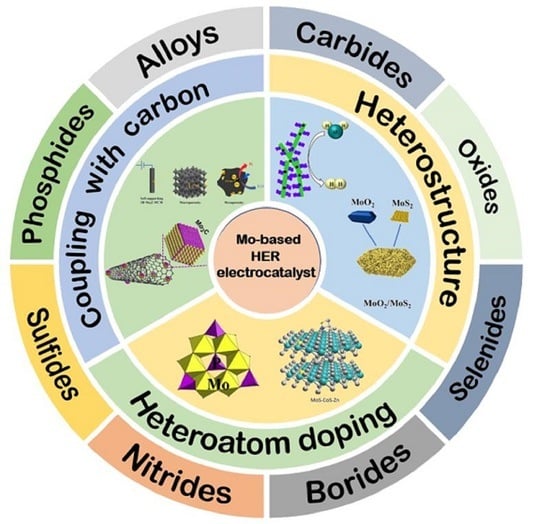
Smart Designs of Mo Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HER Mechanism
3. Mo Based HER Electrocatalysts
4. Smart Designs of Mo Based HER Catalysts
4.1. Carbon/Mo Based Composites
4.1.1. Coupling with Nanoscale Carbons
4.1.2. Coupling with Graphene Based Materials
4.1.3. Coupling with Mesoporous Carbons
4.1.4. Core Shell Structure
4.2. Heteroatom Doping
4.2.1. Nonmetallic Atom Doping
Single Atom Doping
Dual Atoms Doping
Triple Atoms Doping
4.2.2. Metallic Atom Doping
4.3. Heterostructure Construction
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hua, W.; Sun, H.-H.; Xu, F.; Wang, J.-G. A review and perspective on molybdenum-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.C.; Ren, J.-T.; Yuan, Z.-Y. Transition Metal Phosphide-Based Materials for Efficient Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution: A Critical Review. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3357–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Cai, J.; Wang, G. Two-dimensional MoS2 for hydrogen evolution reaction catalysis: The electronic structure regulation. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1985–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huo, J.; Guo, J.; Lu, L.; Shen, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, H. Hierarchical Porous Molybdenum Carbide Based Nanomaterials for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, F.; Song, S. Recent advances in structural engineering of molybdenum disulfide for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Chen, L.; Shi, J. Anion-Containing Noble-Metal-Free Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Overall Water Splitting. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3688–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKone, J.R.; Marinescu, S.C.; Brunschwig, B.S.; Winkler, J.R.; Gray, H.B. Earth-abundant hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Senthil, R.A.; Madhavan, J.; Maiyalagan, T. Review on recent progress in non platinum counter electrode materials for dye-sensitized solar cells. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamesh, M.; Kuang, Y.; Sun, X. Constructing Earth-abundant 3D Nanoarrays for Efficient Overall Water Splitting—A Review. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 1550–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, Y. Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5148–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Veith, G.M.; Diaz, R.E.; Liu, J.; Stach, E.A.; Adzic, R.R.; Khalifah, P.G. Cobalt molybdenum oxynitrides: Synthesis, structural characterization, and catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10753–10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zhao, S.; Feng, H.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Tong, Y.; Lu, X. Engineering Thin MoS2 Nanosheets on TiN Nanorods: Advanced Electrochemical Capacitor Electrode and Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalyst. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, L.; et al. Phase Modulation of (1T-2H)-MoSe2/TiC-C Shell/Core Arrays via Nitrogen Doping for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Yang, F.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Xia, X.; et al. Directional Construction of Vertical Nitrogen-Doped 1T-2H MoSe2/Graphene Shell/Core Nanoflake Arrays for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 1700748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Gao, W.; Dong, G.; Xia, Z.; Yip, S.; Qin, Y.; Qu, Y.; Ho, J.C. Hierarchical NiMo-based 3D electrocatalysts for highly-efficient hydrogen evolution in alkaline conditions. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibsgaard, J.; Chen, Z.; Reinecke, B.N.; Jaramillo, T.F. Engineering the surface structure of MoS2 to preferentially expose active edge sites for electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Song, X.; Feng, K.; Nie, K.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Zhong, J.; Li, Y. Mo2C nanoparticles dispersed on hierarchical carbon microflowers for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11337–11343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Chan, K.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Norskov, J.K. Active edge sites in MoSe2 and WSe2 catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction: A density functional study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13156–13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Sk, M.A.; Thia, L.; Ge, X.; Lim, R.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Lim, K.H.; Wang, X. Molybdenum phosphide as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2624–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.; Zhang, Y.; Scheifers, J.P.; Jothi, P.R.; Encinas, A.; Fokwa, B.P.T. Graphene- and phosphorene-like boron layers with contrasting activities in highly active Mo2B4 for hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12915–12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Sasaki, K.; Ma, C.; Frenkel, A.I.; Marinkovic, N.; Muckerman, J.T.; Zhu, Y.; Adzic, R.R. Hydrogen-evolution catalysts based on non-noble metal nickel-molybdenum nitride nanosheets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6131–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Yu, R.; Xue, N.; Bin Yousaf, A.; Du, H.; Liang, K.; Jiang, N.; Xu, A.W. P doped molybdenum dioxide on Mo foil with high electrocatalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, B.; Zhao, D.; Wang, H.; Selomulya, C. Strategies for developing transition metal phosphides as heterogeneous electrocatalysts for water splitting. Nano Today 2017, 15, 26–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ge, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Wang, X. Facile synthesis of low crystalline MoS2 nanosheet-coated CNTs for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7768–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Zhu, J.; Liao, L.; Scanlon, M.D.; Ge, P.; Ji, C.; Girault, H.H.; Liu, B. Nanocomposite of MoS2 on ordered mesoporous carbon nanospheres: A highly active catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Commun. 