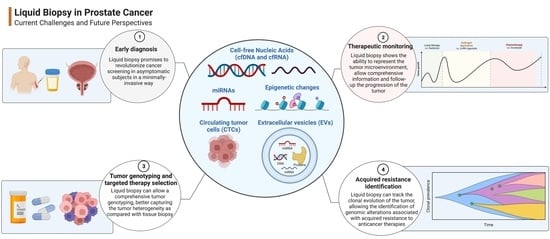
Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Management—Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Blood and Serum Biomarkers in the Detection of PCa
2.1. ctDNA
2.2. ctRNA
2.3. CTC
2.4. EVs
3. Urine Biomarkers in the Detection of PCa
3.1. ctDNA
3.2. ctRNA
3.3. CTC
4. The Role of Liquid Biopsy in Follow-Up
5. Perspectives, Limitations and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. No Title. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandaglia, G.; Leni, R.; Bray, F.; Fleshner, N.; Freedland, S.J.; Kibel, A.; Stattin, P.; Van Poppel, H.; La Vecchia, C. Epidemiology and Prevention of Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, E.; Preisser, F.; Nazzani, S.; Tian, Z.; Bandini, M.; Gandaglia, G.; Fossati, N.; Montorsi, F.; Graefen, M.; Shariat, S.F.; et al. The Effect of Lymph Node Dissection in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Prostatectomy: A Contemporary Analysis of Survival and Early Postoperative Outcomes. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 5, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernar, C.H.; Ebot, E.M.; Wilson, K.M.; Mucci, L.A. The Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a030361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Ross, R.K.; Bernstein, L.; Yatani, R.; Henderson, B.E.; Mack, T.M. Cancers of the prostate and breast among Japanese and white immigrants in Los Angeles County. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 63, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Harris, R.E.; Gao, Y.T.; Gao, R.; Wynder, E.L. Comparative epidemiology of cancers of the colon, rectum, prostate and breast in Shanghai, China versus the United States. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 20, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Carducci, M.; Liu, G.; Jarrard, D.F.; Eisenberger, M.; Wong, Y.N.; Hahn, N.; Kohli, M.; Cooney, M.M.; et al. Chemohormonal Therapy in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdana, N.R.; Mochtar, C.A.; Umbas, R.; Hamid, A.R.A. The Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer and Its Prevention: A Literature Review. Acta Med. Indones. 2016, 48, 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- Grozescu, T.; Popa, F. Prostate cancer between prognosis and adequate/proper therapy. J. Med. Life 2017, 10, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, E.K.; Raghallaigh, H.N.; Page, E.C.; Eeles, R.A. Updates in Prostate Cancer Research and Screening in Men at Genetically Higher Risk. Curr. Genet. Med. Rep. 2021, 9, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietri, M.T.; D’Elia, G.; Caliendo, G.; Resse, M.; Casamassimi, A.; Passariello, L.; Albanese, L.; Cioffi, M.; Molinari, A.M. Hereditary Prostate Cancer: Genes Related, Target Therapy and Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Mateo, J.; Walsh, M.F.; De Sarkar, N.; Abida, W.; Beltran, H.; Garofalo, A.; Gulati, R.; Carreira, S.; Eeles, R. Inherited DNA-Repair Gene Mutations in Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, A.; Paulo, P.; Teixeira, M.R. Hereditary Predisposition to Prostate Cancer: From Genetics to Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.C.; Oyekunle, T.; Howard, L.E.; De Hoedt, A.M.; Kane, C.J.; Terris, M.K.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Amling, C.L.; Klaassen, Z.; Freedland, S.J.; et al. Obesity, race, and long-term prostate cancer outcomes. Cancer 2020, 126, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivas, A.; Price, R.S. Obesity, Inflammation, and Advanced Prostate Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetto, F.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Aveta, A.; Martino, R.; Trama, F.; Caputo, V.F.; Barone, B.; Abate, M.; Sicignano, E.; Cilio, S.; et al. A Comparative Study of the Triglycerides/HDL Ratio and Pseudocholinesterase Levels in Patients with Bladder Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, G.; Crocetto, F.; Di Vito, C.; Creta, M.; Martino, R.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Pesce, S.; Napolitano, L.; Capone, D.; Imbimbo, C. Association of NAFLD and Insulin Resistance with Non Metastatic Bladder Cancer Patients: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacci, M.; Russo, G.I.; De Nunzio, C.; Sebastianelli, A.; Salvi, M.; Vignozzi, L.; Tubaro, A.; Morgia, G.; Serni, S. Meta-analysis of metabolic syndrome and prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Civita, E.; Liotti, A.; Cennamo, M.; Crocetto, F.; Ferro, M.; Liguoro, P.; Cimmino, A.; Imbimbo, C.