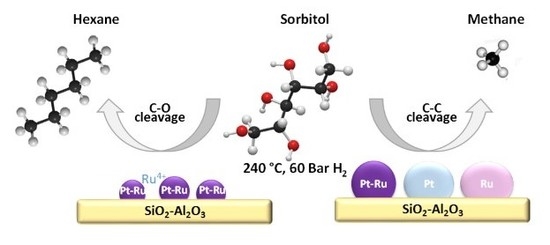
Biofuel Synthesis from Sorbitol by Aqueous Phase Hydrodeoxygenation over Bifunctional Catalysts: In-depth Study of the Ru–Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 Catalytic System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of the Metal Function
- The CI bimetallic catalyst (entry 3) displays two populations of particles coexisting separately on the support (representative TEM pictures were given in Reference [25]): The first one with small sizes (around 1.0 nm) associated to a Pt phase and a second one constituted of Ru large particles (between 10.0 and 40.0 nm, leading to average size of 33.0 nm). This configuration is in line with the respective populations observed on both Pt/S40 and Ru/S40 monometallic samples that were also previously published [25].
- The SI–(Ru–Pt)/S40 catalyst (entry 4) exhibits bimetallic particles well dispersed on the support with relatively homogeneous sizes (average diameter of 2.3 nm, see TEM images in Reference [25]), as on the Pt/S40 monometallic sample. The newly-prepared SI system corresponding to an inverted order of impregnation (SI–(Pt–Ru)/S40, entry 5) leads to a rather large distribution of particles size as observed on the TEM image of Figure 1a (leading to an average diameter of 26.0 nm). This distribution is similar to that of the monometallic Ru/S40 sample. Moreover, EDX analysis reveals the presence of bimetallic particles constituted of variable composition functions of their size (starting from 50%atom to 95%atom Ru for the largest particles).
- For the CR–(Ru–Pt)/S40 catalyst (entry 6), the surface redox deposition favors the formation of a majority of bimetallic particles. Nevertheless, the presence of at least one large particle of isolated Ru observed by TEM on this sample in Reference [25] reveals a limitation of the redox process which may occur for high modifier contents (higher to the value corresponding to a monolayer of Ru on Pt) resulting in the deposition of Ru agglomerates on the support by a simple impregnation. This limitation to deposit exclusively the additive on the metallic atoms of the parent catalyst was already observed in the case of Re–Pd/TiO2 samples [27]. Thus, the Ru loading introduced by catalytic reduction deposition was decreased to prepare three new CR catalysts (entries 7 to 9). As expected, for a lower Ru loading (1 wt.%, entry 8), the TEM-EDX analysis indicates the absence of isolated Ru particles but mainly the presence of bimetallic particles with an average diameter of 3.8 nm and some small isolated Pt particles (Figure 1b).
2.2. Chemical State of the Metal Function Determined by XPS
2.3. Characteristics of the Acidic Function
2.4. Aqueous Phase Transformation of Sorbitol
2.5. Reactivity of Intermediate Species
- pathway (1):
- pathway (2):
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalysts Preparation
3.2. Characterization of the Catalysts
3.3. Aqueous-phase Transformation of Sorbitol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davda, R.R.; Shabaker, J.W.; Huber, G.W.; Cortright, R.D.; Dumesic, J.A. A review of catalytic issues and process conditions for renewable hydrogen and alkanes by aqueous-phase reforming of oxygenated hydrocarbons over supported metal catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 56, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: Chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chheda, J.N.; Huber, G.W.; Dumesic, J.A. Liquid-phase catalytic processing of biomass-derived oxygenated hydrocarbons to fuels and chemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 7164–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, D.M.; Bond, J.Q.; Dumesic, J.A. Catalytic conversion of biomass to biofuels. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1493–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Liu, S.; Tamura, M.; Tomishige, K. Catalytic total hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived polyfunctionalized substrates to alkanes. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1114–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Song, W.; Buhain, J. Bioenergy and biofuels: History, status, and perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneyer, A.; Ennaert, T.; Cavents, G.; Dijkmans, J.; Vanneste, J.; Courtin, C.M.; Dusselier, M.; Sels, B.F. Compositional and structural feedstock requirements of a liquid phase cellulose-to-naphtha process in a carbon- and hydrogen-neutral biorefinery context. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5594–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso, D.M.; Wettstein, S.G.; Dumesic, J.A. Bimetallic catalysts for upgrading of biomass to fuels and chemicals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 8075–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werpy, T.; Petersen, G.; Aden, A.; Bozell, J.; Holladay, J.; Manheim, A.; Eliot, D.; Lasure, L.; Jones, S. Top Value Added Chemicals from Biomass; U.S. Department of Energy: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bozell, J.J.; Petersen, G.R. Technology development for the production of biobased products from biorefinery carbohydrates—the US Department of Energy’s “Top 10” revisited. