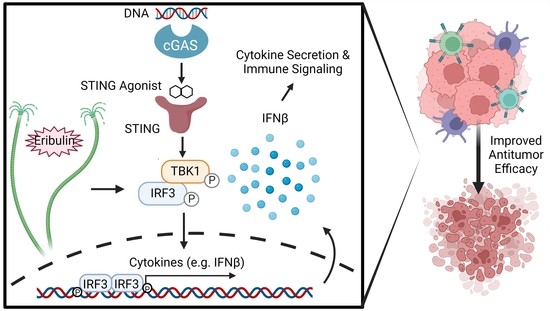
The Microtubule Destabilizer Eribulin Synergizes with STING Agonists to Promote Antitumor Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents
2.2. Quantitative Real Time-PCR Transcriptional Analysis
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Immunoblotting
2.5. Intracellular IFNβ Flow Cytometry
2.6. IFNβ ELISA
2.7. In Vivo Immune Studies
2.8. Antitumor Trial
3. Results
3.1. Eribulin Enhances the IFNβ Response of STING Agonists in Immune Cells
3.2. Eribulin Synergizes with STING Agonists
3.3. Eribulin Enhances the IFNβ Response of STING Agonists in TNBC Cells
3.4. Enhancement of STING Signaling Occurs Downstream of Microtubule Depolymerization and Is Not Shared with Microtubule Stabilizing Taxanes
3.5. Eribulin Enhances STING-Dependent IFNβ Expression through TBK1-IRF3 Signaling
3.6. Eribulin Enhances the Immune Response of Multiple Agonists
3.7. Eribulin Shows Improved Antitumor Efficacy in Combination with ADU-S100
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaul, R.; Risinger, A.L.; Mooberry, S.L. Microtubule-Targeting Drugs: More than Antimitotics. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Volk-Draper, L.D.; Ran, S. TLR4 Is a Novel Determinant of the Response to Paclitaxel in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanderley, C.W.; Colón, D.F.; Luiz, J.P.M.; Oliveira, F.F.; Viacava, P.R.; Leite, C.A.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, C.M.; Silva, C.R.; Silva, R.L.; et al. Paclitaxel Reduces Tumor Growth by Reprogramming Tumor-Associated Macrophages to an M1 Profile in a TLR4-Dependent Manner. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5891–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volk-Draper, L.; Hall, K.; Griggs, C.; Rajput, S.; Kohio, P.; DeNardo, D.; Ran, S. Paclitaxel therapy promotes breast cancer metastasis in a TLR4-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5421–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scripture, C.D.; Figg, W.D.; Sparreboom, A. Peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel: Recent insights and future perspectives. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fermaintt, C.S.; Takahashi-Ruiz, L.; Liang, H.; Mooberry, S.L.; Risinger, A.L. Eribulin activates the cGAS-STING pathway via the cytoplasmic accumulation of mtDNA. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Hamamichi, S.; Abe, T.; Akagi, T.; Shirota, H.; Kawano, S.; Asano, M.; Asano, O.; Yokoi, A.; Matsui, J.; et al. Antitumor effects of eribulin depend on modulation of the tumor microenvironment by vascular remodeling in mouse models. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goto, W.; Kashiwagi, S.; Asano, Y.; Takada, K.; Morisaki, T.; Fujita, H.; Takashima, T.; Ohsawa, M.; Hirakawa, K.; Ohira, M. Eribulin Promotes Antitumor Immune Responses in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X. A Comprehensive Immunologic Portrait of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Ye, L.; He, Y.; et al. cGAS-STING, an important pathway in cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aval, L.; Pease, J.E.; Sharma, R.; Pinato, D.J. Challenges and Opportunities in the Clinical Development of STING Agonists for Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukai, K.; Konno, H.; Akiba, T.; Uemura, T.; Waguri, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Barber, G.N.; Arai, H.; Taguchi, T. Activation of STING requires palmitoylation at the Golgi. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, E.; Mukai, K.; Saito, K.; Arai, H.; Taguchi, T. The binding of TBK1 to STING requires exocytic membrane traffic from the ER. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, M.B.; Kacha, A.K.; Kline, J.; Woo, S.R.; Kranz, D.M.; Murphy, K.M.; Gajewski, T.F. Host type I IFN signals are required for antitumor CD8+ T cell responses through CD8{alpha}+ dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiavoni, G.; Mattei, F.; Gabriele, L. Type I Interferons as Stimulators of DC-Mediated Cross-Priming: Impact on Anti-Tumor Response. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, M.L.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Gajewski, T.F.; Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.X. Targeting the tumor microenvironment with interferon-β bridges innate and adaptive immune responses. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, S.R.; Fuertes, M.B.; Corrales, L.; Spranger, S.; Furdyna, M.J.; Leung, M.Y.; Duggan, R.; Wang, Y.; Barber, G.N.