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P.; et al. Peri-Prostatic Adipocyte-Released TGFβ Enhances Prostate Cancer Cell Motility by Upregulation of Connective Tissue Growth Factor. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Xie, B.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Meng, S.; Ji, A.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; et al. Hypertension and risk of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen-Nielsen, M.; Borre, M. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Prostate Cancer. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 46, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragsdale, J.W., 3rd; Halstater, B.; Martinez-Bianchi, V. Prostate cancer screening. Prim. Care 2014, 41, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamey, T.A.; Yang, N.; Hay, A.R.; McNeal, J.E.; Freiha, F.S.; Redwine, E. Prostate-specific antigen as a serum marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semjonow, A.; Brandt, B.; Oberpenning, F.; Roth, S.; Hertle, L. Discordance of assay methods creates pitfalls for the interpretation of prostate-specific antigen values. Prostate Suppl. 1996, 7, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; De Cobelli, O.; Lucarelli, G.; Porreca, A.; Busetto, G.M.; Cantiello, F.; Damiano, R.; Autorino, R.; Musi, G.; Vartolomei, M.D.; et al. Beyond PSA: The Role of Prostate Health Index (phi). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalona, W.J.; Richie, J.P.; Ahmann, F.R.; Hudson, M.A.; Scardino, P.T.; Flanigan, R.C.; DeKernion, J.B.; Ratliff, T.L.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Dalkin, B.L.; et al. Comparison of digital rectal examination and serum prostate specific antigen in the early detection of prostate cancer: Results of a multicenter clinical trial of 6630 men. J. Urol. 1994, 151, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Lucarelli, G.; de Cobelli, O.; Del Giudice, F.; Musi, G.; Mistretta, F.A.; Luzzago, S.; Busetto, G.M.; Buonerba, C.; Sciarra, A.; et al. The emerging landscape of tumor marker panels for the identification of aggressive prostate cancer: The perspective through bibliometric analysis of an Italian translational working group in uro-oncology. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 73, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeenge, M.; Barentsz, J.; Cosgrove, D.; de la Rosette, J.; de Reijke, T.; Eggener, S.; Frauscher, F.; Kovacs, G.; Matin, S.F.; Mischi, M.; et al. Role of transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) in focal therapy of prostate cancer: Report from a Consensus Panel. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II-2020 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapisarda, S.; Bada, M.; Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Arcaniolo, D.; Polara, A.; Imbimbo, C.; Grosso, G. The role of multiparametric resonance and biopsy in prostate cancer detection: Comparison with definitive histological report after laparoscopic/robotic radical prostatectomy. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 4178–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derin, O.; Fonseca, L.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Roberts, M.J. Infectious complications of prostate biopsy: Winning battles but not war. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, V.; Buckley, R.; Flax, S.; Spevack, L.; Hajek, D.; Tunis, A.; Lai, E.; Loblaw, A.; Collaborators. Transperineal Prostate Biopsies Using Local Anesthesia: Experience with 1287 Patients. Prostate Cancer Detection Rate, Complications and Patient Tolerability. J. Urol. 2019, 201, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; La Civita, E.; Liotti, A.; Cennamo, M.; Tortora, F.; Buonerba, C.; Crocetto, F.; Lucarelli, G.; Busetto, G.M.; Del Giudice, F. Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Urine: A Route towards Molecular Diagnosis and Personalized Medicine of Bladder Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Ferro, M.; Busetto, G.M.; La Civita, E.; Buonerba, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Terracciano, D.; Schalken, J.A. Liquid biopsy in bladder cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 170, 103577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.J.; Garrido-Navas, M.C.; Diaz Mochon, J.J.; Cristofanilli, M.; Gil-Bazo, I.; Pauwels, P.; Malapelle, U.; Russo, A.; Lorente, J.A.