Combination of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 Improves Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Culture Conditions, and Treatment
2.2. Microarray Analysis of the S100A4-Induced Transcriptome
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.4. Western Blot (WB) Analysis and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay (ChIP)
2.6. Luciferase-Based Reporter Assay
2.7. Boyden Chamber Transwell Migration Assaya
2.8. mRNA Expression Analysis of Xenograft CRC Mouse Tumor Tissue
2.9. Immunohistochemistry of Xenograft CRC Mouse Tumor Tissue
2.10. Data Mining of Expression Microarray Data
2.11. Patient Material
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
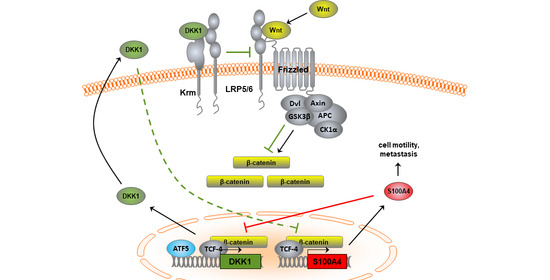
3.1. Inverse Expression Correlation of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 in CRC Cells
3.1.1. Identification of the S100A4-Induced Transcriptome
3.1.2. S100A4 Inhibits Expression of the Wnt Pathway Antagonist DKK1
3.1.3. Inverse Expression Correlation of S100A4 and DKK1 in Further CRC Cell Lines
3.1.4. Expression Regulation of DKK1 in CRC Cells Involves the Transcription Factor ATF5
3.1.5. Transcriptional Cross-Regulation of DKK1 and S100A4 Affects S100A4 Phenotype
3.1.6. Knock-Down of Wnt Target Gene S100A4 Countermands Inhibition of DKK1
3.2. Transcriptional Cross-Regulation of S100A4 and DKK1 Has Prognostic Value for CRC Patient Survival
3.2.1. Inverse Expression Correlation of S100A4 and DKK1 in CRC Microarray Datasets
3.2.2. Prognostic Value of Combining S100A4 and DKK1 Expression in CRC Tumor Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| log2-Fold Change | StDev | Gene Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.04 | 1.21 | APC | Promotes rapid degradation of β-catenin and participates in Wnt signaling as a negative regulator. |
| 4.29 | 0.82 | TBL1Y | Plays an essential role in transcription activation mediated by nuclear receptors. |
| −1.72 | 0.22 | CAMK2D | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase involved in the regulation of Ca2+ homeostasis. |
| −1.72 | 0.36 | CD44 | Cell-surface receptor that plays a role in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion, and migration. |
| −1.73 | 0.36 | HDAC2 | Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). |
| −1.84 | 0.57 | CCND1 | Regulatory component of the cyclin D1-CDK4 (DC) complex that regulates the cell cycle during G1/S transition. |
| −1.99 | 0.43 | EPCAM | Plays a role in embryonic stem cells proliferation and differentiation. |
| −2.13 | 0.35 | PTK2 | Non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulating cell migration, adhesion, formation, and disassembly of focal adhesions and cell protrusions, cell cycle progression, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. |
| −2.23 | 0.57 | DKK1 | Antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling by inhibiting LRP5/6 interaction with Wnt and by forming a ternary complex with the transmembrane protein KREMEN that promotes internalization of LRP5/6. |
| −2.26 | 0.22 | MET | Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes, including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis, and survival. |
| −2.50 | 0.80 | AMOTL2 | Regulates the translocation of phosphorylated SRC to peripheral cell-matrix adhesion sites. Inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, probably by recruiting β-catenin to recycling endosomes, and hence preventing its translocation to the nucleus. |
| −5.22 | 3.81 | TBL1XR1 | F-box-like protein involved in the recruitment of the ubiquitin/19S proteasome complex to nuclear receptor-regulated transcription units. Plays an essential role in transcription activation mediated by nuclear receptors. |
Appendix B

Appendix C

References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucci, M.R.; Robinson, C.R.; Longo, P.; Campbell, P.; Hamilton, S.R. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of aberrant crypt foci in human colorectal mucosa. Hum. Pathol. 1997, 28, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, E.; Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Signaling pathways in intestinal development and cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 695–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N. The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 468, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, U.; Stein, U. Wnt up your mind—Intervention strategies for S100A4-induced metastasis in colon cancer. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2009, 28, F55–F64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R. Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, P.J.; Sparks, A.B.; Korinek, V.; Barker, N.; Clevers, H.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science 1997, 275, 1787–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbst, A.; Jurinovic, V.; Krebs, S.; Thieme, S.E.; Blum, H.; Göke, B.; Kolligs, F.T. Comprehensive analysis of β-catenin target genes in colorectal carcinoma cell lines with deregulated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segditsas, S.; Tomlinson, I. Colorectal cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7531–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebouissou, S.; Franconi, A.; Calderaro, J.; Letouzé, E.; Imbeaud, S.; Pilati, C.; Nault, J.