2012, 22, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Rui, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Ma, J.; Dou, S.X.; Sun, W. Heteroatom-doped MoSe2 nanosheets with enhanced hydrogen evolution kinetics for alkaline water splitting. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Li, P.; Rui, K.; Chen, Y.; Dou, S.X.; Sun, W. CoSe2/MoSe2 heterostructures with enriched water adsorption/dissociation sites towards enhanced alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 11158–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinagawa, T.; Garcia-Esparza, A.T.; Takanabe, K. Insight on Tafel slopes from a microkinetic analysis of aqueous electrocatalysis for energy conversion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Kong, R.M.; Guo, X.; Qu, F.; Li, J. Recent progress in transition metal phosphides with enhanced electrocatalysis for hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21617–21624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Geng, D.; Fu, W.; Dan, J.; Xie, Y.; Kent, P.R.C.; Zhou, W.; Pennycook, S.J.; Loh, K.P. Edge segregated polymorphism in 2D molybdenum carbide. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.E.; Mahmood, M.N.; Man, M.C.M.; Turner, A.K. Preparation and characterization of low overvoltage transition metal alloy electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution in alkaline solutions. Electrochim. Acta 1984, 29, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Liao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, M.; Zschech, E.; Feng, X. Efficient hydrogen production on MoNi4 electrocatalysts with fast water dissociation kinetics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, C. MoO2 nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide/polyimide-carbon nanotube film as efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. J. Power Sources 2016, 304, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Flawed MoO2 belts transformed from MoO3 on a graphene template for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7040–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Shen, P.K. Nanoflower-like metallic conductive MoO2 as a high-performance non-precious metal electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 20080–20085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Yue, X.; Han, Y.; Shen, P.K.; Cui, Y. Porous MoO2 nanosheets as non-noble bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Li, D.; Jin, Q.; Cui, H.; Wang, C. Integrated 3D self-supported Ni decorated MoO2 nanowires as highly efficient electrocatalysts for ultra-highly stable and large-current-density hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 24453–24461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnemann, B.; Moses, P.G.; Bonde, J.; Jørgensen, K.P.; Nielsen, J.H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K. Biomimetic hydrogen evolution: MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5308–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Liu, P.; Jiang, J.; Ai, L.; Shao, Z.; Liu, S. Recent advances in nanostructured metal nitrides for water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19912–19933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Jiang, Q.; Li, J.; Tang, J. A review on non-noble metal based electrocatalysis for the oxygen evolution reaction. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4294–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulliger, F. Crystal chemistry of the chalcogenides and pnictides of the transition elements. Struct. Bond. 1968, 4, 83–229. [Google Scholar]
- Callejas, J.F.; Read, C.G.; Roske, C.W.; Lewis, N.S.; Schaak, R.E. Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties of Metal Phosphide Catalysts for the Hydrogen-Evolution Reaction. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6017–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, R. Birth of a class of nanomaterial. Nature 2019, 575, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, C.; Regmi, Y.N.; Leonard, B.M. Multiple phases of molybdenum carbide as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6407–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Encinas, A.; Scheifers, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Fokwa, B.P.T. Boron-dependency of molybdenum boride electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5575–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrubel, H.; Hu, X. Molybdenum boride and carbide catalyze hydrogen evolution in both acidic and basic solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12703–12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Du, M.; Zhang, M.; Zou, M.; Yang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yao, J. The design and construction of 3D rose-petal-shaped MoS2 hierarchical nanostructures with structure-sensitive properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7680–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, J.; Yan, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S. Space-confined growth of MoS2 nanosheets within graphite: The layered hybrid of MoS2 and graphene as an active catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.B.; Qi, X.; Chen, B.; Bao, S.; Yin, Z.; Wu, X.J.; Luo, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, H. MoS2 nanoflower-decorated reduced graphene oxide paper for high-performance hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5624–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Wu, G.; Yang, Q.; Hong, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Porous molybdenum phosphide nano-octahedrons derived from confined phosphorization in UIO-66 for efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12854–12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, J.; Moses, P.G.; Jaramillo, T.F.; Nørskovb, J.K.; Chorkendorff, I. Hydrogen evolution on nano-particulate transition metal sulfide. Faraday Discuss. 2009, 140, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Dai, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, F.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, X.; Xie, Y. Semimetallic molybdenum disulfide ultrathin nanosheets as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8359–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Liu, S.; Dong, R.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, M.; Feng, X. Engineering water dissociation sites in MoS2 nanosheets for accelerated electrocatalytic hydrogen production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2789–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Peng, S.; Tan, C.; Ang, H.; Tan, H.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Q. Ultrathin S-doped MoSe2 nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5597–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Pohl, D.; Rellinghaus, B.; Dong, R.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, X. Interface engineering of MoS2/Ni3S2 heterostructures for highly enhanced electrochemical overall-water-splitting activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6702–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z. N, P (S) Co-doped Mo2C/C hybrid electrocatalysts for improved hydrogen generation. Carbon 2018, 139, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; Gong, L.; Yang, M.; Huang, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, K.; Ma, L.; Li, R. Nitrogen and phosphorus dual-doping carbon shells encapsulating ultrafine Mo2C particles as electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2019, 553, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lan, X.; Hu, X. Paragenesis of Mo2C nanocrystals in mesoporous carbon nanofibers for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 274, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Tan, H.; Khan, S.U.; Ma, Y.; Zang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. MoP/Mo2C@C: A New Combination of Electrocatalysts for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution over the Entire pH Range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16270–16279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Mo, Q.; He, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, L.; Zeng, J.; Gao, Q. Heterostructured MoC-MoP/N-doped carbon nanofibers as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 299, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Yakobson, B.I.; Goddard, W.A., III; Guo, X.; Hauge, R.H.; et al. Atomic H-Induced Mo2C Hybrid as an Active and Stable Bifunctional Electrocatalyst. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, K.; Xu, X. Mo2C based electrocatalyst with nitrogen doped three-dimensional mesoporous carbon as matrix, synthesis and HER activity study. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 293, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.; Adam, A.; Merzougui, B.; Helal, A.; Abdulhamid, O.; Siddiqui, M.N. Metal–organic framework-guided growth of Mo2C embedded in mesoporous carbon as a highperformance and stable electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16225–16232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Facile and large-scale preparation of Co/Ni-MoO2 composite as high-performance electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20721–20726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Hong, W.; Cai, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, W. Surface electron state engineering enhanced hydrogen evolution of hierarchical molybdenum disulfide in acidic and alkaline media. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 266, 118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Huang, M.; Yan, P.; Isimjan, T.T.; Yang, X. Electron-transfer enhanced MoO2-Ni heterostructures as a highly efficient pH-universal catalyst for hydrogen evolution. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, A.; Tian, C.; Jiang, B.; Fu, H. Porous Plate-like MoP Assembly as an Efficient pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 49596–49606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, K.; Cheong, W.-C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Cao, X.; Wu, K.; Pan, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; et al. Synergistically Interactive Pyridinic-N–MoP Sites: Identified Active Centers for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution in Alkaline Solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8982–8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, X.; Cui, M.; Nie, F.