Removal of NOX Using Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor over Fe/TiO2 Catalysts and an Absorption Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Molar H2O2/NO and Temperature
2.2. Effects of the Gas Hourly Space Velocity (GHSV)
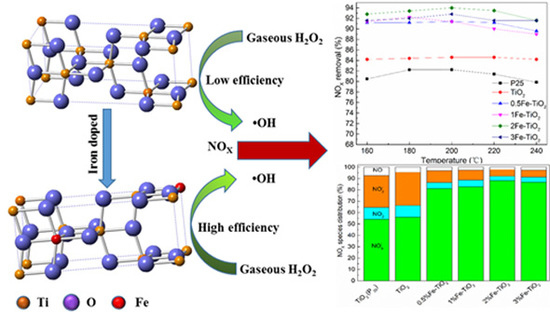
2.3. Effects of Catalyst Type
2.4. Structural Properties of Catalyst
2.5. Mechanistic Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Data Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skalska, K.; Miller, J.S.; Ledakowicz, S. Trends in NOX abatement: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3976–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marberger, A.; Elsener, M.; Ferri, D.; Kröcher, O. VOX surface coverage optimization of V2O5/WO3-TiO2 SCR catalysts by variation of the v loading and by aging. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1704–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Fan, Y.; Ling, W.; Yang, C.; Huang, B. Effect of Ce/γ Addition on Low-Temperature SCR Activity and SO2 and H2O Resistance of MnOX/ZrO2/MWCNTs Catalysts. Catalysts 2017, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, J. Advanced oxidation removal of NO and SO2 from flue gas by using ultraviolet/H2O2/NaOH process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L. Preliminary study on a new technique for wet removal of nitric oxide from simulated flue gas with an ultraviolet (UV)/H2O2 process. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4925–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, S. Catalytic efficiency of iron oxides in decomposition of H2O2 for simultaneous NOX and SO2 removal: Effect of calcination temperature. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 393, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Cai, W. Size-and shape-controlled synthesis and catalytic performance of iron–aluminum mixed oxide nanoparticles for NOX and SO2 removal with hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Song, F.; Bu, Y. Simultaneous removal of NOX and SO2 from coal-fired flue gas by catalytic oxidation-removal process with H2O2. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, B.; Hao, R.; Tao, Z. Low-temperature conversion of no in flue gas by vaporized H2O2 and nanoscale zerovalent iron. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7282–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xiong, Y.; Ge, Y. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO from flue gas with ·OH from the catalytic decomposition of gas-phase H2O2 over solid-phase Fe2(SO4)3. Chem. Eng. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xiong, Y. A novel low-temperature no removal approach with ·OH from catalytic decomposition of H2O2 over La1−XCaxFeO3 oxides. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.M.; Tripathi, M. A review of TiO2 nanoparticles. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousada, C.M.; Yang, M.; Nilsson, K.; Jonsson, M. Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on transition metal and lanthanide oxides. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 379, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousada, C.M.; LaVerne, J.A.; Jonsson, M. Enhanced hydrogen formation during the catalytic decomposition of H2O2 on metal oxide surfaces in the presence of HO radical scavengers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 12674–12679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.; Bagus, P.S.; Pak, S.; Rosynek, M.P.; Lunsford, J.H. Reactions of hydroxyl radicals on titania, silica, alumina, and gold surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, J.; Hao, Z. Catalytic oxidation of NO over TiO2 supported platinum clusters. II: Mechanism study by in situ FTIR spectra. Catal. Today 2010, 158, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Lin, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Fan, M. Effect of fluoride doping for catalytic ozonation of low-temperature denitrification over cerium–titanium catalysts. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 665, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.; Tang, A. Investigation on the removal of NO from SO2-containing simulated flue gas by an ultraviolet/Fenton-like reaction. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 5430–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, B.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S. Establishment of a novel advanced oxidation process for economical and effective removal of SO2 and NO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, J. Photochemical oxidation removal of NO and SO2 from simulated flue gas of coal-fired power plants by wet scrubbing using UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3836–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J. Mechanism of photodecomposition of H2O2 on TiO2 surfaces under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4118–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiabudi, A.; Chen, J.; Mul, G.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. CeO2 catalysed soot oxidation: The role of active oxygen to accelerate the oxidation conversion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 51, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivachandiran, L.; Thevenet, F.; Gravejat, P.; Rousseau, A. Investigation of NO and NO2 adsorption mechanisms on TiO2 at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Nakamura, S.; Kitao, O.; Arakawa, H. Lattice dynamics and dielectric properties of TiO2 anatase: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 155213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, I.; Kumar, P.P.; Gupta, A.K.; Sekhar, P.S.; Radha, K.; Padmanabham, G.; Sundararajan, G. Preparation and characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 powders for solar light response and photocatalytic applications. Proc. Appl. Ceram. 2012, 6, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.K.; Ding, X.M.; He, F.S.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Y.J.; Xie, J.W. Low-temperature synthesis and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 pillared montmorillonite. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.; Zhang, J.; Tian, B.; Chen, F.; He, D. Preparation of Fe3+-doped TiO2 catalysts by controlled hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide and study on their photocatalytic activity for methyl orange degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Böttcher, C.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Dohrmann, J.K. A comparative study of nanometer sized Fe(III)-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization and activity. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adán, C.; Bahamonde, A.; Fernández-García, M.; Martínez-Arias, A. Structure and activity of nanosized iron-doped anatase TiO2 catalysts for phenol photocatalytic degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 72, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiltürk, M.; Sayılkan, F.; Arpaç, E. Effect of Fe3+ ion doping to TiO2 on the photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye under UV and vis-irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 203, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.T. