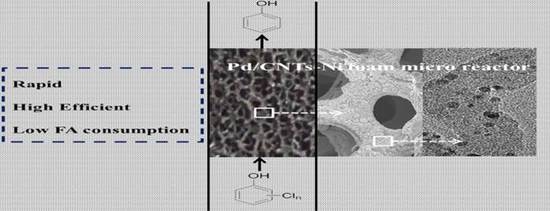
Catalytic Hydrodechlorination of Chlorophenols in a Continuous Flow Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor Using Formic Acid as a Hydrogen Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.2. HDC of 4-CP in Continuous Flow Micro Reactor and Packed Bed Reactor
2.3. HDC of 4-CP in Micro Reactor with Different Pd Contents
2.4. HDC of 4-CP in Micro Reactor under Different FA/Substrate Molar Ratios
2.5. The Longevity, Deactivation and Regeneration of Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor (Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Composite Catalyst)
3.2. Catalytic Performance Evaluation
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Microreactor of Pd nanoparticles immobilized hollow microspheres for catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols in water. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Jin, X.; Sun, F.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Xia, C. Combination of hydrodechlorination and biodegradation for the abatement of chlorophenols. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Wu, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yin, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M. A highly active Pd on Ni–B bimetallic catalyst for liquid-phase hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol under mild conditions. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zuo, W.; Tian, M.; Dong, Z.; Ma, J. Highly efficient and recyclable Ni MOF-derived N-doped magnetic mesoporous carbon-supported palladium catalysts for the hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 423, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.F.; Shen, Z.Y.; Niu, J.F.; Jing, C.; Duan, Y.P. Degradation of pentachlorophenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol by sequential visible-light driven photocatalysis and laccase catalysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9117–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.M.; Chen, K.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, T.Y.; Huang, W.Y. Biobarrier system for remediation of TCE-contaminated aquifers. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 72, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untea, I.; Orbeci, C.; Tudorache, E. Oxidative degradation of 4-chlorophenol from aqueous solution by photo-fenton advanced oxidation process. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2006, 5, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Fabregat, A.; Stüber, F.; Fortuny, A.; Carrera, J.; Font, J. Catalytic wet air oxidation of substituted phenols: Temperature and pressure effect on the pollutant removal, the catalyst preservation and the biodegradability enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Gu, G.; Xia, C. Water: The most effective solvent for liquid-phase hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols over Raney Ni catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J. Pd nanoparticles modified rod-like nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous carbons for effective catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27313–27319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Liang, X. The Pd-catalyzed hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols in aqueous solutions under mild conditions: A promising approach to practical use in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lan, L.; Du, F.; Xia, C. The reaction mechanism for highly effective hydrodechlorination of p-chlorophenol over a Pd/CNTs catalyst. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109023–109029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fang, D. Performance of palladium–tin bimetallic catalysts supported on activated carbon for the hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40437–40443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Wu, T.; Yang, X.J.; Xu, J.; Auzam, J.; Semiat, R.; Han, Y.F. Degradation of trichloroethylene by hydrodechlorination using formic acid as hydrogen source over supported Pd catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 305, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopinke, F.D.; Mackenzie, K.; Köhler, R. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of groundwater contaminants in water and in the gas phase using Pd/γ-Al2O3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 44, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quero, S.; Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Keane, M.A. Solvent effects in the hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over Pd/Al2O3. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quero, S.; Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Keane, M.A. Effect of metal dispersion on the liquid-phase hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over Pd/Al2O3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6841–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.Y.; Ahn, B.J. Catalytic hydrodechlorination reaction of chlorophenols by Pd nanoparticles supported on grapheme. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, E.; McCall, A.; Faba, L.; Sastre, H.; Ordóñez, S. Trichloroethylene hydrodechlorination in water using formic acid as hydrogen source: Selection of catalyst and operation conditions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2013, 32, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopinke, F.D.; Mackenzie, K.; Koehler, R.; Georgi, A. Alternative sources of hydrogen for hydrodechlorination of chlorinated organic compounds in water on Pd catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 271, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State, R.; Papa, F.; Tabakova, T.; Atkinson, I.; Negrila, C.; Balint, I. Photocatalytic abatement of trichlorethylene over Au and Pd–Au supported on TiO2 by combined photomineralization/hydrodechlorination reactions under simulated solar irradiation. J. Catal. 2017, 346, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Di Benedetto, A. Effects of non-equidiffusion on unsteady propagation of hydrogen-enriched methane/air premixed flames. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 7510–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, L.