Catalytic Combustion of Diesel Soot on Ce/Zr Series Catalysts Prepared by Sol-Gel Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Structure of the Catalysts
2.1.1. Morphological Characterization of the Catalysts by Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.1.2. X-ray Diffraction Patterns of the Catalysts
2.1.3. Thermogravimetric-Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis of Soot
2.1.4. Thermogravimetric-Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis of Samples
2.1.5. X-ray Photoelectron-Spectroscopy Analysis of Catalysts
2.1.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy Analysis of Catalyst K/ZC
2.2. Analysis of Catalytic Performance
- (i)
- The lattice oxygen in catalyst reacts very easily with soot towards the formation of active species.
- (ii)
- The lattice oxygen in the catalyst reacts with active species to form CO2
- (iii)
- Oxygen is supplied to the catalyst during continuous aeration, filling the oxygen deficiency in the catalyst, and thus the catalyst is regenerated.
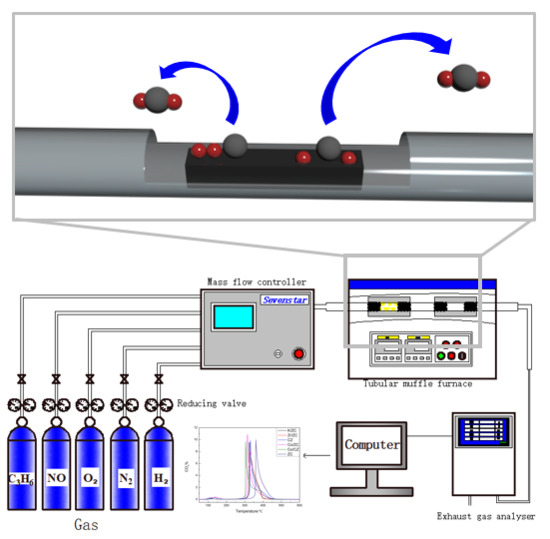
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials Preparation
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Na, F.; Wei, J.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, F. Fabrication of CdS/titanium-oxo-cluster nanocomposites based on a Ti32 framework with enhanced photocatalytic activity for tetracycline hydrochloride degradation under visible light. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 254, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, J.; Cui, W. Highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays wrapped with g-C3N4 nanoparticles for efficient charge separation and increased photoelectrocatalytic degradation of phenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Wu, J.; An, L.; Hu, X. N-doped porous carbons from low-temperature and single-step sodium amide activation of carbonized water chestnut shell with excellent CO2 capture performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, J. The influence of temperature on the phase behavior of ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuler, F.; Banus, E.D.; Zanuttini, M.; Miró, E.; Milt, V. Ceramic papers as flexible structures for the development of novel diesel soot combustion catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, A.-I.; Landry, J.-S.; Matthews, H.D. Climate and health implications of future aerosol emission scenarios. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiland, A. Aerosols, Tiny Particles, Big Impact. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/Aerosols (accessed on 2 November 2010).