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, G.K.; Al-Shehri, A.; Narasimharao, K. Effect of TiO2 morphology on the benzyl alcohol oxidation activity of Fe2O3–TiO2 nanomaterials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 71076–71091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zheng, Q.; van de Krol, R. Creating oxygen vacancies as a novel strategy to form tetrahedrally coordinated Ti4+ in Fe/TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 7219–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhan, E.; Andonova, S.M.; Şentürk, G.S.; Chusuei, C.C.; Ozensoy, E. Fe promoted NOX storage materials: Structural properties and NOX uptake. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Cong, Y.; Tian, B.; Chen, F.; Anpo, M. Synergistic effects of doped Fe3+ and deposited Au on improving the photocatalytic activity of TiO2. Catal. Lett. 2006, 111, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Xing, M.; Zhang, J.; Tian, B. Visible light activated sulfur and iron co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst for the photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Catal. Today 2013, 201, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; van de Krol, R. Selective photoreduction of nitric oxide to nitrogen by nanostructured TiO2 photocatalysts: Role of oxygen vacancies and iron dopant. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9369–9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.-M.; Birnie, D.P.; Kingery, W.D. Physical Ceramics: Principles for Ceramic Science and Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Zhong, Q.; Cai, H.; Zhang, S. Structural characterizations of fluoride doped ceti nanoparticles and its differently promotional mechanisms on ozonation for low-temperature removal of NOX (x = 1, 2). Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over manganese substituted iron titanate catalyst: Reaction mechanism and H2O/SO2 inhibition mechanism study. Catal. Today 2010, 153, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H. Structure-activity relationship of iron titanate catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NOX with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16929–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, C. Effect of manganese substitution on the structure and activity of iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 93, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chu, H.; Tseng, T.K. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 and Fe/TiO2 nanoparticles and their performance for photocatalytic degradation of 1,2-dichloroethane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, N.; Ayissi, S.; Charpentier, P.A. Fe doped TiO2–graphene nanostructures: Synthesis, DFT modeling and photocatalysis. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 305601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Wang, K.W.; Perng, T.P. Electron field emission from Fe-doped TiO2 nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 143102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chu, J. Synthesis, surface morphology, and photoluminescence properties of anatase iron-doped titanium dioxide nano-crystalline films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 13096–13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaylov, M.; Ivanova, E.; Drenchev, N.; Hadjiivanov, K. Coordination Chemistry of Fe2+ Ions in Fe, H-ZSM-5 Zeolite as Revealed by the IR Spectra of Adsorbed CO and NO. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.; Mihaylov, M.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Blasin-Aubé, V.; Marie, O.; Plesniar, A.; Daturi, M. Evidencing three distinct Fe II sites in Fe–FER zeolites by using CO and NO as complementary IR probes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 93, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cen, K.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J. Simultaneous Multi-Pollutants Removal in Flue Gas by Ozone; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.; Vanderschuren, J. Nitrogen oxides scrubbing with alkaline solutions. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2000, 23, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameoka, Y.; Pigford, R.L. Absorption of nitrogen dioxide into water, sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide, and alkaline sodium sulfite aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1977, 16, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H.; Zhang, C. Novel iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 in the medium temperature range. Chem. Commun. 2008, 17, 2043–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Asakura, K.; He, H.; Shan, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C. Influence of sulfation on iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOX with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 103, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; He, H.; Liu, F. Effect of Fe on the photocatalytic removal of NOX over visible light responsive Fe/TiO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer, D.; Sagstuen, E.; Welch, K.; Haugen, H.J.; Tiainen, H. Oxidative power of aqueous non-irradiated TiO2-H2O2 suspensions: Methylene blue degradation and the role of reactive oxygen species. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, L.D.; Taxt-Lamolle, S.F.M.; Hole, E.O.; Krivokapić, A.; Sagstuen, E.; Haugen, H.J. TiO2 suspension exposed to H2O2 in ambient light or darkness: Degradation of methylene blue and EPR evidence for radical oxygen species. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Catalyst | Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | Pore Radius (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P25 | 36.7 | 26.23 | 0.087 | 106.1 |
| TiO2 | 98.6 | 11.16 | 0.162 | 41.3 |
| 0.5% Fe-TiO2 | 80.4 | 12.96 | 0.226 | 48.9 |
| 1% Fe-TiO2 | 92.3 | 11.75 | 0.213 | 42.8 |
| 2% Fe-TiO2 | 66.9 | 11.27 | 0.157 | 44.3 |
| 3% Fe-TiO2 | 66.4 | 10.62 | 0.079 | 25.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lu, Q. Removal of NOX Using Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor over Fe/TiO2 Catalysts and an Absorption Technique. Catalysts 2017, 7, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120386
Chen L, Li Y, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Liang Z, Lu Q. Removal of NOX Using Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor over Fe/TiO2 Catalysts and an Absorption Technique. Catalysts. 2017; 7(12):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120386
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lei, Yuxin Li, Qinxin Zhao, Yungang Wang, Zhiyuan Liang, and Qiang Lu. 2017. "Removal of NOX Using Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor over Fe/TiO2 Catalysts and an Absorption Technique" Catalysts 7, no. 12: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120386
APA StyleChen, L., Li, Y., Zhao, Q., Wang, Y., Liang, Z., & Lu, Q. (2017). Removal of NOX Using Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor over Fe/TiO2 Catalysts and an Absorption Technique. Catalysts, 7(12), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120386