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Casas, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodriguez, J.J. Hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol in water with formic acid using a Pd/activated carbon catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellier, P.P.; Spindler, J.F.; Taillefer, M.; Cristau, H.J. Pd/C-catalyzed room-temperature hydrodehalogenation of aryl halides with hydrazine hydrochloride. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 7191–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Guo, S.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Chen, J. The influence of ion effects on the Pd-catalyzed hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solutions. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.; Le, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Ma, J. Metal organic framework derived magnetic porous carbon composite supported gold and palladium nanoparticles as highly efficient and recyclable catalysts for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18775–18785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wan, H.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, D. Enhanced liquid phase catalytic hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over mesoporous carbon supported Pd catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.B.; Pizarro, A.H.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Aqueous-phase hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols with pillared clays-supported Pt, Pd and Rh catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 148–149, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, R.L.; McMullen, J.P.; Jensen, K.F. Deciding whether to go with the flow: Evaluating the merits of flow reactors for synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7502–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, B.; Cantillo, D.; Kappe, C.O. Continuous-flow technology-a tool for the safe manufacturing of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6688–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naber, J.R.; Buchwald, S.L. Packed-bed reactors for continuous-flow C-N cross-coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9469–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, U.; Panda, D.; Biswas, K.G. Non-lithographic copper-wire based fabrication of micro-fluidic reactors for biphasic flow applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubogo, T.; Ishiwata, T.; Kobayashi, S. Asymmetric carbon-carbon bond formation under continuous-flow conditions with chiral heterogeneous catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6590–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, I. Continuous flow (micro-)reactors for heterogeneously catalyzed reactions: Main design and modelling issues. Catal. Today 2018, 308, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhong, L. Rapid, highly efficient and stable catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols over novel Pd/CNTs-Ni foam composite catalyst in continuous-flow. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 355, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Rodriguez, P.; Borchardt, L.; Foelske, A.; Yuan, J.; Herrmann, A.K.; Geiger, D.; Zheng, Z.; Kaskel, S.; Gaponik, N.; et al. Bimetallic aerogels: High-performance electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9849–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Shi, X.Z.; Shen, C.M.; Hui, C.; Xu, Z.C.; Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, D.K.; Gao, H.J. Synthesis of monodisperse palladium nanocubes and their catalytic activity for methanol electrooxidation. Chin. Phys. B 2010, 19, 106104. [Google Scholar]
- Jadbabaei, N.; Ye, T.; Shuai, D.; Zhang, H. Development of palladium-resin composites for catalytic hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 205, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanovas, A.; Domínguez, M.; Ledesma, C.; López, E.; Llorca, J. Catalytic walls and micro-devices for generating hydrogen by low temperature steam reforming of ethanol. Catal. Today 2009, 143, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Dong, X.; Dong, Y.; Hao, X.; Hampshire, S. Dual-production of nickel foam supported carbon nanotubes and hydrogen by methane catalytic decomposition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 12307–12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, D.; Tøtdal, B.; Zhao, T.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, W.; Holmen, A. Catalytic engineering of carbon nanotube production. Appl. Catal. A. Gen. 2005, 279, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Keane, M.A. Liquid phase hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols over Pd/C and Pd/Al2O3: A consideration of HCl/catalyst interactions and solution pH effects. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 52, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A. A review of catalytic approaches to waste minimization: Case study-liquid-phase catalytic treatment of chlorophenols. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quero, S.; Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Keane, M.A. Liquid phase catalytic hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol over Pd/Al2O3: Batch vs. continuous operation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Gokhale, S.P. Enhancing the hydrogen storage capacity of Pd-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3405–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, J.; Ma, Y. Catalytic Hydrodechlorination of Chlorophenols in a Continuous Flow Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor Using Formic Acid as a Hydrogen Source. Catalysts 2019, 9, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010077
Xiong J, Ma Y. Catalytic Hydrodechlorination of Chlorophenols in a Continuous Flow Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor Using Formic Acid as a Hydrogen Source. Catalysts. 2019; 9(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010077
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Jun, and Ying Ma. 2019. "Catalytic Hydrodechlorination of Chlorophenols in a Continuous Flow Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor Using Formic Acid as a Hydrogen Source" Catalysts 9, no. 1: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010077
APA StyleXiong, J., & Ma, Y. (2019). Catalytic Hydrodechlorination of Chlorophenols in a Continuous Flow Pd/CNT-Ni Foam Micro Reactor Using Formic Acid as a Hydrogen Source. Catalysts, 9(1), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9010077