- Bueno-López, A. Diesel soot combustion ceria catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 146, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Rui, G.; Liang, Y. Study on PM2.5 pollution and the mortality due to lung cancer in China based on geographic weighted regression model. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, D.; Watts, W.; Johnson, J. On-road and laboratory evaluation of combustion aerosols part 1, summary of diesel engine results. Aerosol Sci. 2006, 37, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Andana, T.; Bensaid, S.; Fino, D.; Russo, N.; Pirone, R. Ceria-based nanomaterials as catalysts for CO oxidation and soot combustion, Effect of Zr-Pr doping and structural properties on the catalytic activity. AIChE J. 2016, 63, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Yichuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Yin, H. Catalytic oxidation of soot on mesoporous ceria-based mixed oxides with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB)-assisted synthesis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, K.R.; Fenes, E.; Baidoo, M.F.; Abdollahi, R.; Fuglerud, T.; Chen, D. Highly Active and Stable CeO2-PromotedCuCl2/Al2O3 Oxychlorination CatalystsDeveloped by Rational Design Using a Rate Diagram of the Catalytic Cycle. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7030–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yu, X.; Heißler, S.; Nefedov, A.; Colussi, S.; Llorca, J.; Trovarelli, A.; Wang, Y. Surface Faceting and Reconstruction of Ceria Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, K.; Bueno-López, A.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. Potential rare earth modified CeO2 catalysts for soot oxidation, I. Characterisation and catalytic activity with O2. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 75, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, L.; Matarrese, R.; Lietti, L.; Forzatti, P. Intrinsic reactivity of alkaline and alkaline-earth metal oxide catalysts for oxidation of soot. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 90, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eversfield, P.; Liu, W.; Klemm, E. Effect of Potassium on the Physiochemical and Catalytic Characteristics of V2O5/TiO2 Catalysts in o-Xylene Partial Oxidation to Phthalic Anhydride. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Si, Z. Modification of CeO2-ZrO2 catalyst by potassium for NOx-assisted soot oxidation. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, T.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q.; Xin, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Z. Plausibility of potassium ion-exchanged ZSM-5 as soot combustion catalysts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, F.; Wu, X.; Weng, D. Effect of barium loading on CuOx –CeO2 catalysts, NOx storage capacity, NO oxidation ability and soot oxidation activity. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneggi, E.; de Leitenburg, C.; Dolcetti, G.; Trovarelli, A. Diesel soot combustion activity of ceria promoted with alkali metals. Catal. Today 2008, 136, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Si, Z. NOx-assisted soot oxidation over K/CuCe catalyst. J. Rare Earth 2010, 28, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Yang, L.; Ma, N.; Yang, J. Catalytic Activity and Stability of K/CeO2 Catalysts for Diesel Soot Oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2012, 33, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneggi, E.; Leitenburg, C.D.; Trovarelli, A. On the role of lattice/surface oxygen in ceria–zirconia catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Catal. Today 2012, 181, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atribak, I.; Bueno-López, A.; Garcia-Garcia, A. Combined removal of diesel soot particulates and NOx over CeO2–ZrO2 mixed oxides. J. Catal. 2008, 259, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atribak, I.; Azambre, B.; Bueno-Lopez, A.; Garcia-Garcia, A. NOx Adsorption/Desorption Processes Over Ce0.76Zr0.24O2 and Their Influence on DeSoot Activity, Effect of the Catalyst Calcination Temperature. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atribak, I.; Azambre, B.; López, A.B.; García-García, A. Effect of NOx adsorption/desorption over ceria-zirconia catalysts on the catalytic combustion of model soot. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 92, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atribak, I.; Bueno-López, A.; García-García, A.; Azambre, B. Contributions of surface and bulk heterogeneities to the NO oxidation activities of ceria-zirconia catalysts with composition Ce0.76Zr0.24O2 prepared by different methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 13770–13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wu, Q.; Mei, X.