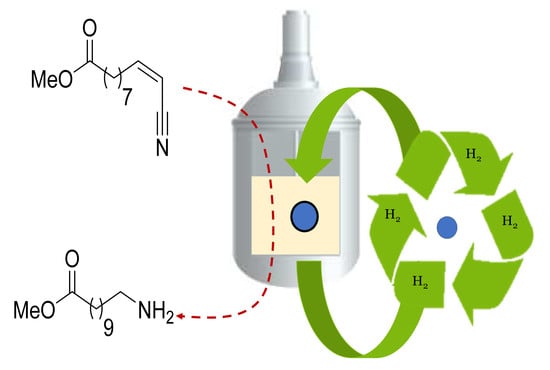
Regeneration of Raney®-Nickel Catalyst for the Synthesis of High-Value Amino-Ester Renewable Monomers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Reaction Conditions
2.1.1. Reaction Time
2.1.2. Influence of UNE11 Concentration
2.1.3. Influence of Ammonia on the Conversion of UNE11
2.1.4. Solvent Influence on the Conversion of UNE11
2.2. Catalyst Reactivation
2.2.1. Catalyst Washed with Methanol and Reaction Solvent
2.2.2. Catalyst Reactivation under Sonication
2.2.3. Caustic Treatment
2.2.4. Catalyst Reactivation under H2 Pressure
3. Repeatability
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Hydrogenation of Methyl 10-Cyanodecenoate (UNE11)
4.2. Treatment of Raney®-Nickel Catalyst
4.3. Reaction Set-Up
4.4. Ultrasound Reactivation Set-Up
4.5. Instrumentation and Acquisition Parameters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilhelm, K. Nickel: An Element with Wide Application in Industrial Homogeneous Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. English 2003, 29, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Halima, T.; Masson-Makdissi, J.; Newman, S.G. Nickel-Catalyzed Amide Bond Formation from Methyl Esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12925–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Miyao, T.; Higashiyama, K.; Yamashita, H.; Watanabe, M. High catalytic performance of ruthenium-doped mesoporous nickel-aluminum oxides for selective CO methanation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9895–9898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Hernández, E.; Alfaro, S.; López Medina, R.; Valverde Aguilar, G.; Albiter, E.; Valenzuela, M. High Selectivity and Stability of Nickel Catalysts for CO2 Methanation: Support Effects. Catalysts 2018, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simakova, I.L.; Simakov, A.V.; Murzin, D.Y. Valorization of Biomass Derived Terpene Compounds by Catalytic Amination. Catalysts 2018, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khusnutdinov, R.I.; Bayguzina, A.R.; Dzhemilev, U.M. Metal complex catalysis in the synthesis of quinolines. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 768, 75–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresch, L.C.; Junges, C.H.; Casagrande, O.D.L.; Stieler, R. Nickel complexes supported by selenium-based tridentate ligands and their use as effective catalyst systems for ethylene dimerisation. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 856, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriel Schmitt, C.; Gagliardi Reolon, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Raffelt, K.; Grunwaldt, J.-D.; Dahmen, N. Synthesis and Regeneration of Nickel-Based Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of Beech Wood Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil. Catalysts 2018, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, T.; Zhao, Y. Tuning Selectivity of Maleic Anhydride Hydrogenation Reaction over Ni/Sc-Doped ZrO2 Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raney, M. Method for producing Finely Divided Nickel. US Patent 1628190, 10 May 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew, C.H.; Farrauto, R.J. Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781118209738. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhartz, W.; Ullmann, F.; Elvers, B. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989; ISBN 9783527201136. [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu, C.; Dietrich, E.; Delmas, H.; Jenck, J. Hydrogenation of adiponitrile catalyzed by raney nickel use of intrinsic kinetics to measure gas-liquid mass transfer in a gas induced stirred slurry reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffaud, T.; Couturier, J.L.; Dubois, J.L.; Devaux, J.F. Composition Made of Amino Acid or Ester with Polymer Quality and Methods for Obtaining Same. US Patent 2018/282259, 4 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bio-Based Renewable Solutions. Available online: https://www.extremematerials-arkema.com/en/product-families/rilsan-polyamide-11-family/bio-based-renewable-solutions/ (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Augustine, R.L. Heterogeneous Catalysis for the Synthetic Chemist; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780824790219. [Google Scholar]