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gan, Y.; Yin, X.; et al. Heterostructured CoP/MoO2 on Mo foil as high-efficiency electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction in both acidic and alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 6732–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Liu, L.; Fang, Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Q. Hard template strategy for the synthesis of porous MoS2/MoO2 hybrid electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 520, 146340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Sha, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Kong, L.; Liu, G. Confined Molybdenum Phosphide in P-Doped Porous Carbon as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17140–17146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Huang, J.; Luo, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Yan, M.; Ye, Z.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Z.; Huang, S. Wrinkled Ni-doped Mo2C coating on carbon fiber paper: An advanced electrocatalyst prepared by molten-salt method for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 319, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, J.; Han, C.; Jia, S.; Tian, P.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y. Molybdenum oxide and molybdenum carbide coated carbon black as an electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic media. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26985–26994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ren, J.; Yuan, G.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Z. Facile synthesis of Mo2C nanoparticles on N-doped carbon nanotubes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction reactions. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 38, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anjum, M.A.R.; Lee, J.S. Sulfur and Nitrogen Dual-Doped Molybdenum Phosphide Nanocrystallites as an Active and Stable Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst in Acidic and Alkaline Media. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3030–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jian, K.; Lv, Z.; Li, D.; Fan, G.; Zhang, R.; Dang, J. MoS2/Co9S8/MoC heterostructure connected by carbon nanotubes as electrocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 79, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, Z.; Ye, L. In Situ Preparation of Mo2C Nanoparticles Embedded in Ketjenblack Carbon as Highly Efficient Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Jin, T.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L. Molybdenum carbide in-situ embedded into carbon nanosheets as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 298, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ziaee, M.A.; Lu, K.; Wang, R. Nanohybrid of Carbon Quantum Dots/Molybdenum Phosphide Nanoparticle for Efficient Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution in Alkaline Medium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9460–9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, A.; Suliman, M.H.; Dafalla, H.; Al-Arfaj, A.R.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Qamar, M. Rationally dispersed molybdenum phosphide on carbon nanotubes for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11414–11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.; Suliman, M.H.; Awwad, M.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Yamani, Z.H.; Qamar, M. Controlled growth of small and uniformly dispersed Mo2C on carbon nanotubes as high performance electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11797–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Shi, Z.; He, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Q.; Tang, Y. Heteronanowires of MoC–Mo2C as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.H.; Li, S.L.; Wang, Y.G.; Dong, L.Z.; Dai, Z.H.; Li, Y.F.; Lan, Y.Q. Coupled molybdenum carbide and reduced graphene oxide electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, B.; Wu, P.; Liang, H.; Yu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, S. Mo2C nanoparticles embedded within bacterial cellulose-derived 3D N-doped carbon nanofiber networks for efficient hydrogen evolution. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Jiao, Y.; Wu, A.; Tian, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Fu, H. Cluster-Like Molybdenum Phosphide Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution over a Broad pH Range. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9530–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Li, S.-L.; Huang, W.; Dong, L.-Z.; Liu, C.-H.; Li, Y.-F.; Lan, Y.-Q. Molybdenum Disulfide/Nitrogen-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite with Enlarged Interlayer Spacing for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Gao, F. Agaric-derived N-doped carbon nanorod arrays@nanosheet networks coupled with molybdenum carbide nanoparticles as highly efficient pH-universal hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 5159–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorahong, S.; Harding, D.J.; Siaj, M. Hollow molybdenum oxide-graphene oxide spheres as a binder-free electrocatalyst membrane with enhanced hydrogen evolution efficiency. Mater. Lett. 2020, 272, 127872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Liang, Y.; Hong, G.; Dai, H. MoS2 Nanoparticles Grown on Graphene: An Advanced Catalyst for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7296–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Xu, B.