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing mediates innate immune recognition of immunogenic tumors. Immunity 2014, 41, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, M.R.; Cheon, H.; Junk, D.J.; Vinayak, S.; Varadan, V.; Telli, M.L.; Ford, J.M.; Stark, G.R.; Jackson, M.W. Interferon-beta represses cancer stem cell properties in triple-negative breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13792–13797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiello, L.; Sestili, P.; Schiavoni, G.; Dattilo, R.; Monque, D.M.; Ciaffoni, F.; Iezzi, M.; Lamolinara, A.; Sistigu, A.; Moschella, F.; et al. Disruption of IFN-I Signaling Promotes HER2/Neu Tumor Progression and Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Hijano, L.; Sainz, B., Jr. The Interactions Between Cancer Stem Cells and the Innate Interferon Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Sweis, R.F.; Hodi, F.S.; Messersmith, W.A.; Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Ingham, M.; Lewis, N.; Chen, X.; Pelletier, M.; Chen, X.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Trial of MIW815 (ADU-S100), an Intratumoral STING Agonist, in Patients with Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors or Lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 28, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Kim, D.-S.; Endo, A.; Fang, F.G.; Huang, K.-C.; Bao, X.; Choi, H.-w.; Majumder, U.; Shen, Y.Y.; Mathieu, S.; Zhu, X.; et al. E7766, a Macrocycle-Bridged Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) Agonist with Potent Pan-Genotypic Activity. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1741–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, A.H.; Kelly, R.J.; Gorbunova, A.; Omstead, A.N.; Salvitti, M.S.; Zheng, P.; Kosovec, J.E.; Lee, S.; Ayazi, S.; Babar, L.; et al. Intratumoral immunotherapy with STING agonist, ADU-S100, induces CD8+ T-cell mediated anti-tumor immunity in an esophageal adenocarcinoma model. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Ding, J. Identification of MSA-2: An oral antitumor non-nucleotide STING agonist. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermaintt, C.S.; Peramuna, T.; Cai, S.; Takahashi-Ruiz, L.; Essif, J.; Grant, C.V.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mooberry, S.L.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Risinger, A.L. Yuanhuacine Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Basal-Like 2 Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer with Immunogenic Potential. Cancers 2021, 13, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermaintt, C.S.; Sano, K.; Liu, Z.; Ishii, N.; Seino, J.; Dobbs, N.; Suzuki, T.; Fu, Y.-X.; Lehrman, M.A.; Matsuo, I.; et al. A bioactive mammalian disaccharide associated with autoimmunity activates STING-TBK1-dependent immune response. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 3.0: An interactive analysis and consensus interpretation of multi-drug synergies across multiple samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W739–W743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.A.; Witteveen, P.E.; Wanders, J.; Law, K.; Edwards, G.; Reyderman, L.; Copalu, W.; Peng, F.; Marchetti, S.; Beijnen, J.H.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of eribulin mesylate in patients with solid tumours receiving repeated oral rifampicin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzegar, A.; Chelvanambi, M.; Filderman, J.N.; Storkus, W.J.; Luke, J.J. STING Agonists as Cancer Therapeutics. Cancers 2021, 13, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almine, J.F.; O’Hare, C.A.; Dunphy, G.; Haga, I.R.; Naik, R.J.; Atrih, A.; Connolly, D.J.; Taylor, J.; Kelsall, I.R.; Bowie, A.G.; et al. IFI16 and cGAS cooperate in the activation of STING during DNA sensing in human keratinocytes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonugunta, V.K.; Sakai, T.; Pokatayev, V.; Yang, K.; Wu, J.; Dobbs, N.; Yan, N. Trafficking-Mediated STING Degradation Requires Sorting to Acidified Endolysosomes and Can Be Targeted to Enhance Anti-tumor Response. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukhele, S.; Boukhaled, G.M.; Brooks, D.G. Type I interferon signaling, regulation and gene stimulation in chronic virus infection. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 43, 101277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Type I interferon: Friend or foe? J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: A Complex Web of Host Defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Li, L.; Maliga, Z.; Yin, Q.; Wu, H.; Mitchison, T.J. Anticancer Flavonoids Are Mouse-Selective STING Agonists. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Searching for Drug Synergy in Complex Dose-Response Landscapes Using an Interaction Potency Model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malyutina, A.; Majumder, M.; Wang, W.; Pessia, A.; Heckman, C.A.; Tang, J. Drug combination sensitivity scoring facilitates the discovery of synergistic and efficacious drug combinations in cancer. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manthri, S.; Sharma, P.; Mejbel, H.; Singal, S.; Jaishankar, D. Third Line Eribulin for Triple-negative Metastatic Breast Ductal Carcinoma Resulting in Extended Progression-free Survival of 57 Months. Cureus 2020, 12, e6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzuti, L.; Krasniqi, E.; Barchiesi, G.; Mazzotta, M.; Barba, M.; Amodio, A.; Massimiani, G.; Pelle, F.; Kayal, R.; Vizza, E.; et al. Eribulin in Triple Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: Critic Interpretation of Current Evidence and Projection for Future Scenarios. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5903–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolowska, O.; Nowis, D. STING Signaling in Cancer Cells: Important or Not? Arch. Immunol. Et Ther. Exp. 2018, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Chen, W. The Promise and Challenges of Cyclic Dinucleotides as Molecular Adjuvants for Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2021, 9, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.S.; Perera, S.A.; Piesvaux, J.A.; Presland, J.P.; Schroeder, G.K.; Cumming, J.N.; Trotter, B.W.; Altman, M.D.; Buevich, A.V.; Cash, B.; et al. An orally available non-nucleotide STING agonist with antitumor activity. Science 2020, 369, eaba6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, M.O.; Prota, A.E. Microtubule-Targeting Agents: Strategies To Hijack the Cytoskeleton. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, N.; Burnaevskiy, N.; Chen, D.; Gonugunta, V.K.; Alto, N.M.; Yan, N. STING Activation by Translocation from the ER Is Associated with Infection and Autoinflammatory Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decout, A.; Katz, J.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Ablasser, A. The cGAS–STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, N.B.; Sciaky, N.; Marotta, A.; Song, J.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Golgi dispersal during microtubule disruption: Regeneration of Golgi stacks at peripheral endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 631–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Milkie, D.E.; Moore, R.P.; Tulu, U.S.; et al. Visualizing Intracellular Organelle and Cytoskeletal Interactions at Nanoscale Resolution on Millisecond Timescales. Cell 2018, 175, 1430–1442.e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valm, A.M.; Cohen, S.; Legant, W.R.; Melunis, J.; Hershberg, U.; Wait, E.; Cohen, A.R.; Davidson, M.W.; Betzig, E.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Applying systems-level spectral imaging and analysis to reveal the organelle interactome. Nature 2017, 546, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Deng, H.; Xu, Z. Targeting macrophage priming by polyphyllin VII triggers anti-tumor immunity via STING-governed cytotoxic T-cell infiltration in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehwinkel, J.; Gack, M.U. RIG-I-like receptors: Their regulation and roles in RNA sensing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulaski, B.A.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Mouse 4T1 breast tumor model. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2001, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semba, T.; Tabata, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Miyano, S.W.; Matsui, J.; Funahashi, Y. Antitumor activity of eribulin in combination with anti-PD1 antibody in a mouse syngeneic breast cancer model. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Watkins-Schulz, R.; Junkins, R.D.; David, C.N.; Johnson, B.M.; Montgomery, S.A.; Peine, K.J.; Darr, D.B.; Yuan, H.; McKinnon, K.P.; et al. A nanoparticle-incorporated STING activator enhances antitumor immunity in PD-L1-insensitive models of triple-negative breast cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e120638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, E.E.; Savage, K.I.; Lioe, T.; Boyd, C.; Halliday, S.; Walker, S.M.; Lowry, K.; Knight, L.; Buckley, N.E.; Grogan, A.; et al. Activation of a cGAS-STING-mediated immune response predicts response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Song, Z.; Shen, A.; Chen, T.; Zhang, A. Small molecules targeting the innate immune cGAS-STING-TBK1 signaling pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 2272–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueckert, C.; Rand, U.; Roy, U.; Kasmapour, B.; Strowig, T.; Guzmán, C.A. Cyclic dinucleotides modulate induced type I IFN responses in innate immune cells by degradation of STING. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novotna, B.; Vanekova, L.; Zavrel, M.; Budesinsky, M.; Dejmek, M.; Smola, M.; Gutten, O.; Tehrani, Z.A.; Pimkova Polidarova, M.; Brazdova, A.; et al. Enzymatic Preparation of 2’-5’,3’-5’-Cyclic Dinucleotides, Their Binding Properties to Stimulator of Interferon Genes Adaptor Protein, and Structure/Activity Correlations. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10676–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Alu, A.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. cGAS-STING pathway in cancer biotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybdal-Hargreaves, N.F.; Risinger, A.L.; Mooberry, S.L. Regulation of E-cadherin localization by microtubule targeting agents: Rapid promotion of cortical E-cadherin through p130Cas/Src inhibition by eribulin. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5545–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Manasrah, B.K.; McGregor, S.M.; Lera, R.F.; Norman, R.X.; Tucker, J.B.; Scribano, C.M.; Yan, R.E.; Humayun, M.; Wisinski, K.B.; et al. Paclitaxel Induces Micronucleation and Activates Pro-Inflammatory cGAS–STING Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komlodi-Pasztor, E.; Sackett, D.; Wilkerson, J.; Fojo, T. Mitosis is not a key target of microtubule agents in patient tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, A.S.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, L.; Zhao, Y.; Monaco, G.; Trefny, M.P.; Yoshida, N.; Martin, K.; Sharma, A.; Olieric, N.; Shah, P.; et al. GEF-H1 Signaling upon Microtubule Destabilization Is Required for Dendritic Cell Activation and Specific Anti-tumor Responses. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3367–3380.e3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes, J.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Loesch, D.; Blum, J.L.; Vahdat, L.T.; Petrakova, K.; Chollet, P.; Manikas, A.; Dieras, V.; Delozier, T.; et al. Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): A phase 3 open-label randomised study. Lancet 2011, 377, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Kalinsky, K.; Kaklamani, V.G.; D’Adamo, D.R.; Aktan, G.; Tsai, M.L.; O’Regan, R.M.; Kaufman, P.A.; Wilks, S.T.; Andreopoulou, E.; et al. Eribulin Plus Pembrolizumab in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (ENHANCE 1): A Phase Ib/II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Dent, R.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kummel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; et al. Event-free Survival with Pembrolizumab in Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Hong, Z.; Bai, X.; Liang, T. Advantages of targeting the tumor immune microenvironment over blocking immune checkpoint in cancer immunotherapy. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Peterson, N.; Khalaj, K.; Vitkin, N.; Robinson, A.; Francis, J.-A.; Koti, M. STING agonist therapy in combination with PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade enhances response to carboplatin chemotherapy in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi-Ruiz, L.; Fermaintt, C.S.; Wilkinson, N.J.; Chan, P.Y.W.; Mooberry, S.L.; Risinger, A.L. The Microtubule Destabilizer Eribulin Synergizes with STING Agonists to Promote Antitumor Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models. Cancers 2022, 14, 5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235962
Takahashi-Ruiz L, Fermaintt CS, Wilkinson NJ, Chan PYW, Mooberry SL, Risinger AL. The Microtubule Destabilizer Eribulin Synergizes with STING Agonists to Promote Antitumor Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235962
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi-Ruiz, Leila, Charles S. Fermaintt, Nancy J. Wilkinson, Peter Y. W. Chan, Susan L. Mooberry, and April L. Risinger. 2022. "The Microtubule Destabilizer Eribulin Synergizes with STING Agonists to Promote Antitumor Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235962
APA StyleTakahashi-Ruiz, L., Fermaintt, C. S., Wilkinson, N. J., Chan, P. Y. W., Mooberry, S. L., & Risinger, A. L. (2022). The Microtubule Destabilizer Eribulin Synergizes with STING Agonists to Promote Antitumor Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models. Cancers, 14(23), 5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235962