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, A.J.; et al. Precision Prevention and Cancer Interception: The New Challenges of Liquid Biopsy. International Society of Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetto, F.; Cimmino, A.; Ferro, M.; Terracciano, D. Circulating tumor cells in bladder cancer: A new horizon of liquid biopsy for precision medicine. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, N.; Rehm, B.H.A.; Sonar, P.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Advanced liquid biopsy technologies for circulating biomarker detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6670–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeurickx, E.; Hendrix, A. Targets, pitfalls and reference materials for liquid biopsy tests in cancer diagnostics. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 72, 100828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrugo-Ramírez, J.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J. Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Clinical and biological significance of circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and exosomes as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55632–55645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crowley, E.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Loupakis, F.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsy: Monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, W.; Lv, Z.; Ni, C.; Xin, Y.; Yang, L. Liquid Biopsy for Cancer: Circulating Tumor Cells, Circulating Free DNA or Exosomes? Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.H.D.; Bender, S.; Krahn, T.; Schlange, T. ctDNA and CTCs in Liquid Biopsy—Current Status and Where We Need to Progress. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Cario, C.L.; Leong, L.; Lopez, K.; Márquez, C.P.; Chu, C.; Li, P.S.; Oropeza, E.; Tenggara, I.; Cowan, J.; et al. Cell-free DNA concentration and fragment size as a biomarker for prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbetta, M.; Chiereghin, C.; De Simone, I.; Soldà, G.; Zuradelli, M.; Giunta, M.; Lughezzani, G.; Buffi, N.M.; Hurlem, R.; Saita, A.; et al. Post-Biopsy Cell-Free DNA from Blood: An Open Window on Primary Prostate Cancer Genetics and Biology. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 654140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, S.; Song, M.A.; Cheng, I.; Loo, L.; Tiirikainen, M. Measurement of circulating cell-free DNA in relation to 18F-fluorocholine PET/CT imaging in chemotherapy-treated advanced prostate cancer. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2012, 5, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patsch, K.; Matasci, N.; Soundararajan, A.; Diaz, P.; Agus, D.B.; Ruderman, D.; Gross, M.E. Monitoring dynamic cytotoxic chemotherapy response in castration-resistant prostate cancer using plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA). BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, N.; Dolling, D.; Sumanasuriya, S.; Christova, R.; Pope, L.; Carreira, S.; Seed, G.; Yuan, W.; Goodall, J.; Hall, E.; et al. Plasma Cell-free DNA Concentration and Outcomes from Taxane Therapy in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer from Two Phase III Trials (FIRSTANA and PROSELICA). Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 83–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, A.W.; Annala, M.; Aggarwal, R.; Beja, K.; Feng, F.; Youngren, J.; Foye, A.; Lloyd, P.; Nykter, M.; Beer, T.M.; et al. Concordance of Circulating Tumor DNA and Matched Metastatic Tissue Biopsy in Prostate Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.S.C.; Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Jeyapala, R.; Zhao, F.; Commisso, K.; Klotz, L.; Loblaw, A.; Liu, S.K.; Vesprini, D.; Fleshner, N.E.; et al. Assessment of Serum microRNA Biomarkers to Predict Reclassification of Prostate Cancer in Patients on Active Surveillance. J. Urol. 2018, 6, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasan, A.H.; Scott, A.W.; Wu, J.J.; Feng, G.; Meeks, J.J.; Thaxton, C.