-C.; Couchy, G.; Laurent, A.; Balabaud, C.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation of CTNNB1 mutations reveals different ß-catenin activity associated with liver tumor progression. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, U.; Arlt, F.; Walther, W.; Smith, J.; Waldman, T.; Harris, E.D.; Mertins, S.D.; Heizmann, C.W.; Allard, D.; Birchmeier, W.; et al. The metastasis-associated gene S100A4 is a novel target of beta-catenin/T-cell factor signaling in colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1486–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Siddique, H.R.; Saleem, M. S100A4 calcium-binding protein is key player in tumor progression and metastasis: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boye, K.; Maelandsmo, G.M. S100A4 and metastasis: A small actor playing many roles. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmann, M.; Okhrimenko, A.; Marcinkowski, P.; Osterland, M.; Herrmann, P.; Smith, J.; Heizmann, C.W.; Schlag, P.M.; Stein, U. RAGE mediates S100A4-induced cell motility via MAPK/ERK and hypoxia signaling and is a prognostic biomarker for human colorectal cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maelandsmo, G.M.; Hovig, E.; Skrede, M.; Engebraaten, O.; Flørenes, V.A.; Myklebost, O.; Grigorian, M.; Lukanidin, E.; Scanlon, K.J.; Fodstad, O. Reversal of the in vivo metastatic phenotype of human tumor cells by an anti-CAPL (mts1) ribozyme. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 5490–5498. [Google Scholar]
- Takenaga, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Sakiyama, S. Expression of antisense RNA to S100A4 gene encoding an S100-related calcium-binding protein suppresses metastatic potential of high-metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene 1997, 14, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahlmann, M.; Sack, U.; Herrmann, P.; Lemm, M.; Fichtner, I.; Schlag, P.M.; Stein, U. Systemic shRNA mediated knock-down of S100A4 in colorectal cancer xenografted mice reduces metastasis formation. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sack, U.; Walther, W.; Scudiero, D.; Selby, M.; Kobelt, D.; Lemm, M.; Fichtner, I.; Schlag, P.M.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Stein, U. Novel effect of antihelminthic Niclosamide on S100A4-mediated metastatic progression in colon cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, U.; Arlt, F.; Smith, J.; Sack, U.; Herrmann, P.; Walther, W.; Lemm, M.; Fichtner, I.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Schlag, P.M. Intervening in β-catenin signaling by sulindac inhibits S100A4-dependent colon cancer metastasis. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sack, U.; Walther, W.; Scudiero, D.; Selby, M.; Aumann, J.; Lemos, C.; Fichtner, I.; Schlag, P.M.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Stein, U. S100A4-induced cell motility and metastasis is restricted by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor calcimycin in colon cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3344–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, C.; Sack, U.; Schmid, F.; Juneja, M.; Stein, U. Anti-metastatic treatment in colorectal cancer: Targeting signaling pathways. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 841–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sancho, J.M.; Aguilera, O.; García, J.M.; Pendás-Franco, N.; Peña, C.; Cal, S.; García de Herreros, A.; Bonilla, F.; Muñoz, A. The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of beta-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, B.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Hoppe, D.; Stannek, P.; Glinka, A.; Niehrs, C. LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature 2001, 411, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafico, A.; Liu, G.; Yaniv, A.; Gazit, A.; Aaronson, S.A. Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, E.; Zhan, F.; Walker, R.; Rasmussen, E.; Ma, Y.; Barlogie, B.; Shaughnessy, J.D. The Role of the Wnt-Signaling Antagonist DKK1 in the Development of Osteolytic Lesions in Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2483–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachner, T.D.; Göbel, A.; Benad-Mehner, P.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Rauner, M. Dickkopf-1 as a mediator and novel target in malignant bone disease. Cancer Lett. 2014, 346, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thudi, N.K.; Martin, C.K.; Murahari, S.; Shu, S.T.; Lanigan, L.G.; Werbeck, J.L.; Keller, E.T.; McCauley, L.K.; Pinzone, J.J.; Rosol, T.J. Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) stimulated prostate cancer growth and metastasis and inhibited bone formation in osteoblastic bone metastases. Prostate 2011, 71, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariz, K.; Ingolf, J.-B.; Daniel, H.; Teresa, N.J.; Erich-Franz, S. The Wnt inhibitor dickkopf-1: A link between breast cancer and bone metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Cong, M.; Peng, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Hu, G. Differential effects on lung and bone metastasis of breast cancer by Wnt signalling inhibitor DKK1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malladi, S.; Macalinao, D.G.; Jin, X.; He, L.; Basnet, H.; Zou, Y.; de Stanchina, E.; Massagué, J. Metastatic Latency and Immune Evasion through Autocrine Inhibition of WNT. Cell 2016, 165, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Xie, L.