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wu, S.-B.; Liu, Y. Advances in the catalytic production and utilization of sorbitol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 11799–11815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, H. Mechanistic insight into the selective hydrogenolysis of sorbitol to propylene glycol and ethylene glycol on supported Ru catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7042–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortright, R.D.; Davda, R.R.; Dumesic, J.A. Hydrogen from catalytic reforming of biomass-derived hydrocarbons in liquid water. Nature 2002, 418, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, G.W.; Cortright, R.D.; Dumesic, J.A. Renewable alkanes by aqueous-phase reforming of biomass-derived oxygenates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1549–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Huber, G.W. Aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of sorbitol with Pt/SiO2–Al2O3: Identification of reaction intermediates. J. Catal. 2010, 270, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, B.M.; Li, N.; Lee, J.; Huber, G.W.; Klein, M.T. Modeling aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of sorbitol over Pt/SiO2–Al2O3. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 23769–23784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.M.; Tucker, M.H.; Braden, D.J.; Dumesic, J.A. Production of alkanes from biomass derived carbohydrates on bi-functional catalysts employing niobium-based supports. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tompsett, G.A.; Huber, G.W. Renewable high-octane gasoline by aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of C5 and C6 carbohydrates over Pt/zirconium phosphate catalysts. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.T.; Dumesic, J.A.; Huber, G.W. Aqueous-phase hydrodeoxygenation of sorbitol: A comparative study of Pt/Zr phosphate and Pt-ReOx/C. J. Catal. 2013, 304, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.M.; Kunkes, E.L.; Simonetti, D.A.; Dumesic, J.A. Catalytic conversion of biomass-derived carbohydrates to fuels and chemicals by formation and upgrading of mono-functional hydrocarbon intermediates. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.T.; Huber, G.W. Aqueous-phase hydrogenation and hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived oxygenates with bimetallic catalysts. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira D’Angelo, M.F.; Ordomsky, V.; van der Schaaf, J.; Schouten, J.C.; Nijhuis, T.A. Continuous hydrogen stripping during aqueous phase reforming of sorbitol in a washcoated microchannel reactor with a Pt–Ru bimetallic catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 18069–18076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.V.H.; Perez, G.; Passos, F.B. Alumina supported bimetallic Pt–Fe catalysts applied to glycerol hydrogenolysis and aqueous phase reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 185, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Thapa, P.S.; Subramaniam, B.; Chaudhari, R.V. Kinetic modeling of sorbitol hydrogenolysis over bimetallic RuRe/C catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6037–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messou, D.; Vivier, L.; Especel, C. Sorbitol transformation over bimetallic Ru-Pt/SiO2-Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of the preparation method. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 127, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epron, F.; Especel, C.; Lafaye, G.; Marécot, P. Nanoparticles and Catalysis; Astruc, D., Ed.; Wiley-VCH verlag GmbH &, Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 279–302. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, B.K.; Tapin, B.; Aouine, M.; Delichere, P.; Epron, F.; Pinel, C.; Especel, C.; Besson, M. Insights into the oxidation state and location of rhenium in Re-Pd/TiO2 catalysts for aqueous-phase selective hydrogenation of succinic acid to 1,4-butanediol as a function of palladium and rhenium deposition methods. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2161–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovič, P.; Selih, V.S.; Sala, M.; Hocevar, S.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Hodnik, N.; Bele, M.; Gaberscek, M. Potentiodynamic dissolution study of PtRu/C electrocatalyst in the presence of methanol. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 211, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlYami, N.M.; LaGrow, A.P.; Joya, K.S.; Hwang, J.; Katsiev, K.; Anjum, D.H.; Losovyj, Y.; Sinatra, L.; Kim, J.Y.; Bakr, O.M. Tailoring ruthenium exposure to enhance the performance of fcc platinum@ruthenium core–shell electrocatalysts in the oxygen evolution reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 16169–16178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzieri, V.; Coloma-Pascual, F.; Arcoya, A.; L’Argentière, P.C.; Figoli, N.S. XPS, FTIR and TPR characterization of Ru/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 210, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, D.; Haleem, Y.A.; Zheng, X.; Ge, B.; Song, L. Role of Ru oxidation degree for catalytic activity in bimetallic Pt/Ru nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 6569–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Palenzuela, A.; Centellas, F.; Garrido, J.A.; Arias, C.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Brillas, E.; Cabot, P.-L. Structural properties of unsupported Pt−Ru nanoparticles as anodic catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4399–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaye, G.; Ekou, T.; Micheaud-Especel, C.; Montassier, C.; Marécot, P. Citral hydrogenation over alumina supported Rh-Ge catalysts: Effects of the reduction temperature. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 257, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemball, C.; Leach, H.F.; Skundric, B.; Taylor, K.C. Reactions of 3,3-dimethylbut-1-ene with deuterium oxide or deuterium over oxide catalysts. J. Catal. 1972, 27, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.S.; Kemball, C.; Rajadhayarsha, R.A. The mechanisms of dimethylbutene isomerization over alumina. J. Catal. 1979, 57, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, H.J. Use of organic probes in detecting active sites in heterogeneous catalysis. J. Catal. 1982, 78, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Duprez, D. Evaluation of the acid-base surface properties of several oxides and supported metal catalysts by means of model reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 118, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.; Pagán-Torres, Y.J.; Hibbitts, D.; Tan, Q.; Pham, H.N.; Datye, A.K.; Neurock, M.; Davis, R.J.; Dumesic, J.A. Selective Hydrogenolysis of polyols and cyclic ethers over bifunctional surface sites on rhodium–rhenium catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12675–12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Karim, A.M.; Engelhard, M.H.; Wei, Z.; King, D.L.; Wang, Y. Correlation of Pt–Re surface properties with reaction pathways for the aqueous-phase reforming of glycerol. J. Catal. 2012, 287, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, E.P.; Ketchie, W.C.; Murayama, M.; Davis, R.J. Glycerol hydrogenolysis on carbon-supported PtRu and AuRu bimetallic catalysts. J. Catal. 2007, 251, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirilin, A.V.; Tokarev, A.V.; Murzina, E.V.; Kustov, L.M.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Murzin, D.Y. Reaction products and transformations of intermediates in the aqueous-phase reforming of sorbitol. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.H.; Sui, Z.J.; Zhou, X.G. Hydrogenolysis of sorbitol to glycols over carbon nanofiber supported ruthenium catalyst. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, M.; Sivasanker, S.; Sankaranarayanan, T.M.; Venuvanalingam, P. Hydrogenolysis of sorbitol over Ni and Pt loaded on NaY. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcocq, L.; Cabiac, A.; Especel, C.; Lacombe, S.; Duprez, D. New insights into the mechanism of sorbitol transformation over an original bifunctional catalytic system. J. Catal. 2014, 320, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinfelt, J.H.; Yates, D.J.C. Catalytic hydrogenolysis of ethane over the noble metals of Group VIII. J. Catal. 1967, 8, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronci, S.; Pittau, B. Conversion of glucose and sorbitol in the presence of Ru/C and Pt/C catalysts. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 23086–23093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolini, E.; Giorgi, L.; Cardellini, F.; Passalacqua, E. Physical and morphological characteristics and electrochemical behaviour in PEM fuel cells of PtRu /C catalysts. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2001, 5, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douidah, A.; Marécot, P.; Labruquère, S.; Barbier, J. Stability of supported platinum catalysts in aqueous phase under hydrogen atmosphere. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 210, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcocq, L.; Cabiac, A.; Especel, C.; Lacombe, S.; Duprez, D. Study of the stability of Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 catalysts in aqueous medium: Application for sorbitol transformation. Catal. Commun. 2011, 15, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieck, C.L.; Marécot, P.; Barbier, J. Effect of Pt-Re interaction on sulfur adsorption and coke deposition. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 145, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Xia, Q.; Shao, Y.; Ding, D.