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Circulating microRNA signature for the diagnosis of very high-risk prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10655–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, M.F.; Kuasne, H.; Barros-Filho, M.C.; Cilião, H.L.; Marchi, F.A.; Fuganti, P.E.; Paschoal, A.R.; Rogatto, S.R.; Cólus, I.M.S. Circulating mRNAs and miRNAs as candidate markers for the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, K.; Tamanna, T.; Matthews, S.; Eng, P.; Sali, A. New Screening Test Improves Detection of Prostate Cancer Using Circulating Tumor Cells and Prostate-Specific Markers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapatero, A.; Gómez-Caamaño, A.; Cabeza Rodriguez, M.Á.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Martin de Vidales, C.; Abalo, A.; Calvo Crespo, P.; Leon Mateos, L.; Olivier, C.; Vega Piris, L.V. Detection and dynamics of circulating tumor cells in patients with high-risk prostate cancer treated with radiotherapy and hormones: A prospective phase II study. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Shin, H.W.; Jung, A.R.; Kwon, O.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y. Prostate-specific extracellular vesicles as a novel biomarker in human prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoosidana, G.; Ronquist, G.; Darmanis, S.; Yan, J.; Carlsson, L.; Wu, D.; Conze, T.; Ek, P.; Semjonow, A.; Eltze, E.; et al. Multiple recognition assay reveals prostasomes as promising plasma biomarkers for prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8809–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggs, C.N.; Siddiqui, K.M.; Al-Zahrani, A.A.; Pardhan, S.; Brett, S.I.; Guo, Q.Q.; Yang, J.; Wolf, P.; Power, N.E.; Durfee, P.N.; et al. Prostate extracellular vesicles in patient plasma as a liquid biopsy platform for prostate cancer using nanoscale flow cytometry. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8839–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casadio, V.; Calistri, D.; Salvi, S.; Gunelli, R.; Carretta, E.; Amadori, D.; Silvestrini, R.; Zoli, W. Urine cell-free DNA integrity as a marker for early prostate cancer diagnosis: A pilot study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 270457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, S.; Gurioli, G.; Martignano, F.; Foca, F.; Gunelli, R.; Cicchetti, G.; De Giorgi, U.; Zoli, W.; Calistri, D.; Casadio, V. Urine Cell-Free DNA Integrity Analysis for Early Detection of Prostate Cancer Patients. Dis. Mark. 2015, 2015, 574120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxman, B.; Tomlins, S.A.; Mehra, R.; Morris, D.S.; Wang, L.; Helgeson, B.E.; Shah, R.B.; Rubin, M.A.; Wei, J.T.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Noninvasive detection of TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcripts in the urine of men with prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKiernan, J.; Donovan, M.J.; O’Neill, V.; Bentink, S.; Noerholm, M.; Belzer, S.; Skog, J.; Kattan, M.W.; Partin, A.; Andriole, G.; et al. A Novel Urine Exosome Gene Expression Assay to Predict High-grade Prostate Cancer at Initial Biopsy. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, D.H.; Lund, M.E.; Nocon, A.L.; Cozzi, P.J.; Frydenberg, M.; De Souza, P.; Schiller, B.; Beebe-Dimmer, J.L.; Ruterbusch, J.J.; Walsh, B.J. Detection of glypican-1 (GPC-1) expression in urine cell sediments in prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, M.W.; Kircher, M.; Hill, A.J.; Daza, R.M.; Shendure, J. Cell-free DNA Comprises an In Vivo Nucleosome Footprint that Informs Its Tissues-of-Origin. Cell 2016, 164, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayrhofer, M.; De Laere, B.; Whitington, T.; Van Oyen, P.; Ghysel, C.; Ampe, J.; Ost, P.; Demey, W.; Hoekx, L.; Schrijvers, D.; et al. Cell-free DNA profiling of metastatic prostate cancer reveals microsatellite instability, structural rearrangements and clonal hematopoiesis. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliere, F.; Chandrananda, D.; Piskorz, A.M.; Moore, E.K.; Morris, J.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Mair, R.; Goranova, T.; Marass, F.; Heider, K.; et al. Enhanced detection of circulating tumor DNA by fragment size analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Vafaei, S.; Gu, X.; Zhong, X. The Prognostic Value of Plasma Cell-Free DNA Concentration in the Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 599602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, D.K.; Ehrich, M.; Van den Boom, D.; Cheville, J.C.; Karnes, R.J.; Tindall, D.J.; Cantor, C.R.; Young, C.Y. Hypermethylation of genes for diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jia, G.; Chao, F.