- Argyle, M.; Bartholomew, C. Heterogeneous Catalyst Deactivation and Regeneration: A Review. Catalysts 2015, 5, 145–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartholomew, C.; Argyle, M. Advances in Catalyst Deactivation and Regeneration. Catalysts 2015, 5, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümer, H.V.; Feuge, R.O.; Cousins, E.R. Raney nickel catalyst of improved stability and reactivity in the hydrogenation of triglycerides. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1964, 41, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3D Printing for Intensified Catalytic Processes. A Case Study from the Print Cr3Dit Project. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338913458_3D_Printing_for_intensified_catalytic_processes_A_case_study_from_the_PrintCr3Dit_project (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Krupka, J. Nitrile Hydrogenation on Solid Catalysts—New Insights into the Reaction. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, H.; Horst, N. Process for the Regeneration of Raney-Nickel Catalyst. US Patent 3,165,478, 12 January 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, H.; Kou, Z.; Xu, G.; Wu, S. Deactivation and regeneration of Raney-Ni catalyst during multiphase dehydrogenation of cyclohexane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3253–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukula, P.; Koprivova, K. Structure-selectivity relationship in the chemoselective hydrogenation of unsaturated nitriles. J. Catal. 2005, 234, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Braun, J.; Blessing, G.; Zobel, F. Catalytic hydrogenations under pressure in the presence of nickel salts. VI. Nitriles. Chem. Ber. 1923, 36, 1988–2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, D.R. Vapor Pressure of Pure Substances. Organic and Inorganic Compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1947, 39, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouilloux, P. The nature of raney nickel, its adsorbed hydrogen and its catalytic activity for hydrogenation reactions (review). Appl. Catal. 1983, 8, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochard, F.; Jobic, H.; Massardier, J.; Renouprez, A.J. Gas phase hydrogenation of acetonitrile on Raney nickel catalysts: Reactive hydrogen. J. Mol. Catal. A. Chem. 1995, 95, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Trials | t (min) | H2 bar | NH3/UNE11 (mol/mol) | AE11 % | UNE11 % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % | Dimer % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 180 | 60 | 1.15 | 92 | - | 3.0 | 0.09 | 4.44 | - |
| 2 | 120 | 60 | 1.15 | 36 | - | 62 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.02 |
| Trials | H2 bar | NH3/UNE11 (mol/mol) | AE11 % | UNE11 % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % | Dimer % | Deactivation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 1.00 | 67 | - | 30 | 0.66 | 0.25 | 0.03 | - |
| 2 | 40 | 1.00 | 41 | - | 57 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 26 |
| 3 | 60 | 1.05 | 91 | - | 11 | 0.09 | 4.44 | - | - |
| 4 | 60 | 1.10 | 47 | - | 50 | 0.19 | 0.91 | - | 44 |
| Trials | UNE11 wt.% (mol/L) | H2 bar | NH3/UNE11 (mol/mol) | AE11 % | UNE11 % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % | Dimer % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31 (1.25) | 60 | 1.10 | 93 | - | 2.2 | 0.1 | 3.7 | - |
| 2 | 40 (1.9) | 60 | 0.90 | 92 | - | 0.2 | 0.1 | 6.1 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 52 (2.15) | 60 | 1.10 | 95 | - | 0.1 | 0.03 | 3.7 | 0.3 |