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhai, L.; Li, S.; Qin, X. Prognostic significance of dickkopf-1 overexpression in solid tumors: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 3145–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurluler, E.; Tumay, L.V.; Guner, O.S.; Kucukmetin, N.T.; Hizli, B.; Zorluoglu, A. The role of preoperative serum levels for Dickkopf-related protein 1 as a potential marker of tumor invasion in patients with stage II and III colon cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sui, Q.; Zheng, J.; Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Ou, Q.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, L.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, B.; et al. Dickkopf-related protein 1, a new biomarker for local immune status and poor prognosis among patients with colorectal liver Oligometastases: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosack, D.A.; Dennis, G.J.; Sherman, B.T.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. Identifying biological themes within lists of genes with EASE. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, G.J.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiho, P.; Kokko, A.; Vanharanta, S.; Salovaara, R.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Järvinen, H.; Mecklin, J.-P.; Karttunen, T.J.; Tuppurainen, K.; Davalos, V.; et al. Serrated carcinomas form a subclass of colorectal cancer with distinct molecular basis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uronis, J.M.; Osada, T.; McCall, S.; Yang, X.Y.; Mantyh, C.; Morse, M.A.; Lyerly, H.K.; Clary, B.M.; Hsu, D.S. Histological and molecular evaluation of patient-derived colorectal cancer explants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gröne, J.; Lenze, D.; Jurinovic, V.; Hummel, M.; Seidel, H.; Leder, G.; Beckmann, G.; Sommer, A.; Grützmann, R.; Pilarsky, C.; et al. Molecular profiles and clinical outcome of stage UICC II colon cancer patients. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2011, 26, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhopuro, P.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Niittymäki, I.; Biström, M.; Raitila, A.; Saharinen, J.; Nousiainen, K.; Lehtonen, H.J.; Heliövaara, E.; Puhakka, J.; et al. Candidate driver genes in microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Iida, S.; Ishiguro, M.; Mogushi, K.; Mizushima, H.; Uetake, H.; Tanaka, H.; Sugihara, K. Clinical Significance of Osteoprotegerin Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2444–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, U.; Walther, W.; Arlt, F.; Schwabe, H.; Smith, J.; Fichtner, I.; Birchmeier, W.; Schlag, P.M. MACC1, a newly identified key regulator of HGF-MET signaling, predicts colon cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilm, K.; Kemmner, W.; Osterland, M.; Burock, S.; Koch, G.; Herrmann, P.; Schlag, P.M.; Stein, U. High MACC1 expression in combination with mutated KRAS G13 indicates poor survival of colorectal cancer patients. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janky, R.; Verfaillie, A.; Imrichová, H.; Van de Sande, B.; Standaert, L.; Christiaens, V.; Hulselmans, G.; Herten, K.; Naval Sanchez, M.; Potier, D.; et al. iRegulon: From a gene list to a gene regulatory network using large motif and track collections. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demchak, B.; Hull, T.; Reich, M.; Liefeld, T.; Smoot, M.; Ideker, T.; Mesirov, J.P. Cytoscape: The network visualization tool for GenomeSpace workflows. F1000Research 2014, 3, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, T.; Rudeen, A.; Neufeld, K. Oncogenic Serine 45-Deleted β-Catenin Remains Susceptible to Wnt Stimulation and APC Regulation in Human Colonocytes. Cancers 2020, 12, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Enge, M.; Whitington, T.; Dave, K.; Liu, J.; Sur, I.; Schmierer, B.; Jolma, A.; Kivioja, T.; Taipale, M.; et al. Transcription factor binding in human cells occurs in dense clusters formed around cohesin anchor sites. Cell 2013, 154, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, S.; Herrington, S.; Prime, W.; Rudland, P.S.; Barraclough, R. S100A4 (p9Ka) protein in colon carcinoma and liver metastases: Association with carcinoma cells and T-lymphocytes. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helfman, D.M.; Kim, E.J.; Lukanidin, E.; Grigorian, M. The metastasis associated protein S100A4: Role in tumour progression and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niida, A.; Hiroko, T.; Kasai, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; Akiyama, T. DKK1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a target of the beta-catenin/TCF pathway. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8520–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glinka, A.; Wu, W.; Delius, H.; Monaghan, A.P.; Blumenstock, C.; Niehrs, C. Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 1998, 391, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semënov, M.V.; Tamai, K.; Brott, B.K.; Kühl, M.; Sokol, S.; He, X. Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, O.; Fraga, M.F.; Ballestar, E.; Paz, M.F.; Herranz, M.; Espada, J.; García, J.M.; Muñoz, A.; Esteller, M.; González-Sancho, J.M. Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 (DKK-1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4116–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, H.; Suzuki, H.; Toyota, M.; Nojima, M.; Maruyama, R.; Sasaki, S.; Takagi, H.; Sogabe, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Idogawa, M.; et al. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of DICKKOPF family genes in human gastrointestinal tumors. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Li, S.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Miao, S.; Du, R.; et al. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) contributes to colorectal tumorigenesis via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by down-regulating Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) [corrected]. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukuda, A.; Endoh, H.; Yasuda, M.; Mizutani, T.; Kawabata, K.; Haga, H. Role of ATF5 in the invasive potential of diverse human cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpel-Massler, G.; Horst, B.A.; Shu, C.; Chau, L.; Tsujiuchi, T.; Bruce, J.N.; Canoll, P.; Greene, L.A.; Angelastro, J.M.; Siegelin, M.D. A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Dominant-Negative ATF5 Peptide Exerts Anticancer Activity against a Broad Spectrum of Treatment-Resistant Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4698–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelastro, J.M. Targeting ATF5 in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, W.; Angelastro, J.M.; Greene, L.A.; Liu, D.X. Identification of a novel DNA binding site and a transcriptional target for activating transcription factor 5 in c6 glioma and mcf-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddiconto, G.; Toto, C.; Palamà, I.; De Leo, S.; de Luca, E.; De Matteis, S.; Dini, L.; Passerini, C.G.; Di Renzo, N.; Maffia, M.; et al. Targeting of GSK3β promotes imatinib-mediated apoptosis in quiescent CD34+ chronic myeloid leukemia progenitors, preserving normal stem cells. Blood 2012, 119, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Bertrand, F.E.; Davis, N.M.; Abrams, S.L.; Montalto, G.; D’Assoro, A.B.; Libra, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Maestro, R.; et al. Multifaceted roles of GSK-3 and Wnt/β-catenin in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis: Opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Leukemia 2014, 28, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gongoll, S.; Peters, G.; Mengel, M.; Piso, P.; Klempnauer, J.; Kreipe, H.; von Wasielewski, R. Prognostic significance of calcium-binding protein S100A4 in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Xie, L.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Qin, X.; Li, S. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of S100A4 overexpression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, J.-M.; Chen, J.-Z.; Sui, H.-M.; Si-Ma, X.-Q.; Li, G.-Q.; Liu, C.; Li, J.-L.; Ding, Y.-Q.; Li, J.-M. A five-gene signature as a potential predictor of metastasis and survival in colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Gao, J.; Leng, X. Dickkopf-1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colon cancer cells and contributes to colon cancer suppression. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, U.; Schlag, P.M. Clinical, biological, and molecular aspects of metastasis in colorectal cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007, 176, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, H. Genistein affects histone modifications on Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) gene in SW480 human colon cancer cell line. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendás-Franco, N.; Aguilera, O.; Pereira, F.; González-Sancho, J.M.; Muñoz, A. Vitamin D and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in colon cancer: Role and regulation of DICKKOPF genes. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahlmann, M.; Monks, A.; Harris, E.D.; Kobelt, D.; Osterland, M.; Khaireddine, F.; Herrmann, P.; Kemmner, W.; Burock, S.; Walther, W.; et al. Combination of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 Improves Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010037
Dahlmann M, Monks A, Harris ED, Kobelt D, Osterland M, Khaireddine F, Herrmann P, Kemmner W, Burock S, Walther W, et al. Combination of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 Improves Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahlmann, Mathias, Anne Monks, Erik D. Harris, Dennis Kobelt, Marc Osterland, Fadi Khaireddine, Pia Herrmann, Wolfgang Kemmner, Susen Burock, Wolfgang Walther, and et al. 2022. "Combination of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 Improves Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010037
APA StyleDahlmann, M., Monks, A., Harris, E. D., Kobelt, D., Osterland, M., Khaireddine, F., Herrmann, P., Kemmner, W., Burock, S., Walther, W., Shoemaker, R. H., & Stein, U. (2022). Combination of Wnt/β-Catenin Targets S100A4 and DKK1 Improves Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 14(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010037