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Urine- and Blood-Based Molecular Profiling of Human Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 759791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerrigter, E.; Groen, L.N.; Van Erp, N.P.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Schalken, J.A. Clinical utility of emerging biomarkers in prostate cancer liquid biopsies. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.T.; Kim, W.J. MicroRNAs in prostate cancer. Prostate Int. 2013, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.W.; Brewer, G.; Jing, Q. MicroRNA degradation and turnover: Regulating the regulators. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abramovic, I.; Ulamec, M.; Katusic Bojanac, A.; Bulic-Jakus, F.; Jezek, D.; Sincic, N. miRNA in prostate cancer: Challenges toward translation. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Stott, S.; Toner, M.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. Circulating tumor cells: Approaches to isolation and characterization. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balázs, K.; Antal, L.; Sáfrány, G.; Lumniczky, K. Blood-Derived Biomarkers of Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapy Response in Prostate Cancer Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehm, T.; Sagalowsky, A.; Clifford, E.; Beitsch, P.; Saboorian, H.; Euhus, D.; Meng, S.; Morrison, L.; Tucker, T.; Lane, N. Cytogenetic evidence that circulating epithelial cells in patients with carcinoma are malignant. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2073–2084. [Google Scholar]
- Scher, H.I.; Armstrong, A.J.; Schonhoft, J.D.; Gill, A.; Zhao, J.L.; Barnett, E.; Carbone, E.; Lu, J.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Luo, J.; et al. Development and validation of circulating tumour cell enumeration (Epic Sciences) as a prognostic biomarker in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 150, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Pang, B.; Li, J.; Gao, N.; Fan, T.; Li, Y. Emerging Role of Exosomes in Liquid Biopsy for Monitoring Prostate Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 679527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenc, T.; Klimczyk, K.; Michalczewska, I.; Słomka, M.; Kubiak-Tomaszewska, G.; Olejarz, W. Exosomes in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Xie, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, X.; Gao, P.; Xue, B. Roles and Clinical Application of Exosomes in Prostate Cancer. Front. Urol. 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaeminck-Guillem, V. Extracellular Vesicles in Prostate Cancer Carcinogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, M.; Yang, B.; Jarrard, D.F. Toward the detection of prostate cancer in urine: A critical analysis. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, P.; Seo, S.P.; Kang, H.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, S.C.; Moon, S.K.; Choi, Y.H.; et al. Urinary cell-free nucleic acid IQGAP3: A new non-invasive diagnostic marker for bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14354–14365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, V.; Freitas, C.; Fernandes, M.G.; Sousa, C.; Reboredo, C.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Mosquera, J.; Hespanhol, V.; Campelo, R. Liquid biopsy: The value of different bodily fluids. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, J. Clinical applications of urinary cell-free DNA in cancer: Current insights and promising future. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 2318–2332. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, S.P.; Mills, R.; Pandha, H.; Morgan, R.; Cooper, C.S.; Clark, J.; Brewer, D.S. The Movember Gap Urine Biomarker Consortium. Integration of Urinary EN2 Protein & Cell-Free RNA Data in the Development of a Multivariable Risk Model for the Detection of Prostate Cancer Prior to Biopsy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2102. [Google Scholar]