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X.S. Graphene-Based Electrodes for Electrochemical Energy Storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1388–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Tsubaki, N.; Wu, M. Highly Dispersed Mo2C Anchored on N,P-Codoped Graphene as Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2300–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ci, S.; Jia, J.; Wen, Z. Graphene Loading Molybdenum Carbide/Oxide Hybrids as Advanced Electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21246–21250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Guo, J.; Xiao, W.; Xuan, C.; Lei, W.; Wang, D. Highly efficient and stable MoP-rGO nanoparticles as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Dong, Q.; Geng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Dong, X. Highly Dispersive MoP Nanoparticles Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for an Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26258–26263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Song, H.; Chen, X. Hollow graphene oxide spheres self-assembled by W/O emulsion. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4867–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Jin, M.; Yao, F.; Kim, T.H.; Le, V.T.; Yue, H.; Gunes, F.; Li, B.; Ghosh, A.; Xie, S.; et al. Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on Graphene/MnO2 Nanospheres and Graphene/MoO3 Nanosheets with High Energy Density. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5074–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Liang, Z.; Lee, H.-W.; Hsu, P.-C.; Zheng, G.; Cui, Y. High Electrochemical Selectivity of Edge versus Terrace Sites in Two-Dimensional Layered MoS2 Materials. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 7138–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, D.H.; Han, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.S. Highly Active and Stable Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysts Based on Molybdenum Compounds on Carbon Nanotube–Graphene Hybrid Support. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5164–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquérol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.Q.; Lin, J.H.; Qin, J.F.; Dong, B.; Yan, K.L.; Liu, Z.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chai, Y.M.; Liu, C.G. A triple synergistic effect from pitaya-like MoNix-MoCx hybrids encapsulated in N-doped C nanospheres for efficient hydrogen evolution. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zou, K.; Zhang, X.; Han, T.; Yang, Y. Hierarchically flower-like N-doped porous carbon materials derived from an explosive 3-Fold interpenetrating diamondoid copper metal-organic framework for a supercapacitor. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 6552–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, K.; Xu, X.; Liu, X. Mo2C-Based Electrocatalyst with Biomass-Derived Sulfur and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon as a Matrix for Hydrogen Evolution and Organic Pollutant Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zou, X.; Yu, G.; Zhao, N.; Fan, F.; Zhu, G. Environmentally friendly synthesis of highly hydrophobic and stable MIL-53 MOF nanomaterials. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7430–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.D.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Hierarchical porous nitrogen-rich carbon monoliths via ice-templating: High capacity and high-rate performance as lithium-ion battery anode materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17787–17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giesche, H. Mercury Porosimetry: A General (Practical) Overview. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2006, 23, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S. Physical electrochemistry. Fundamentals, techniques, and applications by Eliezer Gileadi. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 16, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.J.; Feng, X.J.; Tan, H.Q.; Zang, H.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, E.B.; Li, Y.G. N-doped Graphene-Coated Molybdenum Carbide Nanoparticles as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3947–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Advancing the Electrochemistry of the Hydrogen-Evolution Reaction through Combining Experiment and Theory. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y.; Dai, S.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Metal–Organic Framework Derived Hybrid Co3O4-Carbon Porous Nanowire Arrays as Reversible Oxygen Evolution Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13925–13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Gao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yin, L.; Du, J.; Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Electrocatalytic performance of ultrasmall Mo2C affected by different transition metal dopants in hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6080–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; He, C.; Fan, L.; Asefa, T. Unconventional molybdenum carbide phases with high electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18030–18038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yuan, Z. One-pot Synthesis of Mo2N/NC Catalysts with Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancsó, P.; Popov, Z.I.; Pető, J.; Ollár, T.; Dobrik, G.; Pap, J.S.; Hwang, C.; Sorokin, P.B.; Tapasztó, L. Transition Metal Chalcogenide Single Layers as an Active Platform for Single-Atom Catalysis. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, X.; Su, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q. Mo2C based electrocatalyst with filter paper derived N-doped mesoporous carbon as matrix for H2 production. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibsgaard, J.; Jaramillo, T.F. Molybdenum Phosphosulfide: An Active, Acid-Stable, Earth-Abundant Catalyst for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 14661–14665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, L.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Tang, R.; Zhou, W. Highly Efficient Synthesis of Carbon-Based Molybdenum Phosphide Nanoparticles for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Jia, M.; Guo, P.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J. MoP nanoparticles encapsulated in P-doped carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Catal. Commun. 2020, 140, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gou, J.; Li, X.; Dong, B.; Han, G.; Hu, W.; Shang, X.; Chai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Self-sacrificial template method of Mo3O10(C6H8N)2·2H2O to fabricate MoS2/carbon-doped MoO2 nanobelts as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 216, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X. N,P-Codoped Carbon Layer Coupled with MoP Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Materials 2018, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, A.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Dong, M. Ionic Liquid-Assisted Synthesis of Hierarchical One-Dimensional MoP/NPC for High-Performance Supercapacitor and Electrocatalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6343–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Tian, J.; Hou, L.; Deng, B.; Wang, S.; Li, R.; Yang, F.; Li, Y. Hierarchical MoP Hollow Nanospheres Anchored on a N,P,S-Doped Porous Carbon Matrix as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 4662–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xiong, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Hu, R.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S. Ultrathin N-Doped Mo2C Nanosheets with Exposed Active Sites as Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12509–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Song, X.; Deng, J.; Zha, C.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Ultra-dispersed molybdenum phosphide and phosphosulfide nanoparticles on hierarchical carbonaceous scaffolds for hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 245, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tranca, D.; Zhang, J.; Hernandez, F.R.; Su, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, F.; Seifert, G.; Feng, X. Molybdenum Carbide-Embedded Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Nanosheets as Electrocatalysts for Water Splitting in Alkaline Media. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3933–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Titirici, M.-M.; Zhang, Q. A review of nanocarbons in energy electrocatalysis: Multifunctional substrates and highly active sites. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.H.; Zhou, Q.L.; Du, S.H.; Li, J.; Zhong, J.W.; Deng, X.L.; Liu, Y.L. Porous Co9S8/Nitrogen, sulfur-doped carbon@Mo2C dual catalyst for efficient water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22291–22302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J. Ultrafine Molybdenum Carbide Nanoparticles Composited with Carbon as a Highly Active Hydrogen-Evolution Electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14723–14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraman, R.; Tripkovic, D.; Strmcnik, D.; Chang, K.; Uchimura, M.; Paulikas, A.P.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N.M. Enhancing Hydrogen Evolution Activity in Water Splitting by Tailoring Li+-Ni(OH)2-Pt Interfaces. Science 2011, 334, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, T.; Xing, L.; Xu, K.; Tong, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Yan, W.; Chu, W.; Wu, C.; et al. Atomically Dispersed Iron–Nitrogen Species as Electrocatalysts for Bifunctional Oxygen Evolution and Reduction Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Nie, K.; Shao, Z.-J.; Gao, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Phosphorus-Mo2C@carbon nanowires toward efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution: Composition, structural and electronic regulation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Vasileff, A.; Qiao, S.-Z. The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Solution: From Theory, Single Crystal Models, to Practical Electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7568–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nidamanuri, N.P.; Jiang, A.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Dong, M. In situ construction of tandem nitrogen-doped MoP nanocrystals for high-efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 342, 136059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-S.; Tang, Y.-J.; Liu, C.-H.; Li, S.-L.; Li, R.-H.; Dong, L.-Z.; Dai, Z.-H.; Bao, J.-C.; Lan, Y.-Q. Polyoxometalate-Based Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Hybrid Electrocatalysts for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, H.S.; Zhou, F.; Li, R.M.