Mazal, A.; Buvat, I.; Hérault, J. Experimental characterisation of a proton kernel model for pencil beam scanning techniques. Phys. Med. 2019, 64, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevillot, L.; Bertrand, D.; Dessy, F.; Freud, N.; Sarrut, D. GATE as a GEANT4-based Monte Carlo platform for the evaluation of proton pencil beam scanning treatment plans. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 4223–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winterhalter, C.; Taylor, M.; Boersma, D.; Elia, A.; Guatelli, S.; Mackay, R.; Kirkby, K.; Maigne, L.; Ivanchenko, V.; Resch, A.F.; et al. Evaluation of GATE-RTion (GATE/Geant4) Monte Carlo simulation settings for proton pencil beam scanning quality assurance. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 5817–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansonneur, P.; Mammar, H.; Nauraye, C.; Patriarca, A.; Hierso, E.; Dendale, R.; Prezado, Y.; De Marzi, L. First proton minibeam radiation therapy treatment plan evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marzi, L.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Hierso, E.; Dendale, R.; Guardiola, C.; Prezado, Y. Implementation of planar proton minibeam radiation therapy using a pencil beam scanning system: A proof of concept study. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 5305–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiropoulos, M.; Brisebard, E.; Le Dudal, M.; Jouvion, G.; Juchaux, M.; Crépin, D.; Sebrie, C.; Jourdain, L.; Labiod, D.; Lamirault, C.; et al. X-rays minibeam radiation therapy at a conventional irradiator: Pilot evaluation in F98-glioma bearing rats and dose calculations in a human phantom. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 27, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Patriarca, A.; Prezado, Y. Improving the dose distributions in minibeam radiation therapy: Helium ions vs. protons. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 640–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, G.; Janssens, G.; De Wilde, O.; Bossier, V.; Lerot, X.; Pouppez, A.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; et al. The first prototype of spot-scanning proton arc treatment delivery. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, L.; Indelicato, D.J.; Holgersen, K.S.; Petersen, J.B.; Stokkevåg, C.H.; Lassen-Ramshad, Y.; Casares-Magaz, O.; Vestergaard, A.; Muren, L.P. Towards proton arc therapy: Physical and biologically equivalent doses with increasing number of beams in pediatric brain irradiation. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabe, A.; Karagounis, I.V.; Huynh, K.; Bertolet, A.; François, N.; Kim, M.M.; Maity, A.; Abel, E.; Dale, R. Radiobiological effectiveness difference of proton arc beams versus conventional proton and photon beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 165002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezado, Y.; Deman, P.; Varlet, P.; Jouvion, G.; Gil, S.; Le Clec’H, C.; Bernard, H.; Le Duc, G.; Sarun, S. Tolerance to Dose Escalation in Minibeam Radiation Therapy Applied to Normal Rat Brain: Long-Term Clinical, Radiological and Histopathological Analysis. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertho, A.; Brisebard, E.; Juchaux, M.; Gilbert, C.; Lamirault, C.; Pouzoulet, F.; Prezado, Y. Anti-Tumor Immune Response and Long-Term Immunological Memory Induced by Minibeam Radiation Therapy: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, S121–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmanian, F.A.; Button, T.M.; Le Duc, G.; Zhong, N.; Peña, L.A.; Smith, J.A.; Martinez, S.R.; Bacarian, T.; Tammam, J.; Ren, B.; et al. Response of rat intracranial 9L gliosarcoma to microbeam radiation therapy. Neuro. Oncol. 2002, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaudon, V. Flash radiotheray at very high dose-rate: A brief account of the current situation. Cancer Radiother. 2019, 23, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmanian, F.A.; Rusek, A.; Fois, G.R.; Olschowka, J.; Desnoyers, N.R.; Park, J.Y.; Dioszegi, I.; Dane, B.; Wang, R.; Tomasi, D.; et al. Interleaved carbon minibeams: An experimental radiosurgery method with clinical potential. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eling, L.; Bouchet, A.; Ocadiz, A.; Adam, J.F.; Kershmiri, S.; Elleaume, H.; Krisch, M.; Verry, C.; Laissue, J.A.; Balosso, J.; et al. Unexpected Benefits of Multiport Synchrotron Microbeam Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertho, A.; Ortiz, R.; Juchaux, M.; Gilbert, C.; Lamirault, C.; Polledo, L.; Pouzoulet, F.; Liens, A.; Warfving, N.; Sebrie, C.; et al. First evaluation of temporal and spatial fractionation in proton minibeam radiation therapy of glioma-bearing rats. Cancers 2021, 13, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Case Number | Number of Arrays | Angular Separation | c-t-c | PTV Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of arrays | ||||
| 1 | 13 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 2 | 11 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 3 | 9 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 4 | 7 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| Angular separation | ||||
| 5 | 9 | 20° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 6 | 9 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 7 | 9 | 10° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| c-t-c distance | ||||
| 8 | 13 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 9 | 13 | 15° | 2800 μm | 20 mm |
| 10 | 13 | 15° | 2000 μm | 20 mm |
| PTV size | ||||
| 11 | 13 | 15° | 4000 μm | 20 mm |
| 12 | 13 | 15° | 4000 μm | 30 mm |
| Integral Doses (a.u.) | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTV | Brain | |
| PAT | 1.00 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.02 |
| pMBRT | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 0.32 ± 0.03 |
| pMBAT | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 0.33 ± 0.03 |
| Mean LETd (keV/μm) | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTV | Brain | |
| PAT | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.1 |
| pMBRT | 3.5 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| pMBAT | 3.6 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz, R.; De Marzi, L.; Prezado, Y. Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy and Arc Therapy: Proof of Concept of a Winning Alliance. Cancers 2022, 14, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010116
Ortiz R, De Marzi L, Prezado Y. Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy and Arc Therapy: Proof of Concept of a Winning Alliance. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz, Ramon, Ludovic De Marzi, and Yolanda Prezado. 2022. "Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy and Arc Therapy: Proof of Concept of a Winning Alliance" Cancers 14, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010116
APA StyleOrtiz, R., De Marzi, L., & Prezado, Y. (2022). Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy and Arc Therapy: Proof of Concept of a Winning Alliance. Cancers, 14(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010116