- Mathios, D.; Johansen, J.S.; Cristiano, S.; Medina, J.E.; Phallen, J.; Larsen, K.R.; Bruhm, D.C.; Niknafs, N.; Ferreira, L.; Adleff, V.; et al. Detection and characterization of lung cancer using cell-free DNA fragmentomes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, J.K.; Feng, Z.; Gulati, R.; Fan, J.; Lotan, Y.; Wei, J.T.; Etzioni, R. Projecting Benefits and Harms of Novel Cancer Screening Biomarkers: A Study of PCA3 and Prostate Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeb, S.; Partin, A.W. PCA3 Urinary Biomarker for Prostate Cancer. Rev. Urol. 2010, 12, e205-6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Beroukhim, R.; Schmidt, F.H.; Mosquera, J.M.; Setlur, S.; Tchinda, J.; Tomlins, S.A.; Hofer, M.D.; Pienta, K.G. TMPRSS2:ERG fusion-associated deletions provide insight into the heterogeneity of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8337–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linja, M.J.; Savinainen, K.J.; Saramäki, O.R.; Tammela, T.L.; Vessella, R.L.; Visakorpi, T. Amplification and overexpression of androgen receptor gene in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Biase, D.; Fassan, M.; Malapelle, U. Next-Generation Sequencing in Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisapia, P.; Costa, J.L.; Pepe, F.; Russo, G.; Gragnano, G.; Russo, A.; Iaccarino, A.; de Miguel-Perez, D.; Serrano, M.J.; Denninghoff, V.; et al. Next generation sequencing for liquid biopsy based testing in non-small cell lung cancer in 2021. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 161, 03311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, C.; Cardona, A.F.; Cristofanilli, M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Diaz Mochon, J.J.; Duran, I.; Raez, L.E.; Russo, A.; Lorente, J.A.; Malapelle, U.; et al. Challenges and opportunities of cfDNA analysis implementation in clinical practice: Perspective of the International Society of Liquid Biopsy (ISLB). Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 151, 102978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, M.; Dai, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Long, Y.; Wen, D.; Xie, F.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA-Based Detection of Tumor Suppressor Gene Copy Number Loss and Its Clinical Implication in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 720727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnau, C.G.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Luna-Velez, M.V.; Schalken, J.A. Noncoding RNAs as novel biomarkers in prostate cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 591703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Zendejas, A.P.; Scavuzzo, A.; Jiménez-Ríos, M.A.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Jiménez-Dávila, M.A.; Pérez-Montiel, D.; González-Barrios, R.; Jiménez-Trejo, F.; et al. The promising role of new molecular biomarkers in prostate cancer: From coding and non-coding genes to artificial intelligence approaches. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, A.; Kajau, H.; Margolis, E.; Tutrone, R.; Grimm, T.; Trottmann, M.; Stief, C.; Stoll, G.; Fischer, C.A.; Flinspach, C. Validation of a CE-IVD, urine exosomal RNA expression assay for risk assessment of prostate cancer prior to biopsy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafeie, M.; Zhang, J.; Asadnia, M.; Li, W.; Warkiani, M.E. Multiplexing slanted spiral microchannels for ultra-fast blood plasma separation. Lab. Chip. 2016, 16, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulasinghe, A.; Tran, T.H.; Blick, T.; O’Byrne, K.; Thompson, E.W.; Warkiani, M.E.; Nelson, C.; Kenny, L.; Punyadeera, C. Enrichment of circulating head and neck tumour cells using spiral microfluidic technology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Bai, B. The Expression, Regulation, and Biomarker Potential of Glypican-1 in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rzhevskiy, A.S.; Razavi Bazaz, S.; Ding, L.; Kapitannikova, A.; Sayyadi, N.; Campbell, D.; Walsh, B.; Gillatt, D.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M.; Zvyagin, A.V. Rapid and Label-Free Isolation of Tumour Cells from the Urine of Patients with Localised Prostate Cancer Using Inertial Microfluidics. Cancers 2019, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative Clinical Genomics of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 162, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, B.