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhong, H.; Wang, J. Metallic FePSe3 nanoparticles anchored on N-doped carbon framework for All-pH hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Pan, J.; He, T.; Yan, Y.; Xia, B.Y.; Wang, X. Molybdenum carbide-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 10947–10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Ding, W.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tan, S.; Wei, Z. Ni-doped Mo2C nanowires supported on Ni foam as a binder-free electrode for enhancing the hydrogen evolution performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Iqbal, K.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, R. Ultrafine MoP Nanoparticles Well Embedded in Carbon Nanosheets as Electrocatalyst with High Active Site Density for Hydrogen Evolution. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z. Novel two-dimensional molybdenum carbides as high capacity anodes for lithium/sodium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12145–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Davey, K.; Qiao, S.-Z. Activity origin and catalyst design principles for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution on heteroatom-doped graphene. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Gu, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, M.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Ji, X.; Li, J. Defect-rich and ultrathin N doped carbon nanosheets as advanced trifunctional metal-free electrocatalysts for the ORR, OER and HER. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Zeng, X.; Shang, X.; Dong, B.; Chai, Y.; Liu, C.; Marin, M.; Yin, Y. Embedding RhPx in N, P Co-Doped Carbon Nanoshells Through Synergetic Phosphorization and Pyrolysis for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. N,B-codoped defect-rich graphitic carbon nanocages as high performance multifunctional electrocatalysts. Nano Energy 2017, 42, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Meng, Y.; Cao, Y.; He, S.; Li, X.; Tong, S.; Wu, M. N-, O- and P-doped Hollow Carbons: Metal-free Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution and Oxygen Reduction Reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 248, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.; Grice, C.R.; Meng, W.; Guan, L.; Xu, F.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, D.; Yan, Y. Metal−Organic Framework-Derived CoWP@C Composite Nanowire Electrocatalyst for Efficient Water Splitting. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Gu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Tian, C.; Yan, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Fu, H. Effective Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution in Neutral Medium Based on 2D MoP/MoS2 Heterostructure Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25986–25995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.J.; Li, M.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Feng, C.Q.; Zhang, G.X. Rod-like nonstoichiometric Ni0.85Se as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 12653–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Chai, Y.; Shang, X.; Dong, B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Z. Heterointerface engineering of trilayer-shelled ultrathin MoS2/MoP/N-doped carbon hollow nanobubbles for efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 24783–24792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, C.; Pinna, N.; Lu, X.F. Ni strongly coupled with Mo2C encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers as robust bifunctional catalyst for overall water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803185–1803196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ni, K.; Niu, C.; Guo, R.; Xi, W.; Wang, Z.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, P.; et al. Upraising the O 2p Orbital by Integrating Ni with MoO2 for Accelerating Hydrogen Evolution Kinetics. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, A.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Min, S.; Hedhili, M.N.; Han, Y.; Huang, K.W.; Li, L.J. Rugae-like FeP nanocrystal assembly on a carbon cloth: An exceptionally efficient and stable cathode for hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10974–10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhang, H.J.; Sun, Y.Q.; Li, C.C. Novel Ni(S0.49Se0.51)2 porous flakes array on carbon fiber cloth for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 30119–30125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukola, S.; Merzougui, B.; Creager, S.E.; Qamarc, M.; Pederson, L.R.; Noui-Mehidi, M.N. Nanostructured cobalt-modified molybdenum carbides electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 22899–22912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, K.; Saha, S.; Banerjee, S.; Ganguli, A.K. Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution from MoS2-Functionalized Mo2N Nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19455–19461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Luo, X.; Sun, A.; Wu, Z.; Wang, D. Template-free fabrication of hierarchical MoS2/MoO2 nanostructures as efficient catalysts for hydrogen production. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Dong, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Z. A nanostructured MoO2/MoS2/MoP heterojunction electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 225403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.J.; Gao, M.R.; Liu, C.H.; Li, S.L.; Jiang, H.L.; Lan, Y.Q.; Han, M.; Yu, S.H. Porous molybdenum-based hybrid catalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12928–12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Feng, H.