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, D.; Li, J. Fabrication of Spinel-Type PdxCo3−xO4 Binary Active Sites on 3D Ordered Meso-macroporous Ce-Zr-O2 with Enhanced Activity for Catalytic Soot Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7915–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azambre, B.; Collura, S.; Darcy, P.; Trichard, J.M.; Da Costa, P.; García-García, A.; Bueno-López, A. Effects of a Pt/Ce0.68Zr0.32O2 catalyst and NO2 on the kinetics of diesel soot oxidation from thermogravimetric analyses. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Weng, D. Active oxygen-assisted NO-NO2 recycling and decomposition of surface oxygenated species on diesel soot with Pt/Ce0.6Zr0.4O2 catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atribak, I.; Bueno-López, A.; García-García, A. Thermally stable ceria–zirconia catalysts for soot oxidation by O2. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lukashuk, L.; Akbarzadeh, J.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Peterlik, H.; Föttinger, K.; Rupprechter, G.; Schubert, U. Different synthesis protocols for Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts-Part 1, influence on the morphology on the nanoscale. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Dai, W.L. Support Morphology and Crystal-plane Effect of Cu/CeO2 Nano-Material on the Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties for Carbonate Hydrogenation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Guo, X. A new insight into the morphology effect of ceria on CuO/CeO2 catalysts for CO selective oxidation in hydrogen-rich gas. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3862–3871. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, K.; Bai, X.; Tan, S.; Tian, Y.; Ding, T.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Enhanced catalytic performance for CO preferential oxidation over CuO catalysts supported on highly defective CeO2, nanocrystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Marnellos, G.E.; Asad, M.F.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Effect of cobalt loading on the solid state properties and ethyl acetate oxidation performance of cobalt-cerium mixed oxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 496, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Bastos, S.S.T.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Delgado, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. Exotemplated ceria catalysts with gold for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 381, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Silva, A.M.T.; Dražić, G.; Tavares, P.B.; Figueiredo, J.L. Gold nanoparticles on ceria supports for the oxidation of carbon monoxide. Catal. Today 2010, 154, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Konsolakis, M.; Marnellos, G.E.-N.; Asad, M.F.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Tavares, P.B.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.D.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Ethyl Acetate Abatement on Copper Catalysts Supported on Ceria Doped with Rare Earth Oxides. Molecules 2016, 21, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Marnellos, G.E.; Asad, M.F.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Volatile organic compounds abatement over copper-based catalysts, effect of support. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 455, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykaki, M.; Pachatouridou, E.; Carabineiro, S.A.; Iliopoulou, E.; Andriopoulou, C.; Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Boghosian, S.; Konsolakis, M. Ceria Nanoparticles Shape Effects on the Structural Defects and Surface Chemistry, Implications in CO oxidation by Cu/CeO2 oxides. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 230, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Jin, B.; Zhao, Z.; Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Catalysts of self-assembled Pt@CeO2−δ-rich core–shell nanoparticles on 3D ordered macroporous Ce1−xZrxO2 for soot oxidation, nanostructure-dependent catalytic activity. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4558–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Lin, H.; Zhan, R.; Huang, Z. The catalysts of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Ce1-xZrxO2-supported gold nanoparticles for soot combustion, The metal–support interaction. J. Catal. 2012, 287, 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, B.; Lin, H.; Zhan, R.; Huang, Z. Catalytic combustion of soot over Cu, Mn substitution CeZrO2-δ, nanocomposites catalysts prepared by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 189, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xu, H.; Lin, T.; Cao, Y.; Lan, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Gong, M.; Chen, Y. Promotional effects of Zr on K+-poisoning resistance of CeTiOx catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Weng, X. Deactivation mechanism of Ce/TiO2 selective catalytic reduction catalysts by the loading of sodium and calcium salts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Guo, R.T.; Hu, C.X.; Sun, P.; Pan, W.G.; Liu, S.M.