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, P.; Qin, Z. Complete regression of advanced prostate cancer for ten years: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, V.; Di Zazzo, E.; Galasso, G.; De Rosa, C.; Abbondanza, C.; Sinisi, A.A.; Altucci, L.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Estrogens Modulate Somatostatin Receptors Expression and Synergize with the Somatostatin Analog Pasireotide in Prostate Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Galasso, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Di Santi, A.; Cernera, G.; Rossi, V.; Abbondanza, C.; Moncharmont, B.; Sinisi, A.A.; et al. Prostate cancer stem cells: The role of androgen and estrogen receptors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid biopsies come of age: Towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, S.T.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Gjyrezi, A.; Galletti, G.; Kim, S.; Worroll, D.; Stewart, J.; Zaher, A.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Ballman, K.V.; et al. Expression of AR-V7 and ARv567es in Circulating Tumor Cells Correlates with Outcomes to Taxane Therapy in Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer Treated in TAXYNERGY. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, C.; Gao, X.; Yuan, P.; Gan, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; et al. Prognostic Value of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 in the Treatment of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 562504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.-J.; Hu, Q.; Li, S.-Y.; Mao, W.-P.; Xu, B.; Chen, M. The Role of Androgen Receptor Splicing Variant 7 in Predicting the Prognosis of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211035260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, R.T.; Hendifar, A.; McWilliams, R.R.; Geva, R.; Epelbaum, R.; Rolfe, L.; Goble, S.; Lin, K.K.; Biankin, A.V.; Giordano, H.; et al. Rucaparib Monotherapy in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer and a Known Deleterious BRCA Mutation. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2018, PO.17.00316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sledge, G.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic—Implementation issues and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arneth, B. Update on the types and usage of liquid biopsies in the clinical setting: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Variables | Test Name | Manufacturer | Assay Type | Molecular Targets | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Biomarkers | ctDNA | Qubit 3.0 Fluorometer and dsDNA HS AssayKit | Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA | dsDNA Quantitation | dsDNA | [47] |
| ctDNA | 2100 Bioanalyzer with High Sensitivity DNA Chips | Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA | dsDNA Quantitation purity and fragment size | dsDNA | ||
| ctDNA | Fluorometer and Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | dsDNA Quantitation | dsDNA | [48] | |
| ctDNA | Agilent High Sensitivity D5000 ScreenTape System on Agilent-4200 TapeStation | Agilent Technologies; Santa Clara, CA, USA | dsDNA Qualitative analysis | dsDNA | ||
| ctDNA | ABI 7900HT system | Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA | qPCR analysis of repeated genomic ALU sequences to detect and quantify cfDNA | dsDNA | [49] | |
| ctDNA | Microfluidic electrophoresis using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer and High Sensitivity DNA Chips | Agilent technologies Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA | DNA fragment length analysis | dsDNA | ||
| Gene promoters’ methylation | ND | ND | Sodium bisulfite-PCR | GSTP1, RARB2 | ||
| ctDNA | iCycler iQ Real-Time PCR | Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA | qPCR analysis of long interspersed nuclear elements (LINE1) for ctDNA quantification | dsDNA | [50] | |
| ctDNA | Quant-IT Picogreen HS DNA kit and BioTek microplate spectrophotometer at 480ex/520em | Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA | dsDNA Quantification | dsDNA | [51] | |
| ctDNA | Illumina MiSeq (V3 600 cycle kit) or HiSeq 2500 (V4 250 cycle kit) | Illumina Inc., Towne Centre Drive, San Diego, CA, USA | ctDNA sequencing | AR, SPOP, TP53, PTEN, RB1, APC, CDKN1B, BRCA2, and PIK3R1 | [52] | |