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Yu, M.; Lu, X.; Tong, Y. Porous MoO2 nanowires as stable and high-rate negative electrodes for electrochemical capacitors. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3929–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yang, Y.; Shi, R.; Xia, G.; Chen, J.; Su, J.; Chen, Q. Pt-like electrocatalytic behavior of Ru–MoO2 nanocomposites for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5475–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.-H.; Han, B.; Risch, M.; Giordano, L.; Yao, K.P.C.; Karayaylali, P.; Shao-Horn, Y. Activity and stability of cobalt phosphides for hydrogen evolution upon water splitting. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, G.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H. Micro-nanoporous MoO2@CoMo heterostructure catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraman, R.; Tripkovic, D.; Chang, K.-C.; Strmcnik, D.; Paulikas, A.P.; Hirunsit, P.; Chan, M.; Greeley, J.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N.M. Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3d M(Ni,Co,Fe,Mn) hydr(oxy)oxide catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, G.; Chen, S.; Luo, W. Hydrogen Evolution Reaction: Synergistically Tuning Water and Hydrogen Binding Abilities over Co4N by Cr Doping for Exceptional Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.B.; Cummins, D.; Reinecke, B.N.; Clark, E.; Sunkara, M.K.; Jaramillo, T.F. Core-shell MoO3-MoS2 nanowires for hydrogen evolution: A functional design for electrocatalytic materials. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4168–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, A.B.; Kegnæs, S.; Dahl, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Molybdenum sulfides-efficient and viable materials for electro-and photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Bao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, H.; Wu, Z. Phase engineering of amultiphasic 1T/2H MoS2 catalyst for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pető, J.; Ollár, T.; Vancsó, P.; Popov, Z.I.; Magda, G.Z.; Dobrik, G.; Hwang, C.Y.; Sorokin, P.B.; Tapasztó, L.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, A.; Qi, C.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.; Wang, D. Sulfur-Decorated Molybdenum Carbide Catalysts for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6956–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrubel, H.; Merki, D.; Hu, X. Hydrogen Evolution Catalyzed by MoS3 and MoS2 Particles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Cao, M. A mild route to mesoporous Mo2C-C hybrid nanospheres for high performance lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6151–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bo, X.; Guo, L. An efficient electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction based on molybdenum dioxide nanoparticles embedded porous graphene nanocomposite. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 5569–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Catalyst | Electrolyte | η10/(mV at 10 mA·cm−2) | Tafel Slope/(mV·dec−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP-Mo2C | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 210 | 64 | [56] |
| Mo2C/C | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 117 | 60.5 | [57] |
| 1 M KOH | 121 | 73.5 | ||
| Mo2C/CNFs | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 160 | 66 | [58] |
| 1 M KOH | 92 | 63 | ||
| MoP/Mo2C@C | 1 M KOH | 75 | 58 | [59] |
| MoC-MoP/N-CNFs | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 158 | 58 | [60] |
| 1 M KOH | 137 | 65 | ||
| Mo2C/GNR | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 152 | 65 | [61] |
| 1 M KOH | 121 | 54 | ||
| Mo2C/N-C | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 155 | 73 | [62] |
| 1 M KOH | 78 | 64 | ||
| Mo2C/C | 1 M KOH | 165 | 63.6 | [63] |
| Co/Ni-MoO2 | 1 M KOH | 103 | 80 | [64] |
| MoO2/MoS2|P | 1 M KOH | 45 | 64.2 | [65] |
| MoO2-Ni | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 69 | 31 | [66] |
| 1 M PBS | 84 | 75.3 | ||
| 1 M KOH | 46 | 56.9 | ||
| MoP@NPSC | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 71 | 75 | [67] |
| MoP@NCHSs | 1 M KOH | 92 | 62 | [68] |
| CoP–MoO2/MF | 1 M KOH | 42 | 127 | [69] |
| 0.5 M H2SO4 | 65 | 85 | ||
| MoS2/MoO2 | 1 M KOH | 157 | 119 | [70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Deng, H.; Dai, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Qiu, S.; Lu, X. Smart Designs of Mo Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Catalysts 2022, 12, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010002
Gao X, Deng H, Dai Q, Zeng Q, Qiu S, Lu X. Smart Designs of Mo Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Catalysts. 2022; 12(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xingyuan, Huilin Deng, Qiuping Dai, Quanlong Zeng, Shuxian Qiu, and Xihong Lu. 2022. "Smart Designs of Mo Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction" Catalysts 12, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010002
APA StyleGao, X., Deng, H., Dai, Q., Zeng, Q., Qiu, S., & Lu, X. (2022). Smart Designs of Mo Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Catalysts, 12(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010002