Effect of Ce and Co Addition to Fe/Al2O3 for Catalytic Methane Decomposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
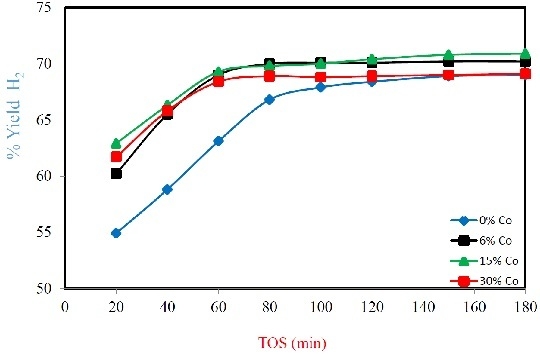
2.2. Catalyst Performance
2.2.1. Effect of Reduction Temperature
2.2.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature
2.3. Characterization of Spent Catalyst
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalytic Characterization
3.2.1. XRD Characterization
3.2.2. Temperature Programmed Reduction/oxidation (TPR/TPO)
3.2.3. Hydrogen Chemisorption
3.2.4. TEM
3.2.5. Raman Spectroscopy
3.2.6. BET Surface Area Measurement
3.3. Catalyst Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amin, A.M.; Croiset, E.; Epling, W. Review of methane catalytic cracking for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2904–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.F.; Wan Daud, W.M.A. Hydrogen production by methane decomposition: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 1160–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Epling, W.; Croiset, E. Reaction and Deactivation Rates of Methane Catalytic Cracking over Nickel. Ind. Eng Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 12460–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cai, Q.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L. Metal-Catalyst-Free Growth of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes on Substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2094–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.M.; Croiset, E.; Constantinou, C.; Epling, W. Methane cracking using Ni supported on porous and non-porous alumina catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9038–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.M.; Croiset, E.; Malaibari, Z.; Epling, W. Hydrogen production by methane cracking using Ni-supported catalysts in a fluidized bed. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 10690–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.M.; Abdullah, E.C.; Jayakumar, N.S.; Sahu, J.N. An overview on methods for the production of carbon nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradov, N.Z. How to produce hydrogen from fossil fuels without CO2 emission. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1993, 18, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodat, S.; Abanades, S.; Sans, J.-L.; Flamant, G. A pilot-scale solar reactor for the production of hydrogen and carbon black from methane splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 7748–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.Z.; Vahdati-Khaki, J.; Zebarjad, S.M.; Bataev, I.A.; Bannov, A.G. Nanocomposite Catalysts Obtaining by Mechanochemical Technique for Synthesizing Carbon Nanotubes. Synth. Reac. Inorg. Met. Org. Chem. 2013, 44, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.T.; Cha, W.S. Hydrogen production by the thermocatalytic decomposition of methane in a fluidized bed reactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Cooper, M.E.; Whan, D.A. Temperature programmed reduction of alumina-supported iron, cobalt and nickel bimetallic catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1982, 3, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manova, E.; Tsoncheva, T.; Paneva, D.; Mitov, I.; Tenchev, K.; Petrov, L. Mechanochemically synthesized nano-dimensional iron-cobalt spinel oxides as catalysts for methanol decomposition. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 277, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeeva, L.B.; Reshetenko, T.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Likholobov, V.A. Iron-containing catalysts of methane decomposition: accumulation of filamentous carbon. Appl. Catal. A 2002, 228, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; Avdeeva, L.B.; Ushakov, V.A.; Moroz, E.M.; Shmakov, A.N.; Kriventsov, V.V.; Kochubey, D.I.; Pavlyukhin, Y.T.; Chuyilin, A.L.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Coprecipitated iron-containing catalysts (Fe-Al2O3, Fe-Co-Al2O3, Fe-Ni-Al2O3) for methane decomposition at moderate temperatures: Part II. Evolution of the catalysts in reaction. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 270, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yamaguchi, D.; Burke, N.; Trimm, D.; Chiang, K. Methane decomposition over ceria modified iron catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Yan, D. Transformation of methane into synthesis gas using the redox property of Ce-Fe mixed oxides: Effect of calcination temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 3471–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, N.; Rezaei, M.; Meshkani, F. Methane decomposition over Ni-Fe/Al2O3 catalysts for production of COx-free hydrogen and carbon nanofiber. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Fakeeha, A.H.; Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Abasaeed, A.E.; Khan, W.U. Methane decomposition over iron catalyst for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 7593–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohitharn, N.; Goodwin, J.G., Jr.; Lotero, E. Fe-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts containing carbide-forming transition metal promoters. J. Catal. 2008, 255, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Mohd Zabidi, N.; Subbarao, D. Correlation between Fischer-Tropsch catalytic activity and composition of catalysts. Chem. Cent. J. 2011, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Choi, H.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Iron-cobalt mixed oxide nanocatalysts: Heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activation, cobalt leaching, and ferromagnetic properties for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 88, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ma, Z.; Lin, H.; Ding, L.; Qiu, J.; Frandsen, W.; Su, D. Template preparation of nanoscale CexFe1−xO2 solid solutions and their catalytic properties for ethanol steam reforming. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carja, G.; Delahay, G.; Signorile, C.; Coq, B. Fe-Ce-ZSM-5 a new catalyst of outstanding properties in the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem. Comm. 2004, 12, 1404–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.K.; Gunasekara, K.; Boolchand, P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Cr- and Ce-Doped Ferrite Catalysts for the High Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction: TPR and Mossbauer Spectroscopic Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Alonso, F.J.; Lopez Granados, M.; Ojeda, M.; Terreros, P.; Rojas, S.; Herranz, T.; Fierro, J.L.G. Chemical Structures of Coprecipitated Fe-Ce Mixed Oxides. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.-H.; Duffy, T.S. Raman spectroscopy of Fe2O3 to 62 GPa. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mendili, Y.; Bardeau, J.-F.; Randrianantoandro, N.; Gourbil, A.; Greneche, J.-M.; Mercier, A.-M.; Grasset, F. New evidences of in situ laser irradiation effects on y-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: A Raman spectroscopic study. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-S.; Kleiman-Shwarsctein, A.; Forman, A.J.; Hazen, D.; Park, J.-N.; McFarland, E.W. Pt-Doped alpha-Fe2O3 Thin Films Active for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3803–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataura, H.; Kumazawa, Y.; Maniwa, Y.; Umezu, I.; Suzuki, S.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Achiba, Y. Optical properties of single-wall carbon nanotubes. Synt. Met. 1999, 103, 2555–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Kojima, R.; Miyauchi, Y.; Chiashi, S.; Kohno, M. Low-temperature synthesis of high-purity single-walled carbon nanotubes from alcohol. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 360, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lou, H.; Zheng, X. The deposition of coke from methane on a Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst. Carbon 2007, 45, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakeeha, A.; Khan, W.; Ibrahim, A.; Al-Otaibi, R.; Al-Fatesh, A.; Soliman, M.; Abasaeed, A. Alumina Supported Iron Catalyst for Hydrogen Production: Calcination Study. IJACEBS 2015, 2, 139–141. [Google Scholar]














| Sample | Surface Area m2/g |
|---|---|
| 30%Fe/Al2O3 | 60.8 |
| 30%Fe-6%Co/Al2O3 | 43.4 |
| 30%Fe-15%Co/Al2O3 | 52.4 |
| 30%Fe-30%Co/Al2O3 | 72 |
| 30%Fe-6%Ce/Al2O3 | 56.25 |
| 30%Fe-15%Ce/Al2O3 | 52.1 |
| 30%Fe-30%Ce/Al2O3 | 95.3 |
| Sample | Fresh Catalyst (Reduced at 500 °C) | Fresh Catalyst (Reduced at 950 °C) |
|---|---|---|
| 30%Fe/Al2O3 | 22.15% | 0.34% |
| 30%Fe-15%Co/Al2O3 | 11.71% | 11.98% |
| 30%Fe-15%Ce/Al2O3 | 13.36% | 15.28% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Amin, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Khan, W.U.; Soliman, M.A.; AL-Otaibi, R.L.; Fakeeha, A.H. Effect of Ce and Co Addition to Fe/Al2O3 for Catalytic Methane Decomposition. Catalysts 2016, 6, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030040
Al-Fatesh AS, Amin A, Ibrahim AA, Khan WU, Soliman MA, AL-Otaibi RL, Fakeeha AH. Effect of Ce and Co Addition to Fe/Al2O3 for Catalytic Methane Decomposition. Catalysts. 2016; 6(3):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Fatesh, Ahmed Sadeq, Ashraf Amin, Ahmed Aidid Ibrahim, Wasim Ullah Khan, Mostafa Aly Soliman, Raja Lafi AL-Otaibi, and Anis Hamza Fakeeha. 2016. "Effect of Ce and Co Addition to Fe/Al2O3 for Catalytic Methane Decomposition" Catalysts 6, no. 3: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030040
APA StyleAl-Fatesh, A. S., Amin, A., Ibrahim, A. A., Khan, W. U., Soliman, M. A., AL-Otaibi, R. L., & Fakeeha, A. H. (2016). Effect of Ce and Co Addition to Fe/Al2O3 for Catalytic Methane Decomposition. Catalysts, 6(3), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030040