| ctRNA | ExiLENT SYBR® Greenassay (Exiqon, Denmark) qPCR was performed on QuantStudio 6 Real-Time PCR System | Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA | qRT-PCR analysis | miR-141, 375, 21, 30c, 145, 26b, 223, 24, and let-7a | [53] | |
| ctRNA | TaqMan MicroRNA Assay, TaqMan PCR master mix and TaqMan probes. ABI Prism Model 7900 HT instrument was used to perform the qRT-PCR. | Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA | qRT-PCR analysis | miR-200c, miR-605, miR-135a, miR-433, and miR-106a | [54] | |
| ctRNA | Sso Advanced Universal SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, USA). The reaction was performed on the 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System Thermocycler | Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA | qRT-PCR analysis | OR51E2, SIM2 | [55] | |
| CTC | ISET®-CTC Test and Immuno-Cyto-Chemistry (ICC) | Rarecells Diagnostics, Paris, France | immuno-cyto-chemistry | PSA | [56] | |
| CTC | CELLSEARCH assay | Menarini, Silicon Biosystems Inc., Bologna, Italy | immuno-cyto-chemistry | epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), cytokeratins, CD45 | [57] | |
| EV | CD63 Exo ELISA Kit (EXOEL-CD63A-1) | System Biosciences, Mountain View, CA, USA | ELISA | CD63 | [58] | |
| EV | CD63 Exo ELISA KitEXOEL-CD63A-1); human glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 (FOLH1) ELISA kit (MBS901525) | System Biosciences, Mountain View, CA, USA;MY BioSource, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA | ELISA | prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) | [58] | |
| EV | Mx-3000 or Mx 3005 instrument | Stratagene, Amsterdam, The Netherlands | qRT-PCR analysis for EV quantification | [59] | ||
| CTC | CellSearch Instrument | Janssen Diagnostics Inc. Huntington Valley, PA, USA | CTC Enumeration | EpCAM+CK+CD45- | [60] | |
| Urine Biomarkers | ctDNA | Qiamp DNA minikit; IQ SYBR green;Rotor Gene 6000 detection system | Qiagen, Milan, Italy; Biorad, Milan, Italy; Corbett Research, St. Neots, UK | qPCR analysis for ctDNA fragmentation index evaluation | c-Myc, BCAS1, HER2, STOX1 | [61] |
| ctDNA | Qiamp DNA minikit; IQ SYBR green;Rotor Gene 6000 detection system | Qiagen, Milan, Italy; Biorad, Milan, Italy; Corbett Research, St. Neots, UK | qPCR analysis for ctDNA fragmentation index evaluation | c-Myc, AR, HER2, STOX1 | [62] | |
| ucfRNA | RNeasy Micro kit; Omni-Plex Whole Transcriptome Amplification (WTA) kit | Qiagen, Inc., Valencia, CA, USA; Rubicon Genomics, Ann Arbor, MI, USA | qRT-PCR | TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion | [63] | |
| EV | ExoDx Prostate IntelliScore urine exosome assay; QIAGEN Rotor-Gene Q MDx System | Exosome Diagnostics, Waltham, MA, USA; Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands | qRT-PCR | ERG, PCA3, SPDEF | [64] | |
| CTC | MIL-38 immunofluorescence assay (IFA) | Minomic International Ltd., Sydney, Australia | immunofluorescence | glycoprotein glypican 1 (GPC-1) | [65] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crocetto, F.; Russo, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Pisapia, P.; Mirto, B.F.; Palmieri, A.; Pepe, F.; Bellevicine, C.; Russo, A.; La Civita, E.; et al. Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Management—Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133272
Crocetto F, Russo G, Di Zazzo E, Pisapia P, Mirto BF, Palmieri A, Pepe F, Bellevicine C, Russo A, La Civita E, et al. Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Management—Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133272
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrocetto, Felice, Gianluca Russo, Erika Di Zazzo, Pasquale Pisapia, Benito Fabio Mirto, Alessandro Palmieri, Francesco Pepe, Claudio Bellevicine, Alessandro Russo, Evelina La Civita, and et al. 2022. "Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Management—Current Challenges and Future Perspectives" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133272
APA StyleCrocetto, F., Russo, G., Di Zazzo, E., Pisapia, P., Mirto, B. F., Palmieri, A., Pepe, F., Bellevicine, C., Russo, A., La Civita, E., Terracciano, D., Malapelle, U., Troncone, G., & Barone, B. (2022). Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Management—Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cancers, 14(13), 3272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133272