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y. Production of hexane from sorbitol in aqueous medium over Pt/NbOPO4 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op de Beeck, B.; Dusselier, M.; Geboers, J.; Holsbeek, J.; Morré, E.; Oswald, S.; Giebeler, L.; Sels, B.F. Direct catalytic conversion of cellulose to liquid straight-chain alkanes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkes, E.L.; Simonetti, D.A.; Dumesic, J.A.; Pyrz, W.D.; Murillo, L.E.; Chen, J.G.; Buttrey, D.J. The role of rhenium in the conversion of glycerol to synthesis gas over carbon supported platinum–rhenium catalysts. J. Catal. 2008, 260, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Okuyama, Y.; Tamura, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Imai, A.; Tomoshige, K. Catalytic conversion of sorbitol to gasoline-ranged products without external hydrogen over Pt-modified Ir-ReOx/SiO2. Catal. Today 2016, 269, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messou, D.; Vivier, L.; Especel, C. Sorbitol transformation into biofuels over bimetallic platinum based catalysts supported on SiO2-Al2O3—Effect of the nature of the second metal. Fuel Proc. Technol. 2018, 177, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Entry | Catalysts/S40 | Ru/Pt 1 (Atomic Ratio) | SBET 2 (m2 g−1) | VP 2 (cm3 g−1) | DP 2 (nm) | đ 3 (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pt | - | 392 | 0.84 | 8.2 | 1.1 | Ref. [25] |
| 2 | Ru | - | 362 | 0.83 | 8.7 | 28.0 | Ref. [25] |
| 3 | CI–(Ru–Pt) | 1.9 | 327 | 0.67 | 8.2 | 1.0 (Pt) 33.0 (Ru) | Ref. [25] |
| 4 | SI–(Ru–Pt) | 1.9 | 300 | 0.72 | 8.6 | 2.3 | Ref. [25] |
| 5 | SI–(Pt–Ru) | 1.9 | 331 | 0.68 | 8.3 | 26.0 | |
| 6 | CR–(Ru–Pt) | 1.9 | 343 | 0.80 | 9.1 | 2.6 | Ref. [25] |
| 7 | CR–(2%Ru–Pt) | 1.3 | 366 | 0.77 | 8.4 | n.d. | |
| 8 | CR–(1%Ru–Pt) | 0.6 | 331 | 0.66 | 8.1 | 3.8 | |
| 9 | CR–(0.5%Ru–Pt) | 0.3 | 336 | 0.81 | 9.5 | n.d. |
| Catalysts/S40 | Pt 4f | Ru 3d | Atomic ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt0 | Ru0 | Ru4+ | C/Al | Pt/Al | Ru/Al | Ru/Pt | Ru0/(Ru0+Pt0) | |
| Pt | 100% 71.1 | - | - | - | 0.010 | - | - | - |
| Ru | - | 100% 279.0 | - | - | - | 0.050 | - | - |
| CI-(Ru-Pt) | 100% 71.0 | 100% 278.9 | - | - | 0.008 | 0.080 | 10.0 | - |
| SI-(Ru-Pt) | 100% 71.3 | 44% 279.7 | 56% 281.2 | 0.043 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 1.8 | 0.44 |
| SI-(Ru-Pt) * | 100% 71.0 | 80% 279.2 | 20% 280.7 | 0.020 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 2.5 | 0.67 |
| CR-(Ru-Pt) | 100% 71.1 | 47% 279.7 | 53% 280.8 | 0.023 | 0.007 | 0.016 | 2.4 | 0.53 |
| CR-(1% Ru-Pt) | 100% 71.2 | 50% 279.4 | 50% 280.6 | 0.024 | 0.008 | 0.012 | 1.5 | 0.43 |
| Catalysts/S40 | Cliq 1 (%carbon) | Identification Ratio 2 | Cgas 3 (%carbon) | Chexane (%carbon) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 74.9 | 1.00 | 5.5 | 3.7 |
| Ru | 59.8 | 1.00 | 23.9 | 9.6 |
| CI-(Ru-Pt) | 65.6 | 0.90 | 20.6 | 2.4 |
| SI-(Ru-Pt) | 49.5 | 1.00 | 32.3 | 24.4 |
| SI-(Pt-Ru) | 67.3 | 1.00 | 28.2 | 2.3 |
| CR-(Ru-Pt) | 49.9 | 0.95 | 31.6 | 1.8 |
| CR-(2%Ru-Pt) | 73.6 | 1.00 | 15.4 | 1.9 |
| CR-(1%Ru-Pt) | 59.1 | 1.00 | 21.8 | 11.4 |
| CR-(0.5%Ru-Pt) | 65.6 | 1.00 | 14.4 | 8.2 |
| Catalysts/S40 | SBET 1 (m2 g−1) | VP 1 (cm3 g−1) | DP 1 (nm) | d 2 (nm) | Carbon 3 (wt.%) | Hydrogen 3 (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt used | 367 | 0.77 | 7.1 | 4.2 | 22.6 | 3.8 |
| SI–(Ru–Pt) used | 313 | 0.72 | 8.2 | 3.0 | 16.3 | 2.5 |
| CR–(Ru–Pt) used | 395 | 0.83 | 7.9 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 1.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messou, D.; Vivier, L.; Canaff, C.; Especel, C. Biofuel Synthesis from Sorbitol by Aqueous Phase Hydrodeoxygenation over Bifunctional Catalysts: In-depth Study of the Ru–Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 Catalytic System. Catalysts 2019, 9, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020146
Messou D, Vivier L, Canaff C, Especel C. Biofuel Synthesis from Sorbitol by Aqueous Phase Hydrodeoxygenation over Bifunctional Catalysts: In-depth Study of the Ru–Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 Catalytic System. Catalysts. 2019; 9(2):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020146
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessou, Davina, Laurence Vivier, Christine Canaff, and Catherine Especel. 2019. "Biofuel Synthesis from Sorbitol by Aqueous Phase Hydrodeoxygenation over Bifunctional Catalysts: In-depth Study of the Ru–Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 Catalytic System" Catalysts 9, no. 2: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020146
APA StyleMessou, D., Vivier, L., Canaff, C., & Especel, C. (2019). Biofuel Synthesis from Sorbitol by Aqueous Phase Hydrodeoxygenation over Bifunctional Catalysts: In-depth Study of the Ru–Pt/SiO2–Al2O3 Catalytic System. Catalysts, 9(2), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9020146