| Trials | NH3/UNE11 (mol/mol) | AE11 % | UNE11 cis % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.70 | 73 | 3.9 | 21 | 0.55 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 1.38 | 75 | - | 8 | 12 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 1.10 | 93 | - | 2.2 | 0.07 | 3.7 |
| Trials | AE11 % | UNE11 % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91 | - | 2.80 | 0.02 | 4.8 |
| 2 | 93 | - | 2.18 | 0.10 | 3.7 |
| Trial | NH3(eq. to UNE11) | AE11 % | UNE11 % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % | Deactivation (loss of yield) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.12 | 91 | - | 2.8 | 0.02 | 4.8 | - |
| 2 | 1.15 | 44 | - | 54 | 0.57 | 1.17 | 47 |
| 3 | 1.1 | 47 | - | 50 | 0.19 | 0.91 | 44 |
| Trial | AE11 % | UNE11 cis % | SNE11 % | Imine % | A2 % | Dimer % | Deactivation % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91 | - | 2.8 | 0.02 | 4.80 | - | - |
| 2 | 44 | - | 54 | 0.57 | 1.17 | 0.02 | 47 |
| 3 | 34 | - | 65 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 57 |
| 4 | 29 | 0.26 | 71 | 0.32 | 0.39 | - | 62 |
| Method | AE11 % | UNE11 cis % | SNE11 % | I2 % | A2 % | Other Species (Higher Retention Time Species) % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 18.7 | - | 44 | 2.0 | 14.7 | 20.5 |
| 3 | 36 | - | 62 | 2.39 | - | - |
| 4 | 47 | - | 50 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| Method | AE11 % | UNE11 cis % | SNE11 % | Imine % | A2 % | Dimer % | Deactivation (Loss of Conversion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44 | - | 54 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.02 | 47 |
| 2 | 44 | 0.14 | 54 | 0.2 | 0.6 | - | 47 |
| 3 | 34 | - | 65 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 57 |
| 4 | 60 | - | 39 | 0.7 | 0.9 | - | 31 |
| Reactivation Assay | Temperature (°C) | H2 (bar) | Reactivation Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 90 | 30 | 60 |
| b | 150 | 30 | 60 |
| c | 200 | 70–80 | 60 |
| d | 200 | 70–80 | 120 |
| e | 200 | 0 | 60 |
| Trial | Reactivation Assay | AE11 % |
|---|---|---|
| 1st cycle reaction | - | 91 |
| 1 | - | 44 |
| 2 | a | 48 |
| 3 | b | 91 |
| 4 | c | 90 |
| 5 | d | 62 |
| 6 | e | 15 |
| Trial | AE11 % | S2 | Sw | 2 × RSD (2 Sigma) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90.2 | 90.1 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 4.2% |
| 2 | 88.2 | ||||
| 3 | 92 |
| Stirrer speed (tr/mn) | 1000–1500 |
| UNE11 concentration (wt.% to solvent) | 30 (1.25 M), 40 (1.9 M), and 50 (2.15 M) |
| Solvent | Toluene or methylcyclohexane |
| Temperature (°C or K) | 90 °C (363 K) |
| Reaction time (min) | 120–180 |
| Catalyst loading (dry eq. wt.% related to UNE11) | 10 wt.% |
| NH3 (equivalents to UNE11) | 0.9 to 1.15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soutelo-Maria, A.; Dubois, J.-L.; Couturier, J.-L.; Brebion, M.; Cravotto, G. Regeneration of Raney®-Nickel Catalyst for the Synthesis of High-Value Amino-Ester Renewable Monomers. Catalysts 2020, 10, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020229
Soutelo-Maria A, Dubois J-L, Couturier J-L, Brebion M, Cravotto G. Regeneration of Raney®-Nickel Catalyst for the Synthesis of High-Value Amino-Ester Renewable Monomers. Catalysts. 2020; 10(2):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020229
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoutelo-Maria, Ana, Jean-Luc Dubois, Jean-Luc Couturier, Magali Brebion, and Giancarlo Cravotto. 2020. "Regeneration of Raney®-Nickel Catalyst for the Synthesis of High-Value Amino-Ester Renewable Monomers" Catalysts 10, no. 2: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020229
APA StyleSoutelo-Maria, A., Dubois, J. -L., Couturier, J. -L., Brebion, M., & Cravotto, G. (2020). Regeneration of Raney®-Nickel Catalyst for the Synthesis of High-Value Amino-Ester Renewable Monomers. Catalysts, 10(2), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10020229