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.W.; Liu, J. The enhanced resistance to K deactivation of Ce/TiO2 catalyst for NH3 -SCR reaction by the modification with P. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 436, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Yu, W.Z.; Du, P.P.; Xu, H.; Jin, Z.; Si, R.; Ma, C.; Shi, S.; Jia, C.J.; Yan, C.H. Crystal Plane Effect of Ceria on Supported Copper Oxide Cluster Catalyst for CO Oxidation, Importance of Metal–Support Interaction. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Ge, C.; Tang, C.; Dong, L. Comparative study on the catalytic CO oxidation properties of CuO/CeO2 catalysts prepared by solid state and wet impregnation. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Mudiyanselage, K.; Xu, W.; Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Hanson, J.C.; Wu, T.; Stacchiola, D.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Zhao, H.; Kevin, A.; et al. Unraveling the dynamic nature of a CuO/CeO2 catalyst for CO oxidation in Operando, A combined study of XANES (Fluorescence) and DRIFTS. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Yu, Q.; Dai, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, F.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y. Influence of cerium precursors on the structure and reducibility of mesoporous CuO-CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 119–120, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.-P.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Lu, J.-Q.; Luo, M.-F. Study of Catalytic Activity at the CuO−CeO2 Interface for CO Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21605–21610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Samples or Soot | Ratio of Catalyst, Soot | Atmosphere/% | Ti/°C | To/°C | Tb/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soot | 10:1 | 10% oxygen & 90% nitrogen | 497 | 603 | 681 |
| K/ZC | 351 | 401 | 507 | ||
| Zr/ZC | 352 | 445 | 521 | ||
| Co/ZC | 362 | 430 | 506 | ||
| ZC | 368 | 447 | 540 | ||
| Co/CZ | 344 | 431 | 491 | ||
| CZ | 361 | 447 | 508 |
| Samples | O K | K K | Ce L | Zr L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K/ZC (two cycles) | 35.70 ± 0.87 | 24.33 ± 3.23 | 20.82 ± 0.82 | 19.15 ± 2.47 |
| K/ZC (five cycles) | 36.72 ± 1.46 | 25.79 ± 0.06 | 20.34 ± 1.19 | 17.15 ± 1.54 |
| Catalyst X | O2/% | The Ignition Temperature/°C | The Temperature of the Max Oxidation Rate/°C | Maximum CO2 Concentration/% | Burnout Temperature (CO2 ≤ 0.10%)/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K/ZC | 6 | 309.0 | 324 | 5.29 | 425.0 |
| 8 | 301.1 | 315 | 7.84 | 401.7 | |
| 10 | 307.5 | 324 | 9.51 | 416.7 | |
| 12 | 301.1 | 317 | 12.67 | 400.0 | |
| 14 | 301.6 | 318 | 14.35 | 395.0 | |
| 21(air) | 289.3 | 299 | 18.38 | 379.2 | |
| Zr/ZC | 10 | 308.0 | 327 | 9.57 | 403.3 |
| CZ | 10 | 309.8 | 330 | 9.82 | 454.2 |
| Co/ZC | 10 | 295.8 | 315 | 10.83 | 446.7 |
| Co/CZ | 10 | 294.2 | 304 | 9.70 | 438.3 |
| ZC | 10 | 338.5 | 360 | 9.99 | 462.5 |
| Catalyst X | Ratio of Catalyst, Soot | Atmosphere | Flow Rate /mL·min−1 | Ti or T10/°C | To or T50/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/ZC | 10:1 | 10% O2 & 90% N2 | 100 | 295.8 | 315 |
| Co/CZ | 294.2 | 304 | |||
| Pt@CeO2-δ/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 [43] | 5% O2 balanced with Ar | 50 | 316 | 408 | |
| Pt@CeO2-δ/Ce0.2Zr0.8O2 [43] | 358 | 440 | |||
| Ce0.8Zr0.2O2(particles) [44] | 5% O2 and 0.2% NO in Ar | 50 | 381 | 449 | |
| Ce0.8Zr0.2O2(3DOM) [44] | 328 | 394 | |||
| Au/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2(3DOM) [44] | 232 | 365 | |||
| Cu0.1Ce0.45Zr0.45O2-δ [45] | 800ppm NO, 6.5 vol% O2 balanced with N2 | 500 | 382 | 494 | |
| Cu0.5Ce0.25Zr0.25O2-δ [45] | 368 | 472 | |||
| Cu0.9Ce0.05Zr0.05O2-δ [45] | 284 | 468 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, W. Catalytic Combustion of Diesel Soot on Ce/Zr Series Catalysts Prepared by Sol-Gel Method. Catalysts 2019, 9, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080646
Ai C, Zhang Y, Wang P, Wang W. Catalytic Combustion of Diesel Soot on Ce/Zr Series Catalysts Prepared by Sol-Gel Method. Catalysts. 2019; 9(8):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080646
Chicago/Turabian StyleAi, Chaoqian, Yaoyao Zhang, Pan Wang, and Wei Wang. 2019. "Catalytic Combustion of Diesel Soot on Ce/Zr Series Catalysts Prepared by Sol-Gel Method" Catalysts 9, no. 8: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080646
APA StyleAi, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., & Wang, W. (2019). Catalytic Combustion of Diesel Soot on Ce/Zr Series Catalysts Prepared by Sol-Gel Method. Catalysts, 9(8), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9080646